Conservation agriculture for maize-legume systems with velvet bean as a dense cover crop [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Kennedy Were
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Tatenda Lemann
Kilimo hifadhi
technologies_5775 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
GEF-UNEP-AGRA-KALRO SLM Projectاسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Carbon Benefits Project (CBP)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
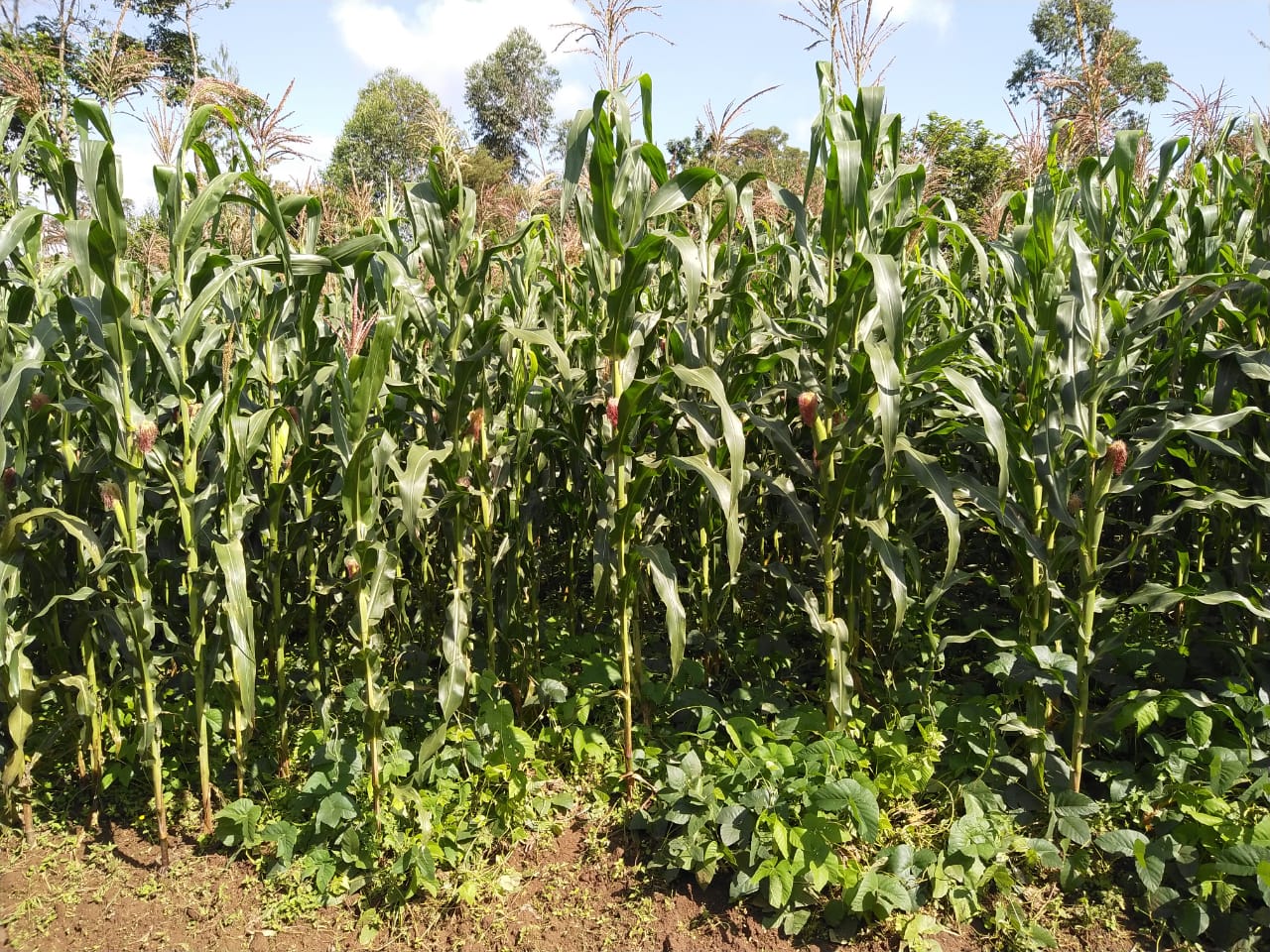
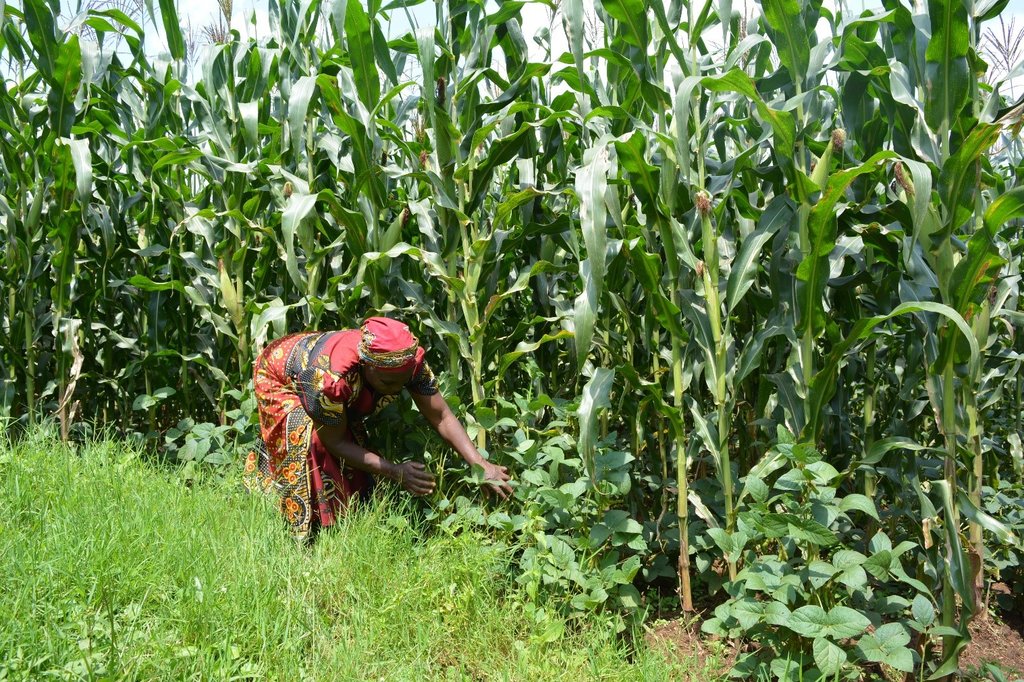
Conservation agriculture for maize-legume systems with velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens) as a dense cover crop is being promoted in western Kenya to address the challenges of land degradation, low crop yields, low incomes, high production costs and climate change.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
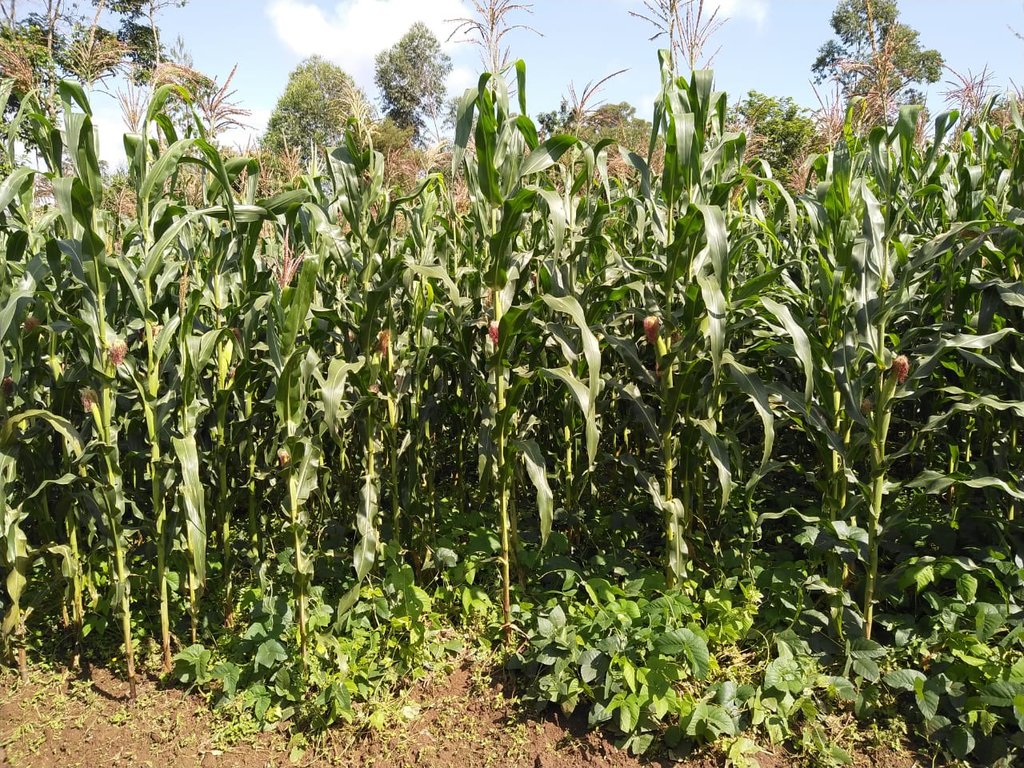
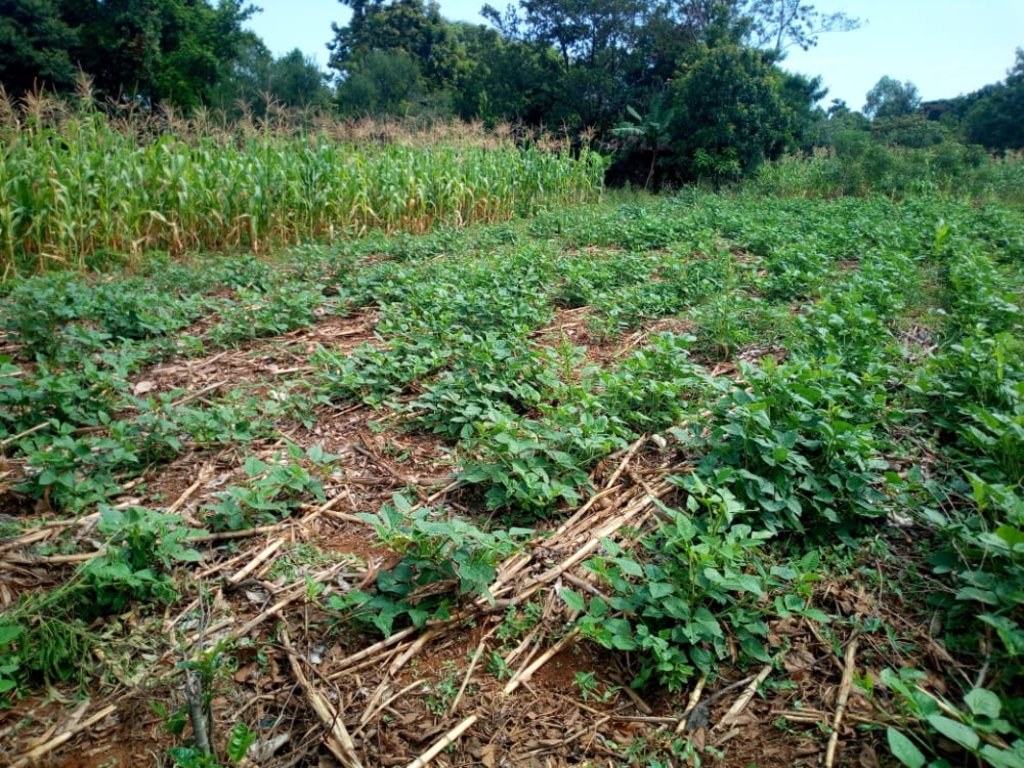
Agriculture in western Kenya suffers from low productivity due to the degraded landscape. The soils are predominantly acidic and low in fertility, with the yields of food staples, such as maize and common bean averaging 1 ton/ ha and 5 tons/ ha, respectively. Consequently, the smallholder farmers have encroached into the adjacent Kakamega and Nandi forests in their quest for supplementary agro-ecosystem services and farm incomes. Degradation of the agro-resource base is underpinned by unsustainable practices carried out under conventional farming; for example, continuous cultivation with low nutrient inputs, mono-cropping, removal of crop residues and full tillage. Some of these practices enhance climate change by intensifying the emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Therefore, widespread adoption of conservation agriculture (CA) technology is being promoted to reduce the adverse impacts of conventional farming and enhance sustainable land management, environmental protection, and climate change mitigation and adaptation in 10 micro-catchments located within a 5-km radius from the edge of Kakamega and Nandi forests. The CA technology is characterized by the principles of minimum mechanical soil disturbance, maintenance of at least 30 percent permanent organic soil cover, diversified cropping through intercropping and crop rotations, and weed control. These principles have been adapted to the local conditions and needs.
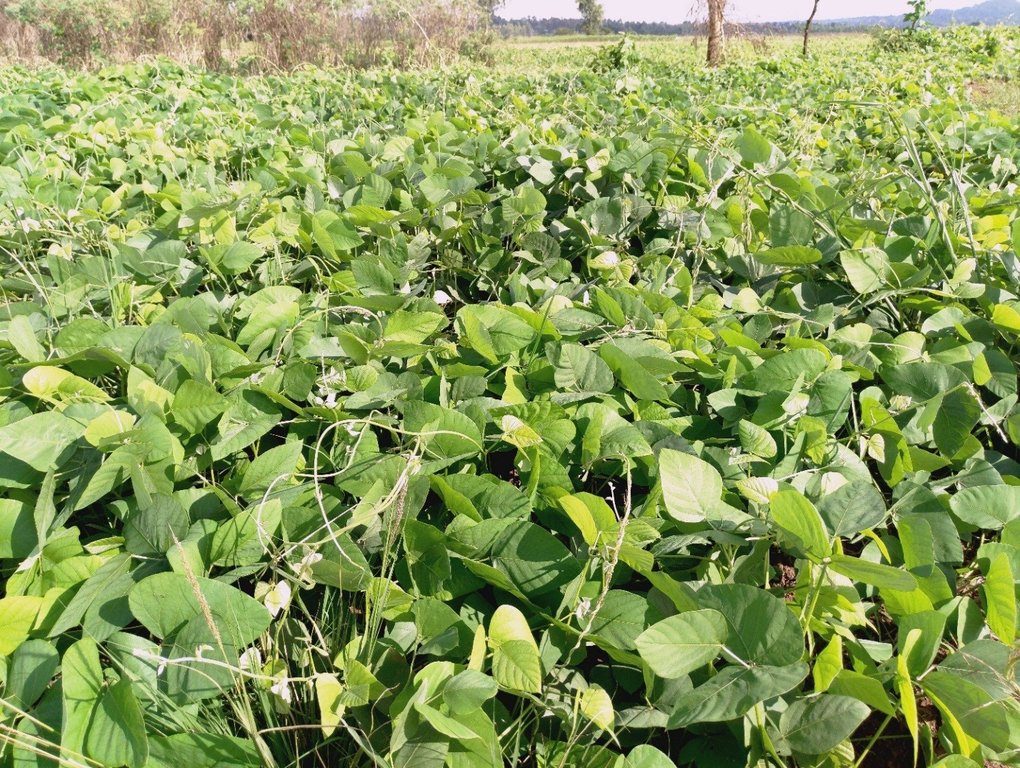
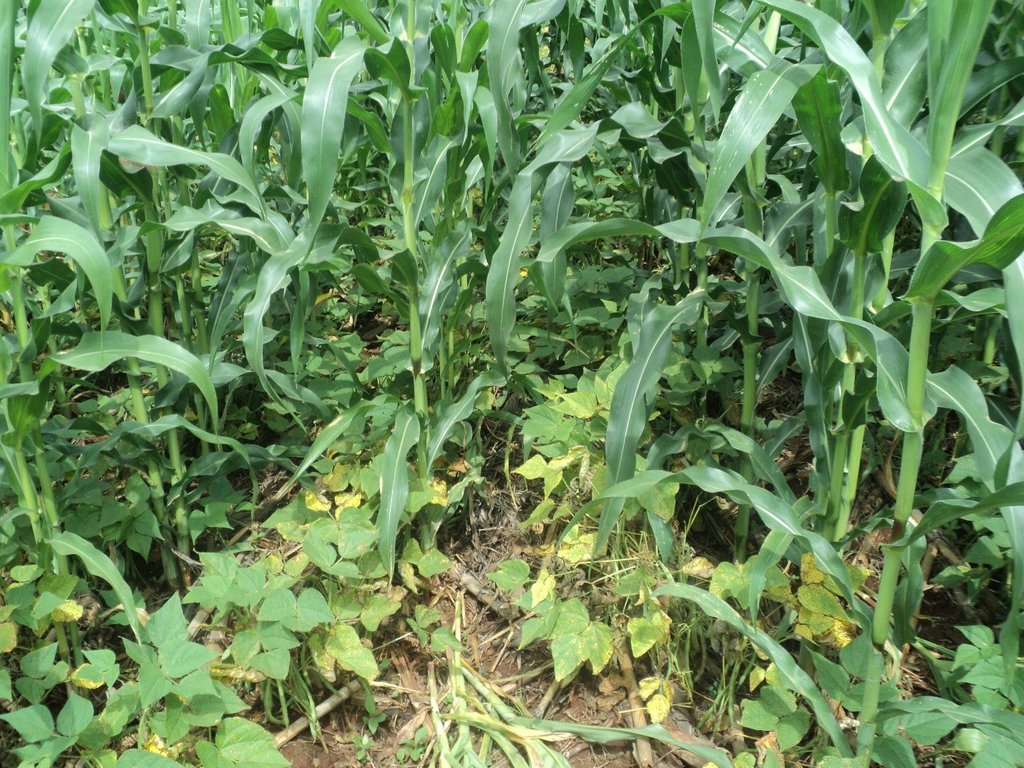
The establishment of CA technology begins with land preparation. That is, the existing weeds and previous crop residues in the field are either slashed, or controlled through the application of appropriate herbicides. All the residues are retained on soil surface as opposed to burning, or removal in the conventional system. Land preparation is followed by planting, where the jab planter is used for precise placement of seeds and fertilizers in un-ploughed field, or within the established planting hills and rip lines to minimize soil tillage. This contrasts with conventional farming practice where a plough, or a hand hoe is used to till the entire field and establish the planting holes for placing seeds and fertilizers. A combination of cereal (maize – Zea mays L.) and legumes (common bean – Phaseolus vulgaris L., soybean - Glycine max, velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens and cowpea – Vigna unguiculata) are either intercropped, or rotated in the field each season to optimize the use of the available soil resources, including water, nutrients, and micro-organisms. The main cereal-legume association involves the establishment of Mucuna pruriens under maize as a dense cover crop. In this cropping system, Mucuna pruriens seeds are sown within a spacing of 1 m × 0.5 m where they grow and spread to completely cover the soil surface. As the cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, enriching the soil’s nutrients, organic matter and fertility. The maize - Mucuna pruriens mix is rotated with either sole common bean, soybean and cowpea crop, or an intercrop of maize with any of the legumes. Weeding is carried out using either selective herbicides, or weed scrapers. When designing the intercropping and rotation plans, crop families (N-fixing vs. non-fixing), root depths (shallow vs. deep roots), and susceptibility to diseases, pests and weeds are all considered.
Generally, CA technologies have multiple benefits for farmers and the environment. In the context of the Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape, the CA plots with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop have shown improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status. It is expected that this will reduce the use of fertilizers over time. Most farmers have also reported that reduced tillage and direct placement of inputs (seeds and fertilizers) save them time, money, fuel, labour and inputs. Aside from saving resources, reduced tillage will ultimately enhance soil living organisms and mitigate atmospheric CO2 emissions through the decrease in fuel consumption and soil disturbance. Moreover, farmers have observed that the maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop remains green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells compared to those under mono-culture, or light mulch. This implies that the CA technology also increases water infiltration and soil water content; thus, acting as insurance against drought. The increase in water infiltration and soil moisture occurs because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff and exposure to wind erosion. In addition, farmers have witnessed the suppression of weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping. Besides, diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases, as well as the risk of crop failure during extreme weather conditions and pest infestations. Specifically, farmers have noticed that the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens intercrop are less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) compared to those under mono-culture. They have also noted that, in seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean is usually harvested even when the common bean fails. Most importantly, these CA benefits have boosted maize yields by over 50 percent, meaning more food and income, and fewer forest encroachments.
Proper adoption of the CA technology by land users within the Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape is being hampered by several factors. Firstly, crop residues are inadequate due to competing uses, such as animal feed and fuel. At times, livestock is even allowed to graze on the stubble field, contravening the CA principles. Besides, some farmers have not fully embraced crop diversification and still grow maize throughout the seasons without rotation with other drought-tolerant cereals, such as sorghum and millet. Conventional ploughing is also quite entrenched. Further, some farmers still do not prefer Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop because of insufficient knowledge on the utilization of its inedible yields. Lastly, some farmers are finding it hard to access CA inputs and tools, such as the jab planters, weed scrapers, herbicides and seeds of Mucuna pruriens owing to either high prices, or shortages.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
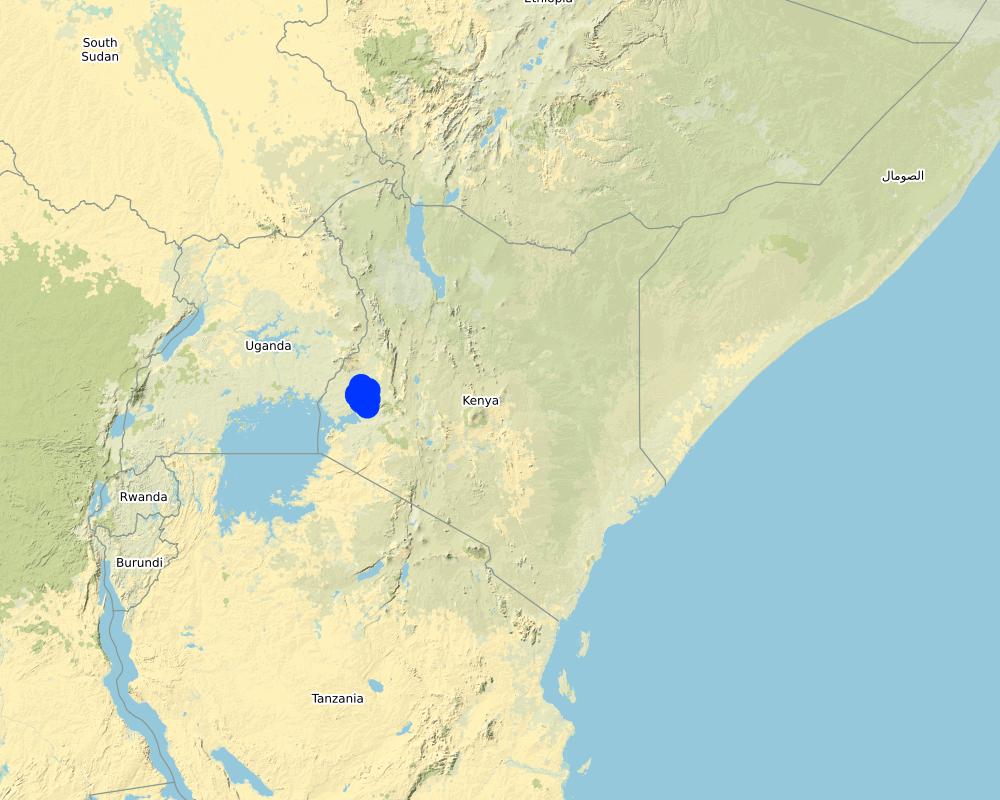
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Western region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2019
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Projects and research focusing mainly on advancing land degradation neutrality and agricultural productivity in the area
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- البازلاء
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول -فول الصويا
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الذرة/الذرة الرفيعة/الدخن في زراعة بينية مع البقوليات
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Long rain season (March to May) and short rain season (October to December)
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Maize and legumes (i.e., common bean, soybean and velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens)
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Maize and legumes (i.e., common bean, soybean and velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens)

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة
نوع الحيوان:
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Manure is used for fertilization and crop residues are used as cattle feed
المنتجات والخدمات:
- روث الحيوانات كسماد/إنتاج الطاقة
- اللحوم
- الحليب
- جلود الجاموس الخام
- النقل/الجر
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
نظام زراعة سنوي:
زراعة مستديمة من الذرة/الذرة الرفيعة/الدخن
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
نوع الحيوان:
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Manure is used for fertilization and crop residues are used as cattle feed
المنتجات والخدمات:
- روث الحيوانات كسماد/إنتاج الطاقة
- اللحوم
- الحليب
- جلود الجاموس الخام
- النقل/الجر
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A 6.4:تم الاحتفاظ بها
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
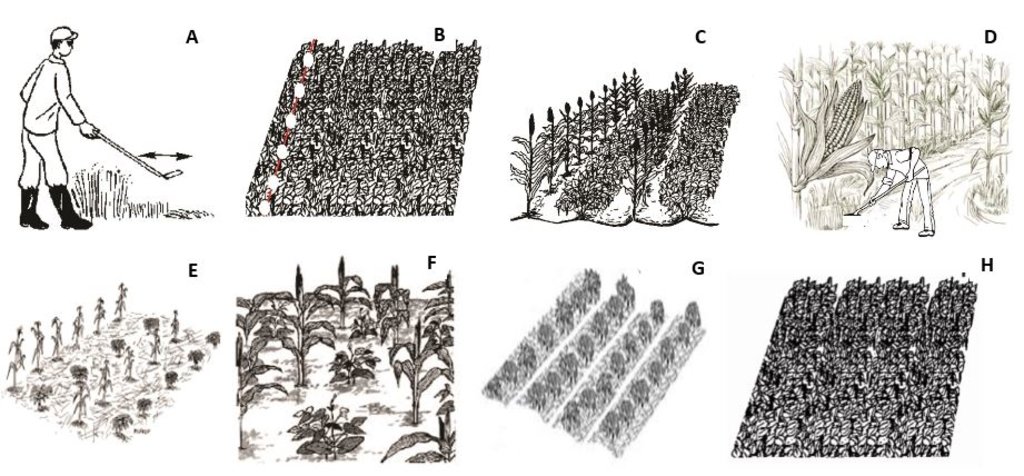
The first technical drawing shows a typical farm under CA with various principles:
A - Clearance of weeds and previous crop residues through slashing in preparation for planting in season 1 (long rains). The residues are retained on the plot.
B - In a plot under total soil cover with Mucuna pruriens, maize seed and fertilizer are placed at the precise planting hills, denoted by the white circles along the red line, using a jab planter to minimize soil tillage.
C - Maize crop establishes under the dense cover of Mucuna pruriens.
D - Weeding of the maize crop is done using a weed scraper.
E & F - In season 2 (short rains), after harvesting maize in the previous maize – Mucuna cropping system and cutting down the residues, either a row intercropping system with alternate rows of maize and soybean (E), or maize and common bean (F) under maize straw mulch is established.
G & H - Alternatively, in season 2 (short rains), either sole common bean (cowpea, or soybean) production under maize straw mulch (G), or total soil cover with Mucuna pruriens (H) is established in the plot.
المؤلف:
Sam Koile, Kennedy Were & George Ayaga
التاريخ:
31/05/2020
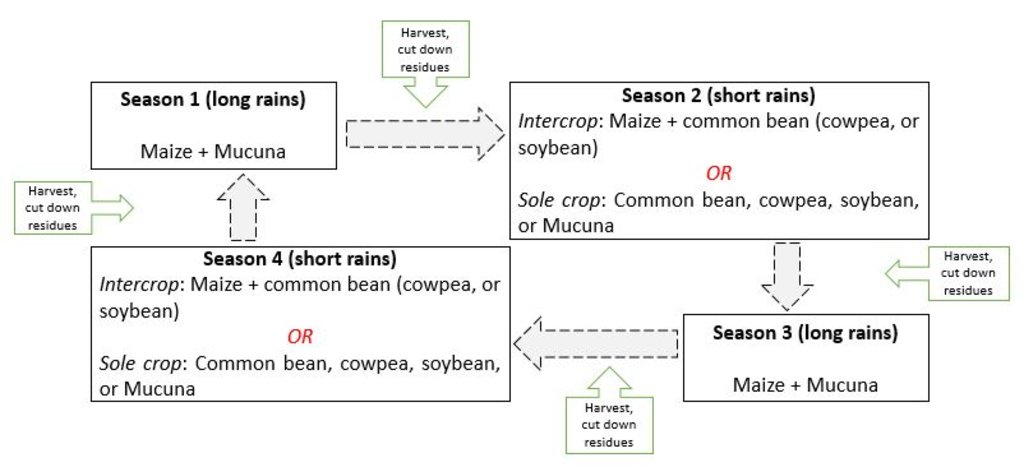
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
The second technical drawing is an illustration of a four season (2-year) rotation of maize, legumes and cover crop
المؤلف:
Kennedy Were, Sam Koile & George Ayaga
التاريخ:
15/07/2020
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 ha
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
2.47 acres
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
KES
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
107,08
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
300
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of CA tools - jab planter, knapsack sprayer, protection gear, slasher, weed scraper, and gunny bag) | Initial stage |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Jab planter | Piece | 2,0 | 1500,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Knapsack sprayer | Piece | 2,0 | 2500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Protection gear | Piece | 2,0 | 1000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Weed scraper | Piece | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Slasher | Piece | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Gunny bag | Piece | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 14500,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 135,41 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation - Slashing | Initial stage |
| 2. | Preparing the planting hills and rip lines | Initial stage |
| 3. | Planting - placing seeds and fertilizer using jab planter | Initial stage |
| 4. | Herbicide application | Initial and growing stages |
| 5. | Pesticide application | Growing stage |
| 6. | Fertilizer application (top-dressing) | Growing stage |
| 7. | Harvesting, drying and shelling | Final stage |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Land preparation - slashing and herbicide application | Man day | 4,0 | 300,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting - preparing the planting hills and placing seeds and fertilizer | Man day | 38,0 | 300,0 | 11400,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Top-dressing and pesticide application | Man day | 8,0 | 300,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Harvesting, shelling and drying | Man day | 30,0 | 300,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Maize seed | Kg | 20,0 | 250,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Legume seed | Kg | 8,0 | 250,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Planting fertilizer | Kg | 125,0 | 60,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Top-dressing fertilizer | Kg | 125,0 | 50,0 | 6250,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Pesticide | Litre | 2,0 | 1250,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Herbicide | Litre | 5,0 | 875,0 | 4375,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Transport | Km | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 59125,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 552,16 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
1. Prevailing market prices of the inputs, equipment and labour.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall is bi-modal with the long rain season starting from March to May, and the short rains from October to December.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
mean annual temperature varies from 18 to 29° C
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
24 bags/ ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
43 bags/ ha
التعليقات/ حدد:
This can be attributed to the multiple benefits of the CA technology, such as improved soil organic matter content and nutrient status. Note: A standard bag weighs 90 kgs.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The multiple benefits of the CA technology, such as improved soil conditions and alleviation of pests and diseases, not only increased crop production (yields), but also the quality of the crops.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased crop production also means increased fodder production because the crop residues are partly used as animal feed
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased crop quality also implies increased fodder quality because the crop residues are partly used as animal feed
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Specifically,
- the maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop have remained green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells. The CA technology increases water infiltration and soil moisture because the dense cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff
- the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens inter-crop have been less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda).
- in seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean has been harvested even when the common bean fails.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers not only grow maize, but also mix or rotate it with common bean, soybean and cowpea
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Operations such as precise and direct placement of inputs and minimum tillage have simplified land management
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Expenses on inputs, such as herbicides and fertilizers increased marginally, because the conventional farming practice had been characterized by low inputs; however, with improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status, as well as reduced incidences of pest, diseases and weeds, it is expected that the use of these inputs will diminish over time
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased crop production means, more surplus and incomes
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Diversified cropping enables the farmers to get income from maize, common bean, soybean and cowpea production
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced tillage has subsequently decreased the farmers' workload because they no longer have to plough the entire field
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased crop production means more food and less hungry periods. The legumes also provide a good source of protein to the farmers' households
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
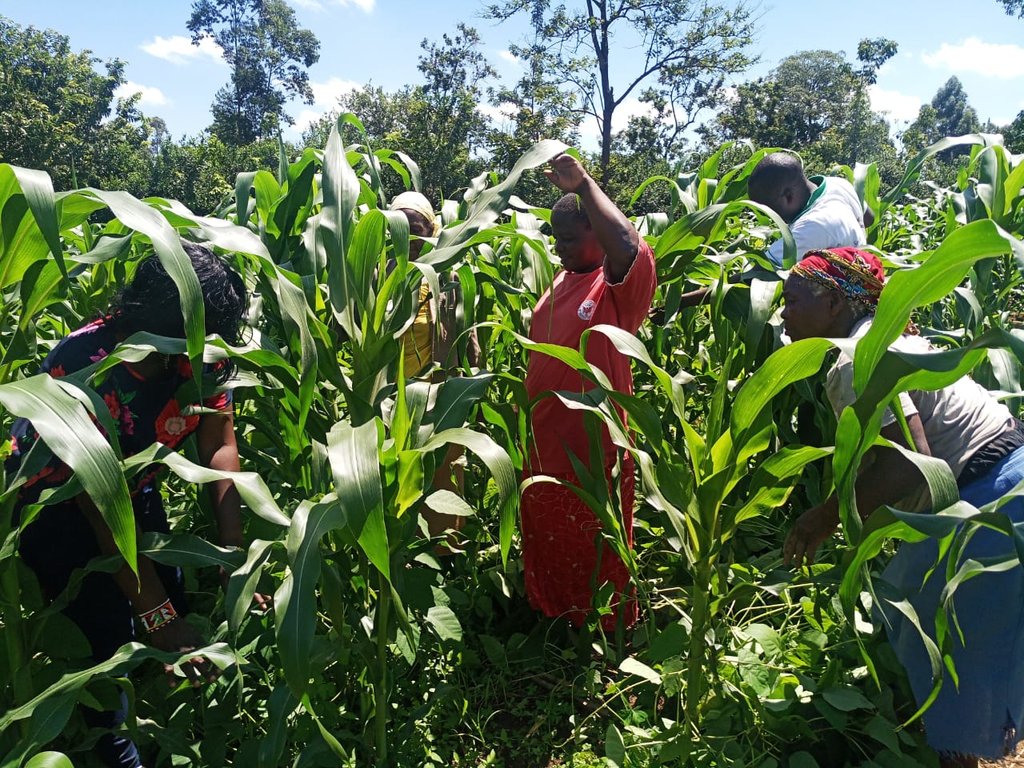
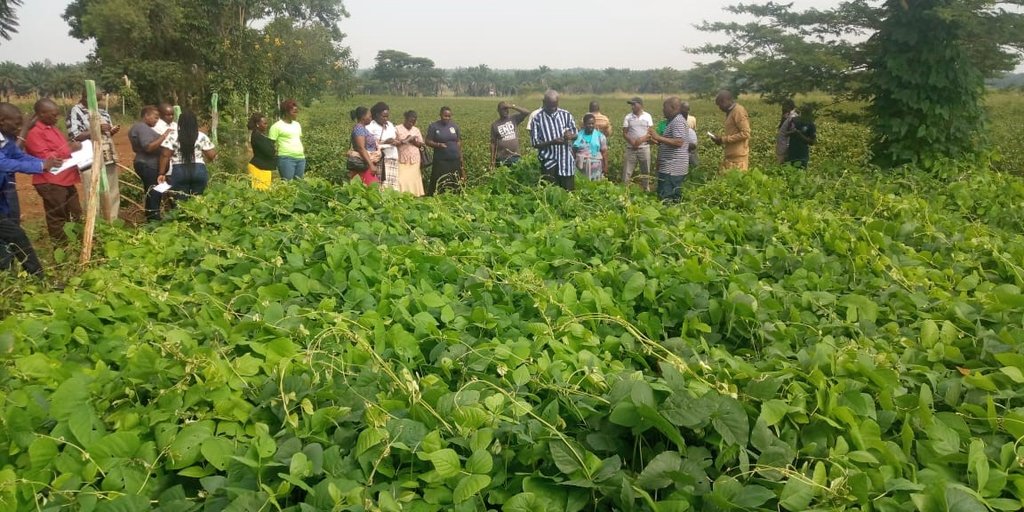
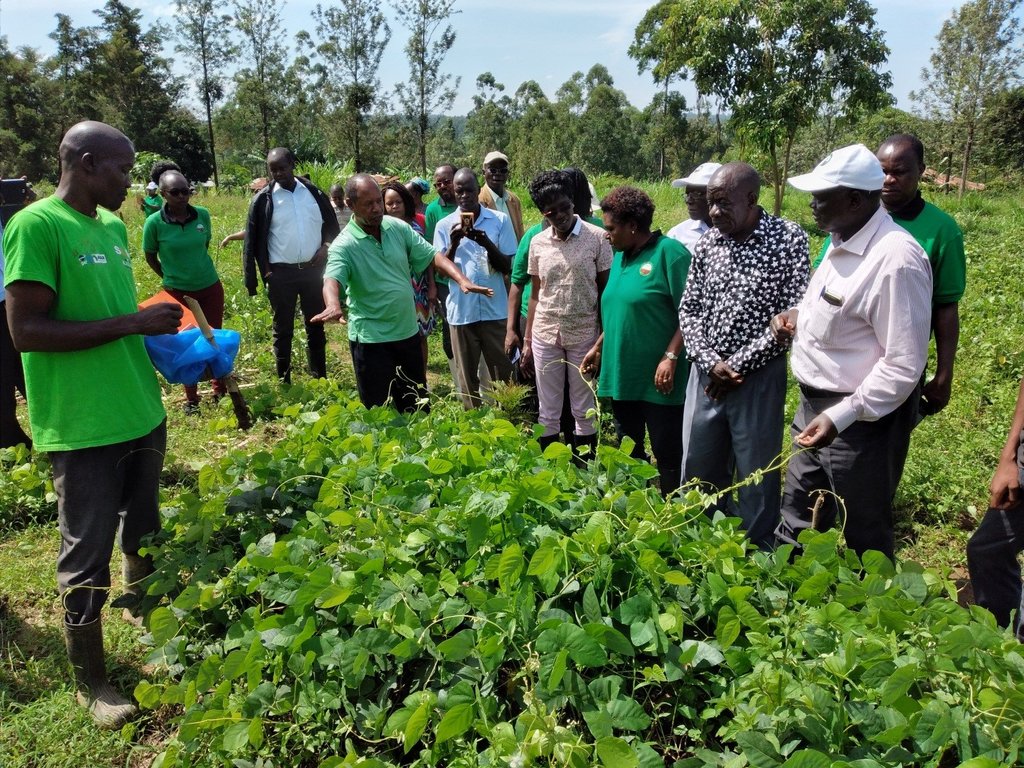
The common interest groups have been greatly involved in the selection of the CA technologies. The strengthening of the community institutions has been done for sustainability and to allow sensitization of the technology to the wider population in the landscape. Some of thaccess by the communities. e promotion approaches have been on-farm demonstrations and training of trainers (ToTs), which have involved and empowered different farmer groups within the communities. Seed producers have also been trained to multiply seeds of specific crops, such as Mucuna pruriens for ease of access
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
On-farm demonstrations of the CA technology and the training of trainers (ToTs) have empowered different stakeholders within the communities with sufficient SLM/ land degradation knowledge
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop reduces surface runoff
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
There has been increase in water infiltration and soil water content because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff. This recharges the aquifer
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop regulates both the soil surface temperatures and evaporation
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The increase in soil water content occurs because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The dense Mucuna pruriens completely covers the soil surface, and is left on the ground even after the harvesting of maize
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop reduces surface runoff and exposure to wind erosion
تراكم التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Accumulation of soil organic carbon has occurred because the dense cover crop has a higher net primary productivity and sheds more leaves on the ground, resulting in more inputs of detritus to the soil. Similarly, retention of the large amount of crop residues especially those obtained from the leguminous crops has increased the inputs of carbon and nitrogen to the soil.
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The cover crop, minimum tillage and crop residues have protected the soil from the impact of raindrops, improved the surface soil structure and aggregate stability by increasing the organic matter content in the soil and stimulated soil biological activity, making the soil resistant to crusting
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced tillage or zero tillage has minimized farm land activities, e.g, ploughing which often result in compaction of soil. Incorporation of deep rooted crops with shallow rooted crops has also helped to break the various soil layers, thus hindering compaction. In addition, accumulation of soil organic carbon has improved soil biological activities that help to reduce soil compaction, through continuous burrowing.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the dense cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, enriching the soils with nitrogen and organic matter
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the dense cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, with organic matter additions.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The dense cover crop has higher net primary productivity/ above-ground biomass C, which is left when the maize crop is harvested.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers grow a mix of crops under the diverse cropping principle, which has increased plant diversity
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers have witnessed the suppression of weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced tillage and accumulation of soil organic carbon have increased beneficial soil living organisms, such as the earthworms.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases through disruption of pest and disease cycles. Specifically, farmers have noticed that the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens intercrop are less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
The maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop has remained green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells. This implies that the CA technology also increases water infiltration and soil water content; thus, acting as insurance against drought.
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced tillage mitigates atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions through the decrease in fossil fuel consumption and soil disturbance. Crop residues are also retained in the field and not burnt; hence, reducing emission of carbon.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدا |
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
For example, it is expected that the associated improvement in soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status will reduce the use of fertilizers in the long term.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 51-90%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop is not adversely affected by the fall army worm (Spodoptera frugiperda) |
| Reduced tillage saves time, money and energy, while the direct placement of inputs (seeds and fertilizers) minimizes wastage. The saved resources can be used to engage in other income-generating activities |
| Maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop remains green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells |
| Weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) are suppressed in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping (rotations and inter-crops) |
| In seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean is usually harvested even when the common bean fails |
| The CA technology has boosted maize yields, meaning more food and income, and reduced cost of feeding the family |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The CA plots with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop have improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status |
| Reduced tillage has enhanced soil living organisms, such as earthworms and decreased fuel consumption and soil disturbance; hence, mitigating atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions and storing carbon in soils |
| The CA technology has increased water infiltration and soil water content (moisture); thus, acting as insurance against drought |
| Diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases, as well as the risk of crop failure during extreme weather conditions and pest infestations |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The Mucuna pruriens used as a dense cover crop intertwines on maize crop, which might increase manual labour | Promote other erect cover crops like the lablab bean (Dolichos lablab), Desmodium and Canavalia that will have less effect on the cereal crop established |
| The yields of Mucuna pruriens used as a dense cover crop are not edible |
- Extension agents and Trainer of Trainees (ToTs) to equip farmers with knowledge on the options available for utilizing Mucuna pruriens yields other than being a cover crop - Promote other erect cover crops like the lablab bean (Dolichos lablab), Desmodium and Canavalia |
| Residue retention reduces the availability of fodder and fuel materials | Adopt an agro-forestry system with tree species that can provide alternative source of fodder and fuel |
| The critical CA inputs and implements, such as the jab planters, weed scrapers, herbicides and Mucuna seeds are hard to access |
- Incentivize and train the local fabricators to fabricate affordable CA tools - Subsidize CA inputs, such as fertilizer and herbicides - Facilitate access to credit - Train more seed producers to multiply the seeds of Mucuna pruriens |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Agro-ecosystem contamination through use of herbicides and inorganic fertilizers | Use the right doses of herbicides and fertilizers |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
31/05/2020
7.4 تعليقات عامة
Simple and clear.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية