Lining geomembrane plastics for water harvesting and storage [رواندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Iwona Piechowiak
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ibidamu
technologies_1551 - رواندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Muligirwa Emmanuel
FAO
رواندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Rwanda Agriculture Board (Rwanda Agriculture Board) - رواندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Participatory approach [رواندا]
This approach is a contribution of different stakeholders and land users in the identification and resolution of a particular crop land problems, which implicate at the end different stage of intervention by all stakeholders to resolve the problem.
- جامع المعلومات: Desire Kagabo
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
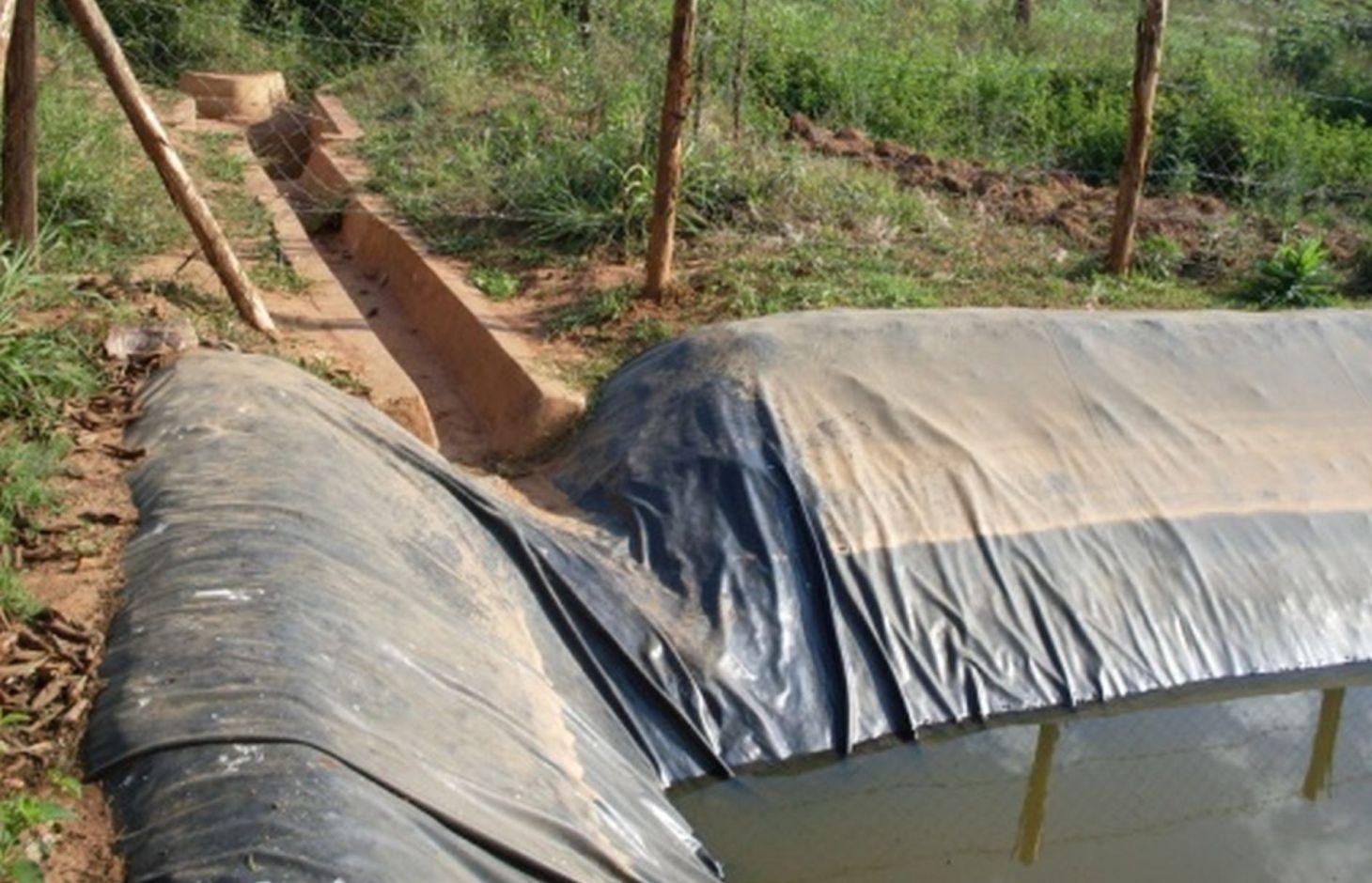
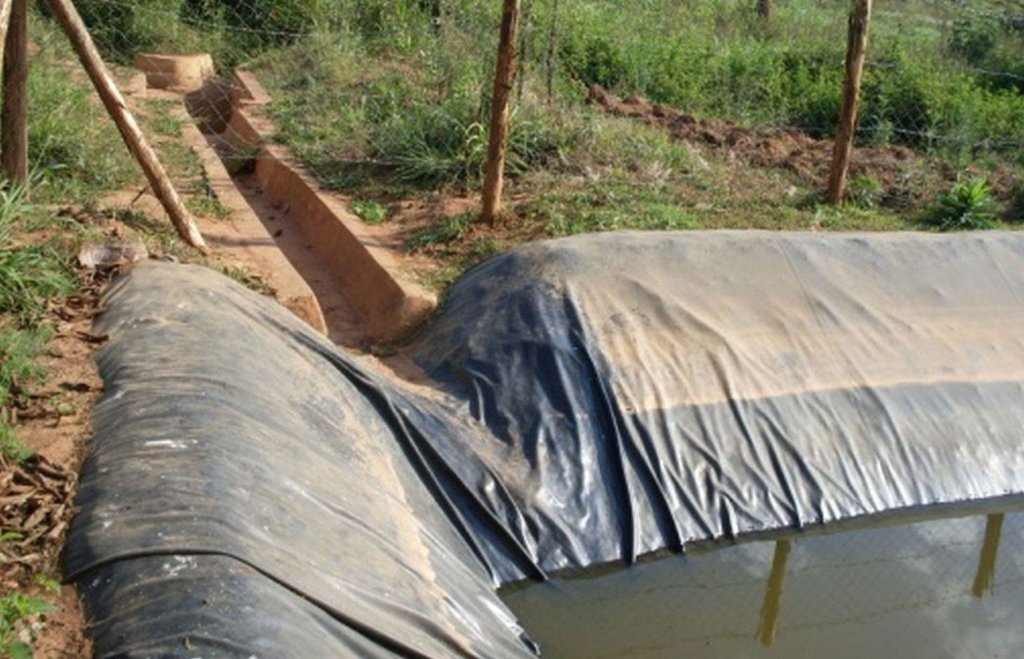
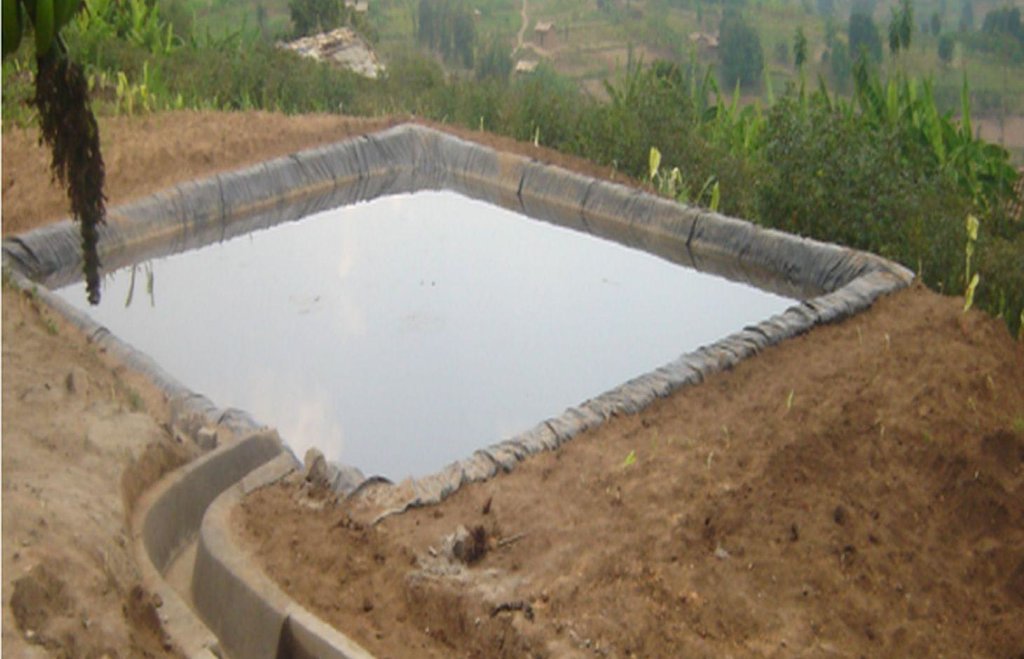
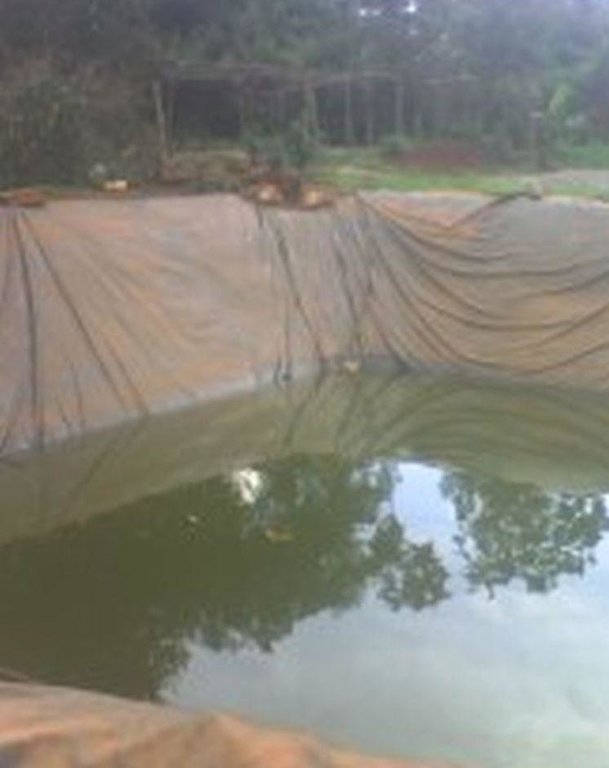
Lining geomembrane plastic for water harvesting and storage is a rainwater harvesting technique used by land users to collect rain water or runoff from a concave watershed to a common well-structured plastic-lined pond for agricultural, domestic and other use.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
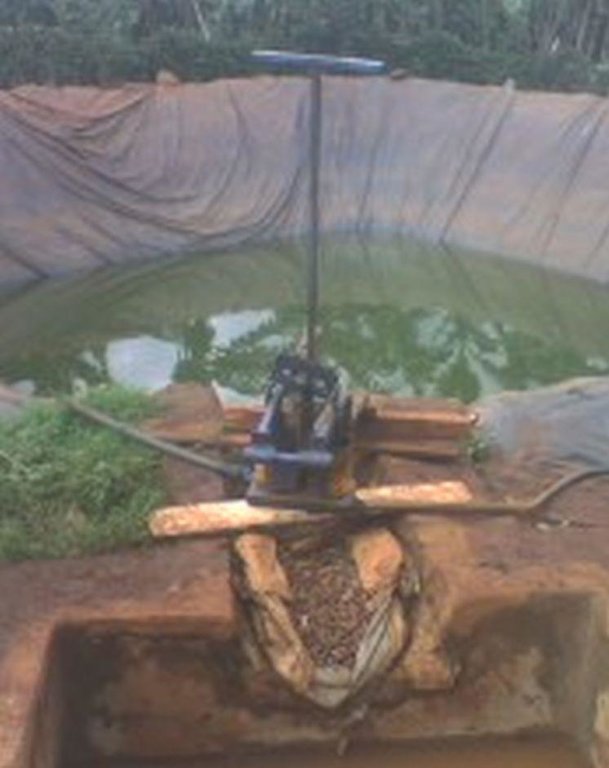
Rainwater harvesting initiatives were introduced in Rwanda in 2007, through a government-supported project on a pilot basis in three districts (Ruhango, Bugesera and Kirehe). By 2011, the technology had expanded at exponential rates such that the demand has exceeded the supply. Now the supply policy has shifted from government to private still there is a shortage of plastic lining. The typical design of each pond is trapezoidal in shape, measuring 10.5 by 9 meters top-width, 6.5 by 5 meters bottom width and 2 meters depth and a total storage volume about 120 m3. The plastic lining is factory–manufactured with standard shape and size to fit these dimensions. The ponds are made with this standard design to enable bulk purchase and supply of geo-membranes, to make use of economies of scale. The cost of the geo-membranes was subsidized by up to 100% by the government until 2010 but now only 20% are provided by the government. When this project was initiated, activities related to soil excavation was done by the government. However, with time the government pulled out and farmers are now covering the total cost of excavation and the government intervenes only for the technical compliance. The government provides technicians to train farmers on the safety and management of ponds. The volume of water harvested and stored in the ponds is on average 90 m3. However, water retention within the ponds over time differs with from farm to farm as affected by usage, evaporation and seepage losses. Treadle pumps are sometimes used to lift water by some of the farmers. Among most households, the water from the pond is used for domestic, livestock and supplemental irrigation, especially of horticultural crops. About 20% of the water is used for seedling and fruit production, 75% for livestock watering and 5% for domestic use. When the excavation of the pond is complete, the beds as well as sides of the pond have to be leveled and prepared for laying the lining plastic. Any rocks, large stones or other projections, which might damage the lining plastic, should be removed from the beds and sides of the excavated ponds.
Purpose of the Technology: Lining geomembrane plastic for water storage is designed to reduce seepage losses in ponds. This water is used by smallholder farmers to cope with the beginning of dry season and enhance crops to reach the maturity stage safely.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A periodical inspection is required for better life of the pond, thus timely maintenance hold the key of success for longer time. The maintenance includes inspection, repairing damages. Regular investigations are required on the pond sides, bottom, the inlet and the emergency outlet. In addition, the pond should be protected from intrusion of animals by constructing a fence around the pond. It is also important to remove aquatic vegetation, silt and sediment periodically that accumulate on the bottom of the pond.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
رواندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Rwanda
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kayonza District (East provice)
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
The area was estimated.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- Government
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
the technology was initiated in 2008
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- access to water
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- خضروات - اخرى
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: September – February; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: March – July
التعليقات:
major cash crop: Vegetables
major food crop: Beans
other: Maize
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There were poor yields of crops caused by elongation of dry season and increase of runoff soil erosion (intensive rain during rainy seasons) at the previous season.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low crop production, soil erosion
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep slopes in many cases over 60%), population pressure (Rwanda’s natural resource is subject to a high density of population with an average of 400 people per ha)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, urbanisation and infrastructure development, poverty / wealth (Farmers have low income and have less access to off farm income or remittances), education, access to knowledge and support services (High rate of irriteracy)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
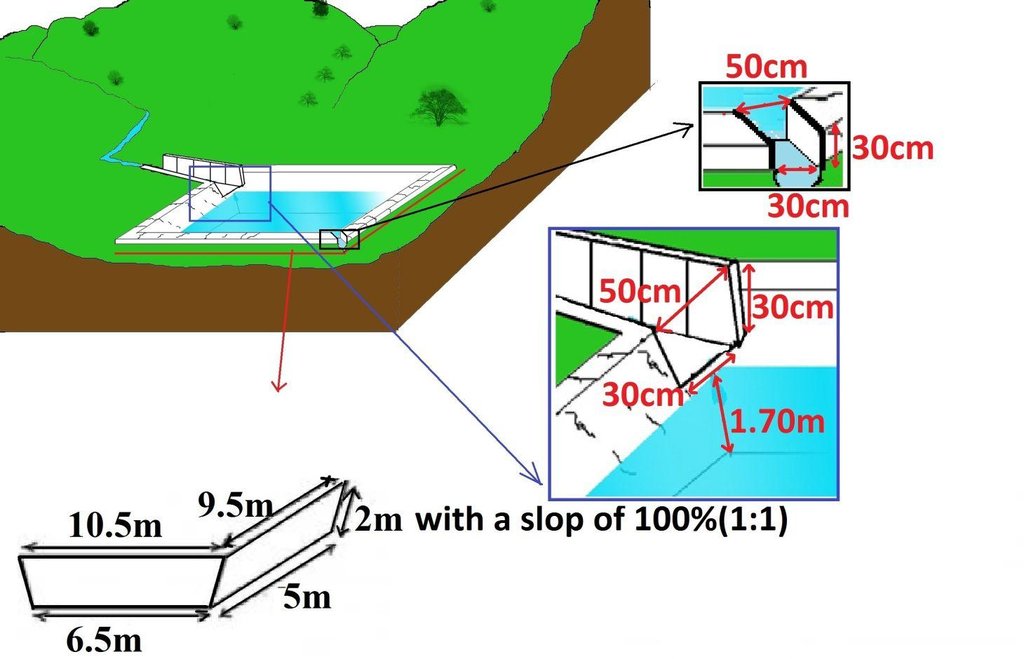
Surface runoff water storage pond have got a reservoir of 10.5m x 9.5m at top and 6.5m x 5m at bottom and a depth of 2m with side slope of 1:1.5. The capacity of one pond is estimated about 120m3.
Location: Kabarondo. Kayonza/West/Rwanda
Date: 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The technology need skilled engineers)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It need moderately skilled labor to construct the technology under supervision of engineers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: water spreading
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 9.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10.5
Construction material (earth): the original land is digging
Construction material (stone): stones are used to concrete the pond inlet and outlet
Construction material (concrete): Cements, sand
Construction material (other): fencing wire and waterproof steering(plastic sheet)
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 120m3
Catchment area: 6ham2
Beneficial area: valleym2
Slope of dam wall inside: 50%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 50%
Dimensions of spillways: 0.8m x0.6mm
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.25
المؤلف:
Kagabo Desire and Ngenzi Guy, RAB, 5016 Kigali
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Rwandan francs
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
640,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1000
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveying | any time |
| 2. | Buying materials | Any time after surveying |
| 3. | Construction of pond | Dry season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Surveying | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 45000,0 | 180000,0 | |
| العمالة | Construction of pond | persons/day/ha | 180,0 | 1000,0 | 180000,0 | 80,0 |
| معدات | Tools | pieces/ha | 100,0 | 3000,0 | 300000,0 | 20,0 |
| مواد البناء | Cements | kg | 300,0 | 200,0 | 60000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Plastic sheet | m2 | 24,0 | 2500,0 | 60000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Stone | m3 | 8,0 | 562,5 | 4500,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Sand | m3 | 8,0 | 390,625 | 3125,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Fencing wire | m2 | 24,0 | 625,0 | 15000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 802625,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1254,1 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | regular maintenance of Channels and all around the pond. | Rainy season |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Regular maintenance | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 15,63 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoes, meter, clinomrter, ect....
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most factors that affects the cost is the construction materials and labor.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium - high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is very high - high
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
55% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: (Begetables)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
200 kg
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
800 kg
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80%
التعليقات/ حدد:
40% of income increases due to increase of agriculture
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology improved the productivity so that farmers had means to take health insurance
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increases up to 15%
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
It has increased income of household hence enhance life.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
60% improved
التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
It increases the predominance of mosquito
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
It require light labor during the maintenance activities
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
260 household covering 90 percent of stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
250 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Income generation How can they be sustained / enhanced? More financial support and trainings |
|
Improvement of production How can they be sustained / enhanced? To make a regular maintenance of ponds |
|
Soil erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Divert more runoff to mitigate the soil erosion downstream and always clean the conveying channel. |
|
Impermeable material How can they be sustained / enhanced? Acquisition of high quality plastics that can last many years |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Occasional accidents | To maintain fences around the pond and increase awareness about accidents around a pond, especially for parents (high risk for small kids) |
| Pond attract various insects and diseases (habitat for Mosquitoes) | Mosquito nets are needed |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Participatory approach [رواندا]
This approach is a contribution of different stakeholders and land users in the identification and resolution of a particular crop land problems, which implicate at the end different stage of intervention by all stakeholders to resolve the problem.
- جامع المعلومات: Desire Kagabo
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية