Retention ponds [سلوفينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Gregor Kramberger
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mokri zadrževalniki vode
technologies_5933 - سلوفينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Istenič Darja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
سلوفينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Škerjanec Mateja
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
سلوفينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Banovec Primož
Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, University of Ljubljana
سلوفينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Curk Miha
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
سلوفينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Cvejić Rozalija
Biotechnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana
سلوفينيا
مستخدم الأرض:
Purgaj Donik Biserka
Fruit center Maribor (demonstrartion plantation centre), Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
سلوفينيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - سلوفينيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Ljubljana (UL) - سلوفينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
With improper implementation and intended use, it can have a negative effect on sustainability in the environment. It can be sustainable if properly anticipated/planned. The construction of the pond is usually subject to an environmental impact assessment where these matters are resolved as to whether it is sustainable or not.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Retention ponds (e.g. flood storage reservoirs, shallow impoundments) are water bodies, storing water to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. They provide storage as well as improving water quality. Retention ponds may also be used for irrigation of farmland.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
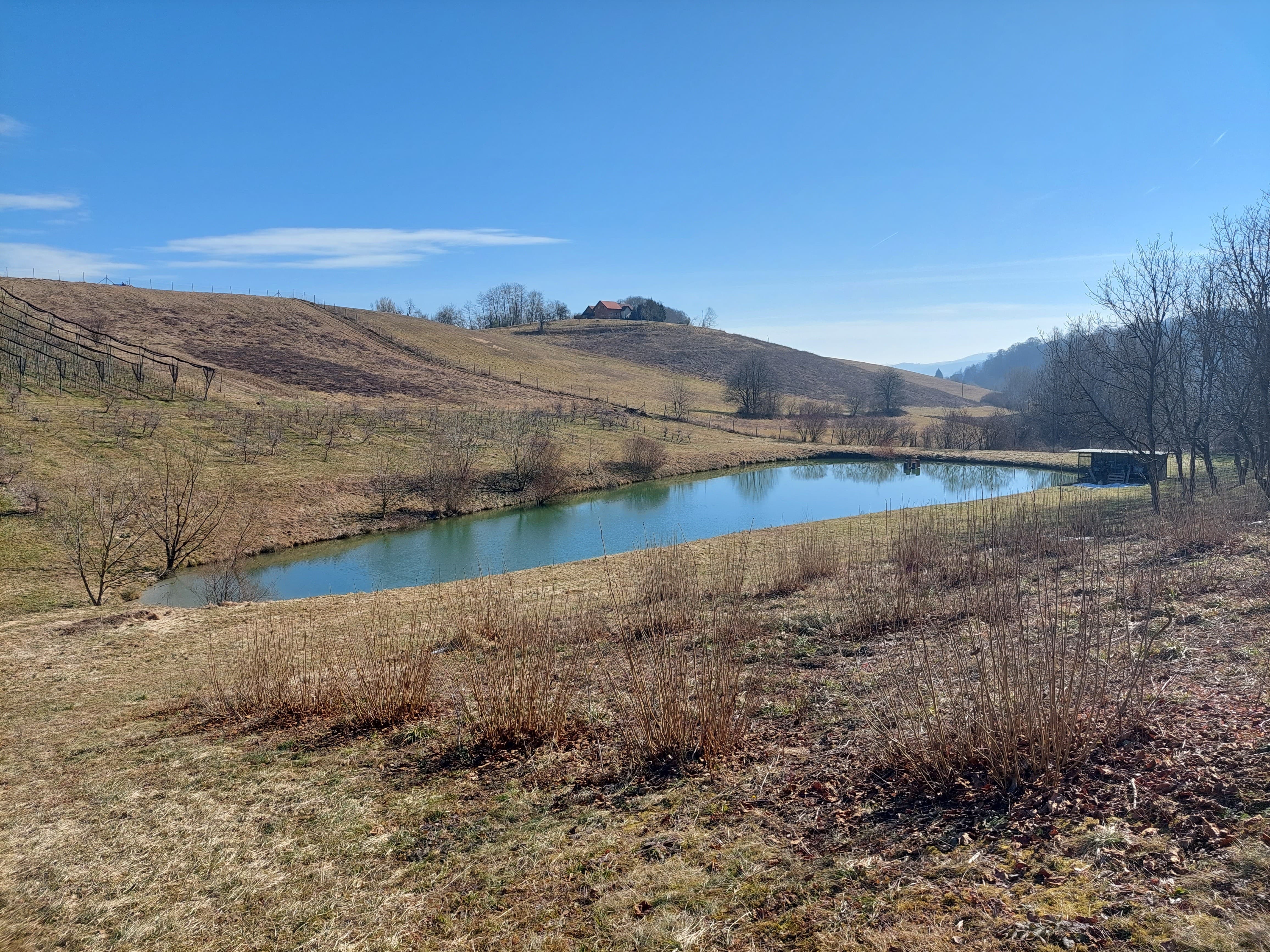
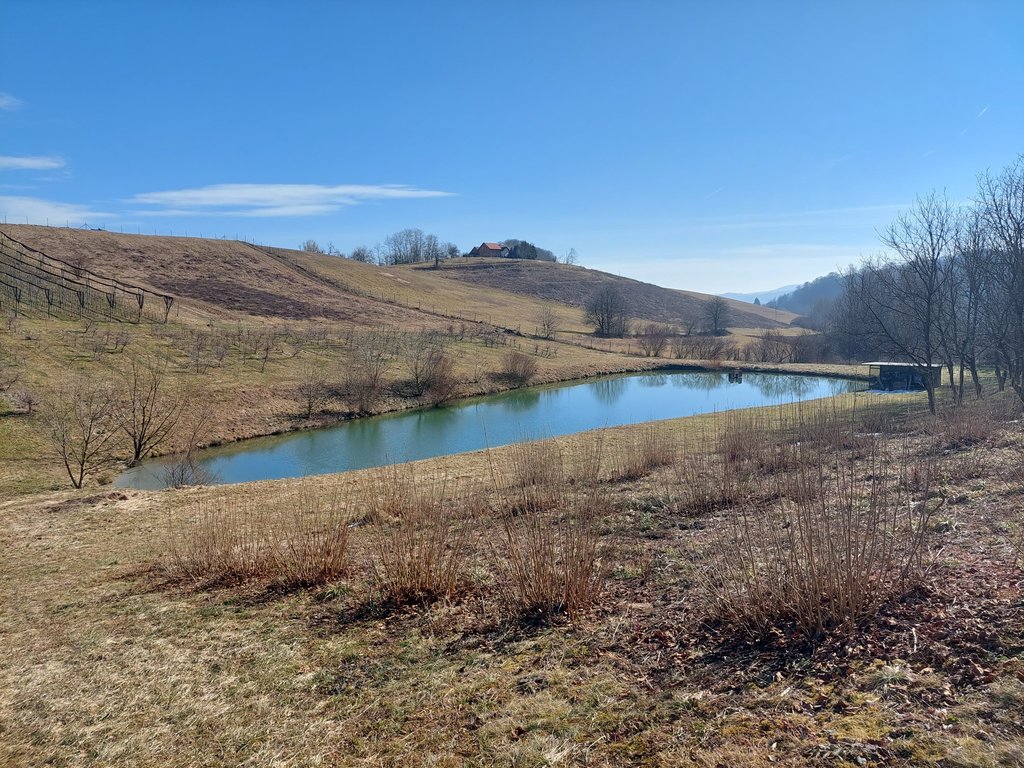
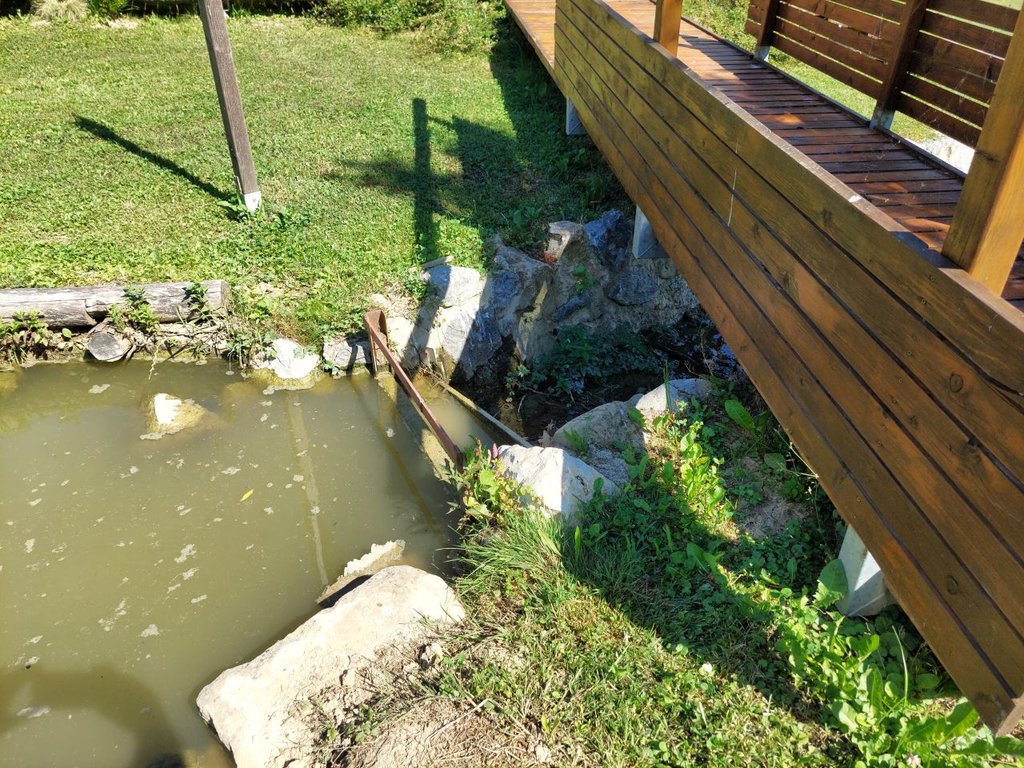
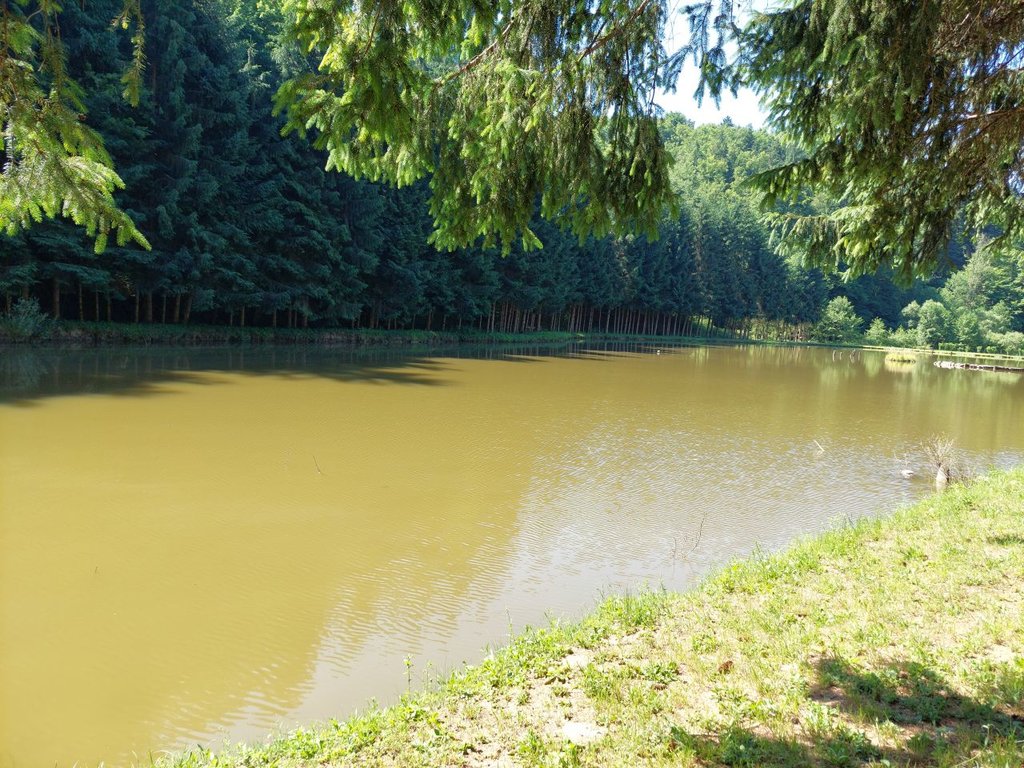
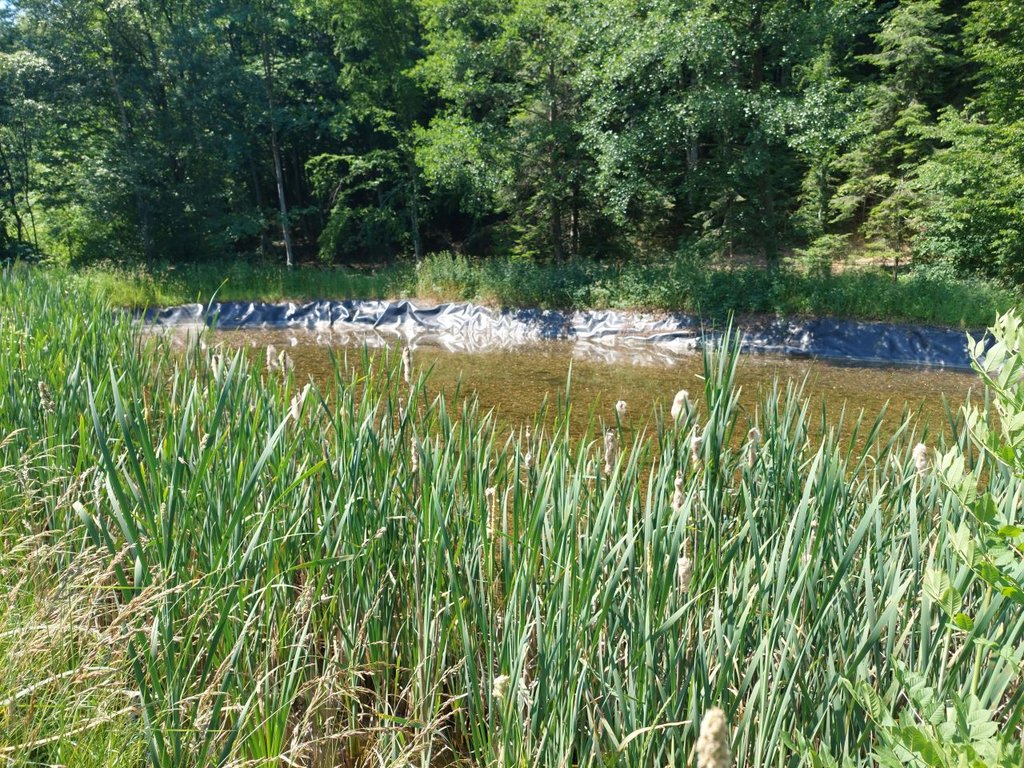
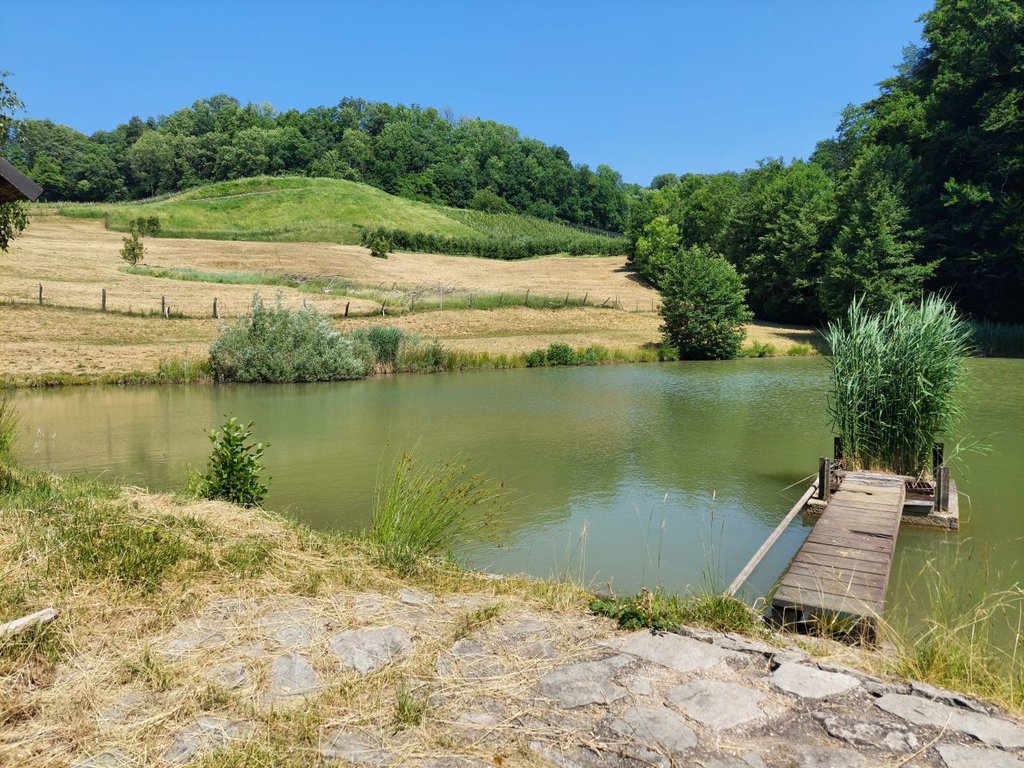
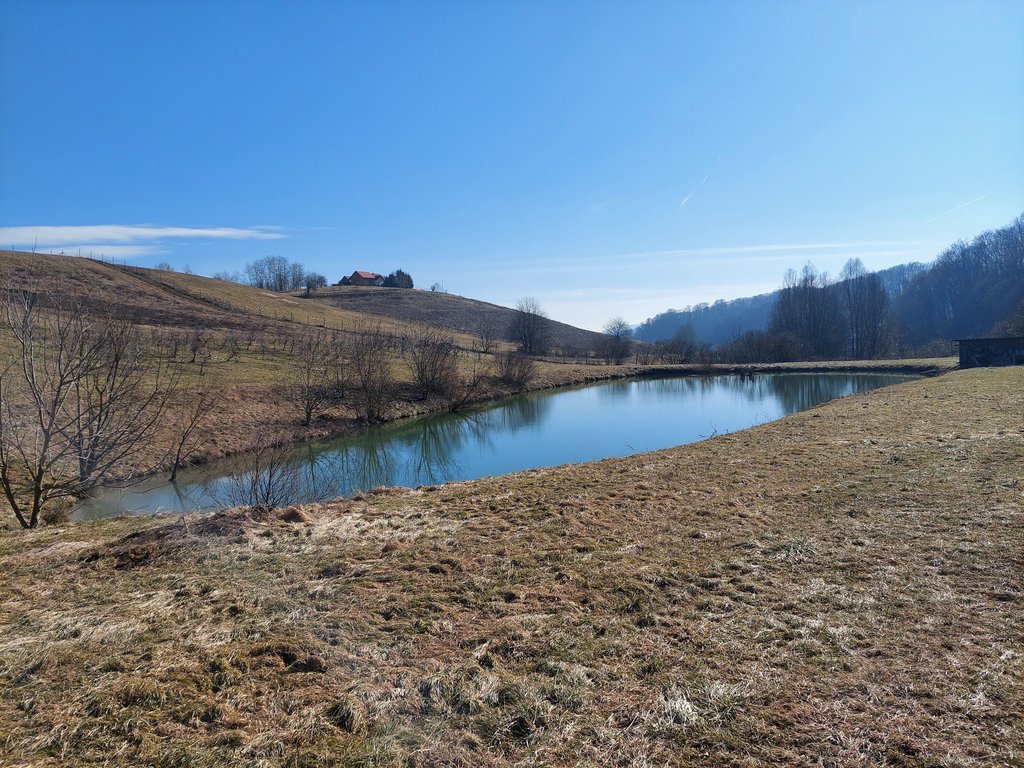
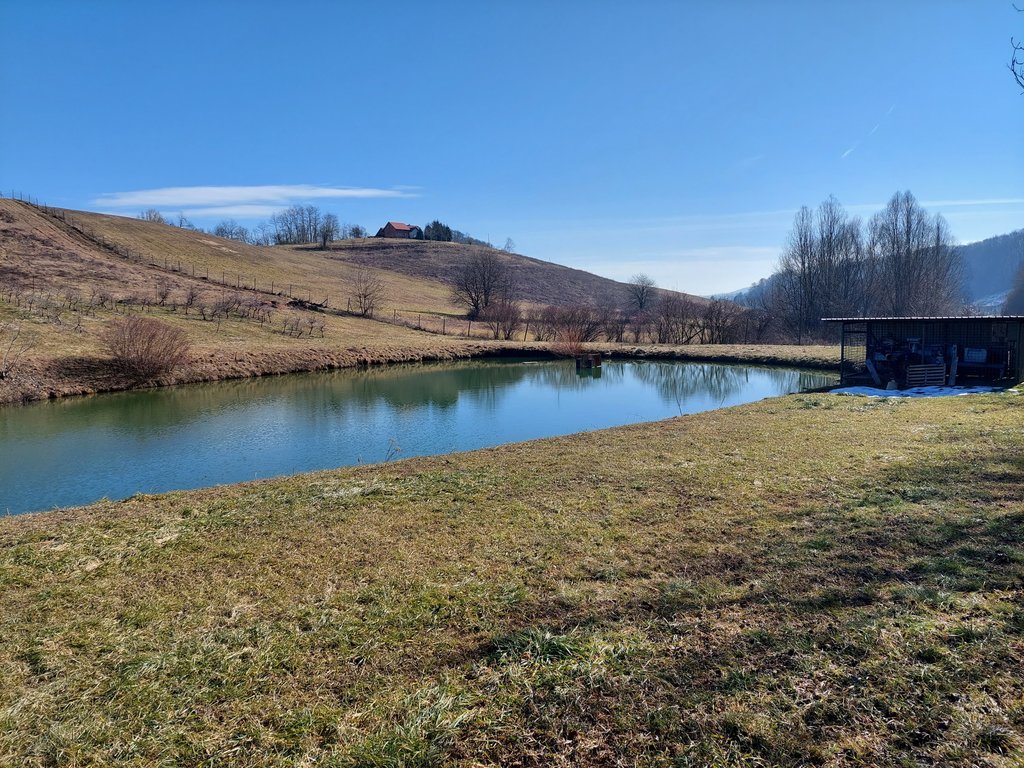
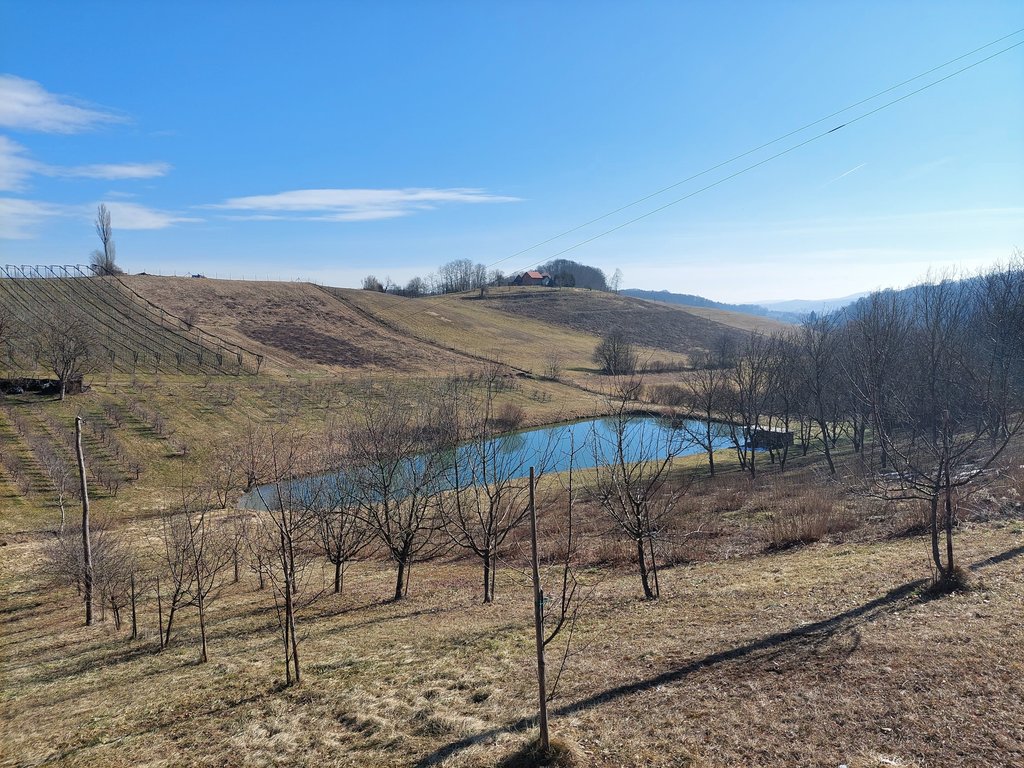
“Retention ponds” comprise both simple, small ponds (up to 2000 m3, up to 4 m deep) and larger, more complex reservoirs (greater than 2000 m3). Retention ponds are designed to provide storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. Each consists of a permanent ponded area with landscaped banks. Retention ponds achieve both storm water attenuation and water quality treatment through supplementary storage capacity of runoff. Water is then released at a controlled rate once the risk of flooding has passed. The technology can be applied in a natural or human environment. Before construction of a pond it is essential to follow legislation, which covers conditions and restrictions for the given location. Once a site is selected, technical documentation is prepared: first the conceptual design, then documentation for obtaining opinion, consent and a building permit. Later there is also project documentation for implementation. If the water is to be used for other purposes as well (e.g. for irrigation), it is necessary to plan for usage and environmental impact. Retention and still water promotes pollutant removal through sedimentation, while aquatic vegetation and biological uptake mechanisms offer additional treatment. Retention ponds are effective in removing urban pollutants and improving water quality.
They are created either by using an existing natural depression, or by excavating a new depression, or by constructing embankments. Existing natural water bodies should not be used however, due to the risk that pollution events and poorer water quality might disturb/damage the natural ecology of the system. A great benefit of retention ponds is that they hold water when there is an excess of it, which can be used later when water is not available (e.g. for irrigation). Irrigation users are farmers, so they see the advantage of using a retention system. In addition to irrigation, water has also been needed in recent years for anti-frost systems (sprinkling a consistent layer of water on the crop during an entire frost event until temperatures are back to safe levels). Disadvantages are mainly restrictions in some areas (e.g. protected areas), preparation of demanding documentation and bureaucracy, and lengthy procedures for obtaining permits.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سلوفينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Podravska region, Slovenia
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Pesnica
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Setting up a measure in a protected area is limited and very difficult due to construction restrictions in such an environment.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
In the 1990s, the state financed the construction of several water reservoirs in the area.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
- البرك والسدود
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Retention of water, collection of water. Retention ponds are ponds or basins designed with additional storage capacity to attenuate surface runoff during rainfall events. In dry years, the water can be used for agriculture, e.g. for irrigation.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
- خطوط الصرف، الممرات المائية
- المستنقعات والأراضي الرطبة
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
To prevent erosion.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
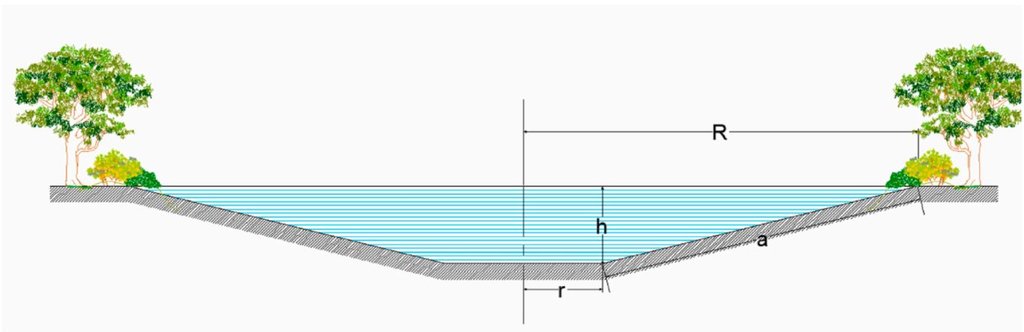
Water retention pond – excavation scheme. R is the top radius of pond, while r is the base radius; h is the height and a refers to the bank slope. Storage volume is estimated by radius r and height h (Figure). We consider potential storage volumes of 5,000 m3 to 10,000 m3.
Prior to start of construction, detention/retention ponds should be designed by a registered design professional. Plans and specifications should be referred to by field personnel throughout the construction process. When placing a detention/retention pond in a space in the first phase it is necessary to produce a conceptual design of the intended construction of a pond, which must show the purpose and goals of the retaining wall, the size of the pond, the location, a list of plots that are encroached upon, distances from neighboring land and neighboring buildings, anticipated activities in the impoundment area, impoundment volume, barrier size data, including stability assessment, and geotechnical data (Hočuršćak 2017). When planning construction of the pond, attention should be paid primarily to the impact on the actual use of space from the point of view of water management regulations, which defines the area of use and activity restrictions, due to the possible negative impact on water and coastal lands, aquatic habitats and the ecosystem created by the construction of the reservoir. After talking with the designer, in order to obtain a water permit and consent from the authorities, it is necessary to prepare technical documentation for the installation and construction, which must also include the basis for monitoring operation and maintenance (Hočuršćak 2017). The technical documentation (dimensioning of the reservoir) may differ from the microlocation and purpose or use of the measure, e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc. We also consider the shape and size of the area to identify those better suited for allocating ponds also in terms of space availability. For example, it is necessary to exclude locations with a greater slope and distance from the river considering higher slope and distance is more difficult and costly to construct. We also exclude locations where the construction of a pond is not possible because they are too narrow or too small. We should consider water retention ponds as elements of a green infrastructure network together with other natural elements (e.g. vegetated riparian zones) and protected areas (e.g. Natura, 2000 sites) with a pond design that embeds features that enhance their ecological functionality. These include mild-sloped sides with vegetated buffers along the shorelines and vegetated floating islands that facilitate the nesting of birds. We refer to excavated ponds, with no weirs or dams, since inline ponds are more costly and may have negative ecological impacts (A. Staccione et al. 2021).
Presentation of the water reservoir at the Sadjarski Center Maribor (translated: Fruit Growing Center Maribor):
The Sadjarski Center Maribor is located on a sloping terrain, which is pedologically and configuratively quite diverse, with slopes ranging from 5-15%. The soil structure is clayey loam with a basaltic substrate. In the lower, flatter part, the soil was waterlogged, which was resolved through drainage systems. These drains are directed towards a drainage ditch, which serves as the foundation for the pond and is fed by two smaller springs. The intake point is located at the lowest point and at the southernmost part of the complex. It covers an area of 3000 m2 and has a depth of up to 3.8 m. Its capacity is 5500 m3 of water when fully filled. At its southern part, there is a concrete overflow structure (spillway) with a height of 3.8 m, which is used to drain excess water and regulate the water level. A concrete pipe, 20 m in length and 80 cm in diameter, is connected to it for the discharge of excess water. On the western side, a concrete pumping platform with a canopy and an oil trap has been constructed. It houses a 185 kW (252 HP) DAF diesel generator and a Capprari flow pump with a capacity of 300 l/min (18.0 m3/h). The pumping unit is used for filling the reservoir of the irrigation fertigation system.
المؤلف:
A. Staccione et al.
التاريخ:
2021
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Ponds should contain the following zones (NWRM.eu, retention ponds):
- a sediment forebay or other form of upstream pre-treatment system (i.e. as part of an upstream management train of sustainable drainage components),
- a permanent pool which will remain wet throughout the year and is the main treatment zone,
- a temporary storage volume for flood attenuation, created through landscaped banks to the permanent pool,
- a shallow zone or aquatic bench which is a shallow area along the edge of the permanent pool to support wetland planting, providing ecology, amenity and safety benefits.
Additional pond design features should include an emergency spillway for safe overflow when storage capacity is exceeded, maintenance access, a safety bench, and appropriate landscaping (NWRM.eu, retention ponds).
NWRM.eu, retention ponds suggest;
- The ratio of flow path length to width in the pond should be between 3:1 and 5:1. Inlets and outlets should be placed to maximise the flow path length through the pond.
- Ponds should be wedge-shaped in plan so flow enters the pond and gradually spreads out, improving the sedimentation process and potential improvement in water quality.
- The depth of the permanent pool should be between 1.2 m and 2.0 m. Deeper pools may be subject to stratification and anoxic conditions. Shallower pools may be prone to algal blooms and high biological activity during summer months.
- Side slopes should not be steeper than 1:3 to ensure public safety and maintenance access.
- Residence time of permanent pond should be at least 20 days to allow for biological treatment of dissolved pollutants where this is required.
- Additional storage volume drained in 24-72 hours after the rainfall event depending on the intensity and duration of the storm and the design specifications of the pond
- Outfall design should be such that at least 50% of the maximum storage volume is discharged within 24 hours to allow for multiple events
- Retention ponds should ideally be combined with upstream sustainable drainage components, such as smaller detention basins and swales, which offer primary treatment and sediment management.
- Regular inspection and maintenance is important for the effective operation of ponds as designed.
Regular maintenance activities include litter and debris removal; vegetation maintenance (including cutting of bank and aquatic vegetation and removal of nuisance plants); inlet/outlet inspection and maintenance; and sediment removal from forebay (where applicable). Less frequent maintenance may include sediment removal from permanent pond; repairs; ongoing inspections and monitoring.
Appropriate signage to warn of water depth must be included for public safety.
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
pond
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
5500
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,97
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
90.90
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Costs of obtaining construction, technical and project documentation | 1-2 years before before starting construction |
| 2. | Construction of a pond | 1st year |
| 3. | Costs of supervision of construction and craftsmanship | 1st year |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
73600,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The construction of a water reservoir can be subsidized from various sources (EU, state, municipalities, etc.). The largest share of support can be obtained through the Rural Development Program, where an investment can receive support ranging from 30% to 50% of eligible project cost (establishment cost).
التعليقات:
The costs include excavation costs and bottom waterproofing costs. Determining the exact establishment costs for the entire project was challenging due to variations in location, topography, size, shape, dimensions, materials, soil permeability, and other factors. The specific establishment cost for the retention pond at the case study location is not available or relevant, as it would be significantly lower than the cost of constructing such a pond today (due to inflation). Therefore, we decided to use projected values based on the maximum eligible costs set by the Ministry of Agriculture for grant applications, which amount to 13.38 €/m3 (2016). This value represents the justified project cost for constructing the retention pond. In this scenario, the estimated establishment cost for a typical 5000 m3 pond would be 66,900.00 €.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Energy for pumping | annually |
| 2. | water fee | annually |
| 3. | Maintenance costs (vegetation management, inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire pond for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, and sealing, etc.) | annually |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
3000,0
التعليقات:
Obtaining precise costs for maintaining the pond and its surroundings is challenging, as it involves various factors. The costs can include anything from labor hours and manual mowing around the pond to considering professionals for inspections, infrastructure maintenance, mulching, invasive species removal, pumping the entire reservoir for cleaning and sediment removal, sludge cleaning, monitoring, bank stabilization, replacement of damaged parts, sealing, and more. The exact costs are difficult to determine due to the highly diverse infrastructure present in different locations. We have estimated the costs per square meter of the area under maintenance, which includes both the surrounding land and the water surface. If it's only about cleaning the surroundings of the reservoir, we consider only the land area. However, if it involves cleaning within the reservoir, we also take into account the water surface area. The best rough estimates we have range from 1 to 5 € per square meter.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Construction costs are affected by the shape, size, depth and microlocation of the pond layout. In addition, the cost is also influenced by the purpose of use (e.g. if pool is intended only to contain high water, sediment or debris laoding, will it be inhabited by aquatic animals, will water be used for irrigation, drinking, etc.). Geomechanically conditions are also important, because ponds and reservoirs can affect slope stability and induce landslides. The value of the investment can vary greatly depending on the design of the pond, location, water content of the area, soil structure, climate conditions,... so it is impossible to determine the exact values for pond construction, but we can only give an estimation.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1080,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are June and August, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Jareninski vrh (1981 – 2010)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Mean annual temperature in year 2014 Jareninski vrh is 11,9°C.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
There are depressions, settlements are in the valley, concave type.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Hydro melioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Manager of an agricultural company - fruit center - poblic demonstration plantation.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- شركة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
They are based on national legal system
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Irrigation has avoided reduction in production due to drought and frost
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved fruit health (protection against drought and frost)
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Protection against drought and frost
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Change of land use (from agricultural land to water body).
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased the complexity of management.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الري
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Production and income stability.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Possible diversification on farm (tourism and recreation).
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Demanding maintenance and increased complexity of management.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Lower risk of production failure, stability in business, motivation to do business in agriculture
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Possible additional activities on farm.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
An example of good practice for the community.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
With positive effects more interest of the farmer in sustainable production.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water available in dry months.
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased in case of irrigation
فقدان التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Planting species near/around the pond.
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Danger in case of improper maintenance.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
For a green reservoir, a lot of green infrastructure is placed next to it, which serves as protection for animals and plants (beneficial).
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
آثار الجفاف
خطر الحريق
التعليقات/ حدد:
Proximity to water.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
It affects the microclimate, more humidity, slower temperature fluctuations
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is slightly increased as the ponds provide water during dry periods.
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved mainly due to water retention during wet seasons for use in dry periods.
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced due to the capacity of ponds to retain excess water during times when rivers may flood.
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
The reservoir also enables sediment retention, preventing sediment from reaching downstream watercourses.
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
Many studies indicate that ponds can trap harmful substances, causing them to settle or undergo processes (acting as natural purification systems, especially when appropriate plant species are involved). This helps maintain cleaner downstream flows in terms of pollutants.
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
The pond's ability to retain pollutants also contributes to its buffering and filtering capacity.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدة جدا | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | جيدة جدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | ليس جيدا |
| جفاف | جيدة جدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فترة نمو ممتدة | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The costs of establishing a retention pond are indeed very high, and it is a substantial investment. However, especially in the case of agricultural land irrigation, the benefits can be quite favorable, particularly in terms of drought protection or frost prevention. In the long run, the investment yields significant advantages, as it enables resilience to climate change. Farmers can also receive support through rural development programs, which provide 30-50% project funding. Although the maintenance costs can be considerable, they are necessary and offer substantial benefits to farmers who irrigate their crops or protect them from frost. From land users' perspective it's positive, if they have improved production results.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
It is worth noting that the availability and extent of government subsidies can vary depending on the location, specific program, and eligibility criteria. In this research area, the majority of projects received partial funding from the government.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Retention ponds are simple if space is provided. |
| They collect water for use in drought conditions. |
| Retention ponds manage storm water quantity and quality, lessening the transfer of pollutants and chemicals into nearby water bodies. |
| Improved storm water collection and flood control. |
| Retention ponds provide habitats for animals, organisms, and insects (biodiversity). |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Local farm water retention systems allow for the detainment of water captured during spring runoff as well as during precipitation events, either directly or due to transport by surface runoff. This provides water storage that can be drawn on when groundwater supplies become depleted. |
| Retention ponds are designed to hold excess storm water runoff and release it slowly to avoid flooding downstream areas. They also serve to reduce downstream peak flow and aid in retaining flood waters which reduces associated flood risks downstream. If water is released from the reservoir, they serve to replenish groundwater stores downstream. |
| Surface water retention systems have shown success in reducing nutrient and sediment loading in various locations worldwide. |
| Under drought conditions these systems enable farmers to draw water from the reservoirs to support crop irrigation. The main value of water retention ponds is related to agricultural water demand in the dry season. They are considered the only effective way to preserve agricultural productivity. The ponds can increase the monetary value of agricultural land that can cope with water needs. |
| In addition to the primary function of retaining high waters, they often also serve a multipurpose use, such as: supply of drinking water, irrigation of agricultural land, protection against erosion, aquaculture, fishing, energy source, preservation of landscape and biodiversity, tourism, recreation and others. |
| Biomass production is another benefit of multi-purpose surface water retention system – cattails bioproduction and nutrient management. |
| In the case of construction of the so-called of a "green" water reservoir, green infrastructure solutions can provide protection for various species of animals and plants, which promotes biodiversity. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Anaerobic conditions can occur without regular inflow. | Proper planning and dimensioning of the pond, location and water level are necessary. It is necessary to ensure adequate flow and depth of the pond. |
| May not be suitable for steep sites, due to requirement for high embankments. | The construction of the pond is planned at a suitable location. |
| Colonisation by invasive species could increase maintenance and pose a danger to cultivated areas. | Regular maintenance and cleaning of the pond bank is necessary. |
| Safety risk in case of slipping and falling into the pond. | It is necessary to fence and isolate the access to the pond. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Large investments in the irrigation system and access to funds for irrigation infrastructure can be difficult to attain. | The size and holding capacity of retention systems also need to be considered to maximize benefits while limiting the initial costs of building a surface water retention system. |
| The construction requires a lot of technical preparation, planning, documentation and there are many bureaucratic obstacles to comply with the spatial acts of the municipality and to fulfil the requirements of the spatial planning authorities, which also includes large initial costs. | The preparation and management of the project should be entrusted to a professional service. Check the conditions ahead of time and plan strategically several years ahead. |
| While irrigation provides an economic gain during drought years, it also increases operational costs for water supplies. | Strategies need to provide drought proofing of crops as well as limiting damages caused by floods in non-drought years to reduce risk to farmers and the region. |
| Experts identified some barriers for greener pond implementation, especially related to reduced efficiency. The higher surface required can cause loss of water stored during summer from the higher rate of evaporation. Another risk is associated with vegetation close to the pond banks which can reduce impermeabilization and increase water infiltration due to root growth in the soil. | Good technical plan with solutions and compromises for best results with natural (green) benefits. Considering the benefits brought by green systems. |
| Unregulated relations between active/potential users, both in the delimitation of water rights, especially in times of water shortage, and in cases of regulating obligations for the proper operation and maintenance. | Collective investments with a good long-term plan for operation and maintenance. Organized management of users from the organization (e.g. municipality, etc.). |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Field visit and conducted interview with the farm manager at the Fruit Growing Center Maribor. A working group was established, where we met 2 times to review and respond to the questionnaire.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Purgaj Donik Biserka is a farm manager of agriculture company "Fruit growing center Maribor" (land user).
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Matjaz Glavan, Istenič Darja, Škerjanec Mateja, Banovec Primož, Curk Miha and Cvejić Rozalija representatives from University of Ljubljana.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
As for the literature, we utilized the following documents:
- Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov (translated: Hydraulic basis for monitoring the operation and maintenance of small reservoirs). Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
- Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/02/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
An economic assessment of local farm multi-purpose surface water retention systems in a Canadian Prairie setting; Pamela Berry, Fuad Yassin, Kenneth Belcher, Karl-Erich Lindenschmidt, Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:4461–4478.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Web
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Natural water retention ponds for water management in agriculture: A potential scenario in Northern Italy; Andrea Staccione, Davide Broccoli, Paolo Mazzoli, Stefano Bagli, Jaroslav Mysiak; Journal of Environmental Management 292 (2021) 112849.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Web
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Natural Water Retention Measures; Report: Individual NWRM - Retention ponds.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Web
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Vodnogospodarske podlage za nadzor obratovanja in vzdrževanja manjših zadrževalnikov. Miljenko Hočuršćak. Aktualni projekti s področja upravljanja z vodami in urejanje voda. 28. Mišičev vodarski dan 2017.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Web
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية