Horsetail Beefwood (Casuarina) Windbreak along Seaside [China]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Seaside Shelter Belt of Horsetail Beefwood' test
technologies_960 - China
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. معلومات عامة
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
Planting Horsetail Beefwood (Casuarina) As Windbreak Along Seaside [China]
Planting Horsetail Beefwood along seaside to protect cropland from sea wind erosion and typhoon destroy.
- Compiler: Unknown User
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Planting Horsetail Beefwood as a shelter belt along seaside to prevent serious wind and water erosion/destroy of the cropland.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Horsetail Beefwood windbreak along seaside is applied to prevent serious wind and water erosion/destroy of the cropland. It is planted as a shelter belt in the cropland. Horsetail Beefwood is a perennial tree growing in sub-tropic and tropic climate. Its timber can be used in industry and fuel timber. It is easy to maintain.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
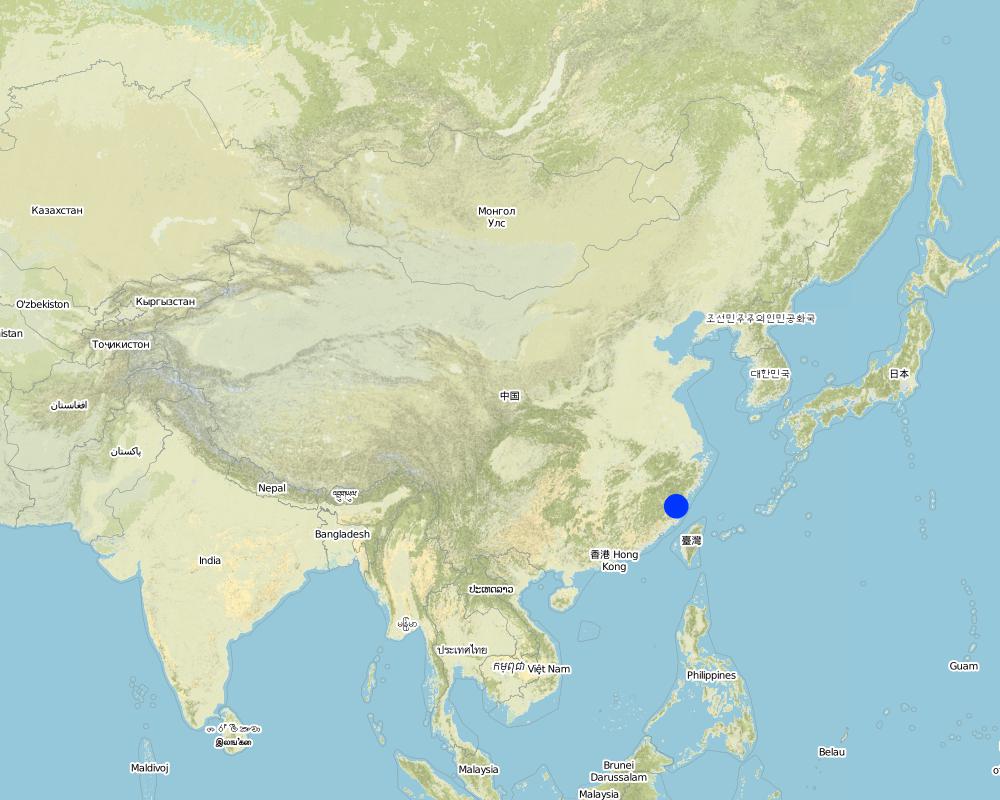
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
بلد:
China
Region/ State/ Province:
Ningde Prefecture
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
2,0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 km2.
It is a vegetative measure applied in the cropland along seaside and has marked effect on prevent wind erosion and destroy in the cropland.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Tai Wan
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
نعم
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

الأراضي الزراعية
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fibre crops - cotton
- rice
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
حددها:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - Dec

Forest/ woodlands
Products and services:
- Timber
- Fruits and nuts
- Other forest products
- Nature conservation/ protection
Mines, extractive industries
حددها:
causing damage of vegetation
Comments:
Grazingland comments: Household grazing tends to standardize and stall feeding.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The forest cover percent increase little, strenghtening the tree planting.
Forest products and services: timber, fruits and nuts, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Rice, cotton
Type of grazing system comments: Household grazing tends to standardize and stall feeding.
Constraints of recreation
Constraints of Urban: Urban construction does not coordinate with environmental protection
Constraints of Industrial/mining: causing damage of vegetation
Constraints of Wilderness
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- windbreak/ shelterbelt
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, lack of knowledge
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: Wind-break
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: Casuarina braches
Quantity/ density: 80%
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Cash & lots of shrubs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 1.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3.50
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting trees(strip) | Spring |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | minimun tillage | spring,summer / twice a year |
| 2. | Planting SWC forest | Spring /once a year |
| 3. | Supplementing trees | Spring /once a year |
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Landforms plateau/plains: plain of seaside
Slopes on average flat: 1.0 - 1.5%
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
2% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 8% of the land.
85% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
3% of the land users are poor and own 2% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The land users who adopt the SWC can get much more subsidies from government or projects and less loss caused by damage of the sea wind or typhoon than those who take no SWC technology.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- group
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
7
Quantity after SLM:
6
Soil
soil loss
Quantity before SLM:
260
Quantity after SLM:
200
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
175 (around 50 percent of the area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
85% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
85 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Low input but marked output.
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Planting Horsetail Beefwood (Casuarina) As Windbreak Along Seaside [China]
Planting Horsetail Beefwood along seaside to protect cropland from sea wind erosion and typhoon destroy.
- Compiler: Unknown User
Modules
No modules