Olive groves under no-tillage operations [اليونان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Ακαλλιέργεια (Greek)
technologies_1035 - اليونان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ioannis Mentzidakis
National Agricultural Research Foundation - NAGREF - Institute for Olive Tree and Subtropical Plants of Chania
اليونان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - اليوناناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Agricultural Research Foundation (NAGREF) - اليونان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Sustainable development of olive groves I [اليونان]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas

Sustainable development of olive groves II [اليونان]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations and plastic nets on the soil surface
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
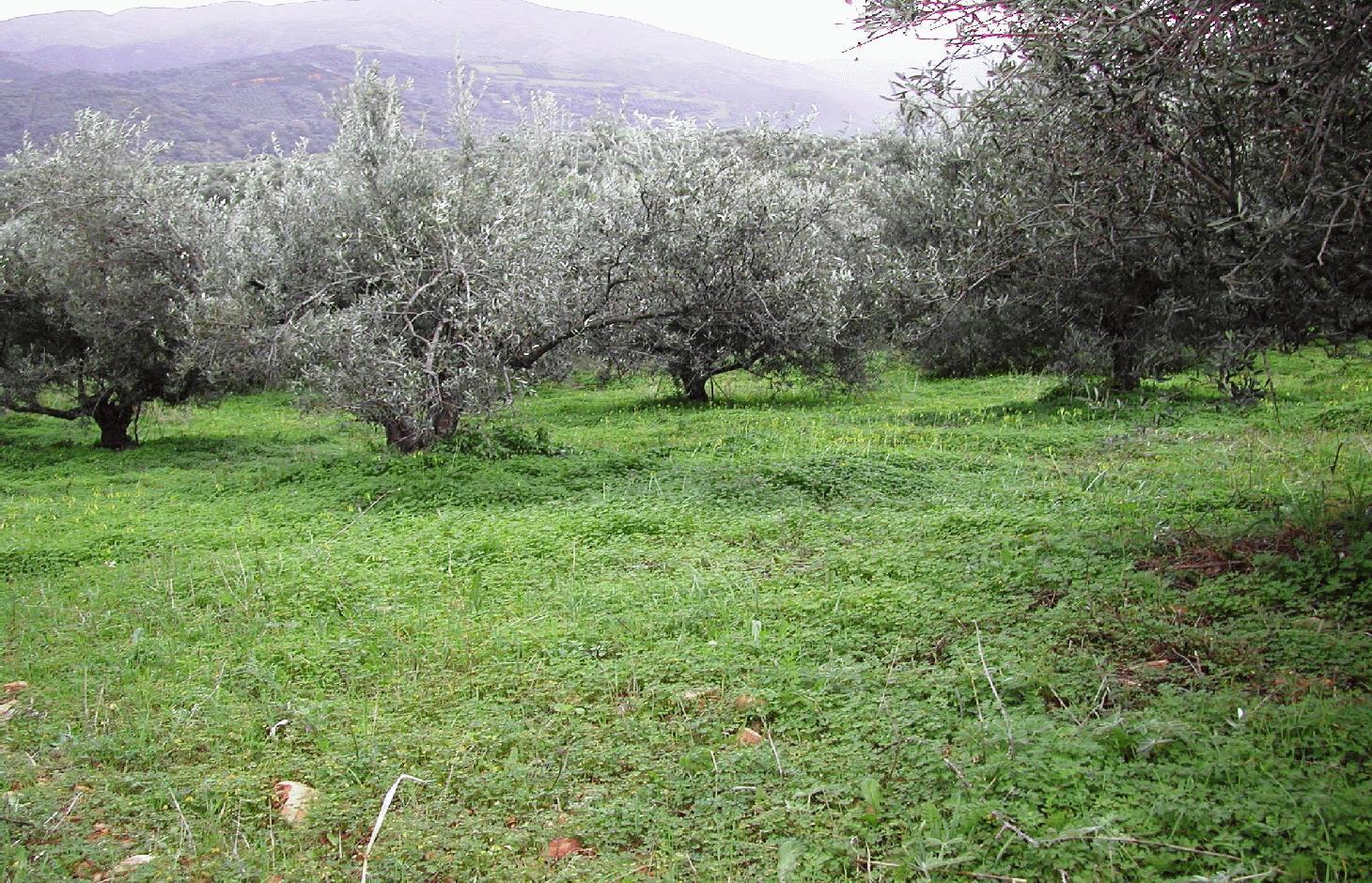
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Olive groves under no tillage and no herbicide application.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
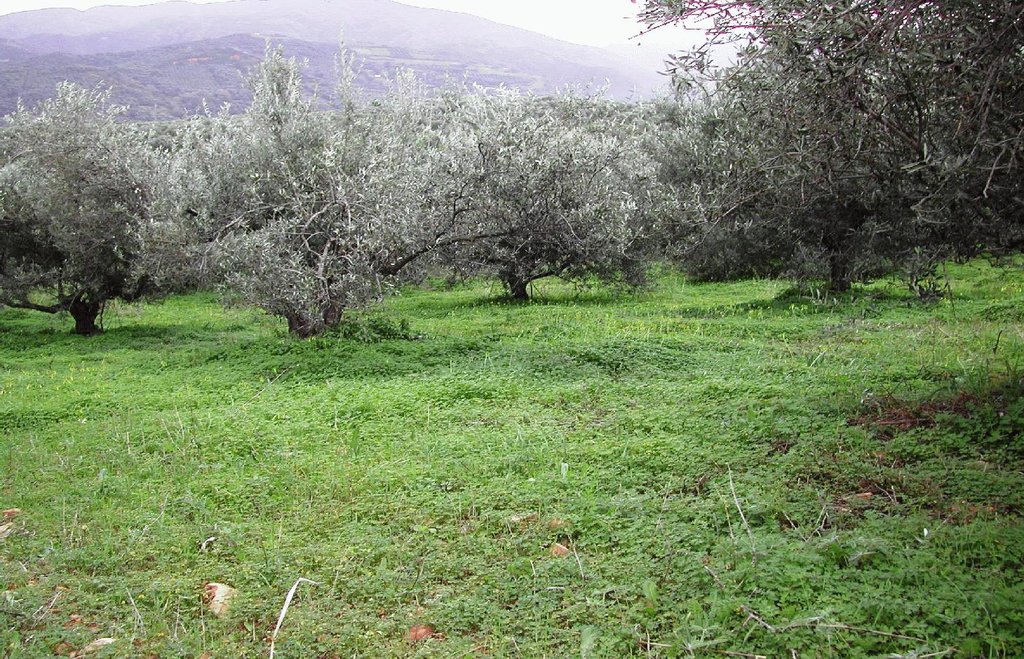
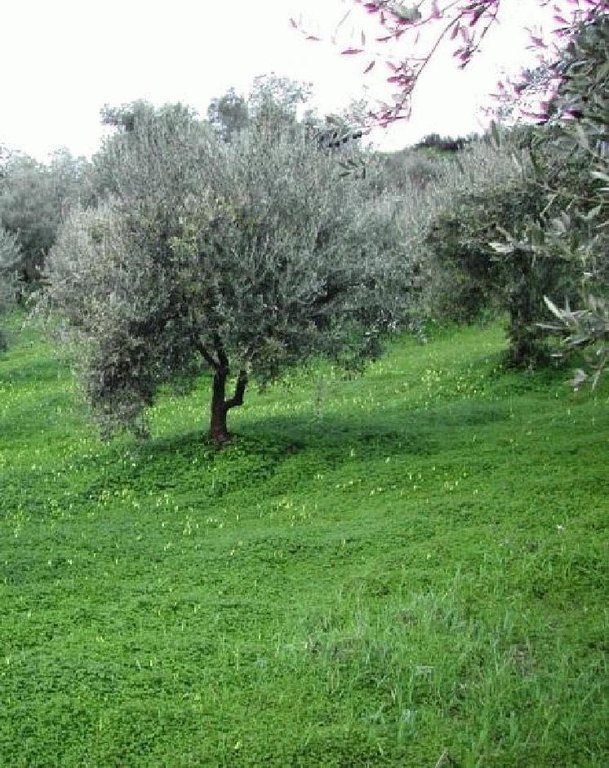
Sustainable farming may include several measures for protecting natural resources. One measure, that of no-tillage, relates to reduced soil erosion. This may have favourable effects on soil aggregation and protection from soil crusting and soil erosion. In a no-tillage system, the residues are concentrated on the surface of the soil, which enhances aggregate stability and protects the soil from erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: Sustainable farming may include several measures for protecting natural resources. One of the applied measures in the context of sustainable farming, related to reduction of soil erosion, is minimum tillage or no tillage operations. No tillage may have favourable effects on soil aggregation and protection of soil crusting and soil erosion. Maximum soil degradation occurs when soil is tilled with a mouldboard plough, followed by disking. In no-tillage system, the residues are concentrated on the surface of the soil enhancing aggregate stability and protecting the soil from erosion.There is no any extra cost for application of the Technology. In the opposite, farm income increases since cost production is decreased without any decrease in olive oil production.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The most frequently used cover crop is Oxalis pescaprae, a species considered as a weed but with a positive effect on soil and water conservation. It is left to grow during winter to improve water infiltration into the soil and to help prevent soil erosion. Owing to its high sensitivity to drought, Oxalis tends to reach wilting point in late spring due to lack of water in the upper soil layer. Disc-ploughing once every four to five years is necessary to destroy the perennial vegetation and incorporate fertilizers and plant residues into the soil. There is no extra cost involved in applying the technology. In fact, farm income increases, since production costs decrease without any reduction in olive oil production.
Natural / human environment: This practice is common locally and was established 30 years ago by the collaboration of national specialists and land users. It has been applied in a variety of natural and human environmental conditions typical of the Mediterranean region.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اليونان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kissamos province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Chania-Crete
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 532 km2.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الزيتون
- Oxalis pescaprae (flower but invasive)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: November to April
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high soil erosion rates and a decrease in groundwater recharge
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increasing production costs when the technique is not applied
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير الإدارية
- M4: تغيير كبير في توقيت الأنشطة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (displacement of soil by ploughing)
Secondary causes of degradation: labour availability
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
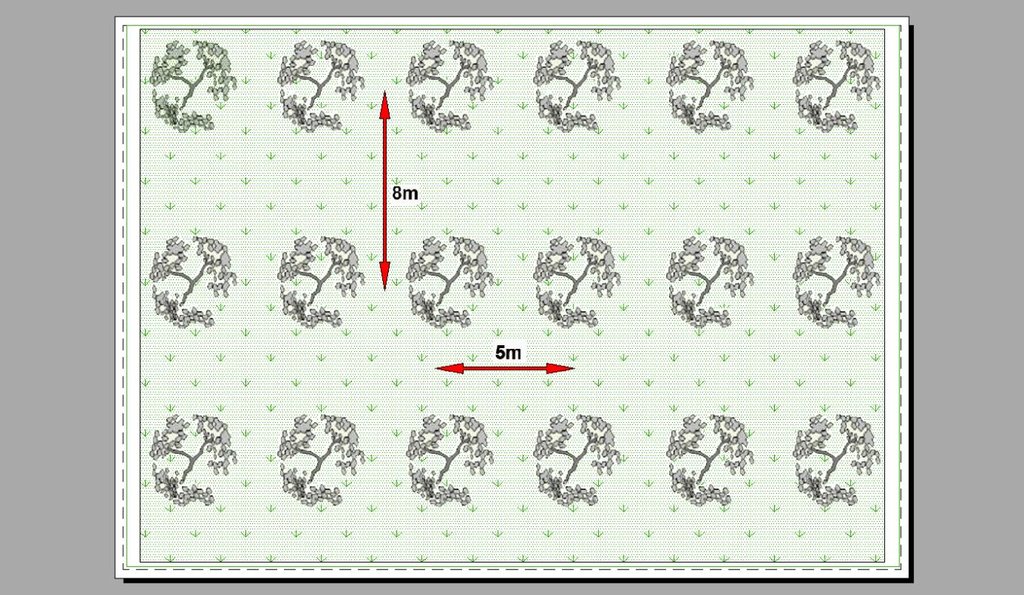
Olive groves occur widely throughout Crete (Greece). One of the main cultivation practices adopted recently is minimum or no tillage. Under this land management practice, weeds are allowed to grow, covering and protecting the soil surface from raindrop impact. The most widely distributed weed is Oxalis pescaprae, a plant species that has positive effects on soil and water conservation. Oxalis grows during winter improving water infiltration into the soil and helping to prevent soil erosion. Owing to its high sensitivity to drought, Oxalis reaches wilting point during late spring due to a lack of soil water in the upper soil layer. The plant is indigenous to South Africa and highly invasive. The plant has a reputation for being very difficult to eradicate once it has become established. Olive trees, planted close together, partially prevent the growth of understorey vegetation. In the Crete study area, rows of olive trees are spaced at intervals of 8 m and trees are planted 5 m apart in the rows
Location: Voukolies. Chania
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness
Mulching
Material/ species: oxalis sp
المؤلف:
C. Kosmas
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of weeds if they interfere significantly with the collection of the olive crop |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 5 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | no maintenance |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: no machinery needed
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
No factors affect costs since Oxalis grows in the area under natural conditions
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- شركة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
2200-2500€/ha
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Hindered farm operations
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in farmers income and reduction the off-site effects
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | غير معروف |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
| arid climatic conditions | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
2650
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 51-90%
التعليقات:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1850 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
800 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Production costs can be cut, but may create problems for olive harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? the necessity to cut weeds during harvesting |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Technologies for conserving soil and water resources and combating desertification in Crete mainly relate to land management. Olive groves are widespread on the island as a result of the importance of olive oil for everyday cooking. Furthermore, olive groves can survive adverse weather and soil conditions providing a significant income for farmers for a relatively low labour input. Land management practices have been adopted in the area based on tradition and knowledge transfer by local institutes and specialists. No-tillage land management practice with olives can be considered as an important technique to protect against land degradation and desertification and increase farmers’ incomes How can they be sustained / enhanced? education of farmers |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The field is ‘clean’ in readiness for harvesting | the necessity to cut weeds during harvesting |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| A slight decrease in water availability for the growing trees | no solution to this problem |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Sustainable development of olive groves I [اليونان]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas

Sustainable development of olive groves II [اليونان]
Sustainable development of olive groves by applying no tillage operations and plastic nets on the soil surface
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية