Minimum tillage in Mediterranean vineyards [البرتغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Carla Ferreira
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Minimum tillage
technologies_2879 - البرتغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Centro de Estudos de Rescursos Naturais, Ambiente e Sociedade (CERNAS) - البرتغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
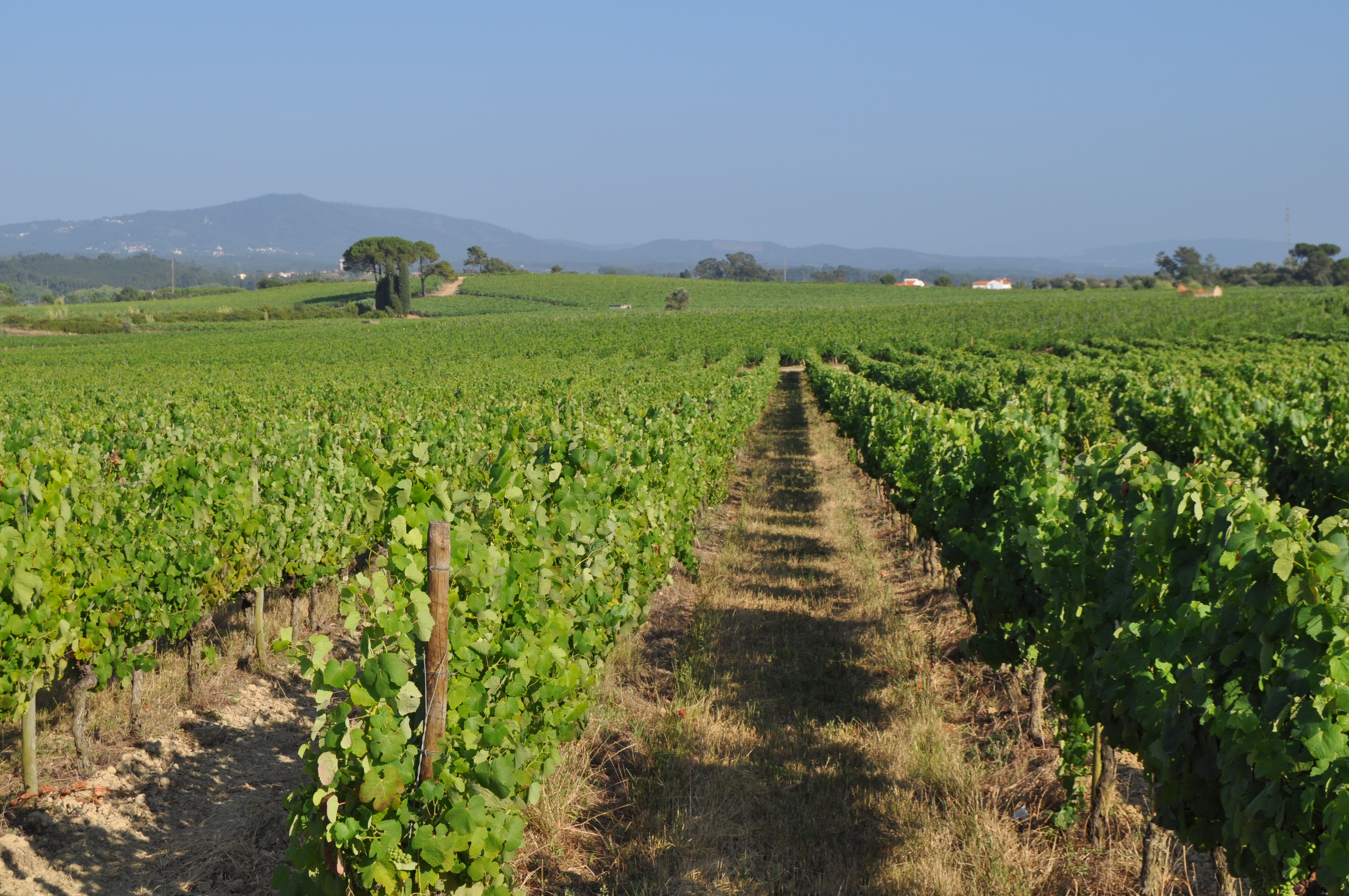
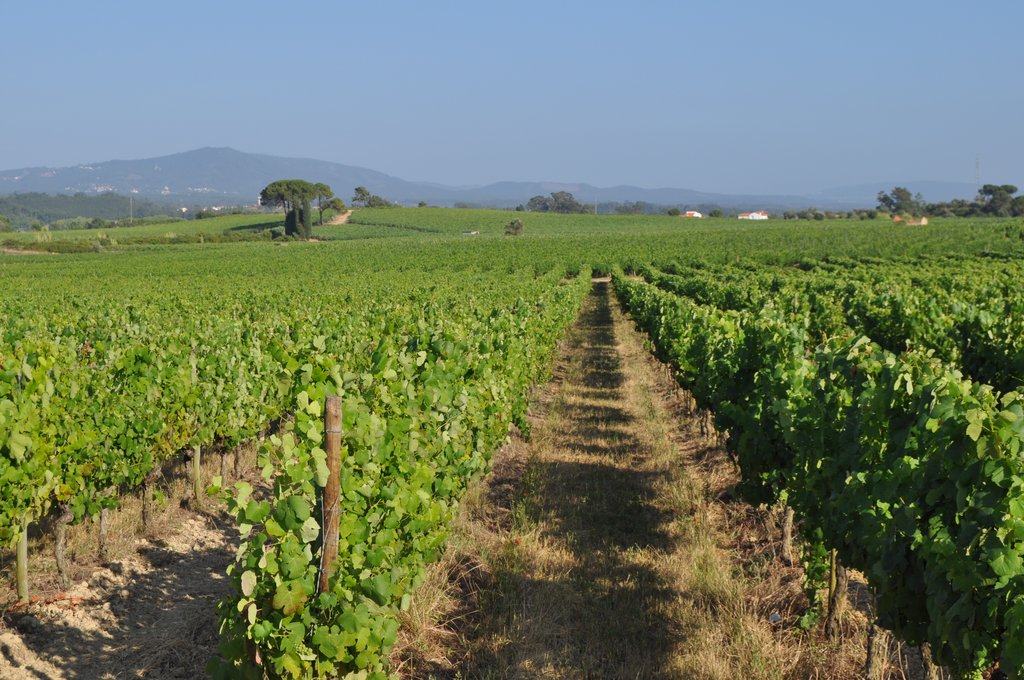
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in alternated inter-row zone, to promote soil decompation and maintain partial vegetation cover.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Portugal is one of the larger wine producers in Europe, with vineyard area covering 27% of permanent crops. Vineyards play an important role in the Portuguese economy, not only due to the impact of wine industry but also the important cultural heritage and great influence on tourism sector. There are thirteen specialized wine regions in the country, from which we highlight Bairrada region, located in central mainland, where minimum tillage is becoming popular. Bairrada has a Mediterranean climate, characterized by a long dry summer, although the strong influence of the Atlantic Ocean. Vineyard is the most relevant crop in Bairrada. In this region, farmland is mostly cultivated by landowners, comprising small winegrowers (5-10ha), most of them members of local farmers associations, as well as large producers (100-500ha) with a relevant position in the world wine market.
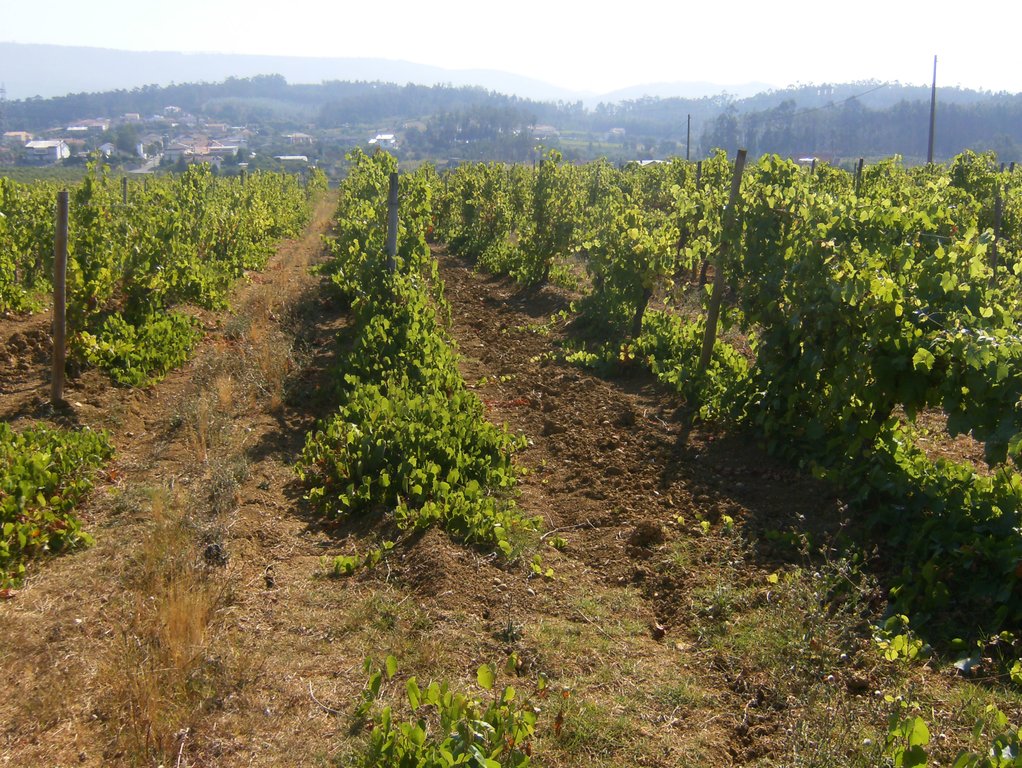
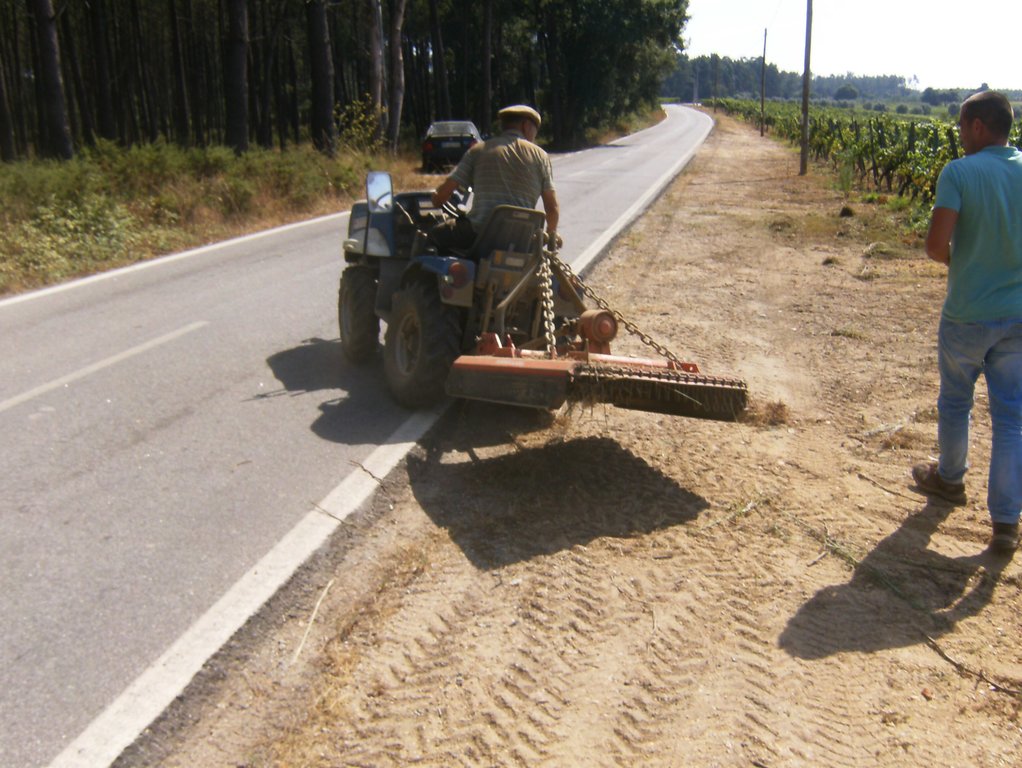
In vineyards, tillage is performed to promote de-compaction of the typical medium/fine soils and weeds control. In Bairrada wine region, soil tillage is usually performed twice per year – in autumn and spring, depending on weather conditions. Tillage is performed with a ripper and disc arrow (10-15cm), since mechanized vineyards require vines arranged according to horizontal wire bundles. However, tillage activities favour soil degradation, namely due to soil erosion and increasing mineralization of organic matter. In order to mitigate land degradation, minimum tillage of inter-row zone was adopted. No tillage is not applied by the farmers due to the need to de-compact the soil, favoured by the relatively high clay content. The minimum tillage is performed in alternated inter-rows, to keep vegetation cover in part of the vineyard. Tillage inter-row switch every time, so that each inter-row is not tilled more than once per year. Weeds control in the non-tilled inter-rows is performed using a rotary brush mower. In the plant zone, weeds are controlled with herbicides, applied twice per year: autumn-winter (before vine plant winding) and spring-summer (during vegetative growth). During the hot dry summer, weeds are naturally controlled due to water-stress. Mechanical intervention is also performed for pest and disease control, generally applied as preventive measures. Phytosanitary treatments are performed upon receipt of notices from Regional Directorate of Agriculture or technicians from local farmers association. These notices also include recommendations about the type of products and the application rate. In the majority of the Region, pruning and harvesting is performed manually. Pruning residues are typically mowed and left at the soil surface.
The adoption of minimum tillage was triggered by governmental subsidies. Farmers recognize the impact of this technology on the environment, namely on preventing soil degradation and enhancing biodiversity. However, soil compaction and water competition between vegetation cover and vines (over the summer) are major concerns.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرتغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bairrada, Central Region
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- motivated by financial support from the government
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Technical recommendations provided by technicians of farmers associations.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- العنب
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
One harvesting per year
التعليقات:
Main crops (cash and food crops): Vineyard
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
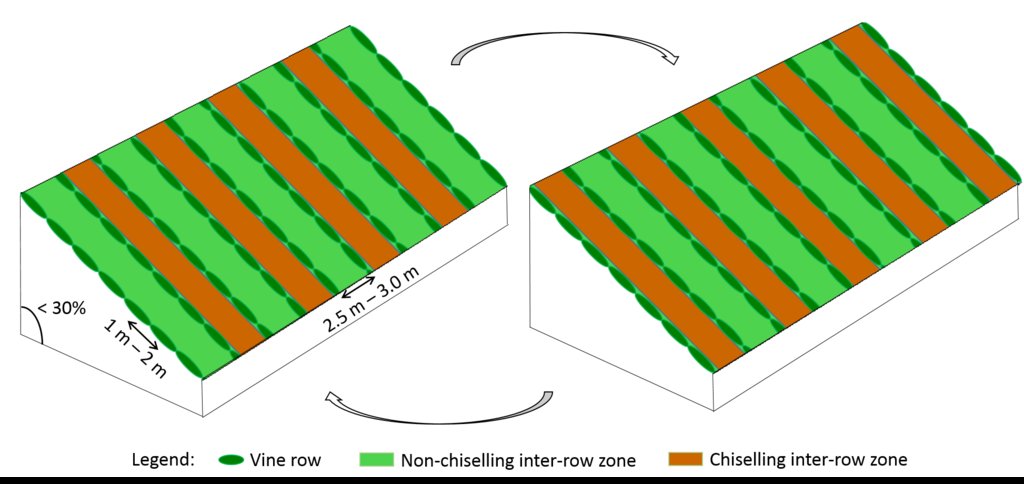
Minimum tillage in vineyards is performed in the inter-row zone, in alternated lines switching between chiselling activities (10-15cm), usually performed in autumn and spring. There is no specific technical recommendations.
Vines are disposed horizontally, supported by wire or cord sustained by wood or metal support. Planting compass varies with soil fertility, type of wine, as well as expected quantity and quality of production, and desired height of the edges. Typically, distance between vine plants within each row ranges from 1m to 2m, and the inter-rows distance from 2.5m to 3.0m, leading to densities of 1000-3000 vines/ha. Generally vineyards are installed on natural surface profile for slopes lower than 30%, and in terraces for hillslopes of 30-50%. Vine plantation is forbidden for slopes greater than 50%.
المؤلف:
Carla Ferreira
التاريخ:
26/06/2017
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 ha per year
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
euro
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,86615
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
30
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chiselling of alternated inter-row zone | Autumn/Spring |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control in alternated inter-row | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chemical control of weeds in plant zone | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Chisel | Equipment | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Rotary brush mower | Equipment | 1,0 | 1600,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Sprayer | Equipment | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 5100,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 5888,13 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Young farmers (<40 years old) may submit agricultural projects for partial government funding.
التعليقات:
The costs provided do not include the tractor aquisition costs.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeds control with herbicides (in vine rows) | Autumn-Winter and Spring-Summer |
| 2. | Mechanical weeds control (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
| 3. | Chiselling (inter-row) | Autumn/Spring |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | For chiselling activities | Person-days | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | For mechanical weed control | Person-days | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | For spraying of herbicides | Person-days | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tractor with chisel | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | Tractor with rotary brush mower | 2,0 | 145,0 | 290,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | Tractor with spraying system | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Herbicides | Litres | 6,0 | 12,0 | 72,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 802,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 925,94 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Machinery and labor
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1077,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The climate is Mediterranean but with a significant influence of the Atlantic Ocean. The dry season extends from July to September and the rainiest period extends from November to February.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
10G/01UG from the Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Csb according with Köppen climatic classification.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Óis do Bairro: 5%; São Lourenço: 10%; Estação Vitivinícola: 9%; Quinta do Valdoeiro: 10%; Pocariça: 14%. Altitude ranges from 25m to 55 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
There is a lack of studies regarding biodiversity.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- تعاونية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Some of the farmers belong to large wine companies, which export the wine to several countries
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
The area of land varies a lot. Individual farmers can have vineyards from 2-15ha, whereas large wine companies own up to 400 ha of vineyards in Bairrada region.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- شركة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
The state also own some vineyards devoted to research.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are no measurements.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Although there are no measurements, it is expected less sediment and nutrient export (linked to decreasing runoff), thus less impacts on aquatic ecossystems.
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Associated with decreasing chiseling activities
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vineyards are relevant for tourism, thus, their sustainability is relevant.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers associations provide knowladge and trainning to farmers.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not measured, but available water in the water cycle is expected.
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is no data, but decreasing runoff will contribute for lower sediment and nutrient exports, thus, improving water quality.
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are no measurements, but field studies performed elsewhere report increasing soil moisture due to vegetation cover.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maintenance of vegetation cover in half of the vineyard inter-rows. However, vegetation cover is limited during dry periods.
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Based on bibliography.
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Although there are no measurements, farmers report that ploughing activities are relevant to reduce soil compaction.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
According with literature review, minimum tillage decrease the mineralization of organic matter.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not measured.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not measured, but expected given the partia maintenance of vegetation cover.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Decreasing runoff will contribute for decreasing downstream flooding
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less runoff and erosion will decrease downstream siltation.
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less runoff will provide lower sediment and nutrient exports to rivers.
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Lower tractor activities contribute for less greenhouse gases emission.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The impacts have not been measured. The response is based on literature review and field observations.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
التعليقات:
The technology does not have an impact on climate related issues.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 11-50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Less herbicides and ploughing decreases maintenance costs. |
| It allows to reduce herbicide application to control weeds, thus favouring biodiversity. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Minimum tillage is best suited for heavy, compacted and/or poorly drained soils, typical of vineyards. |
| It reduces land degradation, by improving soil structure and vegetation cover, important to reduce soil erosion. |
| Improving soil cover will improve soil moisture and aeration conditions, relevant for crop development and soil biodiversity. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Soil compaction due to lower ploughing | Improve soil structure |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to maintain inter-row vegetation cover during the dry season | Replace vegetation cover by other materials (e.g. mulching) |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
More than 10 field visits were performed over a three month period.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Seven
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Two
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Several
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/05/2017
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Biddoccu, M., Ferraris, S., Pitacco, A., Cavallo, E. (2017). Temporal variability of soil management effects on soil hydrological properties, runoff and erosion at the field scale in a hillslope vineyard, North-West Italy. Soil & Tillage Research 165, 46–58.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716301386/1-s2.0-S0167198716301386-main.pdf?_tid=22418bb0-5b58-11e7-980c-00000aab0f6c&acdnat=1498582154_0fb04affbfbcf3f6e729ccdd354527ee
العنوان/الوصف:
Byrne, S., Guire, L.M. (2005) Vineyard Floor Management. Final report to Grape and Wine Research & Development Corporation (RT 04/03-1)
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.mvwi.com.au/items/526/Vineyard%20Floor%20Management%20RT%2004%2003%201.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Cruz, A., Botelho, M., Silvestre, J., Castro R. (2012) Soil management: Introduction of tillage in a vineyard with a long-term natural cover. Journal of Viticulture and Enology 27(1), 27-38.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://www.scielo.mec.pt/pdf/ctv/v27n1/v27n1a03.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Napoli, M., Marta, A.D., Zanchi, C.A., Orlandini, S. (2017). Assessment of soil and nutrient losses by runoff under different soil management practices in an Italian hilly vineyard. Soil & Tillage Research 168, 71–80.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167198716302604/1-s2.0-S0167198716302604-main.pdf?_tid=34c1a784-5b58-11e7-8e6a-00000aacb35d&acdnat=1498582186_a97504bbec990b26b9de92901fae9b9b
العنوان/الوصف:
Puig-Montserrat, X., Stefanescu, C., Torre, I., Palet, J., Fàbregas, E., Dantart, J., Arrizabalaga, A., Flaquer, C. (2017). Effects of organic and conventional crop management on vineyard biodiversity. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 243, 19–26.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880917301603/1-s2.0-S0167880917301603-main.pdf?_tid=1428ce58-5b58-11e7-a61a-00000aacb361&acdnat=1498582131_0ca1f7a72aa834a0345b38122a2f7a05
العنوان/الوصف:
Raclot, D., Bissonnais, Y.L., Louchart, X., Andrieux, P., Moussa, R., Volts, M. (2009). Soil tillage and scale effects on erosion from fields to catchment in a Mediterranean vineyard area. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 134, 201–210.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0167880909002023/1-s2.0-S0167880909002023-main.pdf?_tid=3a75799e-5b58-11e7-8adf-00000aab0f6b&acdnat=1498582195_b808271c0c5bcddc3fa189cccc11fea3
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية