Planting Eucalyptus on rice bunds to lower saline groundwater [تايلاند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Areerat Wangkaew
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Samran Sombatpanit, Pitayakon Limtong, William Critchley
Planting perennial salt-tolerant trees in salt-affected areas of the Northeast of Thailand.
technologies_4099 - تايلاند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Chuenchai Sayan
+66-99-0254108
Ban Muang Pia, Muang Pia Sub-district, Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen 40110
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Sritumboon Supranee
ssritumboon@yahoo.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Pothinam Pornpana
laosuwan18@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rophandung Weera
weerop@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Srihaban Pranee
pranee.782@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Jakkarach Usa
usa.kl@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Janplang Chettaruj
joeshua9@hotmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
National consultant:
Arunin Somsri
ssarunin@gmail.com
Land Development Department
2003, 61 Phaholyothin Road, Ladyao, Chatuchak, Bangkok 10900
تايلاند
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - تايلاند1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/10/2018
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The technology is environmentally suited and very well accepted by the land users.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [تايلاند]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- جامع المعلومات: Areerat Wangkaew
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
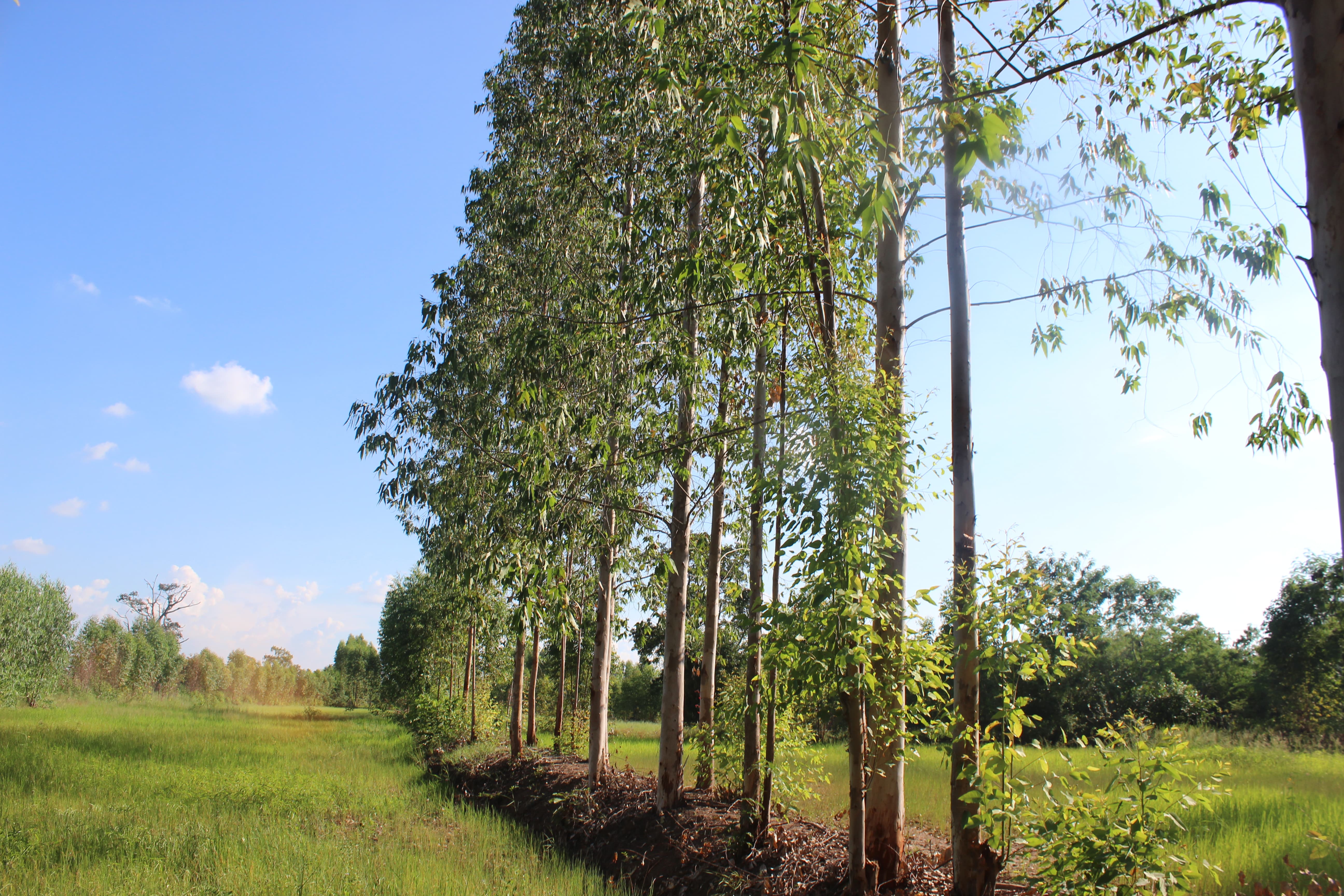
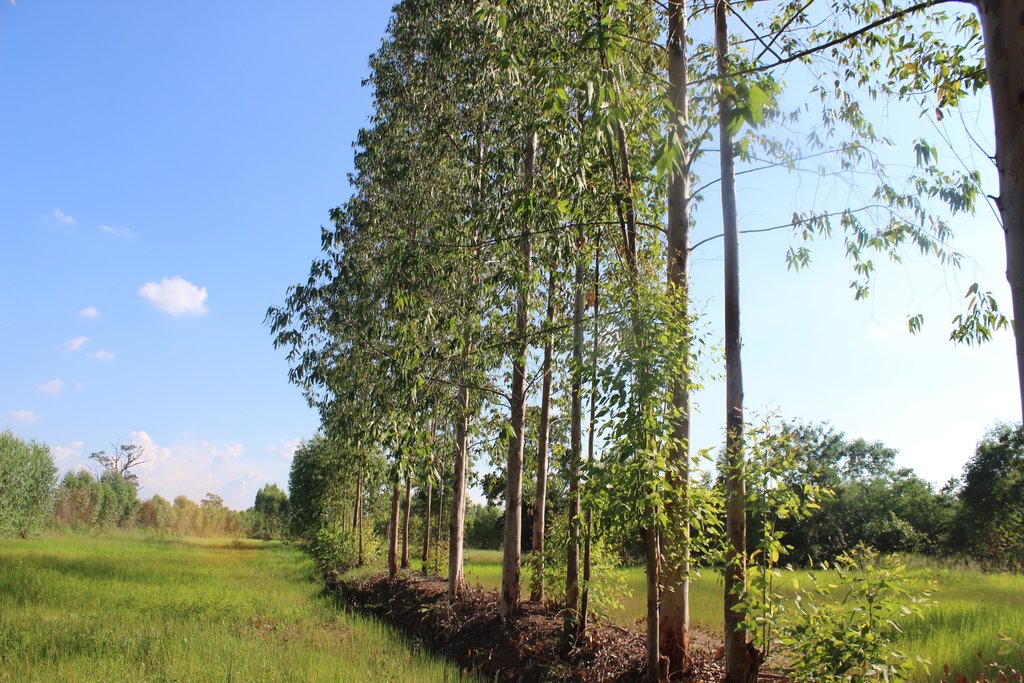
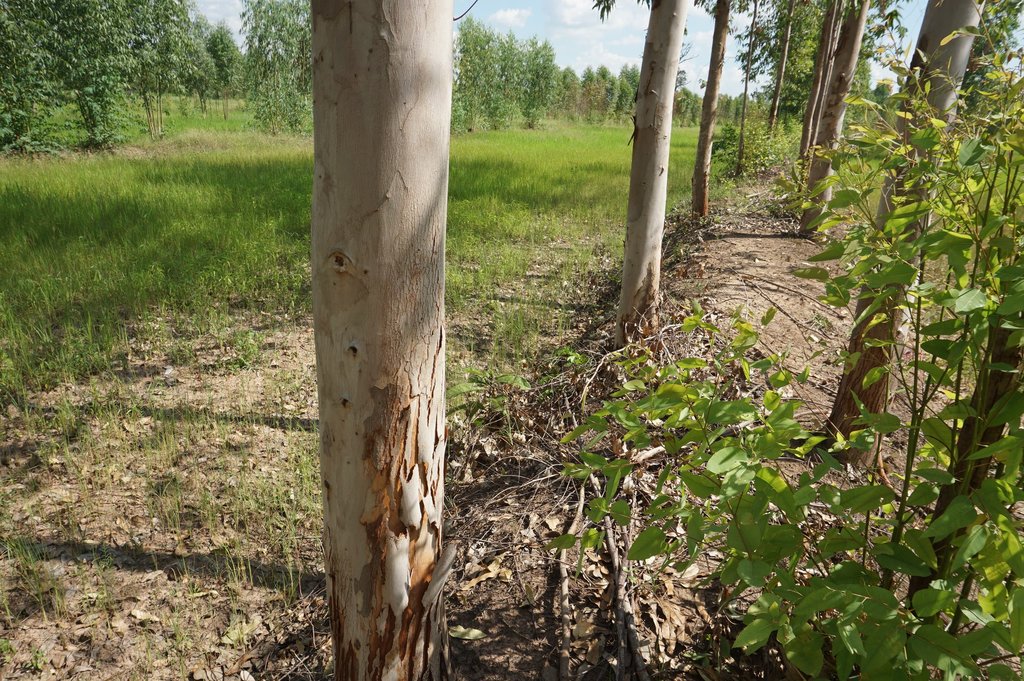
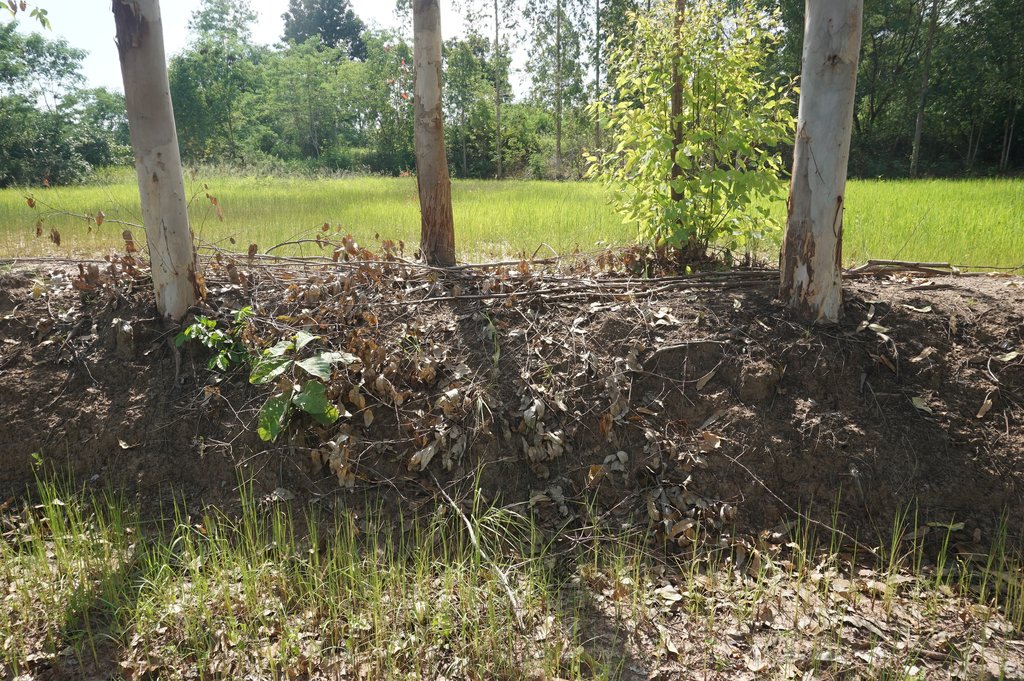
Eucalyptus camaldulensis variety H4 is salt tolerant and has the ability to lower shallow saline groundwater levels; as a result salinity is controlled. Planting eucalyptus on one or two sides of the rice bund in an east-west direction (in single or double rows) at a spacing of 2 m between trees is the most effective technique and well accepted by farmers.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis cultivation on rice bunds to lower shallow saline groundwater levels in low-lying areas is a technology used on salt-affected land. The LDD Perennial Tree Planting project to promote the technology of planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds has been implemented since 1996. The land user interviewed cultivates a moderately salt-affected rice field at Ban Muang Pia District, Khon Kaen Province. The land is used for rice production both glutinous (variety RD 6) and non-glutinous fragrant rice (Hom Mali 105). The average yield of rice is 200-250 kg/rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai). The farmers have planted eucalyptus on bunds in the rice cultivated areas on about 10,000 rai in more than 10 years with the objectives of remedying and preventing salination by lowering shallow saline groundwater levels, through "bio-drainage" as well as increasing income and better utilization of lands on rice bunds for growing trees.
The technology of eucalyptus cultivation on rice bunds has been implemented in farmers' fields in the low-lying salt-affected rice area common in the Northeast of Thailand. It is widely accepted by farmers through the joint partnership between the Land Development Department (LDD), Siam Forestry Co., Ltd. and the local district administration. Eucalyptus seedlings are provided by LDD and are planted in a single or double rows - double rows with trees planted on two sides of the rice bunds in a zigzag manner following an east-west direction to prohibit a shadow effect. The spacing between the trees in a row is 2 m: the rice bund was adapted to be 1.5 m wide and 0.5 m high. This provides more space and convenient access to the rice field. The project provides labour costs for farmers to prepare the land before planting. Many farmers outside the project transplanted their own eucalyptus seedlings on the bunds of 0.5 m or more in width. Farmers buy the seedlings at 1 THB each and plant in pits of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m with 0.5 kg compost and 0.5 kg rice husks from farm by-products. This technology is well accepted by farmers because of the effective control of salinity in the rice fields as well as the higher income obtained from selling eucalyptus wood. Farmers observed the dead patchy spots of rice plants with salt crusts before planting eucalyptus: after 2 cutting cycles no salt patches were observed anymore, and rice yields increased noticeably. There was also extra income from selling poles of eucalyptus every 4 years. The average yield of eucalyptus trees of 2.5-3.0 inches in diameter was 16 tons per rai for the first cutting.
Based on 7 years (2 crops of eucalyptus coppicing), the average additional income was 1,087 THB/rai/yr (according to the farmers' and Siam Forest's information). The main investment was in the first year of planting; later on, the maintenance cost was on labour for weeding, pruning and thinning to 3 stems after coppice/cutting, including adding 15-15-15 fertilizer for each tree. The average income is increased through better rice yields. The benefits of the technology according to interviews are creating a cooler microclimate from eucalyptus trees and changes in biodiversity through better soil quality resulting in more species of flora and fauna such as grasses, wildflowers, dragonflies, earthworms in the rice field and on the bund. Some farmers wanted more trees by planting at closer spacing of 1 m, but this resulted in too great a density of trees thus consuming more surface water and competing with rice for water consumptive use.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
The video shows the area of eucalyptus growing on the rice bund.
التاريخ:
01/10/2018
الموقع:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Supranee Sritumboon
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Farmer interview and SLM discussion.
التاريخ:
01/10/2018
الموقع:
Ban Muang Pia, Khon Kaen
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Supranee Sritumboon
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تايلاند
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khon Kaen
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ban Phai
التعليقات:
The SLM Technology site for planting eucalyptus in a rice production area.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
1996
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
- by other land users
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The project initiated by the government (Land Development Department) collaborated with private enterprises (Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.), local administration, communities and land users.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Rice
التعليقات:
Planting eucalyptus for additional income and more intensive utilization of land on the rice bunds.
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Before planting eucalyptus, rice was the only crop. Due to the shallow saline groundwater of the area, rice had shown symptoms of being salt-affected; however after planting eucalyptus trees, these symptoms disappeared.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Average annual rainfall is 1,200-1,300 mm.
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Land use is for rice production; the technology is planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds.
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
Only few cattle, swine, and boar are in the land user's farm.
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- إدارة المياه الجوفية
- desalination
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
The technology has spread over the area of 10,000 rai (1 ha = 6.25 rai) owned by farmers/land users both under and outside the supported project of planting eucalyptus on rice bunds.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A5: إدارة البذور، الأصناف المحسنة

تدابير أخرى
التعليقات:
Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4 is the salt-tolerant variety used for lowering shallow saline groundwater.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Decreased saline groundwater levels to control salinity distribution in rice cultivated areas.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
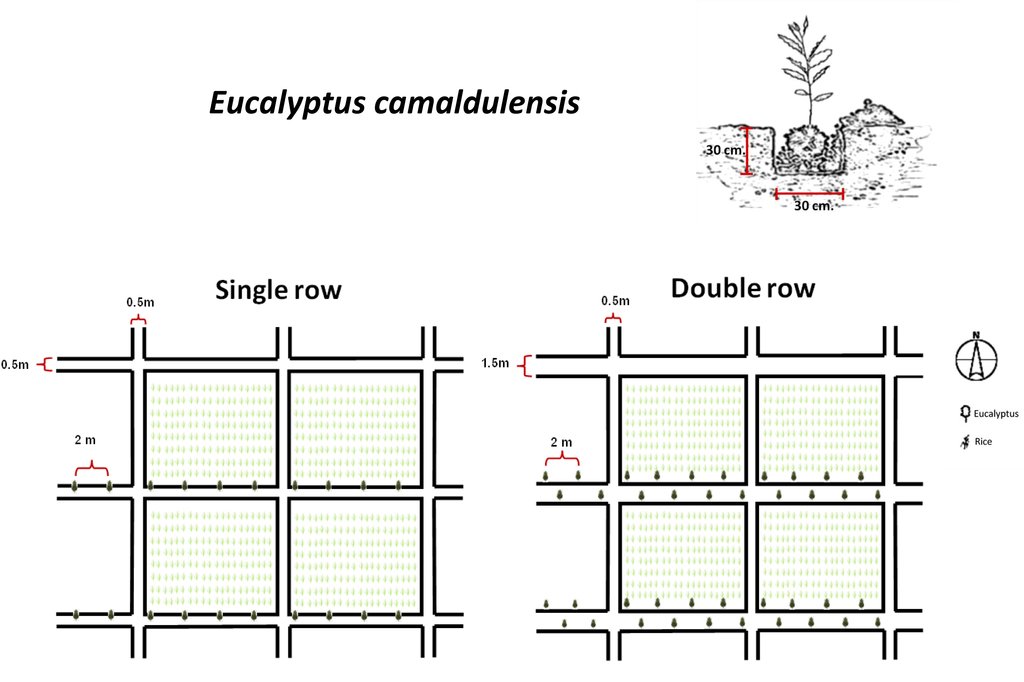
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
1. Seedling of Eucalyptus camaldulensis H4, a salt-tolerant variety, were planted. The age of seedlings was 3-month old. The rice bund was regulated to 0.5 m wide for planting eucalyptus in single row or 1.5 m wide for planting in double rows (in a zigzag manner), 0.5 m high with a spacing of 2 m between the trees along an east-west direction. The number of trees was 80/rai or 500/ha for double rows planting.
2. Planting technique: 0.5 kg of compost mixed with 0.5 kg of rice husks was applied at the bottom of a pit of 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.3 m before seedlings were planted.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
own by one selected land user
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، أشر إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد:
1 hectare = 6.25 rai
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
THB
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
32,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
300 THB
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection of salt-affected area | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-July |
| 2. | Land preparation; bunds construction and seedling preparation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-July |
| 3. | Public hearing, joint meeting between farmers and researchers | تدابير أخرى | May-July |
| 4. | Demonstration plot | زراعية | May-July |
| 5. | Model establishment (Eucalyptus planting method) | زراعية | May-July |
| 6. | Joint monitoring, evaluation and follow up for planting | تدابير أخرى | After planting |
التعليقات:
No irrigation water therefore the planting time depends on the period of early rainy season which will be from May to July.
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour cost for planting eucalyptus (labour wage per day = 300 THB, 1 rai required a labour cost of 600 THB) | Rai | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Eucalyptus seedling cost (80 trees/rai), 1 THB for each seedling | Seedling | 80,0 | 1,0 | 80,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost cost 3.5 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40,0 | 3,5 | 140,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Rice husk cost 4 THB/kg, 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40,0 | 4,0 | 160,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 980,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Land Development Department
التعليقات:
Labour cost for land preparation and planting borne by LDD and seedlings borne by Siam Forestry Co., Ltd.; compost and rice husk were from farm by-products.
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Thinning and pruning after first year of planting | زراعية | 2 times/rain season |
| 2. | Weeding after first year of planting | زراعية | 2 times/rain season |
| 3. | Fertilizer application after first year of planting | زراعية | 2 times/rain season |
| 4. | Cutting and selling logs | زراعية | 4th and 7th year |
التعليقات:
Four years after planting, the poles will be cut and sold. After cutting, the tree coppices, then thinning is needed in order to leave not more than 3 stems, necessary for better growth of the tree trunks. Weeding is important during rainy season to control competition for fertilizer.
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour cost of weeding, pruning, thinning, and fertilizer application for 150 THB/time, 2 times/rai/yr, based on the labour wage of 300 THB/day | Time | 2,0 | 150,0 | 300,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Cost of 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer (13 THB/kg, application rate 50 g/tree; 50 g x 80 trees per rai = 4 kg/rai | kg | 4,0 | 13,0 | 52,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 352,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Land users do the job by themselves without hiring labourers. Furthermore, the fertilizer application will be the same fertilizer and timing as is used for rice. No extra fertilizer needed for trees because the trees will consume fertilizer from the rice field.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Maintenance cost of weeding, pruning, thinning and fertilizer application was 428 THB/rai/yr. Calculation is based on 7 years of planting. Four years after planting, the logs were sold for additional income 5,714.3 THB/rai. On the 7th year, the logs were sold at 4,285.7 THB/rai.
(Income from 2 times of Eucalyptus sale; 4th year = 40,000 THB, 7th year = 30,000 THB. Therefore, total income for 7 years = 10,000 THB/rai. Benefit from Eucalyptus planting = 10,000–2,388 (planting cost + 4 years of maintenance cost) = 7,612 THB/7 years = 1,087 THB/rai/yr.)
Compost and rice husk are from farm by-products and the labour costs are from land users. The income thereore will be higher than 1,087 THB/rai as estimated.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1200,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Average annual rainfall from 2003-2012
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Meteorological Department
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Average temperature 21-36 degree Celsius, relative humidity is 75%
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The geography is in the lower basin of Korat Plateau in the Northeast of Thailand.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Texture of top soil is sandy loam and more than 20 cm below the surface is sandy clay loam; pH = 7 and increasing with depth up to 8.5; soil salinity is moderately to highly affected which is identified by the salt crusts on the soil surface; very low P and K.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
حدد:
Slightly saline
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Shallow saline groundwater exists because of the low-lying discharge area and the source of the salt is under the surface of the land.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Before planting eucalyptus, species and habitat were low. After 7 years, dragonfly, earthworms, birds, rats, and wildflowers that were not seen before now are found.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Diligent farmer seeking more income by raising few cattle, swine, and boar.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Farmers/ land owners outside the project have been planting eucalyptus on rice bunds and get additional income.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
- rainfed
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rice production before planting eucalyptus 150-200 kg/rai
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rice production after planting eucalyptus 200-250 kg/rai
التعليقات/ حدد:
The increase in rice production was due to being less saline condition of the field.
جودة المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
More unfilled grain of rice
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less unfilled grain of rice
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased about 10%
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less stubble
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
More stubble
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased about 10%
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
تنوع المنتج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Only rice was grown before SLM
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rice and Eucalyptus
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased about 50%, Eucalyptus grown in east-west direction only.
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rice bunds were unused before planting eucalyptus.
إدارة الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Planting trees hinder access to the rice field.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الشرب
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
No effect
التعليقات/ حدد:
From rain water
توافر المياه للماشية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Depend upon rainfall
نوعية المياه للماشية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Depends upon rain water
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
No supplementary water available
نوعية مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under rainfed only
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Remain unchanged
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased about 20% (the cost for planting trees in the first year and the maintenance cost of later years).
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Approximately 1,000 THB/rai/yr
التعليقات/ حدد:
Additional income from selling eucalyptus logs besides rice
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Income from only rice
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Income from both rice and logs
التعليقات/ حدد:
Extra income from selling swine and boar
عبء العمل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased about 10% by planting tree and subsequent maintainence.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Self-sufficiency increased through obtaining higher income.
الوضع الصحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Change in microclimate affected in cooler atmosphere
الفرص الترفيهية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to change in microclimate and biodiversity
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
التعليقات/ حدد:
More communication among land users community and local administration.
المؤسسات الوطنية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
National institutions are more recognized by land users.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land users observed less salination.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Saline groundwater level decreased due to the bio-drainage by eucalyptus trees.
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ave. groundwater level < 1 m
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ave. groundwater level > 1 m
التعليقات/ حدد:
Lower groundwater level after 7 years of planting eucalyptus
التبخر
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cooler atmosphere
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to shading
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Shading effect and plant residues
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
تراص التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil properties from crop residues and earthworm activities
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الملوحة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rice production as well as quality of rice increased (and also more percentage of full grains) due to the decrease in salinity level.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rice bunds are used for planting eucalyptus only along east-west direction.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Biomass from eucalyptus trees
التنوع النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
التعليقات/ حدد:
From eucalyptus trees and more local species of grasses and wildflowers
التنوع الحيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Earthworms, birds, rats, ants, etc.
الأنواع المفيدة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Native earthworms
تنوع الموائل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Dragonfly, earthworms, birds and rats
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to cooler atmosphere of the planting sites
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cooler and greener atmosphere
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced groundwater level
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
The planted Eucalyptus trees absorb greenhouse gases.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فترة نمو ممتدة | ليس جيدا |
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The cost of planting trees in the first year was the only main cost. The maintenance cost starts from second year on until the year of cutting and selling logs. After coppicing, maintenance cost starts again until the next cutting. Therefore the benefits will be higher with more cycles of cutting.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
1,600 ha
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
Farmers and land users acknowledge the benefit of the technology that results in decreasing salinity, increasing rice production, and additional income from trees.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
closer spacing of trees
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
Planting eucalyptus has been adapted from growing eucalyptus on rice bunds of 1.5 m wide to 0.5 m wide to save labor cost of land preparation and plant the seedlings on one row instead of 2 rows.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Decrease saline groundwater level resulting in rice yield increase. |
| Get higher income from increasing rice yield and eucalyptus poles. |
| The microclimate in the area has been improved and the air is cooler and the land is greener. |
| Increased indirect returns due to land is greener and used as animal fodders for cattle, swine, and boar. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Decreased saline groundwater level then prevented further salination as a result to protect the land degradation. |
| Increasing farmer's income. |
| To establish better environment for more biodiversity especially earthworms used to disappear now are found and their activities induce better soil properties. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| More birds and rats damage rice yield. | No solution |
| The officers do not visit whenever the land users need help. | The officers need to contact the land users and give advice more often. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Farmers do not understand how eucalyptus trees could decrease saline groundwater level. | Explain, illustrate and demonstrate the cause and effect of salinity. |
| There are pros and cons of planting eucalyptus because the leaves may damage the soil and their shading effect may decrease rice yield. | Organize farmer group visit to some successful sites that no adverse effects have been found. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Visit 1 farmer/ land user's land
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Interview with 1 farmer
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
The Land Development Department officers and planners (6)
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Reports from the Soil Salinity Research and Development Group of the Land Development Department (2)
- projects
The Land Development Department's implementation projects (3)
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Land Development Department
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.ldd.go.th/
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Planting Eucalyptus on bunds: Better way for the Northeast farmers
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.ldd.go.th/
العنوان/الوصف:
Eucalyptus : New opportunity by Siam Forestry
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.scgpackaging.com/others/forestry/eucalyptus/TH
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Advisory system for planting Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice … [تايلاند]
The Thai government promotes planting of Eucalyptus camaldulensis on rice bunds to lower the saline groundwater level and prevent the spread of salt in soils - through cooperation of farmers, land owners, Siam Forestry Co., Ltd., Subdistrict Administration Organization, Land Development Department, and with specialists/ technical advisors.
- جامع المعلومات: Areerat Wangkaew
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية