Littuko Growing for Forest Enhancement [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1708 - الفيليبين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dacumos Evangeline
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Espanto Patrick Benson
Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Soils and Water Management
الفيليبين
Mento Dopinio
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Forest Management Bureau (Forest Management Bureau) - الفيليبين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Community-Based Forest Management [الفيليبين]
Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM) refers to the organized efforts to work with communities in and near public forestlands with the intent to protect, rehabilitate, manage, conserve, and utilize the resources in partnership with the Local Government Units (LGUs) and other stakeholders.
- جامع المعلومات: Isabelita Austria
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Growing of rattan is done by upland farmers as part of the Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM).
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
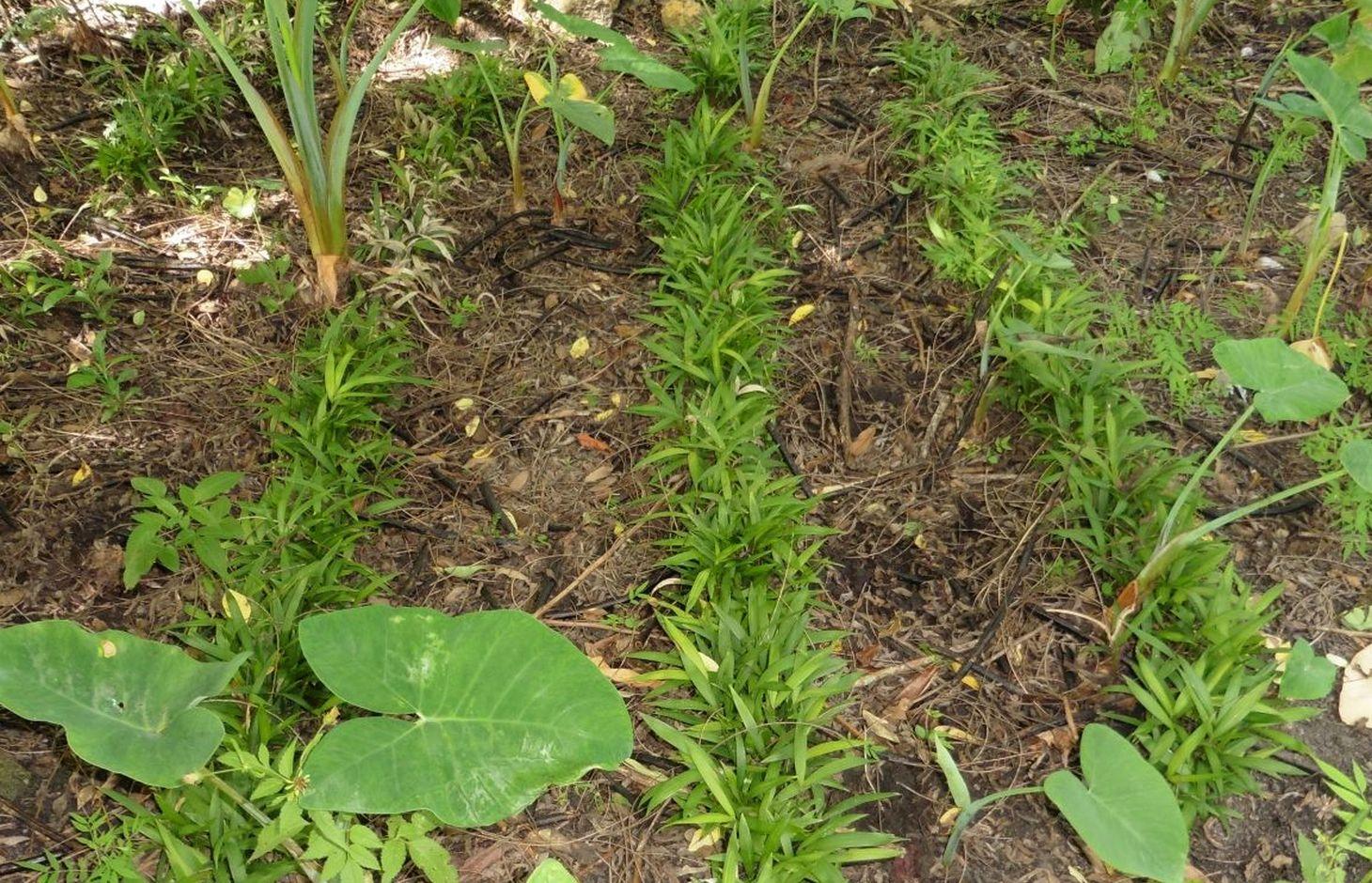
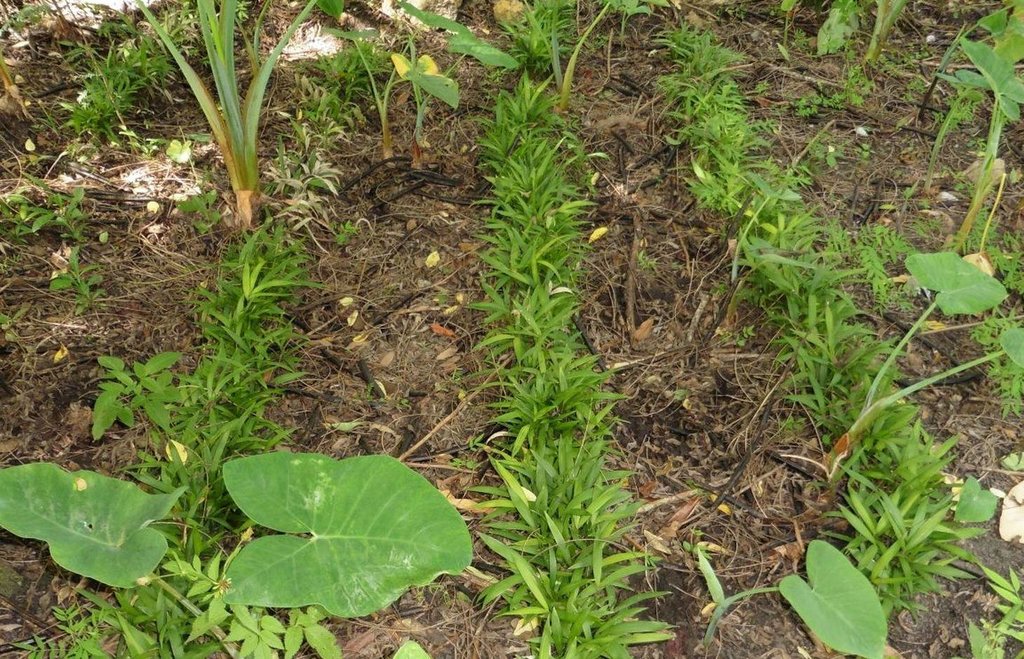
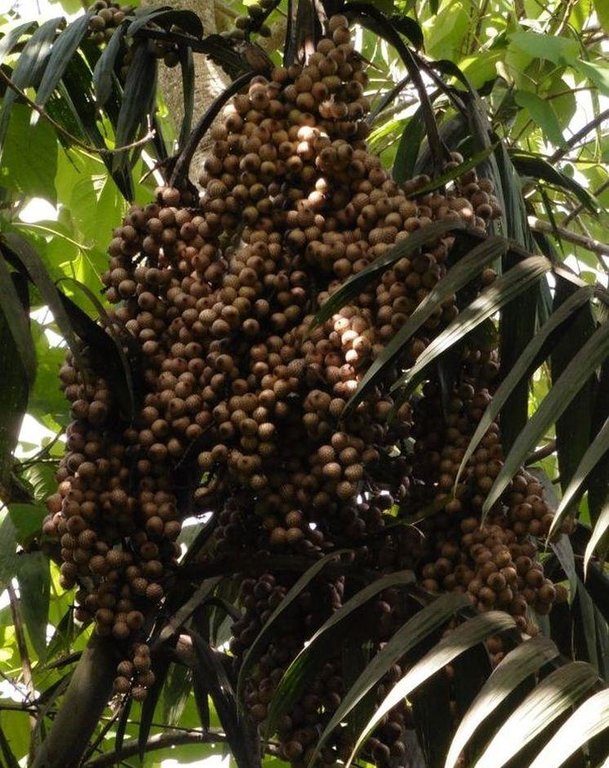
Littuko (Calamus manilensis) is a large rattan variety belonging to the climbing-palm family Arecaceae which is commonly found in the Cordillera, Caraballo, and Sierra Madre mountain ranges. It matures in seven years and bears 50 to 70 kilos of fruits each year. Its fruits are sweetish sour when ripe and are gathered around April to September.
Purpose of the Technology: The littuko provides green cover to the trees even in the dry months and in case of wildfire,they reinforce the forest's capacity to serve as firebreaks or greenbreaks. It also attract a lot of wildlife ranging from insects (bees, fire flies, and beetles) to birds, bats, and cloud rats. Forests with littuko become equipped with natural guards since the littuko's spines with sturdy thorns discourage people and stray animals to freely enter the forest area and disturb the ecosystem.Conservation of trees is also promoted on this technology.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the cultivation of littuko, the following procedures are done: (1) Before planting into a seedbed or polyethylene bags (plastic planting bag), the hilar cover of the littuko seed is gently scraped with the use of a sharp knife. Removing the hilar cover enables the tiny plant to easily break out of the seed. (2) The sprout is transplanted to the designated area under the host tree when it reaches six inches in height and with at least three leaves. The chosen host tree is where the littuko can cling on for support to prevent lodging or breakage of stems. (3) Within one to three years, ring weeding is done around the littuko plant. (4) Maintenance and inputs are needed after three years to ensure its growth.
Natural / human environment: Littuko grows underneath of growing trees in the natural forest. They grow best in rainforests and no cultivation is needed.The area is under a humid agro climate with an average annual rainfall of 2000-3000 mm per year. Land users have an average holding of 0.5-1 hectare for the forestlands or woodlands.Most of them are stewards of the forest through the Community Based Forest Management Agreement (CBFMA) for 25 years and renewable for another 25 years.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bayombong
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Nueva Vizcaya
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
The area for the propagation of rattan is part of the Community Based Forest Management (CBFM).
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
In 1984, 100 littuko seeds were planted by the land users and 70% are male plants.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
- استخدام الغابات غير الخشبية
زراعة الأشجار والتشجير: تحديد أصل وتكوين الأنواع:
- أصناف مختلطة
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Logging, charcoal making and grazing since it was initially a grassland
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fo: Other
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period from month to month: perennial
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

أراضي الرعي
- Extensive grazing
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: Involve the use of vines
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting of trees), land tenure (Insecurity (open access))
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (More on annual crops), overgrazing (Cattle raising), change in temperature, droughts, population pressure (Increase of population that leads to the increase of cutting of trees.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
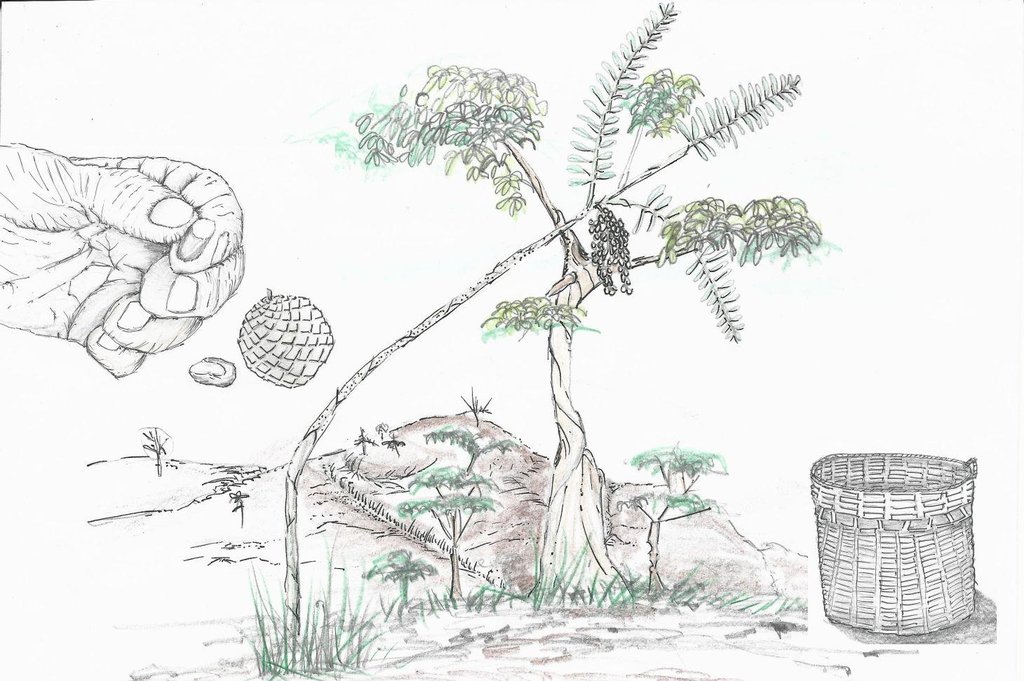
Rattan vine planted in the forest with rattan made basket used in transporting littuko seeds in the market.On top is the scarification of the littuko seed to induce seed growth.
Location: Brgy. Buenavista. Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya
Date: June 25,2015
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Need skills in seed propagation and use of scarification of seeds.)
Main technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), Conservation of trees which serve as host or anchor trees
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), Control weeds
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Other species: Vine (rattan)
المؤلف:
Patricio A. Yambot, Bureau of Soils and Water Management
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Pesos
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
45,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.33
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery establishment through seed bed | Before the onset of rainy seasons |
| 2. | Transplanting | After 8-12 months of seeding |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour for nursery | Person/day | 1,0 | 3,3333 | 3,33 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Transplanting | Person/day | 1,0 | 3,3333 | 3,33 | 1000,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedling | Seeds | 1000,0 | 0,22222 | 222,22 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 228,88 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 5,09 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Once a week for 2 years (maybe done once a month) |
| 2. | Harvesting | After 5-8 years of planting |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Weeding | Person/day | 2,0 | 3,333 | 6,67 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Harvesting | Person/day | 4,0 | 3,333 | 13,33 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 20,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,44 | |||||
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
سطحية
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Just woodland, no crop or grazing land
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
CBFM Agreement, Certificate of Stewardship Contract of 10-25 years
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الخشب
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
توافر المياه للماشية
نوعية المياه للماشية
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Difficulty to harvest
التعليقات/ حدد:
Difficult to harvest since host tree is tall
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الفرص الثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Improved livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The littuko fruits provide additional income to community based forest management implementer/participants.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Conservation of trees
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conservation of trees is promoted because trees serve as hosts for the growing of rattan
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
200 households and 70 percent of land
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
200 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Land users are adopting the technology since littuko seedlings nursery are established for the propagation of planting of rattan in the village and its neighboring area.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Littuko vine is multi-purpose. Its fruits are used for food consumption while its poles are used as handicrafts/furniture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provision of technical assistance in the development of product using rattan as the raw material. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Littuko fruit is not perishable. It could be stored for a period of time under normal conditions. This could be used as condiments and ornaments. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Providing assistance in processing the littuko fruits such as creating jams, candies and others using the fruit. In this way, the marketability and market value of the product will be increased. |
| Low maintenance as a crop. Contributory to trees and it helps in the reduction of soil erosion. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Difficult to harvest since the host tree is tall.It does not grow in open areas and does not stand alone. | Development of a tool that could be used in harvesting the fruit and planting of trees as pole stand to avoid lodging or breakage of littuko vine. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Community-Based Forest Management [الفيليبين]
Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM) refers to the organized efforts to work with communities in and near public forestlands with the intent to protect, rehabilitate, manage, conserve, and utilize the resources in partnership with the Local Government Units (LGUs) and other stakeholders.
- جامع المعلومات: Isabelita Austria
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية