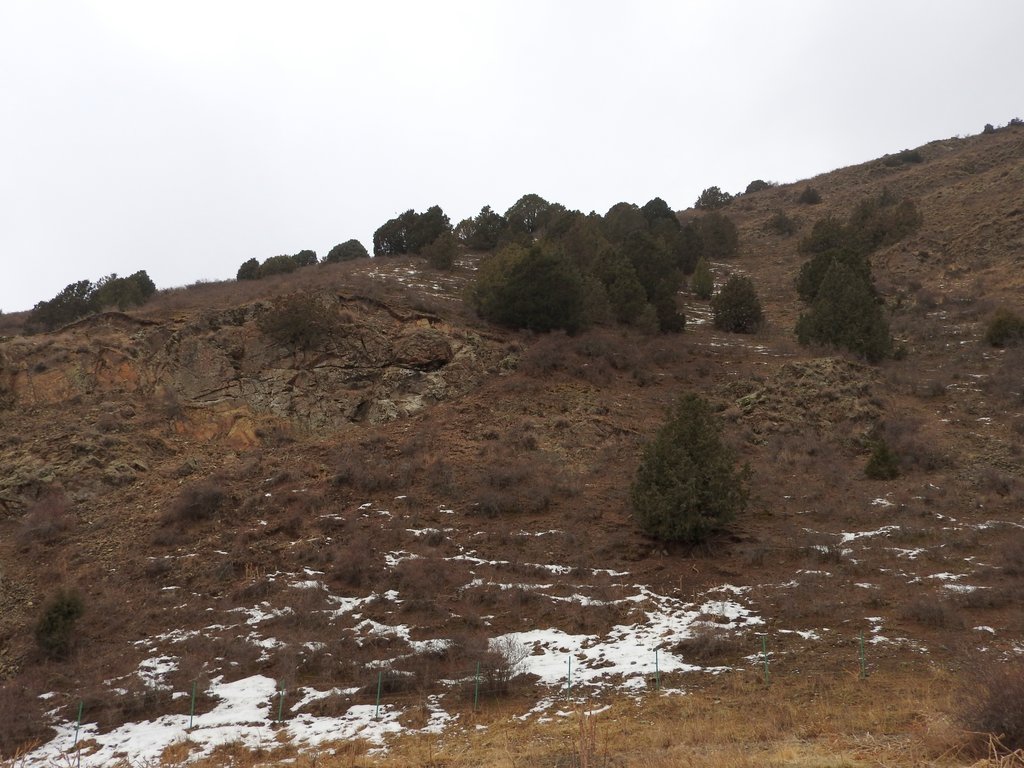
Cultivation of local juniper species for rehabilitation of degrading woodland pastures [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Stefan Michel
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Umed Vahobov
Выращивание саженцев арчы для восстановления деградирующего редколесья горных пастбищ.
technologies_4295 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Shodiev Fakhriddin
Shahriston Forestry Enterprise
طاجيكستان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistanاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
GIZ Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Disaster risk reduction and sustainable land-use by integrated … [طاجيكستان]
A site affected by a debris flow was rehabilitated by joint communal work and integrated preventive measures addressing the upper catchment as well as the valley and the debris conus were implemented in collaboration of community, individual farmers, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
- جامع المعلومات: Stefan Michel
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
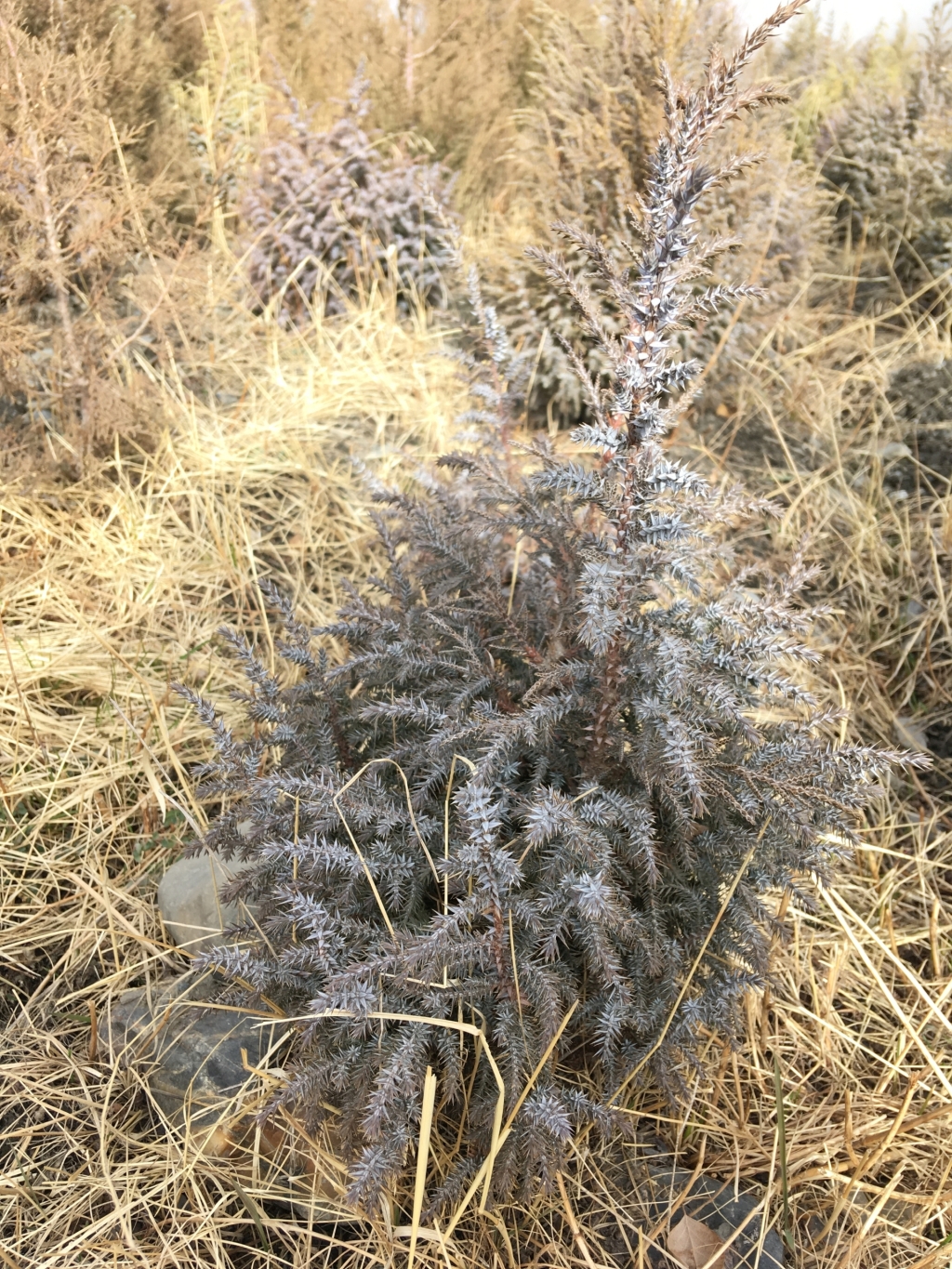
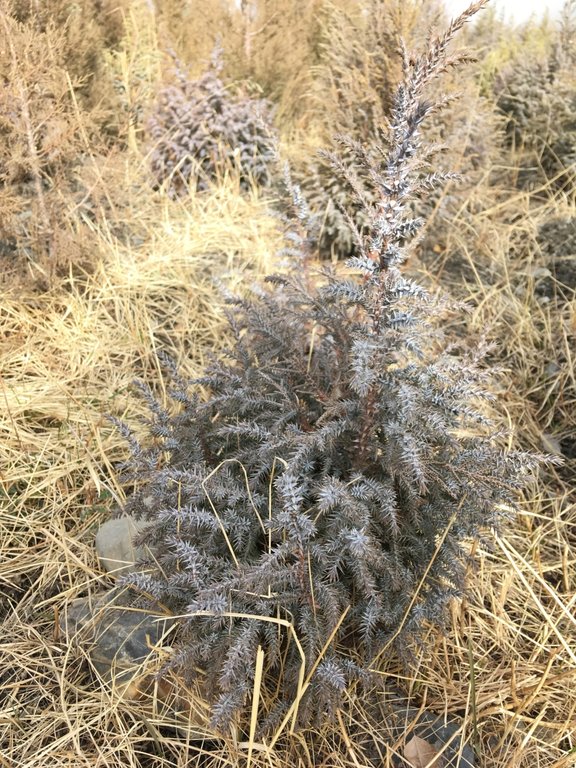
The local species of juniper trees (Juniperus seravschanica, Juniperus turkestanica and Juniperus semiglobosa) are rarely rejuvenating under conditions of intensive grazing and are difficult to propagate in nurseries. The technology describes the propagation of these important trees from locally collected seeds and their cultivation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The technology is used to produce seedlings of juniper trees in the forestry nursery for further replanting in the natural juniper woodlands of the local forestry enterprise. Juniper woodlands are important ecosystems of the mountains of Central Asia, which are typically used for livestock grazing. The tree cover fulfills important functions for the maintenance of ecosystem services – local microclimate, regulation of water infiltration and surface runoff, biodiversity, esthetic value and recreation, fuelwood etc. The local juniper species rarely rejuvenate naturally. Factors hampering natural rejuvenation include intensive grazing, competition by other plant species and weather conditions. Loss of old juniper trees due to natural losses, damage and cutting combined with lacking rejuvenation causes the degradation and loss of juniper stands. Forestry enterprises in Central Asia often in such situations instead of the difficult to cultivate and slowly growing native juniper often plant non-native arborvitae Thuja spec. These non-native species do not provide the natural ecosystem functions of native juniper and are less adapted to the local site conditions.
The purpose of the described technology is therefore the provision of planting material for the rehabilitation of degraded juniper woodland pastures with native trees.
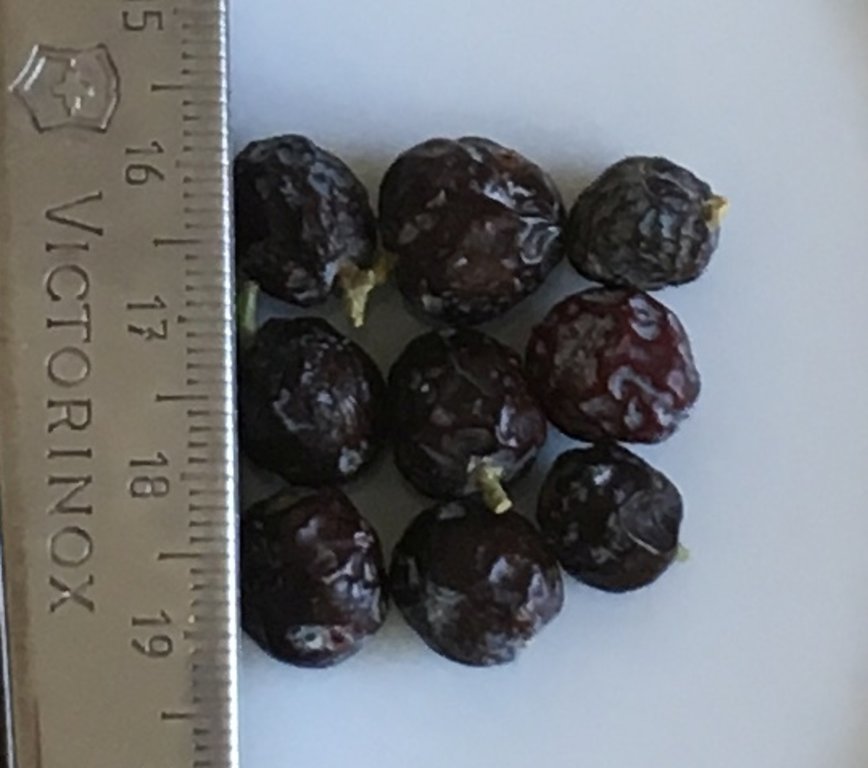
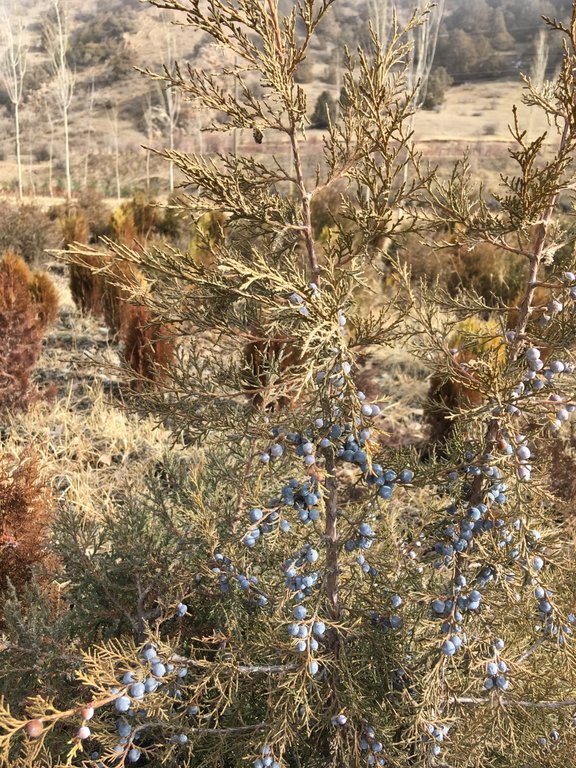
Forestry workers collect ripe juniper fruits from their natural stands during late fall (November – December). The fruits are than mixed with sand and stored in a cold place until spring, or they are further processed to accelerate germination.
In the first case in spring the fruits are crushed on a clean concrete surface either by trampling with boots or by using a vehicle. Afterwards the crushed fruits are washed and air-dried. With the help of wind and a sieve the dried seeds are cleaned from other parts of the fruits. The seeds are then stored under a 5 cm layer of sand until fall and sown in fall (October-November)
In the second case the fruits are initially for one month stored in a barrel with water. Then the fruits are crushed and cleaned as described above. The cleaned seeding material will be stored in a pit, covered with moist sand mixed with some dung from horses or cattle. After one month the seeds are sown into the nursery.
In the area of the forestry enterprise brown bears feed on juniper fruits. In the bear feces many juniper seeds can be found, sometimes directly germinating. This “natural stratification” is sometimes used by forestry workers if they find substantial amounts of bear feces consisting of juniper fruits.
The seeds are sown directly into the soil in the nursery. Each, germination rate and survival are 90%. After five years the seedlings have grown to a height of about 20-30 cm, their roots reach 20 cm deep into the soil and they are ready for replanting.
The seedlings are carefully dug out, deep enough not to damage the root system and together with the earth covering the roots. They are wrapped in plastic bags for keeping the earth cover of the roots during transportation. During the planting the seedlings are put into the tree pits together with the soil from the nursery still covering the root system. The planted seedlings are watered.
After planting the seedlings are five years cared for, including weeding and if necessary watering either from a canal, if available, or with barrels.
The use of containers for seeding and replanting has not yet been tried. It may protect the root system during replanting and reduce the amount of soil to be used for this purpose. On the other hand the technology without containers is not dependent on their availability, no garbage in form of plastic containers is left in the tree pits and the larger amount of soil from the nursery may ease establishment of the seedlings at the woodland rehabilitation site.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Sughd
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Shahriston district; Shahriston Forestry Enterprise
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The approximate locatoion of the nursery is indicated. The planting of produced seedlings takes place in different areas.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology is implemented by Shahriston Forestry Enterprises since several decades.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الحرجي

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
- الترحال الرعوي
نوع الحيوان:
- ماشية - الألبان
- الماشية -لإنتاج اللحوم وليس للألبان
- الماعز
- الخيل
- الأغنام
المنتجات والخدمات:
- اللحوم

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- إزالة الخشب الميت/مخلفات التقليم
- استخدام الغابات غير الخشبية
نوع الغابة الطبيعية /شبه الطبيعية:
- النباتات لطبيعيةفي لأنظمة الجبلية المعتدلة
هل الأشجار المذكورة أعلاه ملحاء أم دائمة الخضرة؟:
- مختلطة ملحاء / دائمة الخضرة
منتجات وخدمات:
- حطب الوقود
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
- الترفيه / السياحة
- الحماية من المخاطر الطبيعية
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of fruits from natural juniper stands | November-December |
| 2. | Stratification, cleaning of seeds | Winter - spring |
| 3. | Seeding | Winter or October-November |
| 4. | Replanting | Fall, five years after seeding |
| 5. | Watering, weeding | Each summer, up to five years |
التعليقات:
Watering not always needed and/or possible. Often only once watered during first summer after replanting.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
The technology is implemented in the frame of the regular activities of the state forestry enterprise. No calculation of costs was available during the time of the documentation.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
التعليقات:
All maintenance activities (weeding, watering) are above indicated as establishment activities. After the planted juniper are established no further maintenance is required.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall is highly variable depending on altitude and aspect.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Shahriston (https://en.climate-data.org/asia/tajikistan/sughd-province/shahriston-28044/)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
Climate depends in altitude and aspect. At higher elevation and northern (eastern and western) aspect climate tends towards subhumid.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Nursery at terrace of valley, woodlands at mountain slopes of varying steepness and altitudinal zones.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil at nursery site may differ from conditions at the actual woodlands. Soil conditions in juniper woodlands can be very diverse.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Juniper typically grows in areas without ground water influence, but locally and where deforestation has not impacted the stands too much, juniper can also grow in riparian areas outside of the immediate influence of the river and subsoil water.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Biodiversity in juniper woodlands varies depending on the specific type of vegetation and use intensity.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The land-user applying the technology is the state forestry enterprise.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Nursery is only few hectares. Woodland rehabilitation takes place in areas of several ten hectares each. The overall area belonging to the land use (forestry enterprise) is >10,000 ha.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The forestry enterprise issues permits for seasonal use of juniper woodlands for livestock grazing by associations or individual livestock herders.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
التعليقات:
Not relevant for this technology.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
There are no scientific assessments of on-site impacts available. The assesment here represents a rough guess of impact of juniper woodland rehabilitation in moderately degraded pasture areas.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
There are no scientific assessments of on-site impacts available. The assesment here represents a rough guess of impact of juniper woodland rehabilitation in moderately degraded pasture areas.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | فصل جاف | انخفاض | باعتدال |
التعليقات:
Juniper trees grow at sites with a broad range of climate conditions, some of them rather extreme. They can therefore expected to cope with increasing aridity and short-term extremes at their natural stands. In the nursery drought can be compensated by watering, although intensive watering may hamper adaptability and survival of replanted saplings.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Rehabilitation of juniper woodlands provides only long-term economic benefits. Costs of cultivation in nurseries are partly compensated by combined growing of decorative coniferous treees (thuja, spruce) for commercial sale.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The technology is well established for the propagation of native juniper saplings and for the rehabilitation of juniper woodlands. |
| The technology has the advantage of allowing for the establishment/rehabilitation of tree stands with native species, which are adapted to local site conditions and are an integral component of the ecosystem. |
| The area of juniper woodlands in various stages of degradation in the country makes up many ten thousands of hectares. While resources (labour, nursery capacity) are prohibitive for replanting juniper in all areas, the technology allows for rehabilitation of key areas, identified by need and/or rehabilitation potential. In particular other forestry enterprises in the country with juniper woodlands could potentially adopt the technology. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Same as land user's view. |
| Same as land user's view. |
| Same as land user's view. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Substantial amount of work required. | Nothing suggested. |
| Juniper grows slower than other species. | Nothing suggested. |
| None mentioned |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Same as land user's view. | Consider facilitation of natural rejuvenation through grazing management (temporary exclusion of sites or reduction of grazing intensity or adaptation of herd compostion - no goats). |
| Same as land user's view. | Natutral feature of the native juniper tree species, which cannot be changed, but needs to be taken into consideration during production of planting material and in the management of the woodlands. |
| Over grazing may hamper success of woodland recovery. | Support establishment of replanted saplings through grazing management (temporary exclusion of sites or reduction of grazing intensity or adaptation of herd compostion - no goats). |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Site visit at nursery (November 2018), many site visits in juniper woodlands of Tajikistan and adjacent countries since 1993.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Interview with forest protection engineer of Shahriston Forestry Enterprise
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Interview with forest protection engineer of Shahriston Forestry Enterprise, with GIZ experts Negmatjon Negmatov (agricultural expert) and Nodir Muhidinov (DRR expert).
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
27/11/2018
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The documentation of the technology is based on the site visit at the nursery and one single interview with the forest protection engineer of Shahriston Forestry Enterprise. It was not possible to observe the entire process of propagation, cultivation and replanting of juniper and to verify the recieved information. The compiler took into consideration additionally his ecological knowledge and expertise. Given the importance of juniper woodlands as ecosystems in Central Asia, their large-scale degradation, the difficulties of their rehabilitation and the prevalence of non-native species in reforestation projects this technology deserves documentation and further consideration.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Disaster risk reduction and sustainable land-use by integrated … [طاجيكستان]
A site affected by a debris flow was rehabilitated by joint communal work and integrated preventive measures addressing the upper catchment as well as the valley and the debris conus were implemented in collaboration of community, individual farmers, Committee of Emergency Situations and forestry enterprise.
- جامع المعلومات: Stefan Michel
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية