Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [زامبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Silenga Wamunyima
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1187 - زامبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
زامبيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
زامبيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - زامبيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Participatory Research and Development [زامبيا]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- جامع المعلومات: Arthur Chomba
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
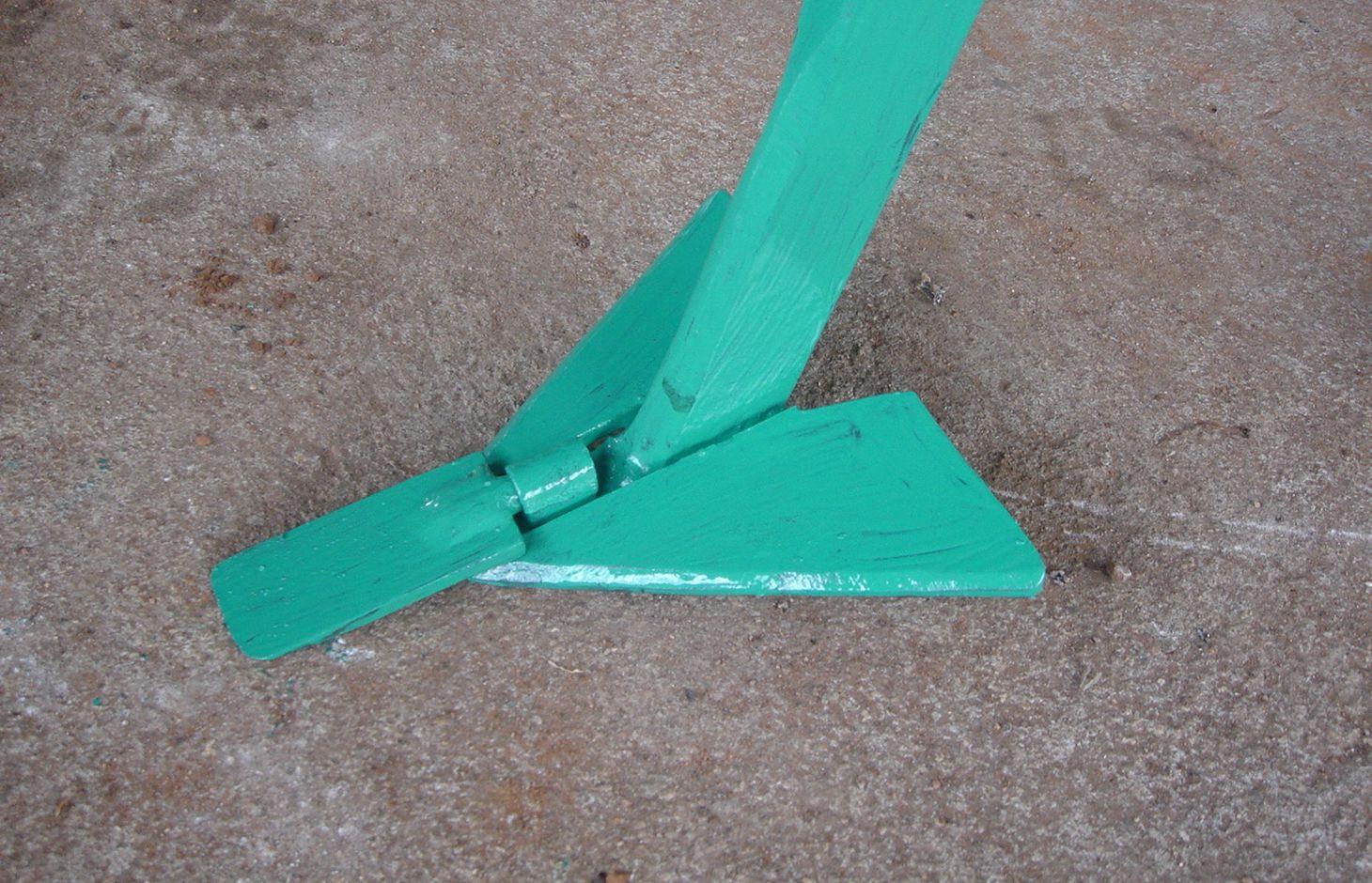
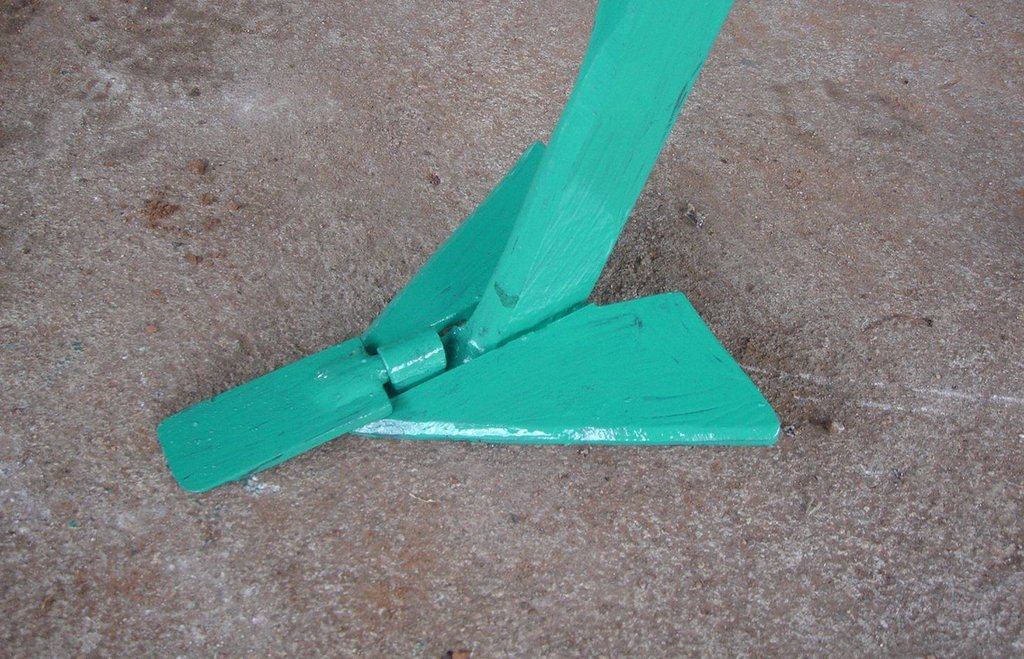
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
زامبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Zambia/Southern Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mazabuka/Magoye
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
التعليقات:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- محاصيل الألياف - قطن
- المحاصيل الزيتية - الفول السوداني
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March

أراضي الرعي
نوع الحيوان:
- ماشية - الألبان
- الماعز
- الدواجن

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
- A7: أخرى
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.1: لا حرث
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A6.1: محترق
التعليقات:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
- انسداد مسام التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
التعليقات:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
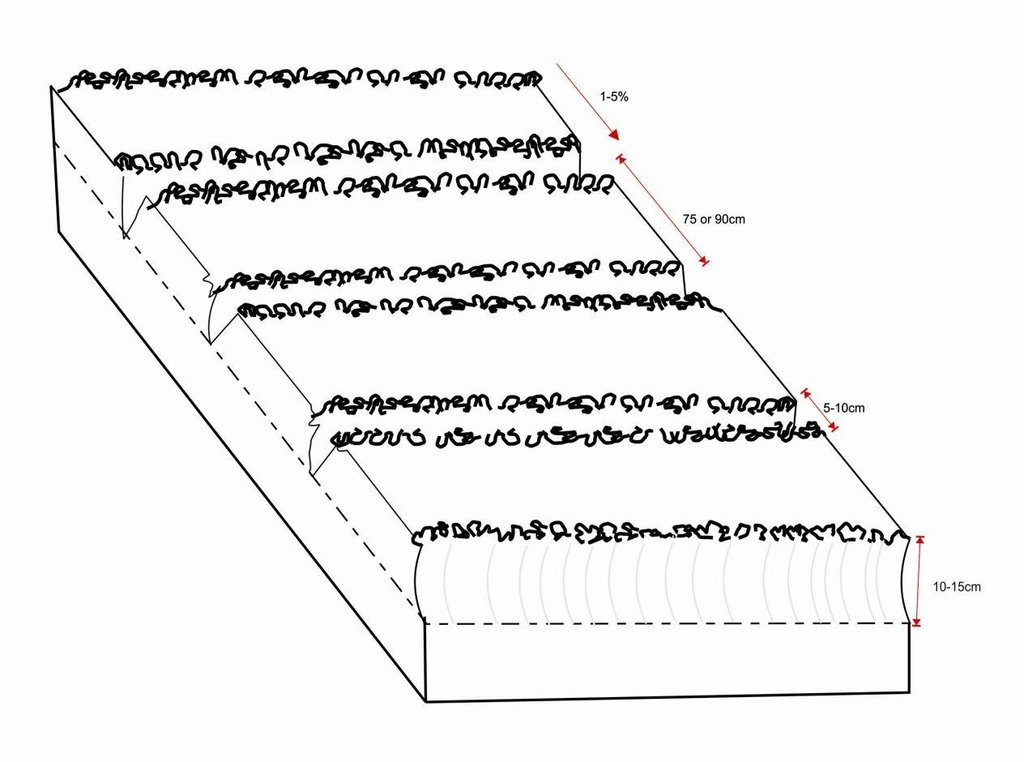
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
المؤلف:
Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.40
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | |
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 580,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 580,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | April-May |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8,0 | 2,5 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 2,5 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | kg/ha | 20,0 | 2,5 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400,0 | 0,8 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Herbicides | l/ha | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Lime | kg | 1000,0 | 0,042 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 621,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 621,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Summer rains from November to March
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3tons/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5tons/ha
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to early planting
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Residues needed for soil cover
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Better resistance
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2-3ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
>10ha
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
More time and labour freed for other activities
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to incresed yields
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less time spent on farm operations
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil cover
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil cover
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved soil structure
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to good drainage
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil cover
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to better soil cover
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to non-inversion tillage
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to deep tillage
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
الملوحة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to good drainage
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Resistance to chemical weed control
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Ground water contamination
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Only if applied over an extensive area
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Only if applied over an extensive area
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Only if applied over an extensive area
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Only if applied over an extensive area
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
FAO
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
عنوان الرابط URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Participatory Research and Development [زامبيا]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- جامع المعلومات: Arthur Chomba
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية