Index Based Livestock Insurance [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Duncan Collins Khalai
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
IBLI
technologies_3361 - كينيا
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 9 مايو، 2019 (inactive)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 3 سبتمبر، 2018 (inactive)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 7 يونيو، 2018 (inactive)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 13 مايو، 2018 (inactive)
- Index Based Livestock Insurance: 25 يناير، 2018 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Index Based Livestock Insurance, Kenya (IBLI)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ILRI International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
24/01/2018
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Index-Based Livestock Insurance (IBLI) is a product that was designed to help protect pastoralists and their livestock against the effects of prolonged forage scarcity. IBLI triggers payment to pastoralists when the forage situation deteriorates to levels considered to be severe, as compared to historical conditions over time.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In the event of severe seasonal drought, forage and grazing resources are depleted and livestock may die because of starvation. Index Based Livestock Insurance (IBLI) is the technology applied in the provision of forage based livestock (asset) protection insurance. IBLI uses Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), a satellite-derived indicator of the amount and vigor of vegetation, based on the observed level of photosynthetic activity (Tucker et al., 2005). NDVI is derived from 10-day composites of 250m filtered eMODIS processed by the United States’ National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and transformed by The Earth Resources Observation Systems (EROS) Data Center (EDC) of the US Geological Survey (USGS). NDVI data from the AQUA satellite platform are available from July 2002 to present at https://lta.cr.usgs.gov/emodis.
In the case of IBLI, the index is a deviation of cumulative forage availability (ZCumNDVI) in the insured season. It measures forage conditions over a defined time period and compares the observed NDVI over a particular season, with the observed NDVI over a given historical period (e.g. 15 years). A set threshold below which payouts must be made is called the trigger level. Therefore, when the forage situation in a given season is worse than the 20th worst season in the last 15 years, a payout is triggered. In other words, IBLI will compensate if the forage conditions fall below the worst 20th percentile of seasonal pasture levels cumulated over the historical drought seasons in the past 15 years. IBLI therefore uses the satellite-based vegetation index to measure forage availability and to trigger timely payouts to pastoralists based on the costs of providing supplementary feeds to the animals for the specific season that a drought is triggered.
For precision and proper administration each insured county is broken down into smaller units of insurance which are referred to as Unit Areas of Insurance (UAIs). Each UAI represents a geographical area whose forage availability index data are aggregated as one unit for insurance purposes. The identification of the geographic areas that constitute UAIs is a key step in IBLI contract design because the use of average NDVI over insurable units is based on the premise that drought is a covariate shock and that pastoral communities affected in a particular area are deemed to suffer in equal measure.Thus, for accuracy and acceptability, the index should be tightly correlated with forage scarcity and reflect relative conditions on the ground. Also forage access should be relatively homogeneous for herders residing in the same insurable unit. The process of demarcating UAIs is known as clustering. It is done through a combination of active participatory community engagement and scientific methods .
Insured pastoralists are not always paid when there is drought. They are only paid when drought is so severe that the amount of forage falls below the strike level. Insured pastoralists will not receive payments if the forage availability is more than the strike level. This is an annual policy which covers forage availability as measured by satellite Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) in up to 2 rainy seasons as per the bimodal rain patterns in Kenya. Pastoralists who do not hold insurance contracts are not covered by under, and therefore do not receive payments, even if they live in the same UAIs as the ones who have insured their livestock.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Cattle, Goats, Sheep and Camels.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

تدابير أخرى
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

آخر
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- التكيف مع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
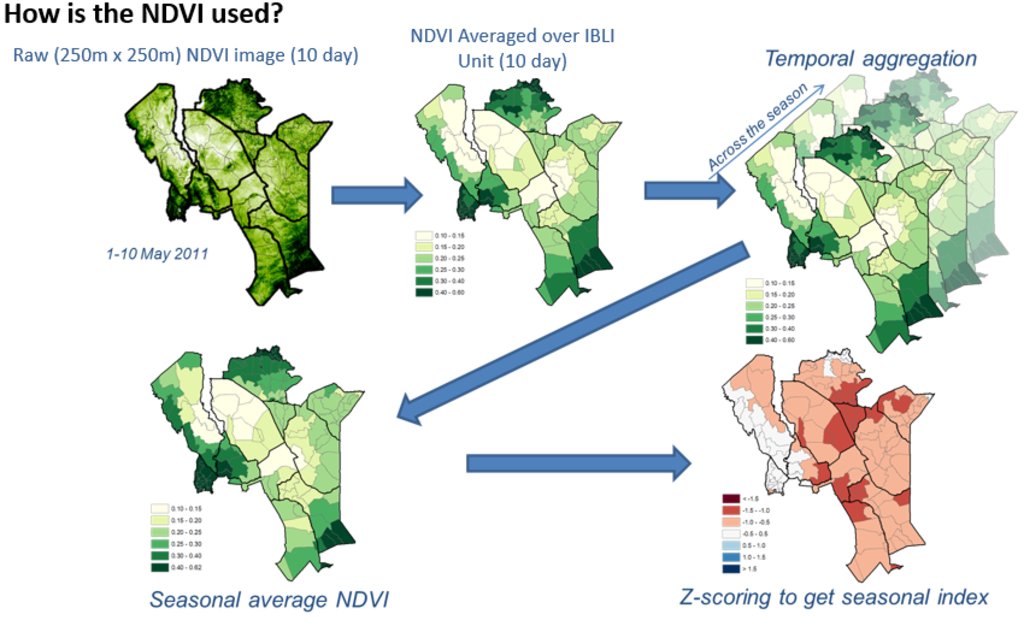
Picture 1 &2: Monthly NDVI for each insured unit in a month is derived by averaging the 10-day NDVI values for each Insured Unit over the three 10-days periods in each month, where the 10-day NDVI value for each Insured Unit is derived by averaging the pixel-level NDVI of all the pixels that fall within the insured unit boundary.
Picture 3: An accumulation of monthly NDVI over the critical months of each season starting from the beginning of the season (March for LRLD and October for SRSD).
Picture 4: There is a representation of a cumulation of monthly NDVI (CumNDVI) which represents the evolution of green vegetation and can be used as a proxy of the green biomass that has developed, and as such a proxy of the available forage across the season.
Picture 5: Deviation of Cumulative NDVI from normal conditions of the particular season and insured unit (ZCumNDVI) - is derived by
subtracting CumNDVI derived for each season and each insured unit by the long-term historical average value and dividing by long-term historical standard deviation of the particular season (SRSD or LRLD) in each
insured unit. ZCumNDVI thus measures the deviation from the historical mean,
expressed as a standard deviation. A positive ZCumNDVI value therefore indicates above normal vegetation cover while negative ZNDVI value indicates below normal vegetation. The purpose of this transformation is to provide an indicator that expresses current forage conditions in comparison to average forage conditions for each specific insurance unit
at the prescribed period within the season.
NOTE: The delineations used in this figure are just for purposes of illustration, assuming Kenya as an entire unit. However, IBLI used smaller delineated units which can be seen in the lines with lighter shade within the map.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Kenya Meteorological Department
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Most land is communal
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الآثار الايكولوجية
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
Reduction of livestock mortality as a result of forage scarcity due to drought.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة الأخرى المرتبطة بالمناخ (الكوارث)
| أخرى (حدد) | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ |
|---|---|
| Forage scarcity | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
over 25,000 households
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A key concern of index-insurance products is that there might occur variances in perceived loss versus the actual payouts (basis risk) | Proper contract design should be backed with ground truthing efforts together with awareness creation. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Chelang'a et. al 2017
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Tucker et al., 2005
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
IBLI website
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://ibli.ilri.org/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية