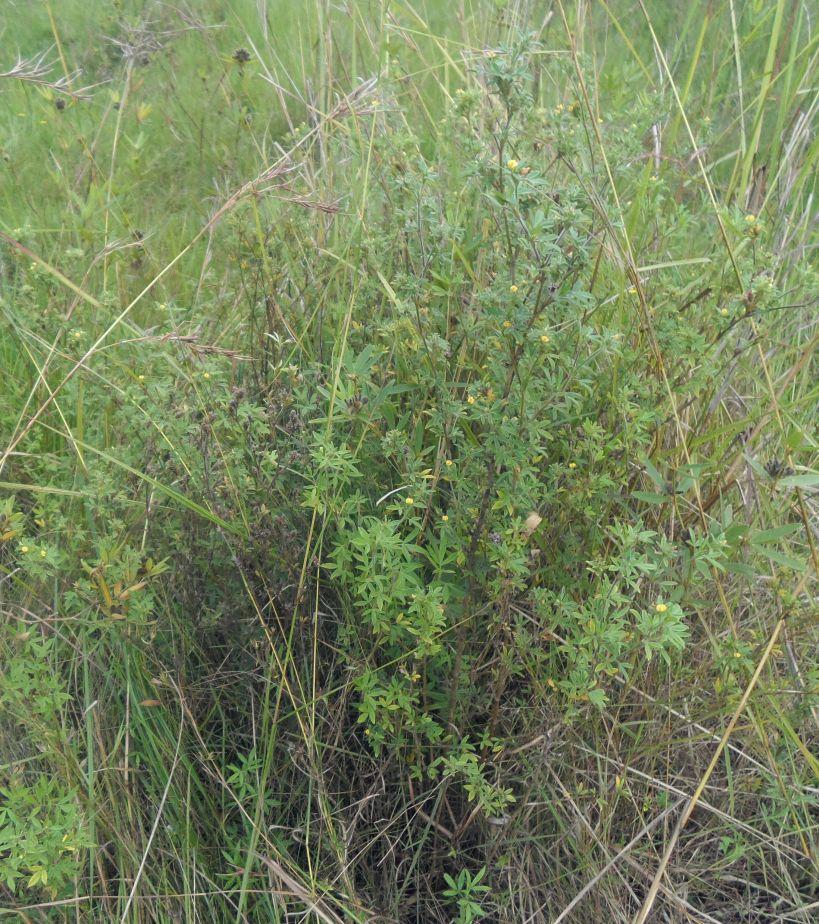
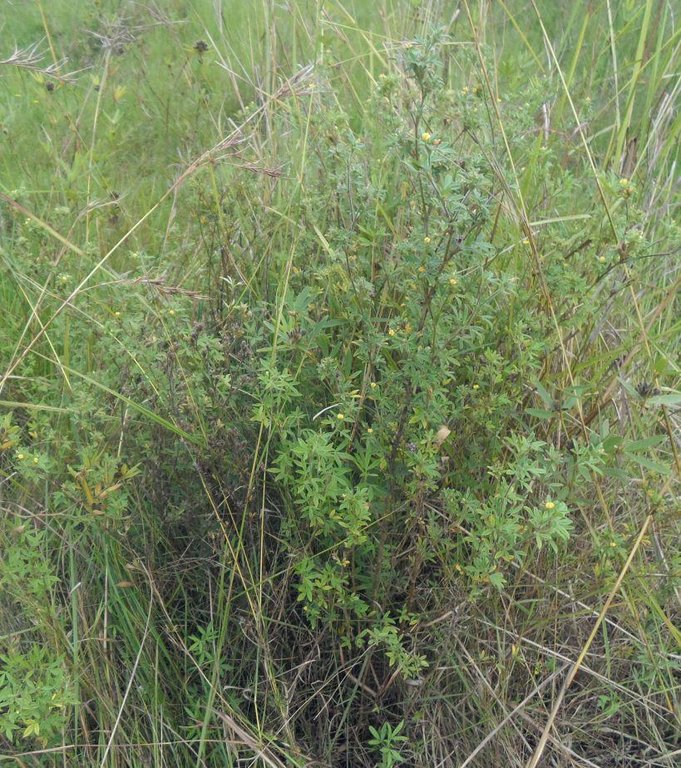
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: ALLAN BUBELWA
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدةاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
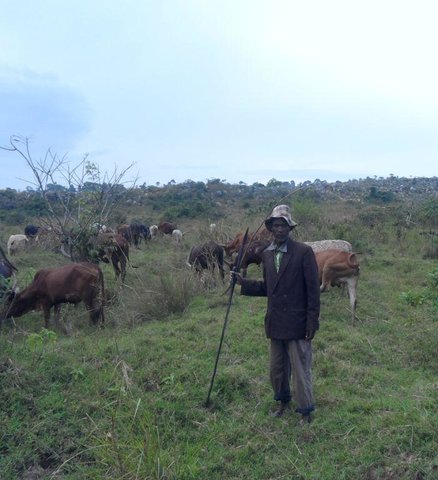

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- جامع المعلومات: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tanzania/Kagera
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الرعي المرتحل
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- الأغنام

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- Ficus thonigii
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إغلاق المنطقة (إيقاف الاستخدام، دعم الاصلاح)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير الإدارية
- M7: أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wr):انجراف ضفة النهر

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Tanzanian shillings
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1700,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.12
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | once |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| العمالة | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| العمالة | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | |
| معدات | Tools | Number | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 235,29 | 235,29 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,65 | 117,65 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | kg | 125,0 | 0,588 | 73,5 | |
| غير ذلك | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 651,9 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,38 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Weekly |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,76466 | 26,47 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,53 | 52,95 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 432,36 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,25 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
سطحية
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5.0 ton/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
6-7.0 ton/ha
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2 acres/annum
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10 acre/annum
التعليقات/ حدد:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
جودة العلف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8
التعليقات/ حدد:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1200litres/cow/yeer
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2000litres/cow/year
التعليقات/ حدد:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
weak
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
strong
التعليقات/ حدد:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resultant of vergetation cover
التبخر
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
التربة
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved vegetation cover
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
تراص التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
التعليقات/ حدد:
Controlled fire burning
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Controled bush fire
خطر الحريق
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
high
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
03/06/2014
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- جامع المعلومات: ALLAN BUBELWA
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية