Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources [تشاد]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Bonnet Bernard
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Simone Verzandvoort, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter
Projet Almy Al Afia
technologies_3356 - تشاد
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 12 مارس، 2019 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 مايو، 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 28 مايو، 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 13 مايو، 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 مايو، 2018 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bernard BONNET
IRAM
فرنسا
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Degradation of natural resources is taken into account in the management of water resources for pastoral land, and in the social approach prior to the development of the technology. For example, the locations of new sites for water supply structures should correspond to the capacity of the grazing land in terms of the period of access, the quantity of available resources and the integration of the area into a larger coherent landscape (especially the complementary relationship between the agropastoral zones in the south and the pastoral zones in the north). Several impact assessments and preliminary analyses have been carried out, including diagnoses of the pastoralist system with regard to the logistics of the movements of the herds, the social organisation related to the management of the areas, diagnoses of the grasslands, geophysical analyses, etc.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Securing the mobility of pastoralism through access to water sources (open wells and ponds in pastoral areas) and marking the livestock routes for transhumance: the case of the project Almy Al Afia in Chad and its consultative approach.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
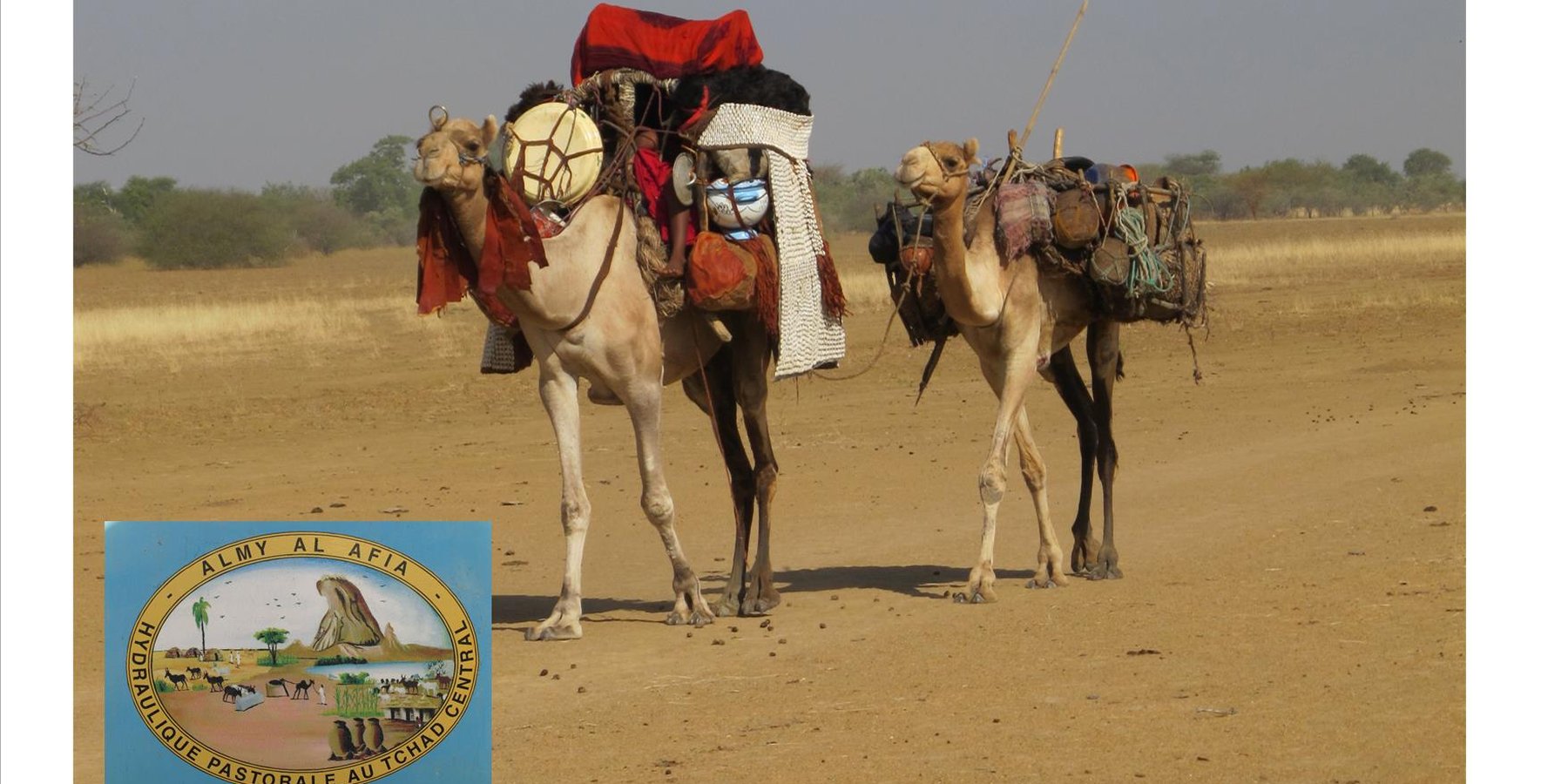
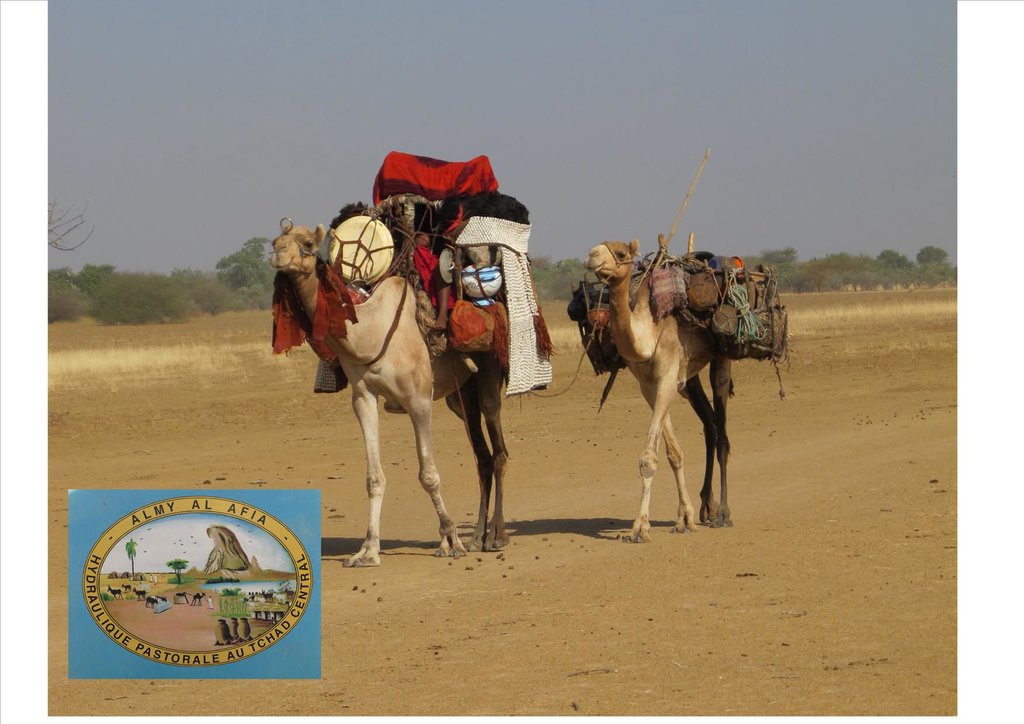
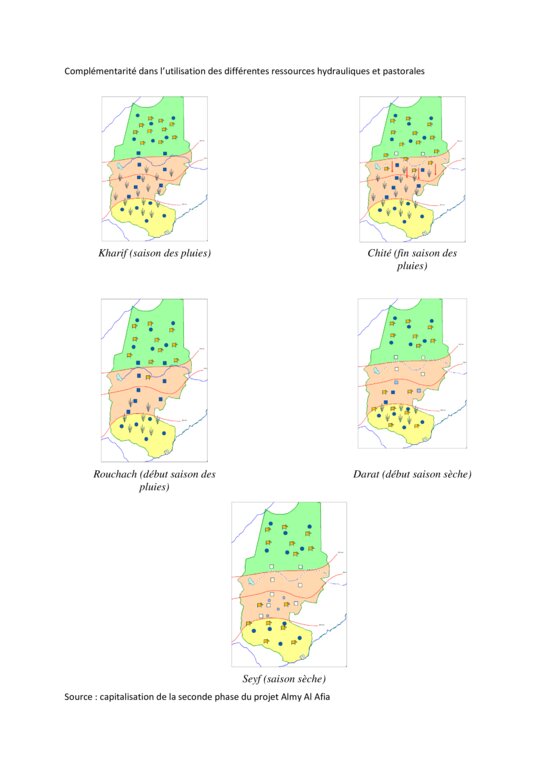
Livestock keeping is one of the main economic resources in Chad (in support of 40% of the population and 18% of the GDP, Ministry of Livestock, General census). Pastoralism in the country is based on the mobility of herds in a context of irregular precipitation and variable forage resources in time and space, and benefits from complementary relationships between the different ecological zones. In Chad, herds are taken in regular movements with the seasons between the Sahelian and the Sudanese grazing areas. The former are nutritious but limited in quantity, while the latter are more abundant but of lower quality, and not accessible until the fields are cleared after the harvest (meta-evaluation of projects on pastoral water sources, IIED, 2013). Thus, pastoral livestock keeping is founded on mobility and rangeland management, and on building complementary relationships and trade around farming systems and cultivated areas. The pastoralist systems are economically competitive (limited use of food inputs), and occur in marginal land which is characterized by conflicts, riots and a high level of insecurity (Conference of N'Djamena: 'Pastoral livestock keeping: a sustainable contribution to development and security in Saharan and Sahelian regions'). In the pastoral zone of Chad, where access to water is limited, the management and control of water sources by a social group in practice also leads to the monitoring and control of the use of grazing land which becomes available when water is present.
The project Almy Al Afia (2004-2016), developed by a partnership between the AFD and the Ministry of Water of Chad, operated in two regions of central Chad. The project Almy Al Afia was based on an entry 'development', concurrently with a process to consult and involve joint agencies. The project has improved approaches of preceding initiatives: concerted action and identification of water sources derived from the dialogue between users and authorities, and development of the local management of infrastructures and rangeland. The latter counteracts an exclusively private management or, instead, an ineffective public management which promotes free access to water sources and grazing land.
The project has enabled to address the following points:
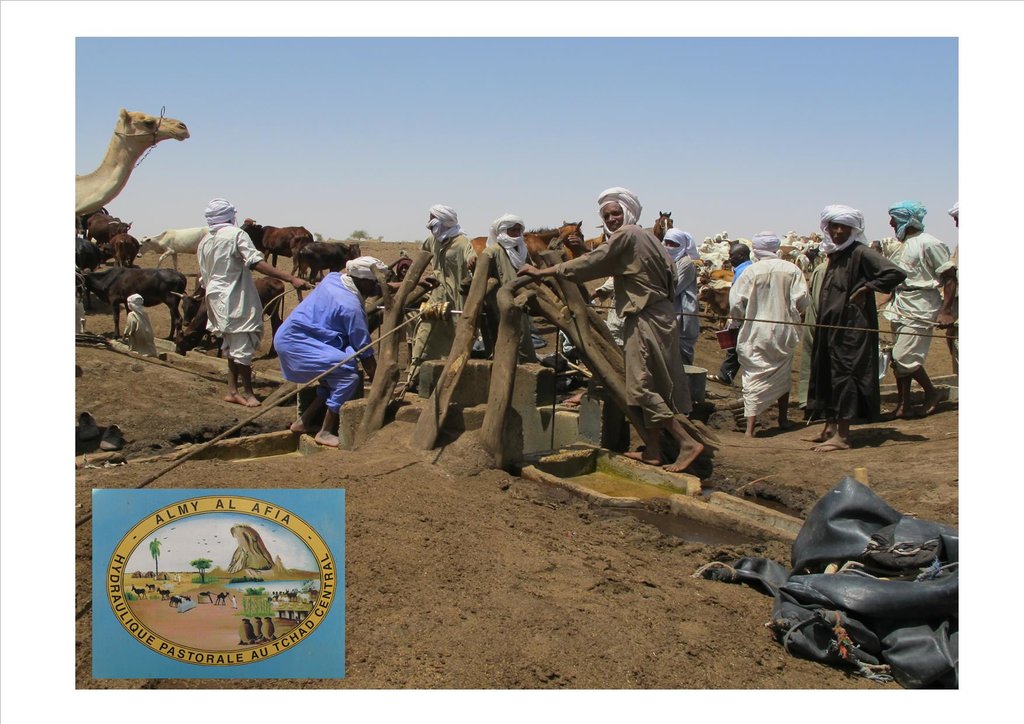
1. Support mobility in pastoralism by enhancing the access to water (rehabilitation and construction of 160 wells; digging of 31 ponds for pastoral use);
2. Maintain or build processes of consultation and restoring security (joint committees for consultation and prevention of conflicts during transhumance);
3. Promote the proper use of water supply structures, in time and space (rehabilitated and new wells, excavated ponds) by context-specific management (strengthening of traditional management systems) and encourage the maintenance of infrastructure.
The pastoral ponds should be constructed in locations of existing water sources (natural ponds in suitable places, i.e. with a clayey soil capable to retain water). The existing water source is enlarged and improved by rural engineering (enlargement of the surface, deepening).
The wells are rehabilitated. Most wells were constructed several decades ago and are severely damaged. The water supply structures all have different and complementary functions. The deep wells in the pastoral zone are generally used throughout the year, and are overexploited. The way in which these structures are managed is strongly anchored in the region. The District officer delegates the management to 'Heads of Wells'. These old wells, which are used day and night, are often in a poor condition. Rehabilitating degraded wells is given priority over digging new wells because of the substantial potential for conflict. The water supply structures in areas of dry forest are less old and smaller in number. These wells are less frequently used and function as an alternative water source when the traditional ponds, water reservoirs and wells have dried up. They allow to delay the movement of the herds towards grazing areas in the Sahelian zone.
The strip between these two zones is used for agropastoralism. Herds cannot remain there. Therefore the project has facilitated the movement of the herds to the zones further south. The pastoral ponds close to the livestock routes for the transhumance were created in a way to be easily used by the herders, but also to encourage short stays.
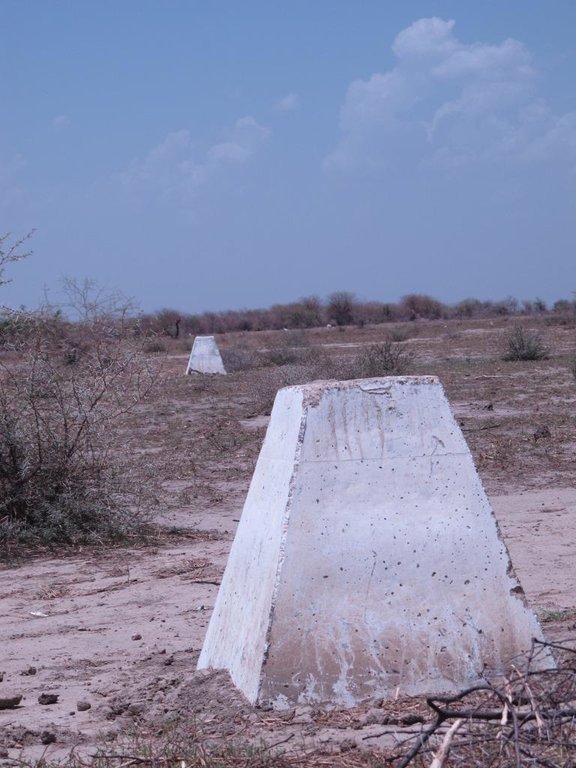
The approach was combined with consultation through joint committees for the prevention of conflicts, and at a later stage by marking of sections of the livestock routes for the transhumance. Many meetings were held with the users of the land management structures and policy makers, with the aim to identify and negotiate the target sites and to anticipate methods for the management and maintenance of the structures. This has enabled to maintain an atmosphere of social stability conducive to cooperation. Along almost 550 km of the livestock routes for the transhumance, sections were marked ('mourhals' in Chadian Arabic). The demarcation was not intended to enclose the herds in the livestock corridors (from which they can move freely outside the growing seasons for agricultural crops), but rather to implement the results of the consultations on the land use on the ground. The committees for the prevention of conflicts, which were supported by the project, also played a major role.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تشاد
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Regions of Batha and of Guéra
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Although the sites where the technology was applied are at the local scale, the project has considered pastoralism and the relationships between the two regions at the broader landscape scale.
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
التعليقات:
Main towns of the two relevant regions (Ati for the region of Batha and Mongo for the region of Guéra).
The water sources constitute an anchorage point for the herds. The surrounding grazing land is controlled by the access to the water supply points (impact zone with a radius of 15 to 20 km around the wells). Apart from the area directly influenced by the technology, complementary relationships between the zones provide an added value: hence the zone targeted by the decision-making process of the herders is very large.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2018
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Projects on pastoral water resources like the project Almy Al Afia primarily focus on the development of water sources for pastoralism. The phases preceding the implementation are extremely important, because they are based on consultation and on the appreciation of local management systems. These phases include registration, selection of construction sites and the development of guidelines.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
- رعي شبه مرتحل
نوع الحيوان:
- الجمال
التعليقات:
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: Variable depending on zones and seasons.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
In these zones, rainfall is erratic in terms of spatial distribution and in quantity. Hence, grazing areas are not uniformly covered from year to year. The mobility of herds is the only way to adapt to this variability.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- إدارة المياه الجوفية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- منشآت المرافق الصحية/مياه الصرف

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
The wells (new and rehabilitated) and the demarcation of the livestock routes are the outcome of a long process of outreach. The communications between the local level (taking account of the views of future users) and the level of decision-making (administration) enable social agreements to be formalized. These agreements set the rules for the selection of the locations of the water supply structures, their management and maintenance.
المؤلف:
Project Almy Al Afia
التاريخ:
2016
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Structure (new well, rehabilitation or km of markings)
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
FCFA
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1000 FCFA
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Outreach / awareness raising | Four to six meetings prior to the signing of the social agreements |
| 2. | Construction of the facilities | Four to six months, depending on the type of structure and its depth |
| 3. | Monitoring the management | Regular visits of the project team to support the implementation of adapted management practices |
التعليقات:
The implementation of the different phases varies greatly in terms of the location of the outreach activities and the duration of the construction work.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| مواد البناء | Rehabilitated wells (mean depth 56 m) | 1 | 93,0 | 10497939,0 | 976308327,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Geophysical assessment for new wells | 1 | 158,0 | 17979914,0 | 2840826412,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Exploration drilling for new wells (mean depth 96 m) | 1 | 220,0 | 6005415,0 | 1321191300,0 | |
| مواد البناء | New wells (mean depth 45 m) | 1 | 62,0 | 45145740,0 | 2799035880,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Pastoral ponds (6000 m3 on average) | 1 | 31,0 | 23008065,0 | 713250015,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Markers (8 signs / km) | 1 | 492,0 | 1069203,0 | 526047876,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Outreach on new wells (/site) | 1 | 62,0 | 213428,0 | 13232536,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Outreach on rehabilitation (/site) | 1 | 93,0 | 248695,0 | 23128635,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Outreach on marking (/km) | 1 | 492,0 | 52088,0 | 25627296,0 | |
| غير ذلك | None | None | ||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 9238648277,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 9238648277,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The context of pastoralism has taken the project approach to not ask compensation from users: if the users are never the same, then who should be charged? Who will collect the payments and manage the collected funds? In addition, most of the water supply structures are far from financial institutions, which causes problems in securing these funds. Therefore the users contribute in terms of day-to-day maintenance of structures, by mobilizing labour in particular.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mobilising indigenous groups for day-to-day maintenance of structures (dredging, cleaning) | Depending on the type of structure (generally monthly) |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Support missions for the management and maintenance of the water supply structures (2 missions per structure for the entire project) | 1 | 155,0 | 53000,0 | 8215000,0 | |
| العمالة | Support mission for the management and maintenance of the markings | 1 | 100,0 | 53000,0 | 5300000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 13515000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 13515000,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The amount of financial support varied with the type of structure (more support for management and maintenance is needed for new structures than for rehabilitated structures) and with their location or specific problem (in the case of structures located in the agropastoral zones). Financial support to the markings of the livestock corridors was indirectly provided through the committees for the prevention and management of conflicts.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The costs of the constructions are highly dependent on their location (costs for the supply and disposal of equipment and materials), on the price of inputs (cement, etc.), and especially on the type of structure (depth of the wells, geological environment). The costs of the supply and disposal of equipment and materials include costs for the installation of the structures (water, cement, labour, machinery) on the construction sites (which are often far away from routes and towns), and costs for the disposal of the equipment after the construction is completed. The costs of supply and disposal can be significant with respect to the costs of the structure itself.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
One rainy season per year (from June to September)
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Ati
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
The target region includes large areas extending over important gradients (encompassing boundaries of the desert zone, the forested zone and the cotton-growing zone).
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
حدد:
Depending on the zones: presence of sodium carbonate.
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
- مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
Transhumance, and more generally pastoral mobility, applies to large geographical scales and long periods. The areas involved are very large, far above 10.000 ha.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- لمجموعة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expansion of the areas covered by water supply points. Reduced closure of water supply points (rehabilitation), opening-up of new grazing land, securing the movement of livestock and people.
نوعية المياه للماشية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Preserving the capacity of herders and their families to move, to choose their trajectories rather than responding to imposed conditions.
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
التعليقات/ حدد:
Upgrading of traditional management systems of water supply structures.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduction of the impacts of the concentration of livestock and people in small areas. Promotes the complementary relations between the zones (pressure relief in some zones and use and maintenance of other zones), and over the seasons.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التنوع النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
n/a
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased access to groundwater through the rehabilitation of wells and the construction of new wells.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
As explained above, in these zones with low rainfall and scarce natural water sources of temporary character (ponds), it is essential to combine the use of surface water with the use of water from deep permanent groundwater bodies. When they have the choice, herders almost exclusively choose sources with surface water (avoiding effort to extract the water). But when these sources run dry, they fall back on using wells (and deep groundwater). The rehabilitation of old wells and the construction of new wells in zones without wells contributes to increasing the availability of water.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | ليس جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The profitability is considered in relation to the number of animals/herds involved. The costs of construction and rehabilitation are certainly significant, but the water supply structures are used for thousands of animals (in case of the most heavily used wells); most animals drink every two days. Therefore the costs per head of livestock are limited. The wells are long lasting, and therefore the returns are positive in the short and the long term.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
The technology responds to a substantial need, but also corresponds to the capacity of land users to use and maintain the structures. The energy supply is provided by animal traction, and does not require external energy sources.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
Access to water is such a large problem that it requires all the land users who enter the zone to be informed when a water supply structure is rehabilitated or constructed. The involvement of traditional leaders in the management of the structures, and the system of representatives of the traditional leadership in the various other zones (Khalifas) contributes to the spontaneous dissemination of the information.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Permanent access to water. |
| Reopening of water supply structures and consolidation of access to water at some degraded sites. |
| Agencies and authorities for conflict prevention. |
| Marking of sections of livestock corridors with conflict situations. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Full commitment of groups (access to water is a major problem). |
| Continuation of the approach through the development of other projects and inclusion at the national level. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Interventions are limited with regard to the needs (rehabilitation in particular). | By larger investments and better integration of the approach in public action. |
| There is a need to extend the approach, in particular the support to the consultative bodies. | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
|
Recognition of the experiences, the approach and the methodology in other interventions. Outreach and awareness raising are performed during the project, but at the end the management of the infrastructure is no longer supported. The government should be able to follow up on the support (mechanism for monitoring and maintenance). |
Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| There is a need to mainstream outreach and consultation (lengthy process). | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Progress reports and thematic reports of the project Almy Al Afia
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Follow-up and evaluation of the project activities (logbook, annual update)
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Creating value from lessons learned in the project Almy Al Afia (Republic of Chad, Ministry of Water)
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
2016
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Capitalisation des enseignements de la deuxième phase du projet Almy Al Afia, Main document, DHP, Antea/Iram, March 2016
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Document de Suivi-Evaluation des activités du PHPTC II, tableau de bord des activités du projet, DHP, Antea/Iram, mars 2016
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Note Entretiens Techniques du PRAPS, Accès et gestion durable des espaces pastoraux (chemins de transhumance, aires de pâturages et de repos), PRAPS, 2016, B. Bonnet, A. H. Dia, P. Ndiaye, I. Touré
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Evaluation et capitalisation de 20 ans d’intervention du Groupe AFD portant sur le secteur de l’Hydraulique Pastorale au Tchad, IIED, May 2013, S. Krätli, M. Monimart, B. Jallo, J. Swift, C. Hesse
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Platform on pastoralism in Chad
عنوان الرابط URL:
www.plateforme-pastorale-tchad.org/
العنوان/الوصف:
Website of PRAPS-TD
عنوان الرابط URL:
www.praps.cilss.int/index.php/praps-pays-tchad/
العنوان/الوصف:
Website of Iram
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.iram-fr.org/elevage-pastoralisme-et-hydraulique-pastorale.html
العنوان/الوصف:
AFD in Chad
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.afd.fr/fr/page-region-pays/tchad
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية