Rotational grazing supported by additional water points [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Чаронидани даврави бо нуктахои обнуши ва чойхои дамгири
technologies_1519 - طاجيكستان
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 21 أغسطس، 2019 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 8 أغسطس، 2017 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 19 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Rotational grazing supported by additional water points: 14 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Knowledge Management for Integrated Watershed Management and Disaster Risk Reduction (SDC / IWSM)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
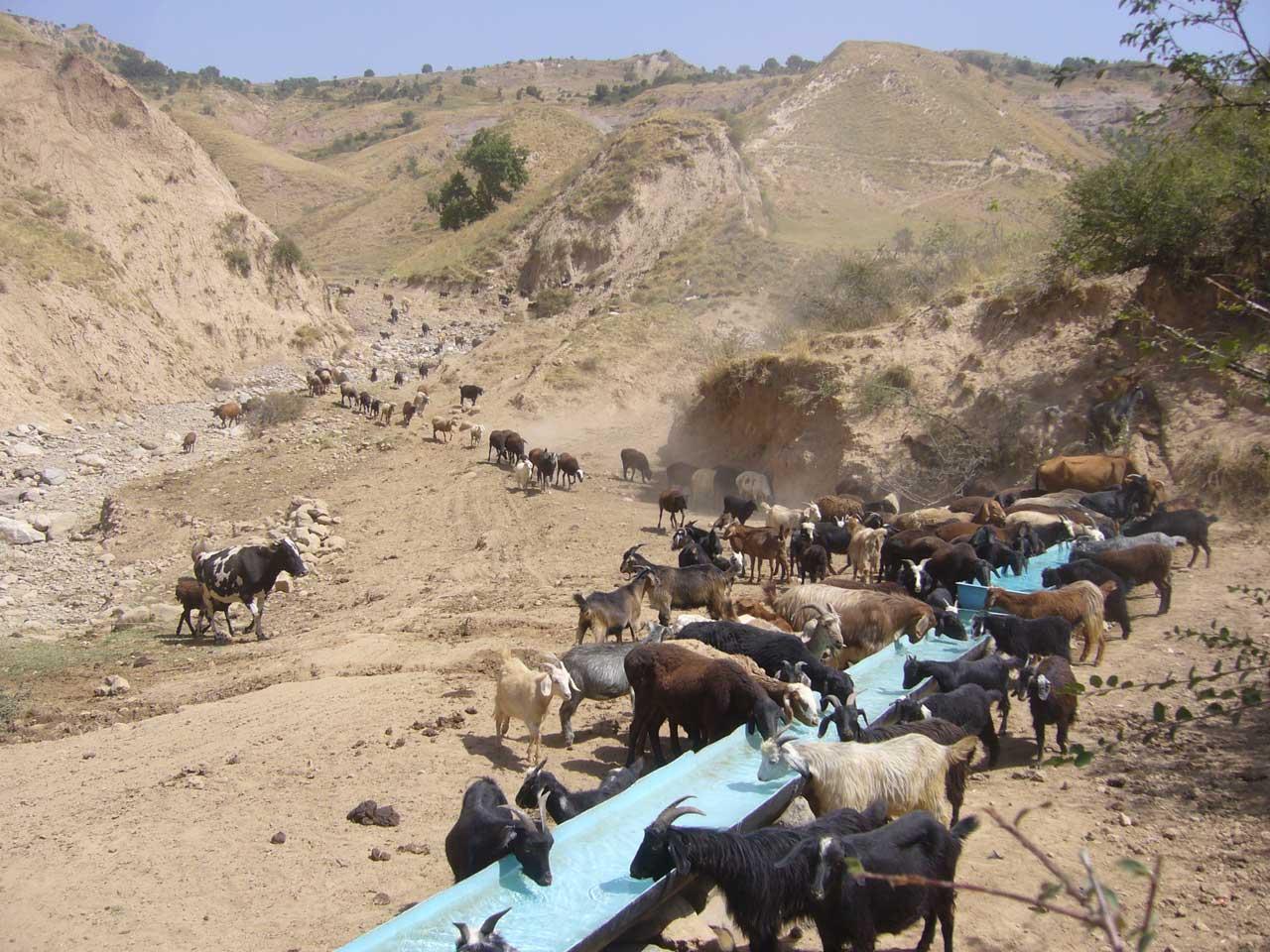
After the end of the Soviet era, an increased number of livestock with less grazing land available, has led to the deterioration of the pastures, including overgrazing, reduction of plant diversity, poor livestock health and soil erosion. To tackle the problem, Caritas Switzerland together with livestock committees at village level introduced rotational grazing supported by extra water points and rest places.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
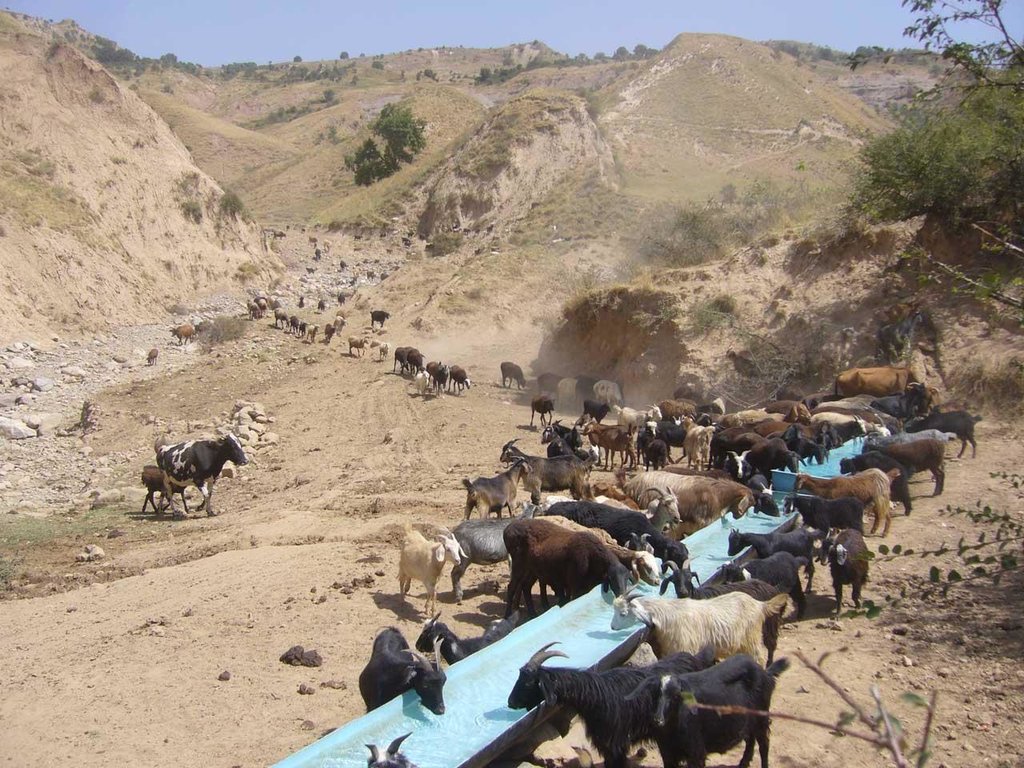
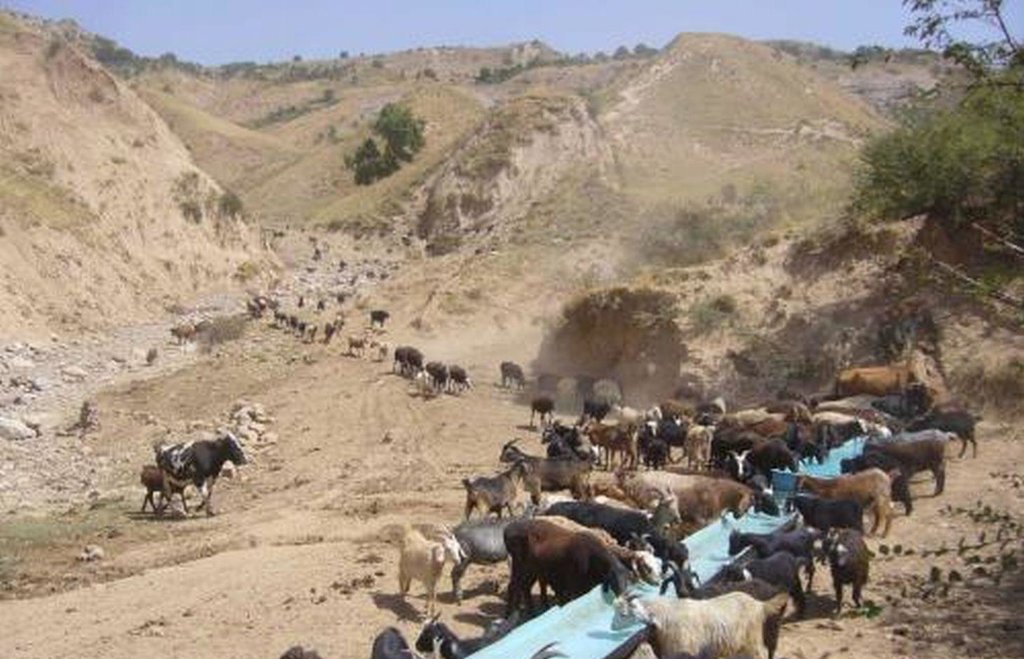
When in 2009 the project started in the two watersheds of Fayzabad and Gesh in Muminabad district, the communities had identified insufficient livestock water points in the pastures, and poor pasture management as top priorities concerning natural resource management in the watersheds. At that time, one of the biggest problems for livestock and herders was the difficult access to water when grazing the daily pastures above the villages. At lunch time, herds had to walk long distances (4-5 kilometers) and actually had to come back to the villages for drinking water. Climbing twice a day to the pasture costs the cattle a lot of energy leading to a yearly loss of up to 40-50 kg, according to a Caritas Switzerland study. One initial measure to improve the condition of the livestock was therefore to establish water points in the pastures. At first, water sources that supply water throughout the year were identified.
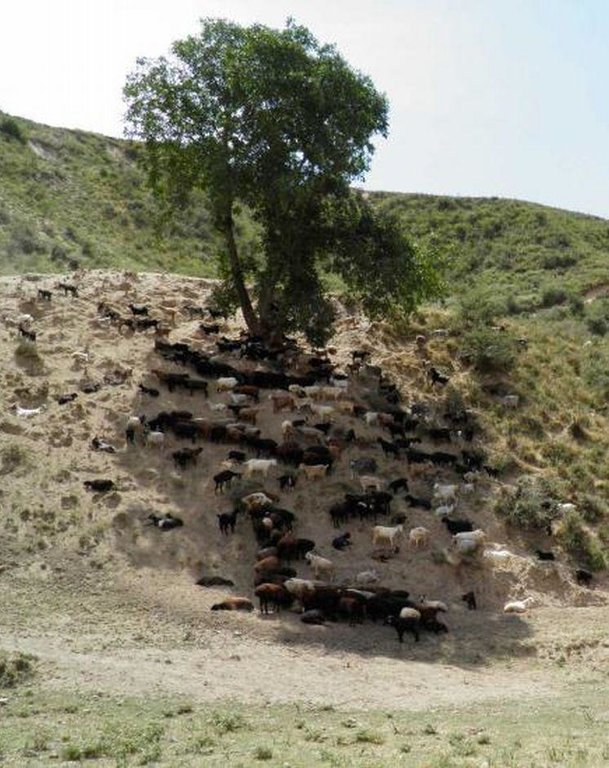
Purpose of the Technology: The water is now collected in a cement catchment, from where it is channelled through pipes to the drinking water points for animals. In some cases water tanks are placed above water points, to collect water and to distribute it to the water points. Additionally, rest places were found for the livestock, where they can have a rest in the shade after drinking water on hot summer days.
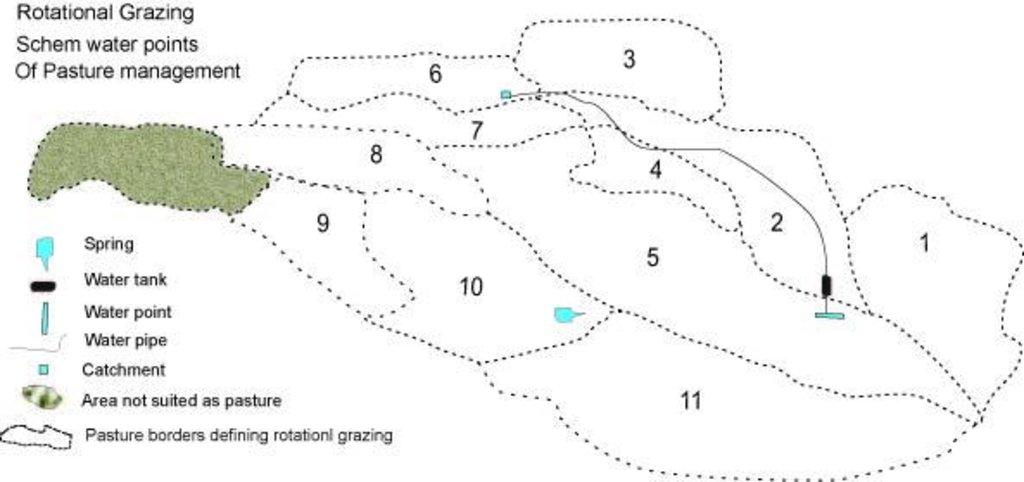
In conjunction to the establishment of water points, a rotational grazing scheme was introduced. The pasture land in the watershed was divided into ten parts and in each plot the animals were allowed to graze for five to eight days, assuring longer growing times for grass on specific pastures and thus increasing the quantity of grass and the quality of the pastures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Livestock committees, consisting of five people, were organised. They took the lead in developing appropriate grazing schemes and discussing the location of the water points with the villagers. They are in charge of further maintenance of the water points, and the daily organisation of the rotational grazing. One of the five committee members is the shepherd. Every morning he accompanies the herd and checks the water points and the rest places. Once a month he collects one Somoni from each family to cover costs arising from this method of pasture management in the watershed.
Natural / human environment: The technology is implemented on pasture land where animal drinking water is readily available only in spring, and during the rest of the year the distances to water sources are long. Daily pastures in stony terrain with steep slopes and pastures situated higher up are difficult to reach. The livestock grazing on common grazing land are controlled by the head shepherd with the task of coordinating the different helpers and having overall responsibility for herding the livestock.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tajikistan, Khatlon
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Muminabad
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 93.74 km2.
11 projects applied this technology, however, in the cost section of this case study costs are calculated for only one of these 11 projects (Faizabad watersheds)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- التوت
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- أشجار الجوزيات (جوز البرازيل، الفستق، الجوز، اللوز، الخ.)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 145Longest growing period from month to month: March-September

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
- rotational grazing
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- Livestock density (if relevant): > 100 LU /km2

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Animal trampling and little vegetation cover, wind erosion, water erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Bad pastures, bad access to water points.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: rotational grazing
Grazingland comments: Healthy livestock go out to the summer pastures and cows that are used for milk stay in the village along with the sick animals.
Type of grazing system comments: Healthy livestock go out to the summer pastures and cows that are used for milk stay in the village along with the sick animals.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (bad management of pastures), population pressure (many animals in the pastures)
Secondary causes of degradation: inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Rotational grazing map for pasture management.
Location: Muminabad district. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Date: 2010-12-27
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5.00
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6.00
Trees/ shrubs species: maple
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mulberry, wallnut
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 80.00%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from grazing land to rotational grazing land
Layout change according to natural and human environment: water points
المؤلف:
Sa'dy Odinashoev, Muminabad
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
6.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting trees to create rest places for livestock | spring |
| 2. | Planting trees to create rest places for livestock | |
| 3. | water points | 2 months |
| 4. | construction of the pipeline from the spring to the water points | 1 month |
| 5. | catchment device on the spring | |
| 6. | catchment device on the spring | |
| 7. | calculating carring capacity and number of days of grazing period on each plot | |
| 8. | calculating carring capacity and number of days of grazing period on each plot |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Planting trees incl. seeds | Persons/day | 20,0 | 5,5 | 110,0 | 20,0 |
| العمالة | Waterpoints construction labour | Persons/day | 160,0 | 5,5 | 880,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Pipeline Construction incl. Watertanks etc | pipeline | 1,0 | 6648,0 | 6648,0 | 30,0 |
| معدات | Catchement device | device | 1,0 | 353,0 | 353,0 | 20,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 7991,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 7991,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Caritas
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | 2-3 years |
| 2. | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | |
| 3. | Watering of trees (done by sheperd) | 1-2 years |
| 4. | Watering of trees (done by sheperd) | |
| 5. | rotational grazing and checking the water catchment and distribution system (salary for shepherd) | 8 months |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | rotational grazing and checking the water catchment and distribution system | ha | 800,0 | 0,7975 | 638,0 | |
| العمالة | Protecting young trees with dead branches from thorny bushes | Persons/day | 20,0 | 5,5 | 110,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 748,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 748,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: spade, possible water tap, shovels, spades
The costs were calculated for infrastructure establishment, labour etc. applying to the whole area of 800 ha.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Distance to the water source, and the availability of high resolution satellite maps (the technology is cheaper if maps are available because the planning process gets facilitated).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms occure also in ridges.
Slopes on average are also moderate sometimes.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average can somtimes be deep.
Soil fertility is low on spring pastures, medium where the animals are grazing and high on the top of the watershed.
Topsoil organic matter is on the top high and medium in the middle.
Soil drainage / infiltration is good on the top of the watershed and medium in the middle of the watershed.
Soil water storage capacity is high on the top, medium in the middle and very low on the bottom.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table is everywhere 5-50 m
Water quality (untreated) is als sometime poor.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The men do most of the work out in the fields, such as carrying water and walking to the fields.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
2% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: most families have remittances from Russia
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
Common grazing land (500ha / 400 households)
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
in the upper area more grass
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
perenial plants
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
milk, meat
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
التعليقات/ حدد:
No water available previously
نوعية مياه الشرب
التعليقات/ حدد:
No water available previously
توافر مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
less money spent on vets
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
more milk prduced
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
less walking for herders
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
pasture area
التعليقات/ حدد:
road to the new pastures
Water payments
التعليقات/ حدد:
No payment previously
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
livestock commitee have respect in the village
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
villagers
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Previously a lot of conflict in this area, regular meeting have helped reduce these.
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Empowerment of women and marginalised groups. Women are involved in the workshops
collaboration between different stakeholders
التعليقات/ حدد:
watershed group in livestock committee in the village
Livelihood and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
water points
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
filtering in the spring
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
more grass
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cattle do not need to walk over soem areas
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to better management
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
more plants
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
grass
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Increase in temperature --> install more water points
Increase or decrease in rainfall --> adapt the rotational grazing system
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
500 households in an area of 93.7 km^2 (10 persons/km^2)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
التعليقات:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
480 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: nine other villages would like to adopt this technology
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
More water points How can they be sustained / enhanced? Less risks for their animals |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Rotational grazing to improve grass cover |
|
Better incomes for the farmer and at the same time pasture ressources are better managed How can they be sustained / enhanced? more meetings and workshops |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| difficult to work with maps | one day workshop |
| one person had to share their water with the rest of the village | organise meetings --> good communication, show the advantages to everybody |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| One year for such a project is too short | project should be extended to 2-3 years as within three years the trees in the rest places will be well established |
| only one water point it is not enough to improve soil and water conservation | rotational grazing and rest places have to be implemented together with water points |
| young trees have to be protected | Using PET bottles or thorny bushes |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
16/07/2010
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية