Soil productivity improvement and BXW control in epidemically affected banana zone [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: ALLAN BUBELWA
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Ursula Gaemperli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1204 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Pesha
Kyerwa District Council
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدةاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدةاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Kyerwa District Council - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Restoring banana production through temporal crop substitution and the use of SLM and recommended husbandry practices in controlling the deadly BXW disease.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
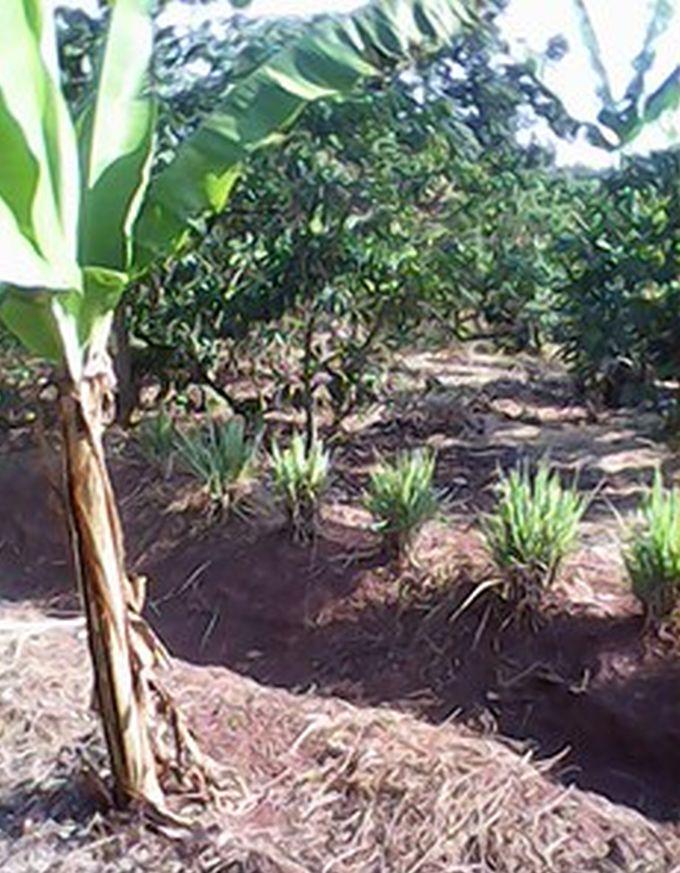
This conservation measure is used in BXW epidemically affected areas. Land users in affected areas are trained on the principle behind the diseases and means and ways to overcome it. Banana plants in seriously affected farms are uprooted and destroyed and non disease host crops usually maize and common beans are grown for starvation and destruction of BXW pathogen. The land is not used for banana production for a period of 6 months and instead substitute crops ensures food and income security to land users. Leguminous cover crops (beans) and crop residual management skills applied on the farm revitalize the soil health in terms of biomass, moisture and nutrient recycling. After 6 months, banana production is resumed where production is based on recommended husbandry practices combined with SLM conservation measures. The use of certified banana cultivars, optimal plant geometry and disease control cultural practices are some of the basic recommendation. Certified banana cultivars are planted at a space of 3m x 3m. The size of a hole used to plant banana is 0.9x0.9 m wide and 0.6 deep. During digging top soil is separated from subsoil. 2 -3 tins of manure are mixed with the top soil and the mixture is put in the bottom of the hole. The holes are left for microbial decay to take place and banana planting is done after 1 or 2 months. The tied Fanya chini water retention ditches are water harvesting and conserving structures constructed by digging trenches along the contour where dug soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. A-FRAME method is used to mark a contour line and on the other hand ARM OUTSTRETCHED LEVEL method determines how far apart the Fanya chini retention ditch should be. Unlike other retention ditches, the dug ditches are not continuous but instead are tied at regular interval with small cross–ties of 0.4-0.6m length. Ties intercept the ditch at right angle to form a series of narrow rectangular segments of infiltration ditches each of 5 meters long, 0.6m wide and 0.6m deep arranged in series within a contour line. Ties helps to prevent irregular flow of runoff and to ensure an evenly distribution of captured water. Fanya chini embankments are stabilized by planting crops on them the common crops are pigeon pea (space used between plant is stand is 1m x 1m), lemon grass (30cm x 30cm) or pineapples (60cm x 60cm). Mulching is done using grasses. The dominant grass species used is Hyperrenia rufa where a mulching depth of 15 cm is used.
Purpose of the Technology: PURPOSE: Improved food and fodder productivity, soil moisture and water holding capacity, nutrient recycling, and organic matter content, biomass cycle, crop tolerance to drought, income and food security, poverty reduction and health. Prevent unproductive evaporation of green water, combating soil erosion by water runoff and biological degradation due the deadly BXW disease.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: ESTABLISHMENT: procurement and mobilization of working tools, uprooting and destruction of infected plants in affected fields, land tilling and harrowing, planting of alternative crops or creation of a productive disease free buffer zone, temporal harvesting of maize and beans, land preparation/ demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting, digging holes, manure application before planting, banana planting, demarcation of contour line for construction of Fanyachini contours with ties, digging and construction of Fanya chini contours with ties, vegetative stabilization of Fanya chini bunds (using lemon grass, pineapples or pigeon pea), random planting of castor oil plants for future anchoring support of plants with heavy bunches and mulching application. MAINTENANCE: hand weeding to control noxious weeds combined with other pest and disease control (control of nematodes and weevils), de-suckering to leave the mother plant and two baby plants, de-trashing or trimming of unproductive leaves, regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector , recurrent manure application, removal of sediments and maintenance of Fanyachini bunds, harvest of bananas, maize, pineapples and pigeon pea. INPUTS USED: largely includes labour (strenuously varying from light, medium and heavy), tools (hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade, mattock and A-frame), seedlings; improved or certified banana varieties, pineapples suckers, lemon grass and castor oil, seeds (beans, maize and pigeon pea), farm yard manure and mulching materials (preferably Hyperennial spps).
Natural / human environment: NATURAL ENV: The land use type is cropland with annual, perennial and some fruit tree crops. The technology involves a combination of agronomic, vegetative, structural and management conservation measures. Management measure involves all activities related to temporal shift to alternative crops for making the farm disease hot free and for staving and destroying the disease pathogen. Climatic zone is sub-humid with an average of 210 days of growing period (LGP). Average slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. A soil texture class is sandy loam with medium depth categories. HUMAN ENV: the level of mechanization is hand tools. Production system is mixed (both subsistence and market or commercial oriented). The average costs of inputs required is 3015.68 USD. Land ownership is largely individual not titled and partly communal.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kagera Region Tanzania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kyerwa District Council
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
The area includes the totality of all farms of FFS members who applied the technology after being trained.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
This is one of the technologies tested and demonstrated under the support of the Trans Boundary Agro Ecosystem Management Project. Analysis and documentation of this technology is based on perspectives and experiences of field SLM specialist and FFS group members.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- root crops, pigeon pea, lemon grass
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- أناناس
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- البن، في مزارع مفتوحة
- البن، المزروع في الظل
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September to December; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Major land problems without land conservation are BXW disease, poor soil fertility, and moisture stress and soil erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): BXW disease.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Banana is the major food crop but in the recent years the crop was substituted by maize and beans due the out break of BXW.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
- crop substitution
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A7: أخرى

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
- V5: أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك

التدابير الإدارية
- M7: أخرى
التعليقات:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Use of leguminous plants
Specification of other structural measures: Water retension ditches with fanya chini bunds and ties.
Specification of other management measures: Temporal substitution of a dominant crop by non disease host crops for pathogen distruction
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Flat cultivation on slopy land and nutrient mining without replenishment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor practices that encourage spread of BXW.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (No use of cross slope barriers.), change in temperature (Unproductive loos of green water due direct hit of of the soil by sunshine), change of seasonal rainfall (Due to climatic change and variability), poverty / wealth (Incapacity to invest in capital heavy conservation measures), labour availability (Rural to Urban migration of the enegetic youths), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (High input expenses.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Ignorance of SLM and shortage of field extension workers.), governance / institutional (Low capacity of rural based environmental/land committees)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Due unpredictable climatic change and variability), population pressure (Continuous land fragmentation)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Most of the concepts and principles were taught to field/agricultural advisers at the college.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (New innovations and change of mind set is crucial e.g. the use of A-frame, the principle behind BXW and cultural methods of controlling the disease.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Mulching
Material/ species: Hyperania grass
Quantity/ density: 15 m3 /ha
Remarks: Across the slope
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Farm Yard Manure
Quantity/ density: 40ton/ha
Remarks: 3 tin applied to each banana plant.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6
Trees/ shrubs species: pegion peas
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Pineapples
Grass species: lemmon grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 12
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 70
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70
Construction material (earth): Soil
Other type of management: Temporal substitution of the a diseased plant with other non-host plants for staving and complete wipe out of the disease causing pathogen. (BXW affected bananas substituted with maize and beans)
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.353
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | |
| 2. | Initial manure application (before banana planting) | |
| 3. | Initial banana seedlings (certified varieties) | |
| 4. | Initial mulching application | |
| 5. | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants in affected fields. | Before onstart of rain |
| 6. | Land tilling and harrowing. | Before onstart of rain |
| 7. | Planting of alternative crops (maize and beans) for starving and killing the pathogen. | After the first rains (usually September) |
| 8. | Demarcation of contour line using A-frame for construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 9. | Digging and construction of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | December |
| 10. | Planting of lemon grass , pineapples and pigeon peas on bunds. | After constrution of fanya chini retension ditches with ties |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Planting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 5,0 | 2,353 | 11,77 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Demarcation of contour line | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,26857 | 15,88 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Digging and construction of Fanya | persons/day | 10,0 | 2,353 | 23,53 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Uprooting and destruction of infected banana plants | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Procurement and mobilization of working tools | ha | 1,0 | 76,47 | 76,47 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Lemon grass and pidgeon seeds | kgs | 5,0 | 2,94 | 14,7 | |
| المواد النباتية | Pineapple seedlings | pieces | 513,0 | 0,0588304 | 30,18 | |
| المواد النباتية | Initial banana seedlings | pieces | 660,0 | 0,441181818 | 291,18 | |
| المواد النباتية | Maize and bean seeds | kgs | 81,0 | 0,947654 | 76,76 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Initial mulching application | bundles | 900,0 | 0,1764666 | 158,82 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Initial manure application | tons | 28,0 | 10,084 | 282,35 | |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Land tilling and harrowing | persons/day | 11,0 | 2,353 | 25,88 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Planting of alternative crops | persons/day | 9,0 | 2,353 | 21,18 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1054,58 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1054,58 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 9 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting and hole digging for planting bananas | Before onstart of rain |
| 2. | Manure application before planting Banana | Before onstart of rain |
| 3. | Banana planting | one to two months after manure application |
| 4. | Recurrent mulching application | once per season |
| 5. | Hand weeding to control noxious weeds, De-suckering, De-trashing and trimming | April and December |
| 6. | Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence (male bud) using a forked wooden pole once the bunch is completed to prevent BXW transition through insect vector | Routinely as need be |
| 7. | Recurrent manure application | September/October |
| 8. | Banana harvesting | Routinely after mature |
| 9. | Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas. | April |
| 10. | harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | |
| 11. | Removal of sediments and reshaping/maintenance of Fanya chini retention ditches with ties. | May |
| 12. | Weeding and thinning | (twice) first and second |
| 13. | Harvesting of maize and beans. | January/February |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Land preparation, demarcation and spacing of holes for resumed banana planting | persons/day | 35,0 | 2,353 | 82,36 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Manure application before planting Banana | persons/day | 33,0 | 2,353 | 77,65 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Banana planting | persons/day | 13,0 | 2,353 | 30,59 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Recurrent mulching applicatio | persons/day | 6,0 | 2,205 | 13,23 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mulching material | bundles | 900,0 | 0,176464 | 158,82 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Compost/manure | tons | 16,0 | 13,235 | 211,76 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Labour: Maintenance of Fanya chini | persons/day | 3,0 | 2,353 | 7,06 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Labour: Weeding an thinning | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05916 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Labour: Harvesting of maize and beans | persons/day | 12,0 | 2,05915 | 24,71 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Hand weeding to control noxious weeds | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Regular removal/de-bud of inflorescence | persons/day | 15,0 | 2,353 | 35,3 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Recurrent manure application | persons/day | 22,0 | 2,353 | 51,77 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Banana harvesting | persons/day | 16,5 | 2,353 | 38,82 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Weeding and gap filling of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Harvesting of lemon grass, pineapples and pigeon peas | persons/day | 7,0 | 2,353 | 16,47 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 825,02 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 825,02 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattocks and forked wooden poles., Hand hoe, forked hole and machetes, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, spade, mattock and A-frame, hand hoe, forked hole, machetes, sickles, spade and mattock.
The above cost were calculated per unit of one land user's land (1.5 acres) where the technology was applied and estimate also done per hectare.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Manure is the most determinant factor
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature is 21°C
Average length of growing period is 210 days.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture (topsoil): The average soil texture is sandy loam
Topsoil organic matter: Low use and application of mulching and cover crops
Soil fertility is low due to continue washout of the soil surface with rainfall runoff
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium because slope effect minimize the time required for water to infiltrate into the soil.
Soil water storage capacity is low because of low amount of humus and underused of mulching
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Only a few perennials and annual crops and minimal fauna diversity due to the washout of organic matter by rainfall runoff
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
15% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some of the land users who are using the technology are running petty business and groceries (selling local brew).
Level of mechanization: Dominated by the use of small tools/implements.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5 fingers
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
12 fingers
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased banana yield due to use of SLM and good husbandry practices
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Risk due to low moisture
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Caused by the use of mulching and manure
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Income accrued from increased production and diversification to pineapples and lemon grass
عبء العمل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Attributable to added tasks from use of SLM
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved nutrition from e.g. introduction of pineapples
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Use of FFS have induced togetherness and group working spirit
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
SLM knowledge and skills gained through FFS trainings
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Indiscriminate participation of all genders, age and ethnicity
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Initially the technology has resulted to increased production, diversification to production of other income generating crops and dietary enrichment crops. The overall result is farmers capacity to meet education and health expenses
attraction to theiving
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Good looking banana bunches attract thieving
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Use of mulching and water retension ditches
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Following use of mulching and manure
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
90%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved soil coved caused by the use of grass mulching
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Controll of soil erosion attributable to use of mulching and construction of water retension ditches.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Use of luguminous plants, application of manure and mulching
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Use of manure
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
90%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Biomass result from use of mulching and improved managment of crop residuals
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased richness of soil fauna caused by the use of manure
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
95%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Control of BXW
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased tolerance to drought and BXW infestation
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Managment of crop residues and manure
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Of the neighbouring Kashasha wetland
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Attributable to use of closs slope barriers
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Retention ditches supported with ties to prevent flow of water and to encourage evenly distribution of water. The fanya chini bunds are stabilized by planting vegetation on them (pineapples, pigeon peas and lemon grass).
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The high investment costs cause slight realization of rewards but in the long run very positive benefits are realized by land users.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
42 households covering 77 percent of the stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
التعليقات:
42 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Supplied with banana suckers, farm yard manure and grass mulch.
42 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: land users who received suckers from neighbors but procured grass mulch and manure.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: most of the land users are impressed with the results attributable to the technology in terms of control of BXW, increased banana production, control of soil erosion and promising increase in income.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The technology useful to the community and is easy to learn. |
| Encouraging results in terms of improved productivity and general performance of banana and other crops like coffee within the technology area attributable to use of technology. |
| The technology has made significant achievement in terms of decrease of BXW infestation. |
| Soil health has improved as the result of use of mulching materials, manure, leguminous plants and application water harvesting cross slope barriers. |
| There is positive change of mind set towards the use of SLM |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Good and attractive crops that consumers are willing to purchase at a high price have resulted to emergence of thieving. | Spread the technology and supply improved banana suckers to other farmers so that more farmers are engaged in banana production. Strengthen community police. |
| The technology initially is labour and capital intensive | Encourage group working spirit. |
| Unplanned Changes of service providers which may fall in the hands of untrustworthy service providers. | Pluralism in service delivery should be planned with doubly consciousness to take care of untrustworthy service providers. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/07/2014
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية