Minimum Tillage [الاتحاد الروسي]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
Минимальная обработка
technologies_1315 - الاتحاد الروسي
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Sustainable land management in the Russian steppes (KULUNDA / GLUES)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Vocational Training [الاتحاد الروسي]
Regular in-service training of land use specialists and farm managers in the fields of sustainable land use management, and monitoring in the agrarian sector.
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt
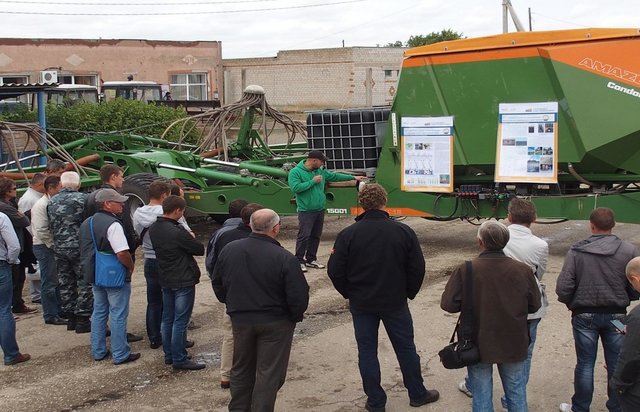

Field days [الاتحاد الروسي]
Field days are events for regional stakeholders, mainly farmers in the study area, to discuss their demands regarding scientific help, and to be informed about the activities and results of new methods and technologies for conservation agriculture.
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
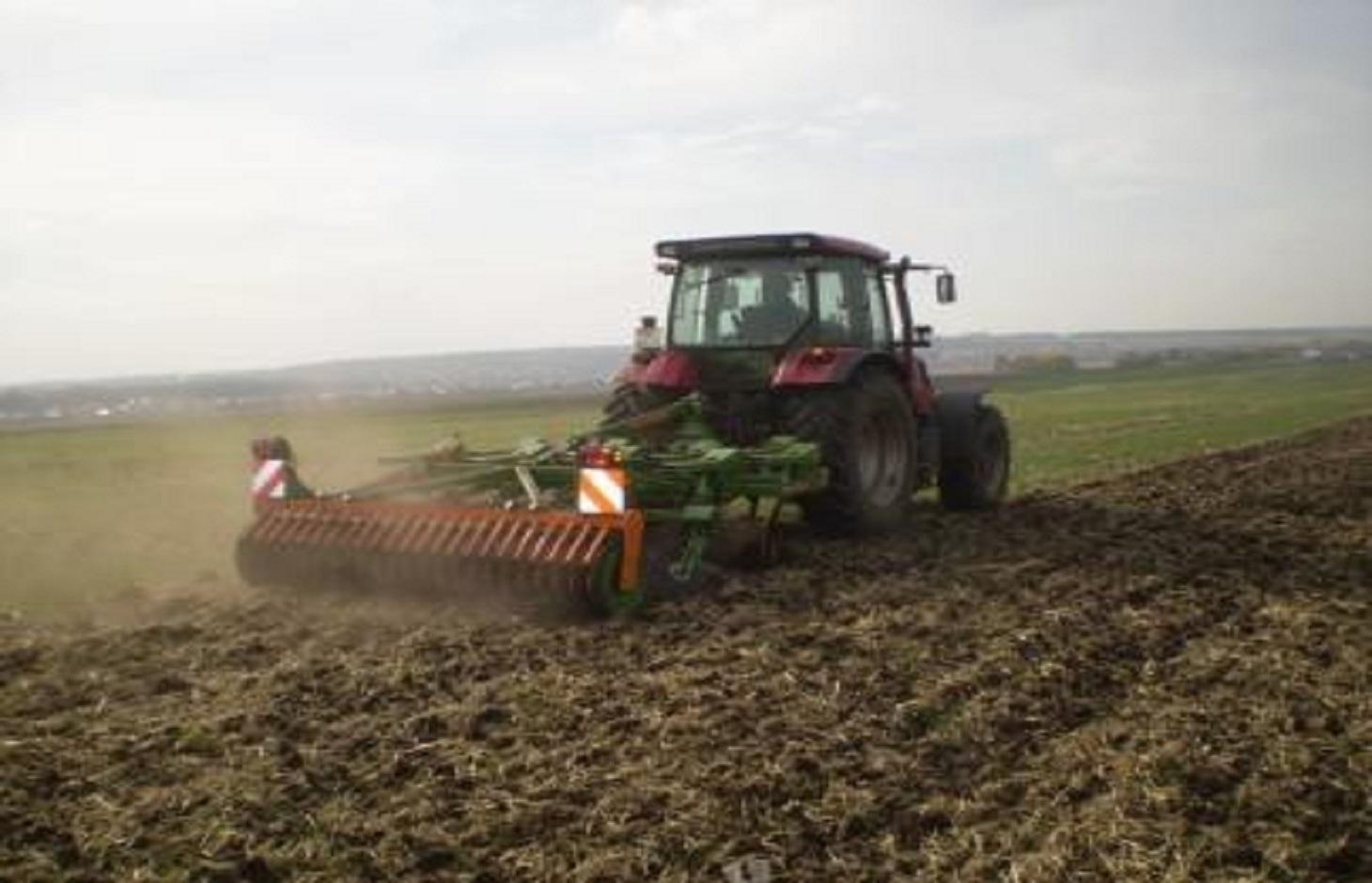
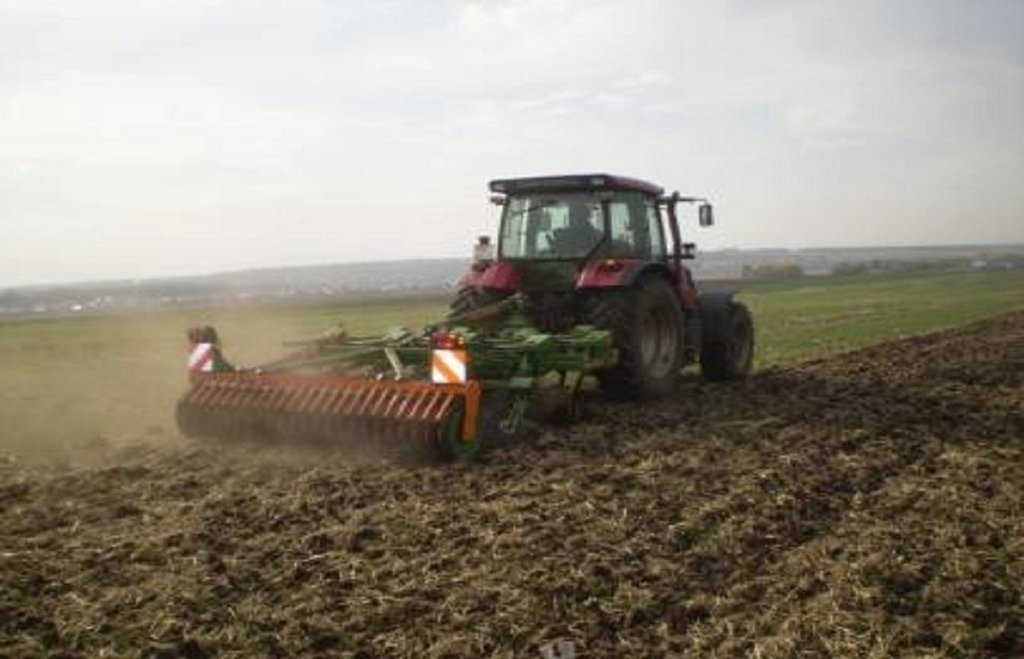
Minimum tillage is a one-pass operation combined with sowing, using a classic Russian seeder modified for seedbed preparation and soil mixing. It can include shallow stubble cultivation after harvesting.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Minimum tillage is a key element of the "adapted Soviet cropping system", which aims at more sustainable land use but based on predominantly local technologies. For successful implementation of minimum tillage, adaption of the whole cropping system is required, including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. Stubble cultivation in autumn is best performed with the "Catros" compact disc harrow for a quick, shallow operation. Seedbed preparation is carried out using a classic Russian seeder modified with wing shares for shallow seedbed preparation including soil mixing. In general, the performance of this drill is very close to that of a cultivator.
Minimizing tillage, saves time and fuel, and also helps to reduce evaporation, as well as protecting the soil against erosion. Shallow tillage with disc harrows after harvest ensures better stubble mixing and stimulates the germination of weed seeds. The adapted seeder, SZS 2.1, works with wing shares that open the soil and place the seed. Thus traditional deep tillage operations for the preparation of the seedbed can are omitted: that helps to reduce costs. With respect to crop protection, the first and most important element is to implement a full crop rotation. To control late germinating weeds and seeds of the previous crop, a disc harrow is used for shallow cultivation – this can be supplemented by the application of a non-selective herbicide if there is germination - to avoid the risk of flowering before the hard frost sets in. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under minimized soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system.
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that minimizing tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The adapted Soviet system is more profitable, due to higher gross margins.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الاتحاد الروسي
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
0,13
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
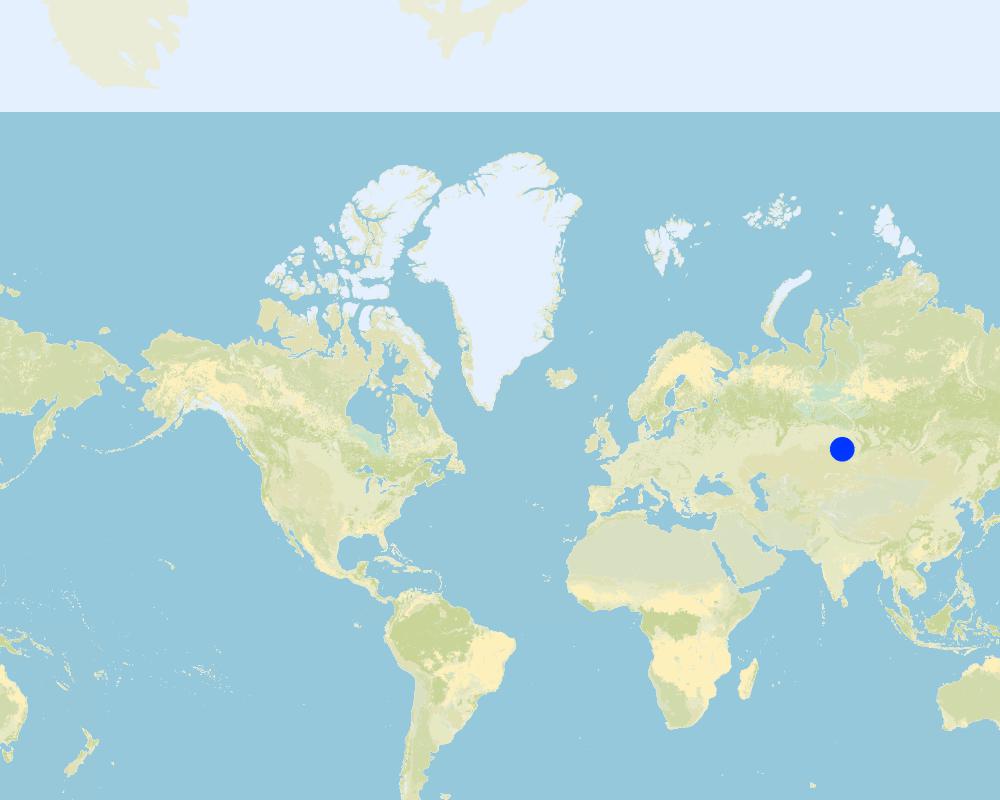
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 km2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to the test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha ; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha and 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha all managed by Minimum Tillage. This questionnaire is related to the test site in Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Already during the Soviet land use periode temporal,especially after the Virgin land campagne (1954-'63)efforts were made to minimize soil tillage intensity to obtain from conventional ploughing system. An important scientific thinker for this innovative farming systems was T. C. Malcev. But at this time the new approaches for minimized tillage systems were not seriously implemented in Russia. Only in the last decade a significant trend towards minimum soil tillage can be recodnized in the Russian agriculture
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils and loss of topsoil depth has led to a decrease in soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation, and the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation, is a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land users who were involved in the studies and implemented the new farming practices have a similar opinion. But there are still a lot of farmers that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from conventional/ traditional soil management.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional (intensive) soil tillage by phloughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow (without any vegetation cover)), wind storms / dust storms (Strong wind and storm (local name: Sukhovey) from the south-western central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (The linkages between research, education, extension services and end users need to strengthened, for better knowledge creation and transfer. Need for more efficient and qualified advisory service), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
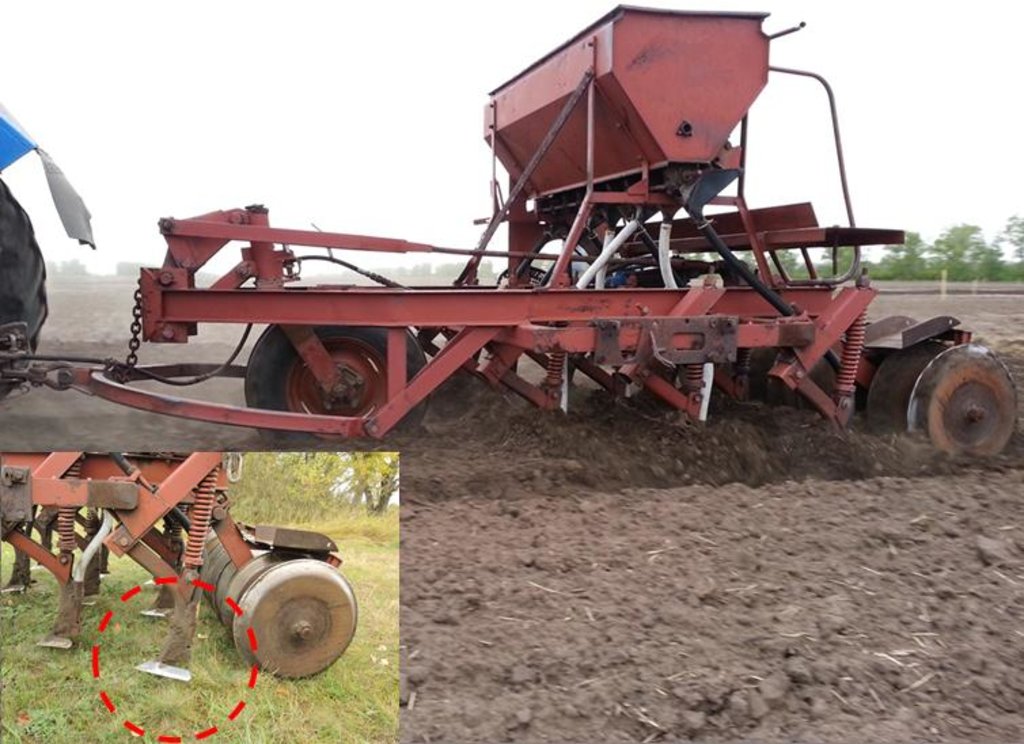
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Soviet Seeder SZS 2.1 with wing shares for shallow soil mixing and seed bed preparation.
Location: Poluyamki. Altai Krai
Date: 20.05.2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Mulching
Material/ species: stubble cultivation with disc harrow or harrow weeder
Quantity/ density: 1/year
Green manure
Material/ species: pea
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: fertilization with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: (100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-raps
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
المؤلف:
Lars-Christian Grunwald
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
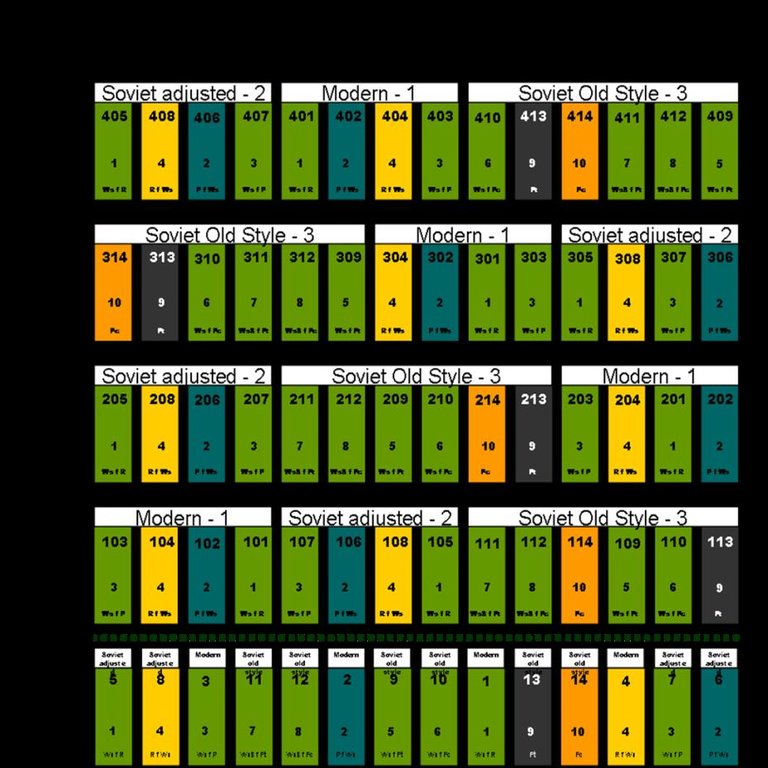
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stubble cultivation | september |
| 2. | Seeding | late april/early may |
| 3. | Seeding (extension) | |
| 4. | Pest management | period of vegetation |
| 5. | Pest management (extension) | |
| 6. | Harvest | september |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,34 | 4,34 | 100,0 |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 37,4 | 37,4 | 100,0 |
| معدات | fuel | ha | 1,0 | 47,34 | 47,34 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 25,3 | 25,3 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 30,83 | 30,83 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | pesticides | ha | 1,0 | 9,42 | 9,42 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 154,63 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 154,63 | |||||
التعليقات:
The costs refers to 1ha land of the test field in Poluyamki.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The highest cost factors of minimum tillage are equipment, fuel, fertilizer and seeds. Compared to the conventional deep ploughing often without fertilizer application, fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري جدا
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the agricultural sector are not so attractive for woman.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
mainly for initial investments and herbicides in the first years
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
but increase of costs for herbicides and fertilizer; decrease for fuel and labor
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Increase use of herbicide applications
التعليقات/ حدد:
particular necessary in the first years after the imlementation of the minimum tillage system
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
In general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Technology makes a contribution to the long-term productivity of the soil – the most important factors in the rural areas of the Kulunda region. Furthermore, it leads to an increase in efficiency and to an improvement of the economic situation of farms, which might lead to a decrease in out-migration of the youth.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الأنواع المفيدة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Increased use of herbicide application
التعليقات/ حدد:
Especially in the first years after the implementation of the minimum tillage system.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
there is a higher content of soil moisture under minimum tillage than under traditional ploughing especially in dry weather periods / drought periods.
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
The increase of air temperature and wind lead to an increase of the evapotransporation rate and consequently, as well as rainfall decrease and droughts, to a decrease of soil water content that is one of the most important limiting factor in crop production. The minimization of soil tillage intensity helps to reduce the evapotranspiration rate and thus leads to a higher soil water content. The stubble slow down the wind, that protect the soil against erosion and reduce the evapotranspiration rate.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms/ sites where minimum tillage was tested were already interested in conservation technologies and were able to invest in new machinery, which is not representative of the whole Kulunda region. There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers.
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. An advantage of the tested Adapted Soviet System in contrast to the Modern Soviet System is the less need for new machinery through the use of old Soviet machinery.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through the mulch layer |
| Protection of soil organisms thus ensuring natural soil forming processes |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations. |
| A great advantage of the tested ‘minimum tillage’ in contrast to ‘no till‘ is that the former needs no new machinery because of the use and adaptation of old Soviet machinery. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Need for comprehensive system knowledge and risk of significant crop losses in case of incorrect implementation | Knowledge transfer, Capacity building and extension services, State support (subsidies for new technologies) |
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| Challenging straw management that leads to higher risk of fungal infestation and poorer field crop emergence | Good straw management: effective straw chopping and spreading as well as stubble cultivation for an optimal straw/ soil ratio. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
23/06/2016
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Vocational Training [الاتحاد الروسي]
Regular in-service training of land use specialists and farm managers in the fields of sustainable land use management, and monitoring in the agrarian sector.
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt

Field days [الاتحاد الروسي]
Field days are events for regional stakeholders, mainly farmers in the study area, to discuss their demands regarding scientific help, and to be informed about the activities and results of new methods and technologies for conservation agriculture.
- جامع المعلومات: Peter Liebelt
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية