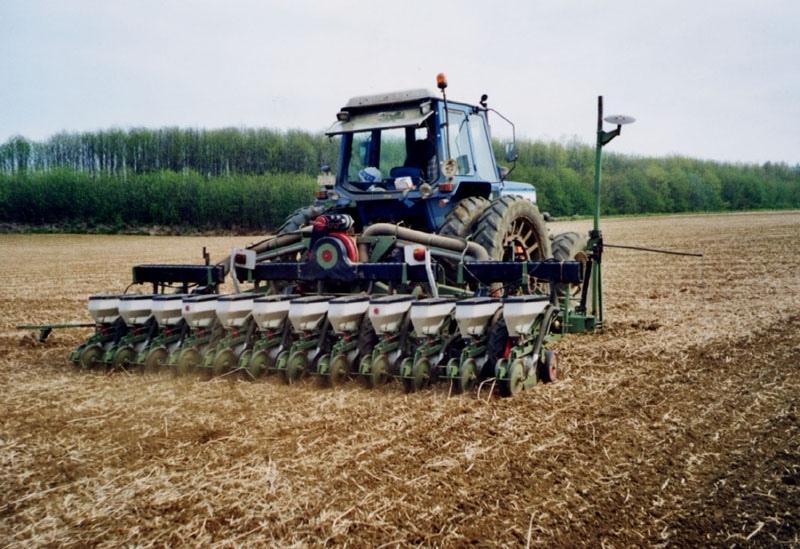
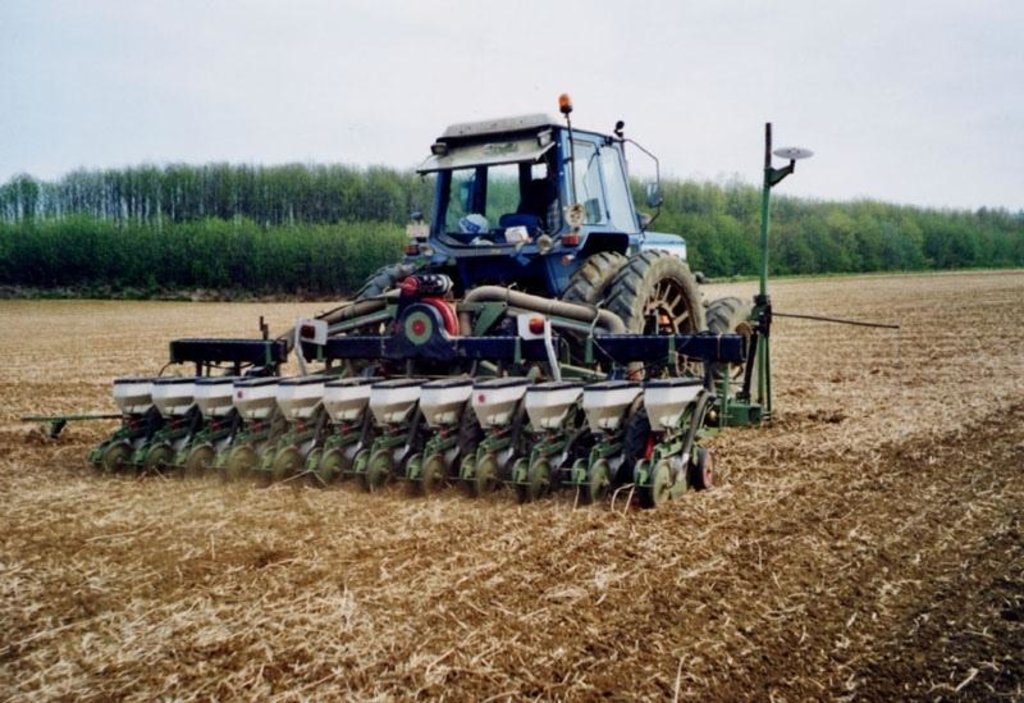
Non-inversion deep cultivation [بلجيكا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Diepe, niet-kerende bodembewerking
technologies_967 - بلجيكا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Gillijns Katleen
Catholic University of Leuven
بلجيكا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Govers Gerard
Catholic University of Leuven
بلجيكا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Catholic University of Leuven (KU Leuven) - بلجيكا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [بلجيكا]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
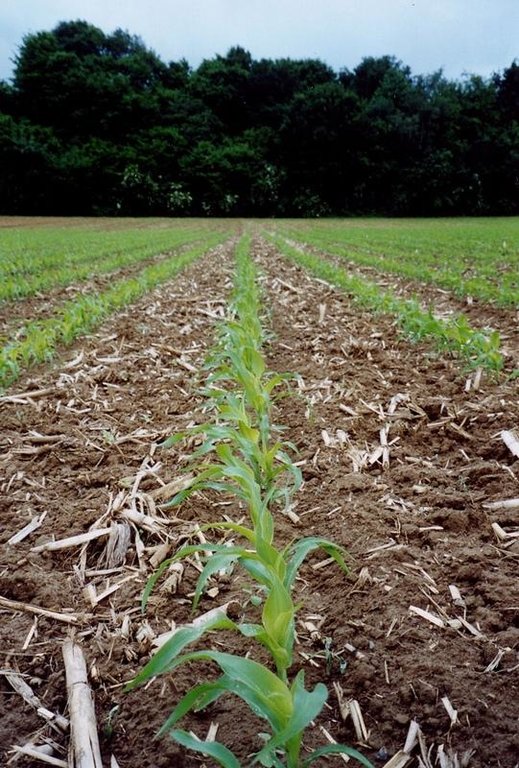
The technology consists of the use of cover crops and of a non-inversion seedbed preparation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The technology consists of agronomic measures. The most important thing is that the farmers are not allowed to invert the soil by ploughing. Farmers may only cultivate their fields at plough depths. Farmers also have to use a cover crop, if possible. In this way the soil is always covered with residues of a previous crop or with residues of the cover crop. The improvement of the ground cover protects the soil against different kinds of water erosion. In the long term period, the soil structure will improve (more organic matter in top soil) and more earthworm activity will be determined. The infiltration will increase.
Purpose of the Technology: Protecting the soil against erosion and increasing infiltration.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The farmer may never plough.
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on cropland with annual crops.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بلجيكا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Flanders
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Vlaams-Brabant
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
0,0046
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0046 km2.
It's a field trial with 3 treatments. Every treatment is 4620 m² (see map). The 3 treatments are: non-inversion shallow cultivation, non inversion deep cultivation and conventional ploughing. In the region of this field, other farmers are also experimenting with the technology on their own fields.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
In the Walloon part of Belgium and in the surrounding countries (France, Germany), farmers are already applying this technology for a long time. In Flanders, the technology was introduced in the 1970' by professor De Ploey of our Faculty. Farmers didn't see the benefits of the technology and decided not to implement the technology. Now, time has changed: farmers know that they have to do something against the erosion problem.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطس
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية -الشمندر السكري
- wheat
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct; Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Nov
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat - potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat -sugar beet

أراضي الرعي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil loss by water erosion. Soil erosion related environmental problems 'muddy floods, retention pond sedimentation, declining water quality due to sediment and sediment - fixed contaminants)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Strong nitrogen regulations and EU rules are hindering the farmer.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: normal sequence of crops at the farm: sugar beet - wheat - potatoes - maize. Crop rotation at the experimental field: maize - wheat -sugar beet
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
- انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (soil erosion), lack of knowledge
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes, hevay machinery)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter
Cover cropping
Material/ species: maize 2004
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: winter wheat 2004-2005
Agronomic measure: cover cropping
Material/ species: oats 2005-2006
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover
Remarks: by not ploughing, every year.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: injection of slurry 2004
Quantity/ density: 40000l/ha
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N with seed 2004
Quantity/ density: 200 kg/ha
Remarks: 26%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 120 kg/ha
Remarks: 38%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: spraying N 2005
Quantity/ density: 175 kg/ha
Remarks: 39%
Agronomic measure: manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: broadcast N 2005
Quantity/ density: 45 kg/ha
Remarks: 27%
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: 30 % K
Quantity/ density: 800 kg/ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: every year
Minimum tillage
Remarks: every year
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | injection of slurry, spraying paraquat (to kill previous crop) | mar 04 |
| 2. | sowing maize, nitrogen fertiliser | apr 04 |
| 3. | herbicides | may 05 |
| 4. | harvesting maize, sowing winter wheat | nov 04 |
| 5. | nitrogen fertiliser | mar 05 / apr 05 |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Comparing to ordinary field operations, there are normally no additional costs if applying the new technique. The farmer will not plough anymore, this is an economic benefit. In some cases and for some crops the farmer will use another machine, for example: the farmer will need a direct drilling machine for sowing sugar beets in stead of a normal sowing machine. In Flanders, always agricultural contractors are sowing beets (not the farmers). The agricultural contractor will ask the same price for the normal sowing machine as for the direct drilling machine. Although farmers have no additional costs, they get subsidies (80€/ha.year for shallow cultivation, 200€/ha.year for no tillage) from the Flemish Government for practicing the new technique - subsidies are mainly given to encourage the farmers.
Additional info: herbicides - apr 05 / 2 herbicides - may 05 / 2 nitrogen fertiliser - jun 05 herbicides - jun 05 harvesting winter wheat - aug 05 fertiliser (manure) - sep 05 fertiliser K - sep 05 sowing oats - sep 05
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
780,10
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: 10 %
Landforms: The main topographgy is a plateau (100 above sea level) in which rivers are incised. The technology is applied at fields situated on the slopes between the plateau and the valley.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: The loess deposits, which vary in thickness between a few dm to several m cover Terti
Soil texture (topsoil): 60 % loam, 30% sand and 10% clay.
Topsoil organic matter: 1,2% (experimental field)
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration
Soil water storage capacity is medium and sometimes very high
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are rich and own 80% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The farmer is only working at his own farm.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Because of reduced working time and lower fuel consumption
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
special equipement
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
farmers opinion of a non-ploughed field
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
34
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
18
التعليقات/ حدد:
Also 21 before, 18 after
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
More residues
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
28.26
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
التعليقات/ حدد:
Significant reduction in soil loss
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
biodiversity
التعليقات/ حدد:
More earthworms
use of herbicides
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Because of less runoff
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nowadays about 49% of the farmers in the region are practicing conservation tillage, whereas only 33% was doing it in 2001. At the beginning of the project 63% of the farmers intend to cultivate their fields in a conservative way into 3 years. (based on e
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| less soil erosion |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The technology clearly reduces the erosion risk while maintaining profitability. |
| The new technology also ha other benefits on soil structure and biodiversity. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| high investment costs for buying new agricultural machinery | |
| more attention to crop damages caused by slugs and mice should be given. | |
| practising the new technology requires a relative dry soil |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Practising the new technology requires a greater skill of the farmers | education, training |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
SOWAP Project. 2003-2006www. Sowap.org.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Introduction of conservation agriculture in a highly mechanised … [بلجيكا]
Combination of 'dissemination of the SWC technology 'non-inversion tillage'' and research.
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية