Odaltaal-10 Single Use Water System [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Jhuna Kattel
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Renate Fleiner
Tanki
technologies_5185 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
Water user:
Salami Kham Bahadur
N/A
النيبال
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Prospects and challenges of water use systems as climate adaptive option for sustainable water management in Himalayan Regionاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Kathmandu University (KU) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
This is a Single Use Water System implemented in order to preserve the water sources through their sustainable use.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
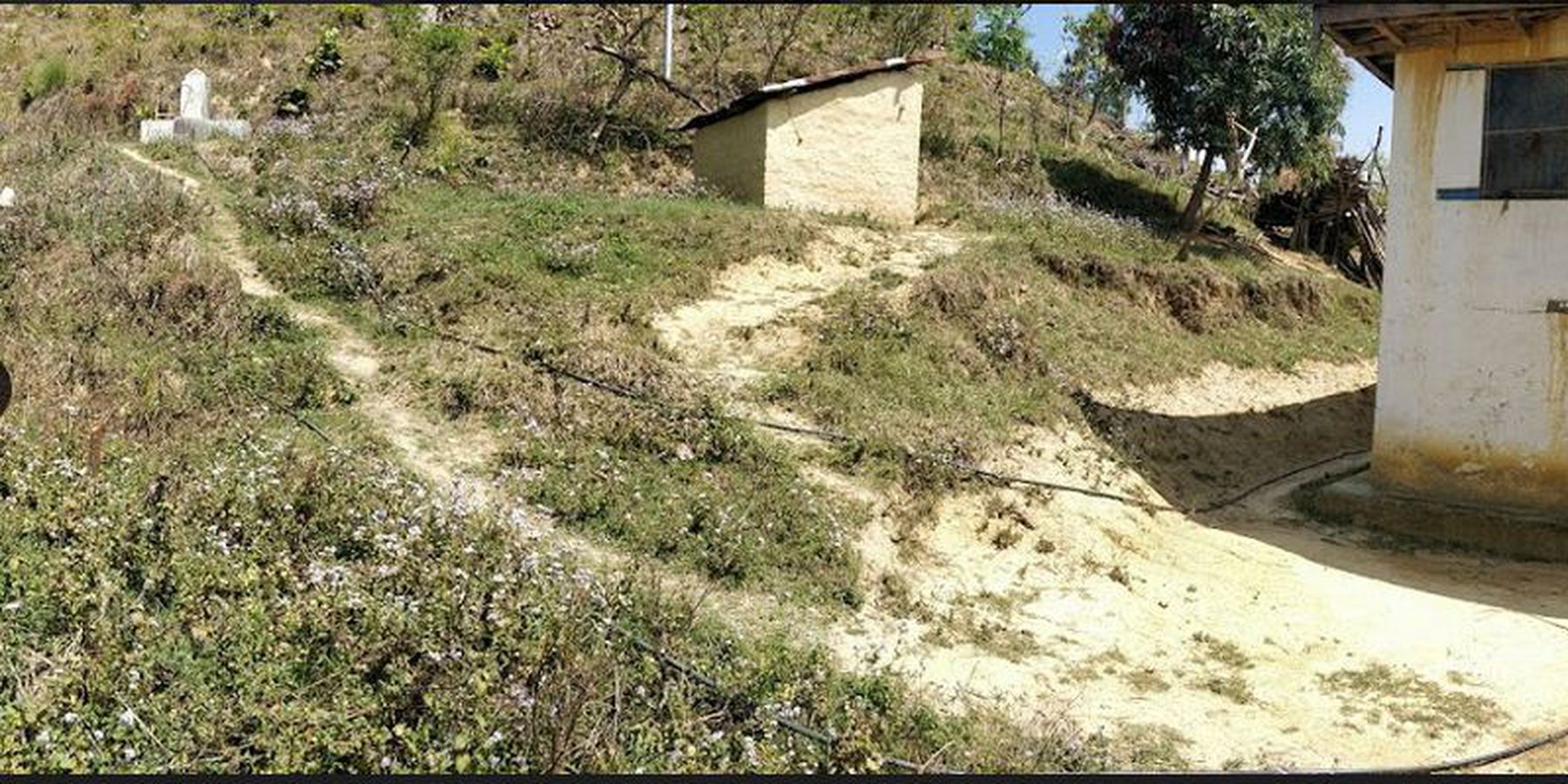
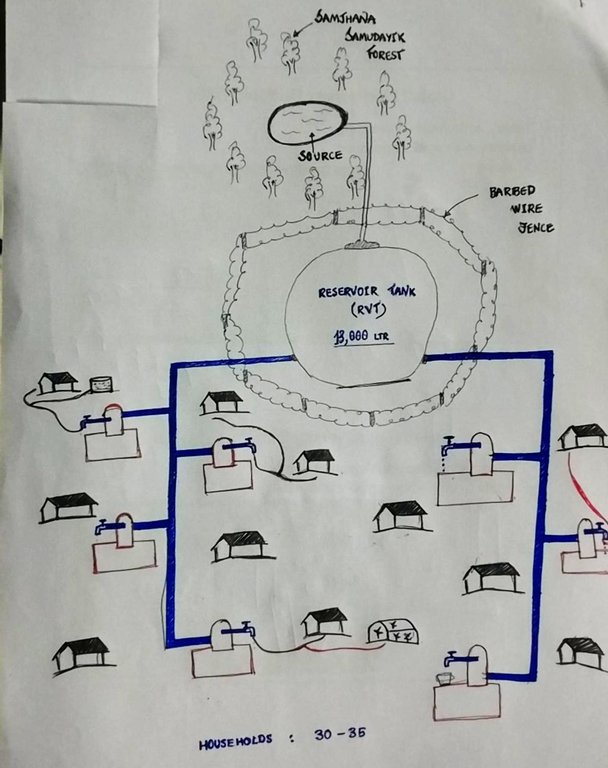
Water from source is collected in a reservoir tank ( RVT) of volume 13000 Ltr and then distributed to each household for Single Use. Traditionally, the system was constructed to serve a single purpose-drinking (hence the name "Single Use" water system). However, due to increasing demand and need to meet multiple uses, the water users are using the same water for different purposes like drinking, irrigation and other domestic uses.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A Single Use Water System (SUWS) is the one in which the supplied water serves a single purpose. Traditionally, the system was constructed in order to meet the growing demand and serve a single purpose i.e. supply drinking water to households ( hence the name "Single Use" water systems). However, people's demands and needs increased and supplied water was then used for various purposes like for irrigation, animal husbandry, domestic chores like bathing, washing, etc.
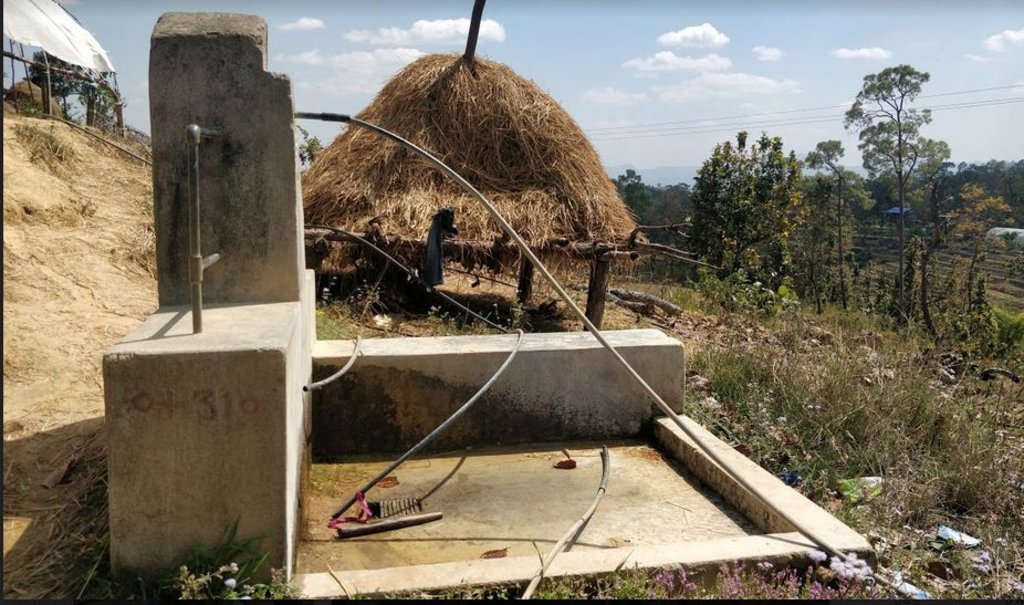
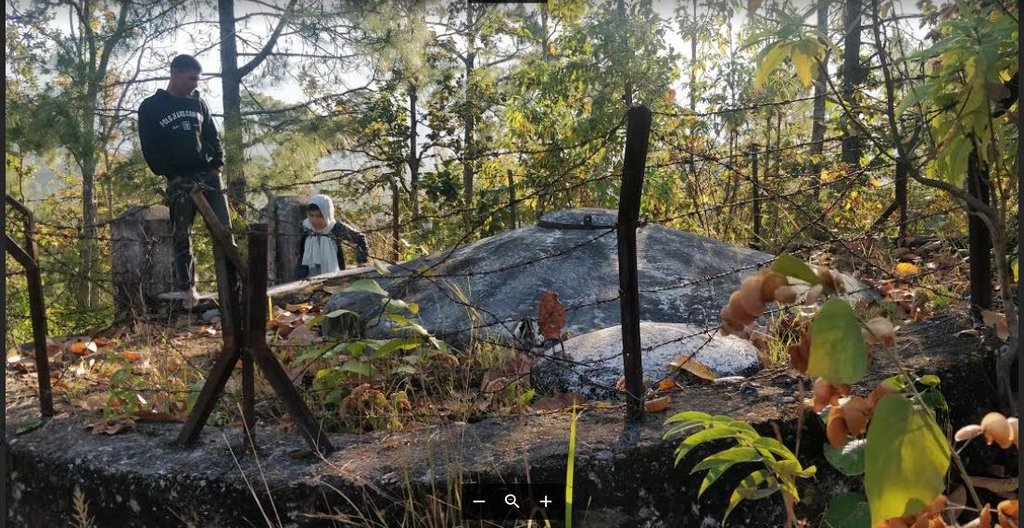
The technology is applied in a natural environment (community forest). The source of water is a natural source that lies in a community forest and hence, the availability is seasonal. The land where the source falls is owned by the government and the implementation of the technology was primarily assisted by the Village Development Committee (VDC). Its use rights falls under the water users. The main elements include a concrete Reservoir tank (RVT), pipeline and tap system or tap towers with faucets. The major functions of this technology are to store water and distribute to the 30-35 households and to ensure the preservation of natural water source through its sustainable use. Major activities are labor and construction activities for building the reservoir tank and laying down the pipeline. Maintenance work, if and when it is needed, is carried out with the help of the water users. No specific group or committee has been formed that looks onto the matters of discussion of the committee. No investment has been made by the local water users' group towards the construction of the technology. Benefits of the technology are the availability of clean drinking water at household level and the preservation of the natural source of water that ensures its perennial availability. Water users admire the overall improvement of their health status through the availability of clean drinking water.
They dislike the fact of water scarcity during dry seasons and the poor management of the system. The quantity of the water is adequate for most of the year. However, scarcity of water during the dry months (when the source dries out) is still eminent. Quality of water is good with low salinity and or iron and other elements but persistence of lime in the water remains.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيبال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Province 6, Karnali, Mid - Western Development Region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kunathari VDC -10, Odaltaal
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Community Forest ( Samjhana Samudayik Ban)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
It is based on a traditional system, but improvised to construct a reservoir tank (RVT) and water supplied through a pipeline. The traditional system contained a reservoir pond dug up and water was supplied through feeding rubber and plastic pipes to the households with no faucets. This caused the water to flow through the pipes without stopping and there was loss of precious water due to excess drainage. The dug up pond caused sediments, dirt, insects and leaves to collect in the water, clogging the pipes and making water unsafe for drinking.
The construction of concrete RVT with lid ensured water stayed free from sediments and falling leaves. Construction of tap towers with taps and faucets ensured water was not wasted. The use of Poly-Vinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe with pipeline system was done to the traditional system of supply of water to households.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- drinking water purpose ( to improve water security at a household level)
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
هل الأشجار المذكورة أعلاه ملحاء أم دائمة الخضرة؟:
- دائمة الخضرة
منتجات وخدمات:
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
التعليقات:
Samjhana Samudayik Ban ( Community Forest)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
أخرى (مثل ما بعد الفيضانات):
- Natural Water Source
التعليقات:
Natural Spring water source inside Community Forest
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة المياه الجوفية
- water management ( for Drinking purpose) - Gravity Fed Single Line
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
- S11: غير ذلك
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- غير قابل للتطبيق
التعليقات:
The "intended" sole purpose of the technology was to serve a single purpose- to supply drinking water at a household level. Hence, no significant effect with regard to land degradation was intended to have been achieved; hence omitted.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Reservoir Tank (13,000 LTR in volume). Both the source and the RVT are located inside community forest ( Samjhana Samudayik Ban). The water then flows due to the effects of gravity onto the tap towers, wherein water is supplied for 30-35 households for Single Use. Even though single use (drinking) was considered in the construction of technology, people have been fulfilling various needs with the water supplied ( eg. Drinking, irrigation, and other domestic uses).
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
10 Dhurs
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
1 ha= 590.70 dhurs
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
NPR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
113,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
N/A
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of Reservoir Tank | |
| 2. | Laying down the pipeline |
التعليقات:
The SUWS system was contributed by the VDC but exact costs couldn't be recollected by the locals. Similarly, the locals vaguely remember the season of construction. As per some of the water users, the construction was started during summer, but could only be completed after winter season was over due to rains disturbing the work in between.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Voluntary | |||||
| معدات | Construction of RVT | |||||
| معدات | Laying down pipeline |
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
1400,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Village Development Committee contributed 100% of costs, pipeline contributed by a NGO ( RRN), DFID helped with other miscellaneous costs and Newasanstha helping with other running costs.
التعليقات:
Since exact estimation and/or recollection of the costs of construction of the technology was not possible; an estimation was made based upon the then prices of materials, pipes and labor costs- which estimated to be roughly 70 USD.
It has to be kept in mind that the 70 USD that was used was almost 50 years ago. Keeping in line with the inflation rates, it could be worth more than 15-20 times of the original cost ( >1400 USD).
Hence, to make it easier to compare with the construction VS maintenance costs, the figures have been rounded off to today's value as 1400 USD.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Laying down pipeline ( by RRN) | Once (2056 B.S,) during winter |
| 2. | Operation and maintenance costs (borne by a NGO- DFID) | Once (2071 B.S.) during summer |
| 3. | Changing of pipes ( borne by NGO- Newasanstha and the locals) | 6-7 times ( during summer, winter and during rains) |
التعليقات:
The running and maintenance costs borne by various non-governmental organizations and the local community as and when required.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Voluntary Labour contribution by locals | 100,0 | ||||
| معدات | Changing of PVC Pipes | 25,0 |
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
700,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Non-Governmental organizations like DFID, NewaSanstha and Village Development Committee contributed from time to time
التعليقات:
The exact costs couldn't be calculated. But as per the locals, the costs of changing the PVC pipes 6 times came to around 700 USD.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The construction materials, pipelines were the ones which costed the most.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Total annual rainfall of the region was around 1609 mm; however no literature could give an idea on the annual "average" rainfall. Thus, estimated rainfall was mentioned.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Meteorological Forecasting Division, Nepal ( www.mfd.gov.np)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
The climate is overall humid with monsoon consisting of 2-3 months ( June - August) and dry and arid conditions during the winter seasons.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- أطفال
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Most of the community are literate ( finished upto classes 4/5 ) . The ratio of male: female is almost equal. Most of the users are middle-aged ( 40-50 yrs age-group) . The ethnicity consists of Thakuri, Dalits and Janajatis. Total land holding of the water users is around 20 ropanis. ( 1 hectare = 19.65 ropanis)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
around 10 Dhurs of land is occupied by the technology. (1 hectare = 590.70 dhurs)
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The water source is owned by the state / government. The access to water is open ; however during the time of crisis, its use is limited to each household.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
The access to all these services is limited as the locals have to traverse a distance of almost 30 minutes to bazaar area / marketplace. The road infrastructure is good.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية
خطر فشل الإنتاج
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
نوعية مياه الشرب
توافر المياه للماشية
نوعية المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
نوعية مياه الري
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Prior to the adoption of the technology, typhoid, jaundice, diarrhea and dysentery used to be a problem during the summer and rainy seasons. However, after the adoption of technology, the number of cases of such illnesses have drastically decreased and overall health status of the people greatly improved due to availability of clean drinking water.
الآثار الايكولوجية
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The "intended" sole purpose of the technology was to serve a single purpose- to supply drinking water at a household level. Hence, no significant effect with regard to other ecological impacts have been achieved; hence omitted.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water can be made available to distant places with the connection of a PVC pipe to the faucet in SUWS tap towers. Thus, more people are being benefitted from the technology.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
Estimated maintenance and running costs could not be exactly calculated, but weighing down the pros with the costs; the benefits outweigh the costs.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Availability of clean source of drinking water is ensured. |
| Need to travel long distances to fetch water not prevalent due the the availability of taps with drinking water at household levels. |
| Water being used for various purposes like drinking, irrigation, domestic purposes, etc. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Water scarcity during arid and dry winters decreased if not stopped overall. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Water not available all year-round | By construction of another reservoir tank (RVT) |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Pipeline severely damaged due to lime | Lime treatment and changing of pipes to more resistant ones ( GI ) pipes instead of feeble PVC ones used |
| No specific committee / group set up to discuss the problems | Setting up water users' committee and donating a small sum per household every month that goes onto a fund, that can be later used to address various problems that may arise in the future. |
| Water being supplied for a single use only | upgrading the technology to Multiple Use Water Systems (MUWS) in place of Single-Use Water Systems (SUWS) could address the multiple uses of water users. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
> 10
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
> 1
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
15/06/2019
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية