Postpone grassland renewal [هولندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Jason Stuka
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Uitstellen van graslandvernieuwing
technologies_1662 - هولندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
هولندا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
هولندا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Leever Henk
Hoeduurzaam
هولندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Hoe Duurzaam - هولندااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - هولندااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - هولندااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Ministerie van Economische Zaken - هولندااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Gemeente Berkelland - هولندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Regional process, social innovation [هولندا]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- جامع المعلومات: Simone Verzandvoort
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
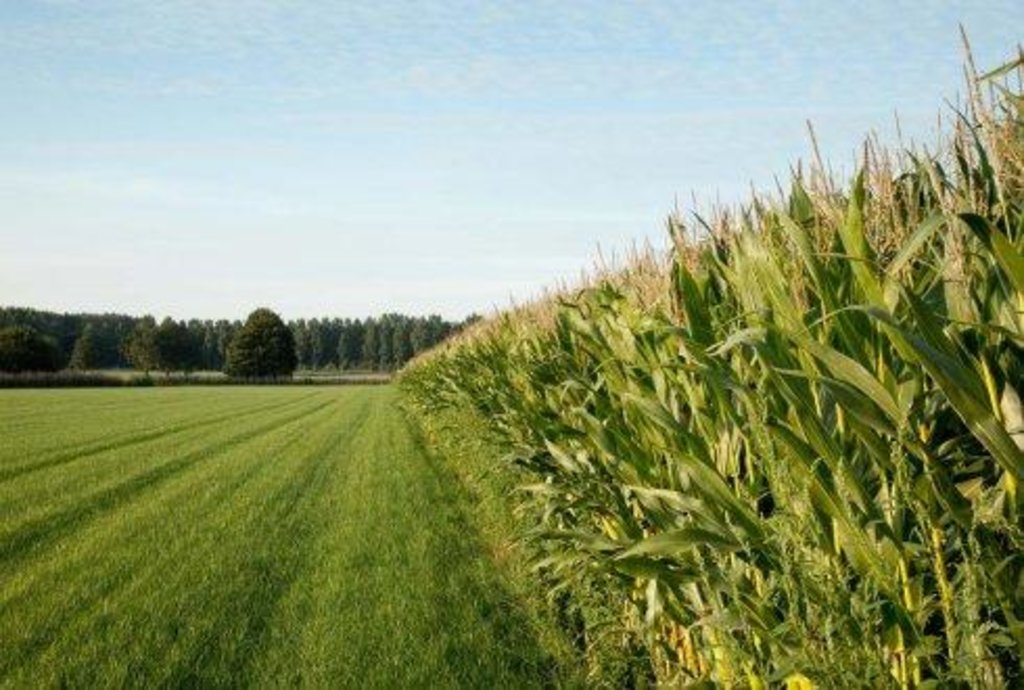
Postponing the timing of ploughing a grassland field by one or two years to reduce nutrient losses and organic matter decomposition.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
On the sandy soils in this part of The Netherlands permanent grassland seems the best measure to increase the organic matter content of the soil, to reduce the leaching of minerals and to reduce loss of soil moisture.
Customary maintenance of grassland fields is to plough and reseed or rotate the grass every 5 years. 5 years is the minimum length of time required by legislation. For growth and field rotation purposes, many farmers have preference to rotate fields in intervals less than 5 years. Under this technology, farmers instead wait 6 or 7 years before ploughing.
Purpose of the Technology: Ploughing grasslands increases the breakdown and decomposition of organic matter in soils. Farmers post-pone ploughing to increase soil organic matter content and reduce losses.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A well established permanent grassland requires good drainage, frequent liming (possibly from residual products from water purification), deep rooting grass, reseeding after 10-15 years, and fertilisation using sufficient organic manure.
Natural / human environment: Dairy farmers on sandy soils in the eastern part of The Netherlands. In the pilot Gezond Zand 44 farmers participated, owning 720 ha agricultural land, of which 344 in use as permanent grassland.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
هولندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Gelderland
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
In entire area there is 344 ha of grassland owned by 44 farmers. Only 2 of those farmers implemented the technology.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- مربى ماشية محدد
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decrease of soil organic matter content.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience decreasing organic matter content in soil.
Ranching: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: farmers also keep cattle in stable to prevent unequal grazing and dispersed manuring
Improved pasture: Yes
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 250 Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (ploughing intensive grassland renewal)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (rotation with more corn and less grassland)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
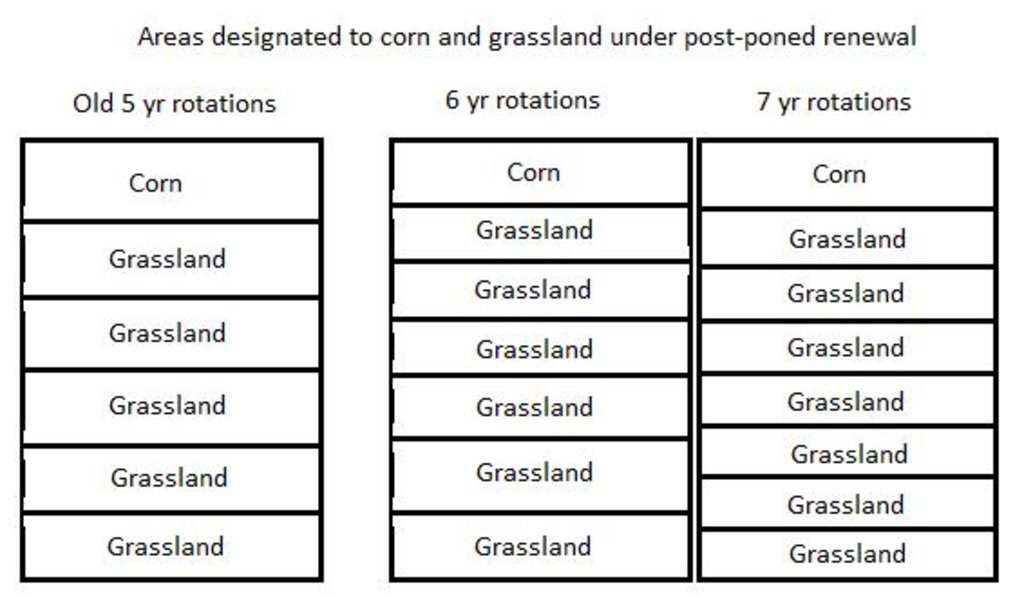
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Demonstrating area designated to corn and designated to grassland under old management of renewing grasslands every 5 years and comparing to the area under the new technology of renewal every 6 or 7 years.
Location: Wageningen. Gelderland
Date: March 20, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (knowledge is required on the maintenance of permanent grassland, the proportion of grassland in the total farm, the frequency of reseeding and rotations with arable crops, in particular for grassland)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge is required on the maintenance of permanent grassland, the proportion of grassland in the total farm, the frequency of reseeding and rotations with arable crops, in particular for grassland)
Main technical functions: Reduce decomposition of organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Plough grassland every 6 to 7 years instead of every 5 years.
Major change in timing of activities: Plough grassland every 6 to 7 years instead of every 5 years.
المؤلف:
Jason Stuka, Wageningen University
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Information on costs for the technology are not yet available, and therefore no information on costs was entered into section 2.6.
Costs involved with postponing grassland renewal include the costs of yield foregone from rotations with arable crops that have not taken place, and costs of manuring of the grassland.
Costs avoided include all costs of management operations and inputs associted with rotations of grassland and arable crops that would have taken place in the life cycle of the permanent grassland (6-7 till 15 years).
Benefits include 1320 kg of additional DM/ha, or € 145,-/ha additional revenues.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The life cycle of permanent grassland determines both the costs foregone due to missed yields from shorter term rotations with arable crops and costs avoided due to saved operations and inputs on shorter term rotations which have not taken place.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
182 days of precipitation annually
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Gentle (only incidentally)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Deep (A en B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area). Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm.) and very deep (deep topsoils rich in organic matter in Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture: Coarse/light ( Most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area). and very high (fimic Anthrosols originating from application of farmyard manure since medieval times.)
Topsoil organic matter is medium (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water. Sandy soils.) and medium (some shallow groundwater)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (dependent on soil organic matter content)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality or craft work. No B&B activities or educational services.
Market orientation is subsistence (grass is used to feed the cattle of dairy farmers, not sold)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
Average grassland is 7.8 ha per household.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
التعليقات:
All agriculture land is owned by farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. There are some regulations on land uses set by communities.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. More grass, less corn. Overall less yield.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Uncertain. More grass but less corn.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven.
Less rotation and management flexibility.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Created farmer's foundation
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers collaborating with water company
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet. Little to no
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not measured.
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not measured.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
التعليقات:
Less frequent rotation and fertility for corn production, but better for soil health.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measures and subsidy or payment for environmental service to compensate foregone revenues if rotations with arabale crops would be inserted. |
|
increases grassland quality and yield in the long term; estimated added value of postponing grassland renewal is € 145,-/ha How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measure, preferably maintain life cycles of 10-15 year for permanent grassland |
|
reduces leaching of nutrients, herbicides and pesticides to the groundwater How can they be sustained / enhanced? financial support from the drinking water company Vitens, who has interest in reduced influx of substances to the groundwater. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? continued implementation of the measures and subsidy or payment for environmental service to compensate foregone revenues if rotations with arabale crops would be inserted. |
| increases available soil moisture |
|
reduces leaching of nutrients, herbicides and pesticides to the groundwater How can they be sustained / enhanced? financial support from the drinking water company Vitens, who has interest in reduced influx of substances to the groundwater. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| long-term investment, requires time to return improved grassland yield |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| long term permanent grassland prevents rotations with arable crops; this may reduce farmer's income | reward the benefits of increased SOM through subsidy or payment for environmental services by the drinking water and dairy companies |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden Eibergen By Willem Rienks and Henk Leever 2014 Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The Netherlands Arjan Reijneveld 2013RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2 Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort 2014
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdfWageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden EibergenBy Willem Rienks and Henk Leever2014
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdfWageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Regional process, social innovation [هولندا]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- جامع المعلومات: Simone Verzandvoort
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية