No tillage operations, plastic nets permanently on the soil surface [اليونان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Κάλυψη με πλαστικά (Greek)
technologies_1087 - اليونان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mentzidakis Ioannis
National Agricultural Research Foundation - NAGREF - Institute of Olive
اليونان
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - اليوناناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Agricultural Research Foundation (NAGREF) - اليونان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
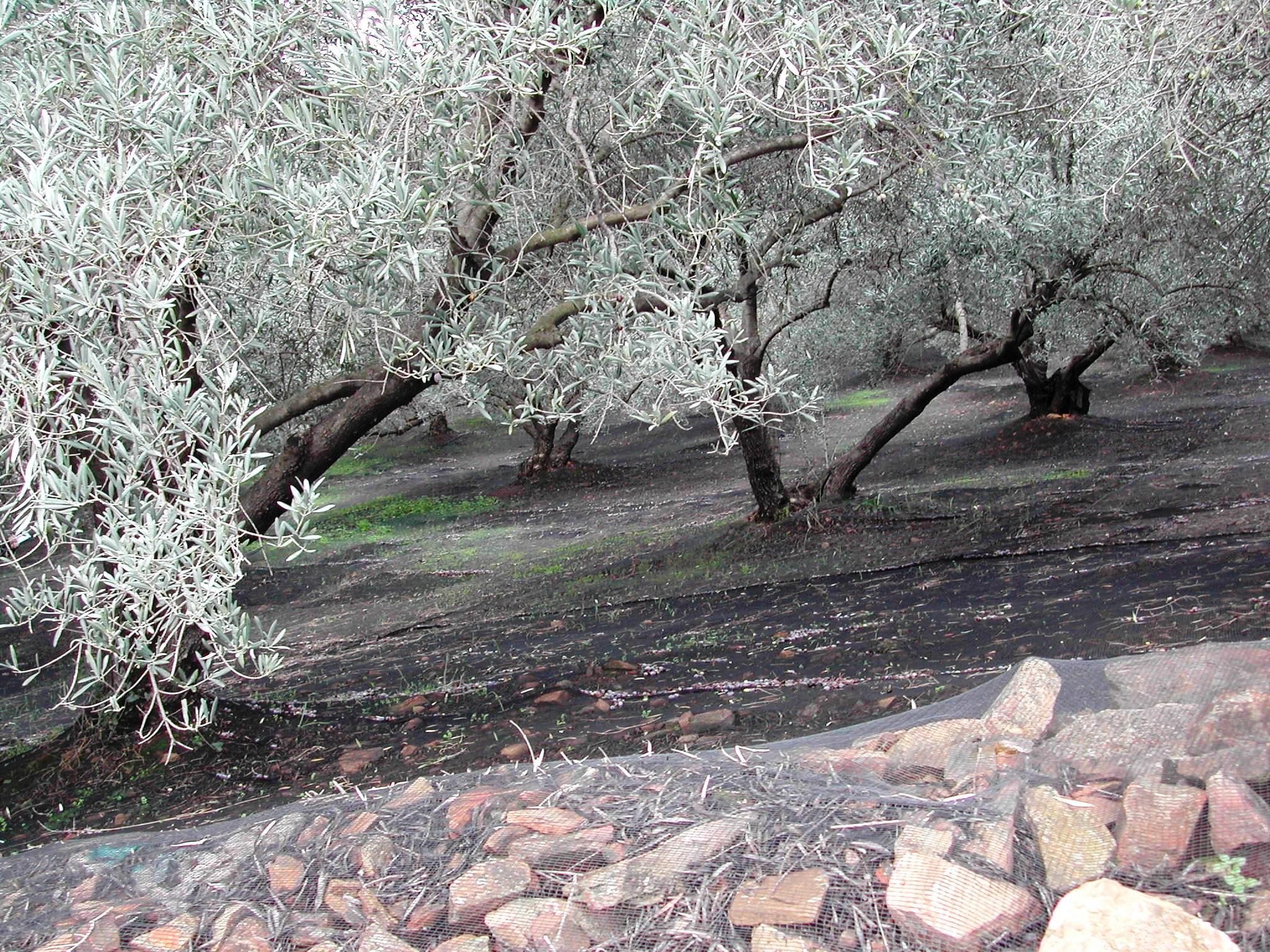
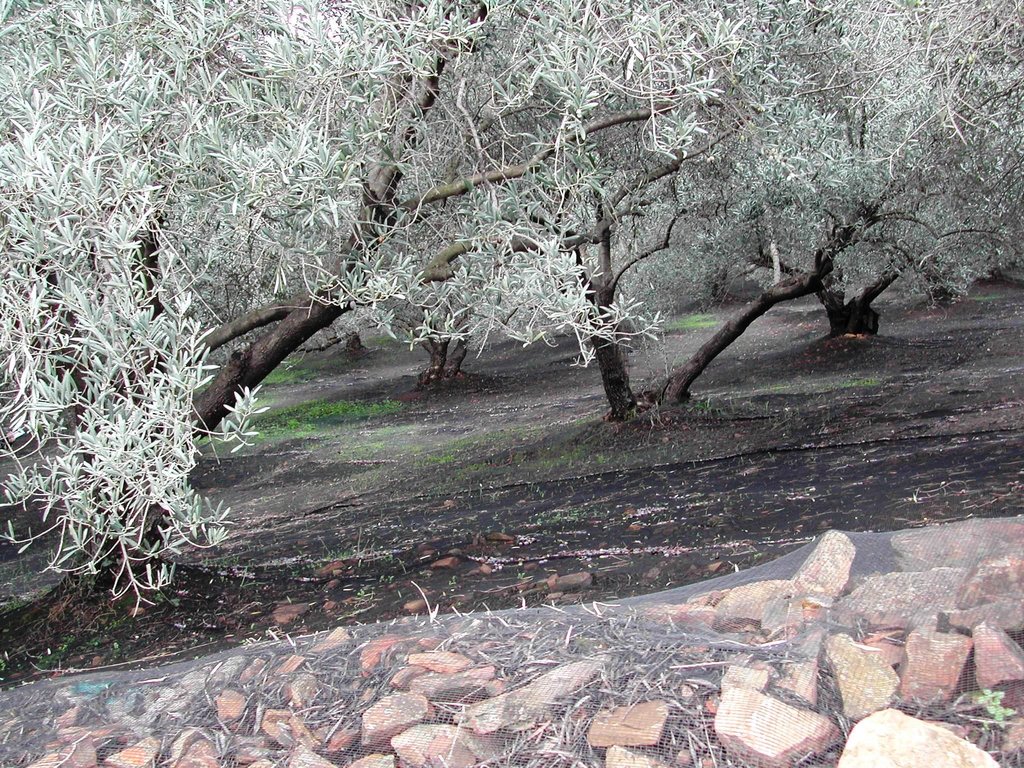
A technology which combines no tillage operations and the cover of the ground with plastic nets
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
This technology has the same main advantages and characteristics as no tillage operation against soil erosion and water lconservation. Soil erosion is drastically reduced since soil surface is protected from raindrop splashing by the existing annual vegetation and the plastic nets. Soil water evaporation is also reduced due to the mulching provided by the plant residues and the nets. Furthermore, higher amount of rain water is infiltrating into the soil compared with other traditional LMPs. The specific technique has emerged as a need to overcome obstacles to the collection of olive fruits and protection of the nets from animals. Nets are spread in the whole field (intensive cultivation) covering completely the soil surface or part of the field (extensive cultivation), so olive fruits falling down can be periodocally collected by the farmer. Furthermore, a problem arises if nets are removed from the ground and stored. Animals, like mice, prefer to go in and make their nets by destroying them. Therefore, by keeping nets in the field during the whole year they are protected from such damages. Nets are installed in the field by stones or using metallic pins of about 15 cm long which are entered into the soil. Nets can remain in the field at least 10 years. Referring to the map showing areas undergoing tillage and non-tillage operations in the study area of Chania, it can be noted that the combined technique using cover nets is applied mainly in areas with high altitude and at a rate of approximately 15% of the no tillage area.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اليونان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kissamos province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Chania-Crete
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 km2.
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الزيتون
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 150Second longest growing period from month to month: March to June
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high soil erosion rates and lack of water for irrigation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Hig cost of olive oil production
3.4 إمدادات المياه
التعليقات:
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (soil erosion), poverty / wealth (loss in farm income)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: oxalis sp
Mulching
Material/ species: plastics
Quantity/ density: plastics a
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green manure, oxalis sp
Remarks: natural growing plant
Zero tillage / no-till
Remarks: tillage is not allowed since nets will be destroyed
In blocks
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Perennial crops species: olives
Other species: existing vegetation
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Euro
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1,49
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
80.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy the nets |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Installation | ha | 1,0 | 320,0 | 320,0 | |
| معدات | Nets | ha | 1,0 | 2700,0 | 2700,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 3020,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 2026,85 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.1 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | replacing destroyed nets | 0.2 days/ha/year |
| 2. | reinstalling nets removed by winds or other reason | 0.5 days/ha/year |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: no tools
the cost has been calculated for the year 2009
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
the purchase of materials
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
With 6 months of dry period
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Water quality (untreated): good drinking water, for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Yes women are used to work mainly in the house
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are rich.
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Problem if a minimum tillage LMP is applied since nets must be removed
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1800 Euro/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3200 Euro/ha
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in farmers income and reduction the off-site effects
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
protection of the area from flooding or from animal passing over
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Reduction of labor and protection of of harvesting materials
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
500
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Reduce cost production but create problems to the cultivation of olive groves. The major cost in olive production is labour for harvesting. By applying this technology harvesting labour is minimized to about one tenth. It can be viable at small to medium scale farms, prone to water erosion, on very steep slopes where harvesting of olive fruits by the traditional methods become very difficult. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Providing financial support |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Technologies on conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete are mainly related to land management. Olive groves can survive under adverse climatic and soil conditions supporting a significant farmer’s income under relatively low labour. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and transfer knowledge by the local institutes and specialists. The no tillage land management practice combined with plastic nets on the soil surface can be considered as an important technique protecting the land from degradation and desertification and increasing farmer’s income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By explaining the advantages and disadvantages of the technology to the farmers |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Difficulties in removing perrenial natural vegetation and spreading the fertilizers. | applying fertilizers by the irrigation system |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Too many plastics spread around in an area. Recycling of plastics is a great problem. | no overcome |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية