Basket compost [مدغشقر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Harifidy RAKOTO RATSIMBA
- المحررون: Felana Nantenaina RAMALASON, Dimby RAHERINJATOVOARISON, Siagbé Golli, Tahiry Ravivonandrasana, Natacha Rabeary
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Fambolena mangahazo, Basket compost
technologies_6475 - مدغشقر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
TORANO Augustin
مدغشقر
مستخدم الأرض:
RABOTOZAFIARIMBOLA Samuelson
مدغشقر
مستخدم الأرض:
RAZANAPELA Jean Baptiste
مدغشقر
مستخدم الأرض:
RAZAFIMANDIMBY Pascal
مدغشقر
مستخدم الأرض:
RAVOLOLONINDRIANA Marie Lucie
مدغشقر
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
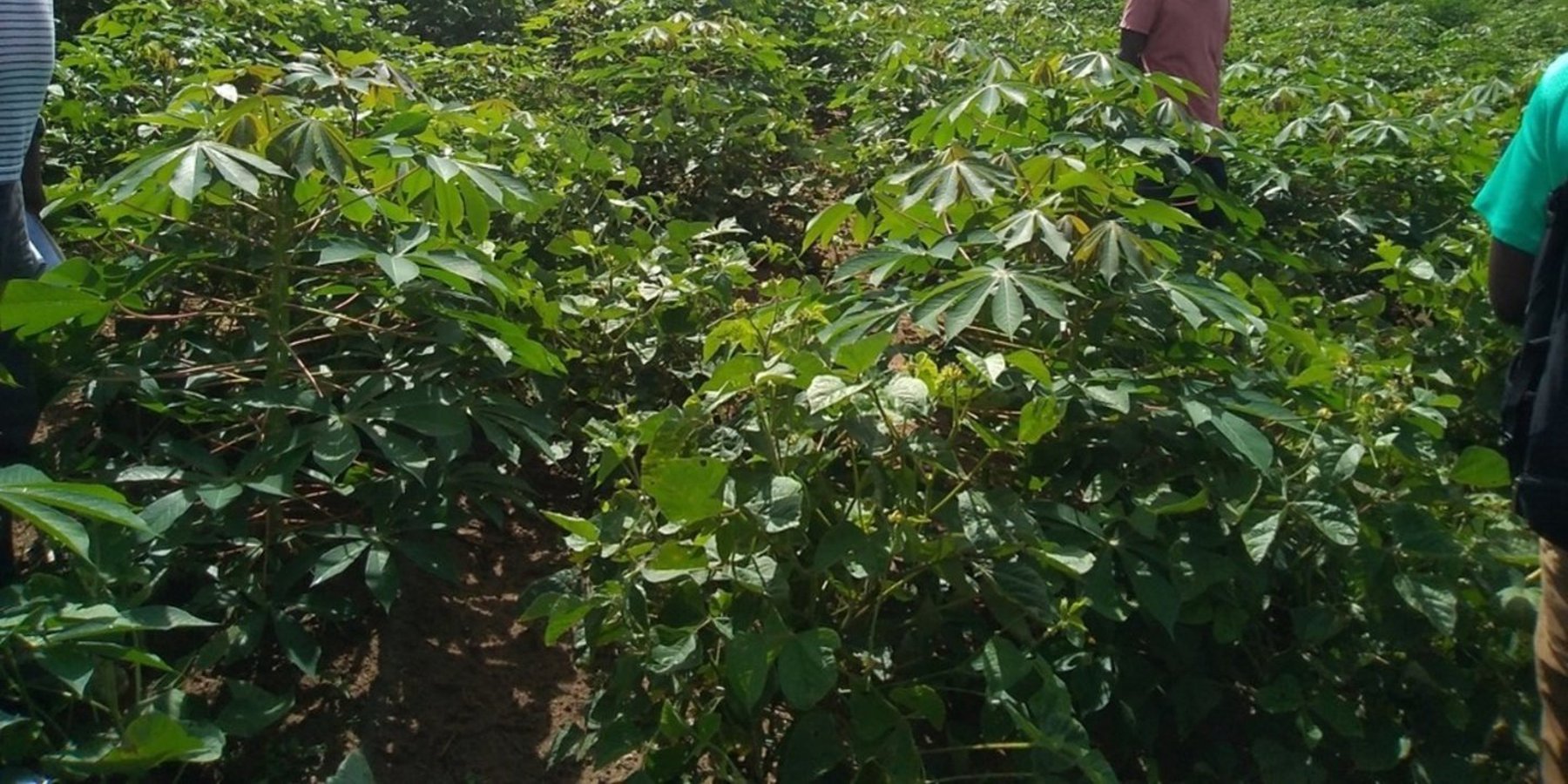
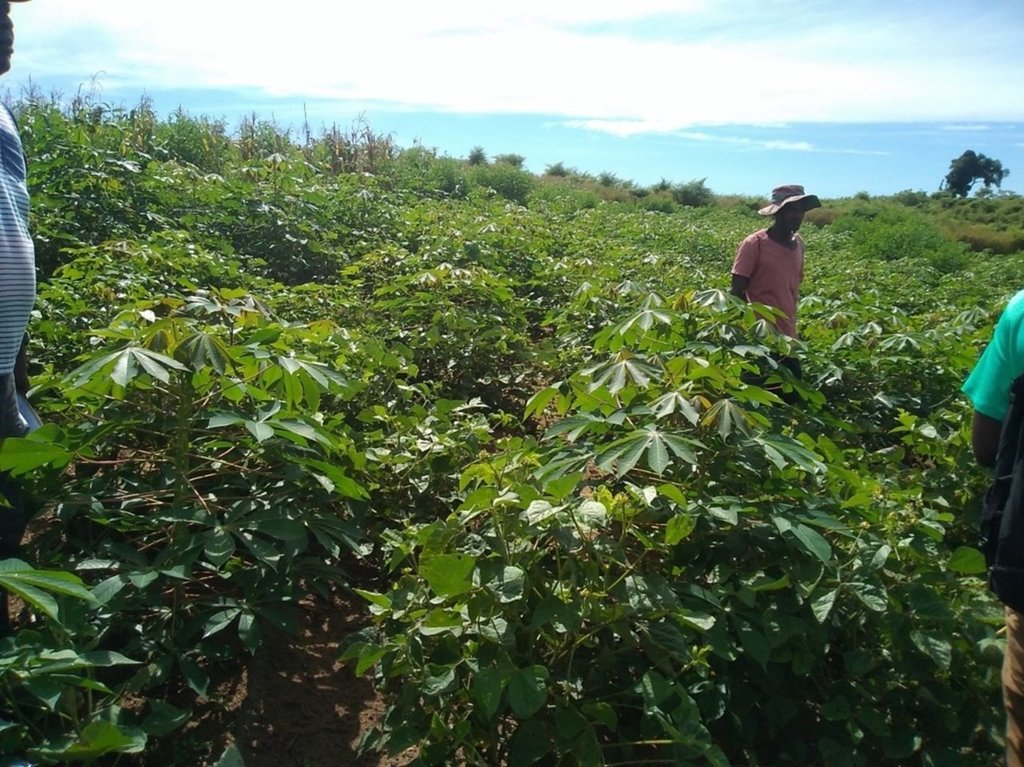
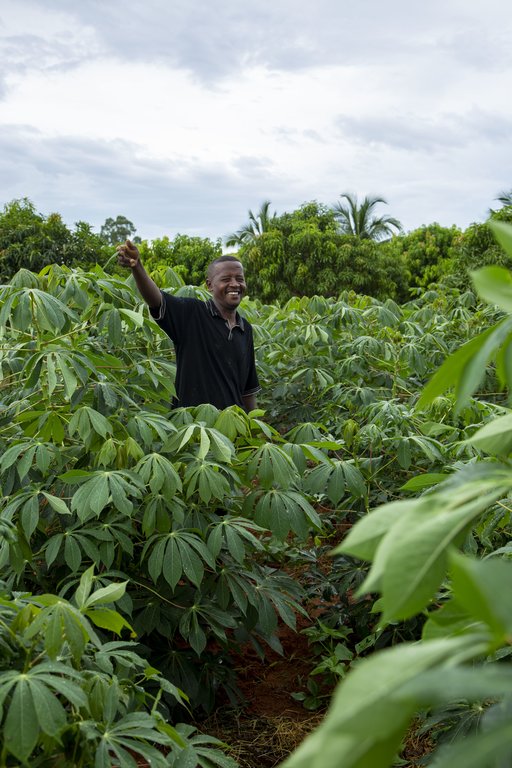
Le Basket compost est une technique d'intensification agricole pour améliorer la production des tubercules comme le manioc en concentrant la matière organique dans un trou (herbes sèches, matières vertes et si possible, un peu de déjections animales) et en y implantant une bouture saine. Cette technique est très profitable pour les petits exploitants agricoles n’ayant que de petites surfaces agricoles car elle permet de maximiser la production sur une superficie restreinte.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
D'une manière générale, la technique de basket compost peut être utilisée pour la culture de certains tubercules, tels que : l’igname, le manioc, ou aussi le taro. Mais la technologie décrite ici , concerne seulement la culture de manioc pratiquée par les exploitants dans la zone.
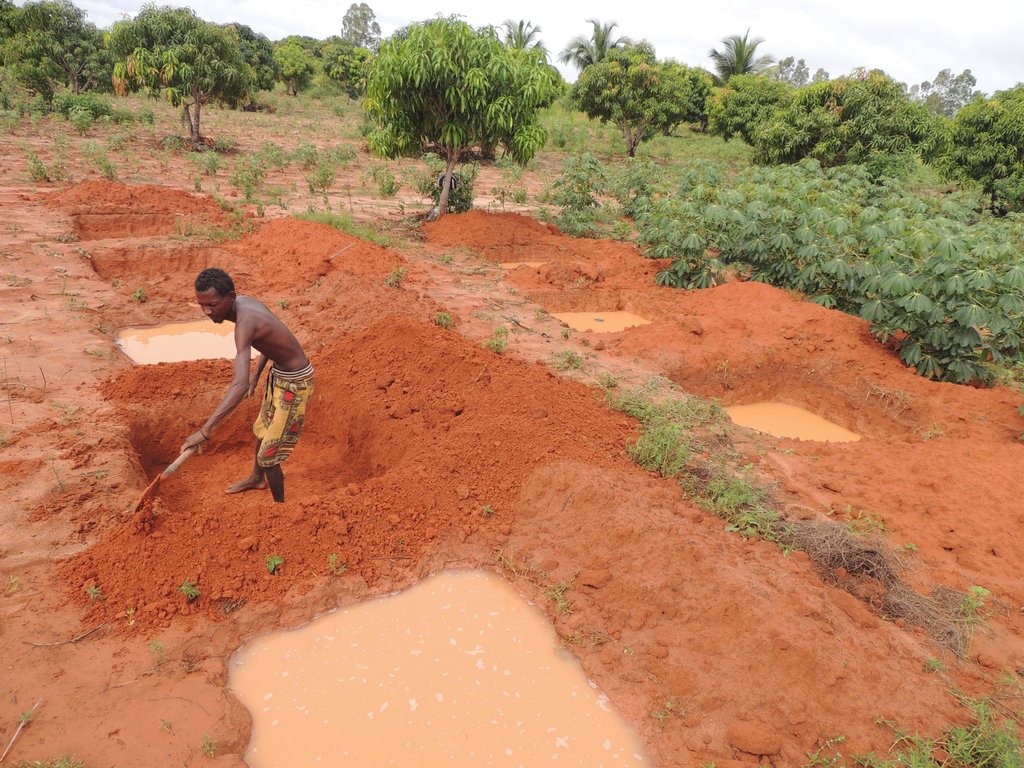
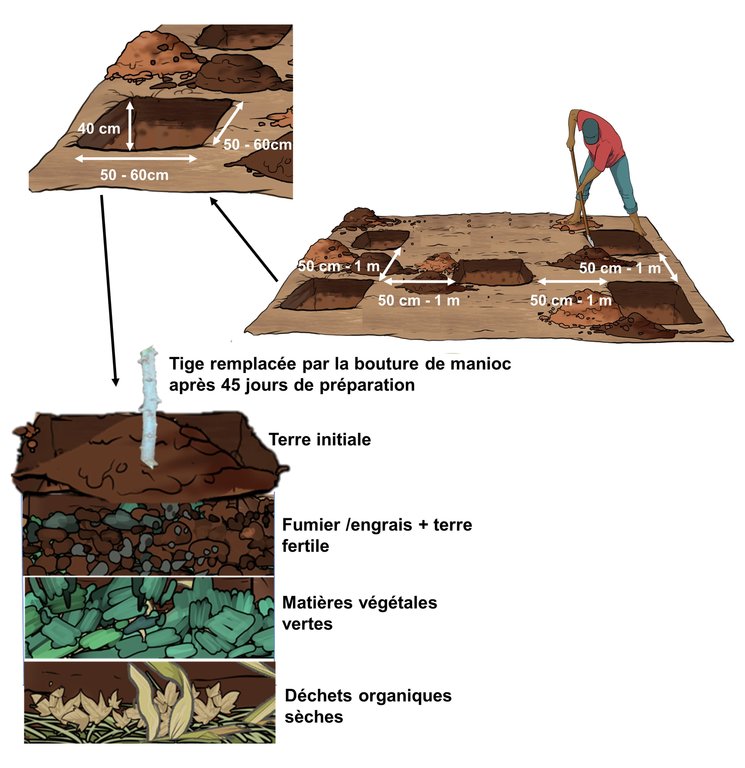
Le terrain de culture de manioc doit être bien choisi pour effectuer le Basket compost. Il devrait se situer proche des habitations, à l’abri de la divagation des animaux. Cette technologie permet de maximiser la production de manioc par pied et peut être appliquée sur tout type de terrain. Elle améliore la fertilité du sol et permet de restaurer les sols dégradés. Les principes de trouaison doivent respecter les dimensions suivantes : 40 cm de profondeur, 60 cm de largeur et 60 cm de longueur. Chaque trou doit être espacé de 1 m. La préparation du Basket compost se fait comme suit :
- remplir de matières organiques sèches la moitié du trou puis écraser les déchets pour bien les entasser ;
- mettre une couche de matières vertes bien coupées en morceau ; plus les matières végétales sont petites, plus la décomposition est rapide ;
- mettre une couche d’engrais mélangée avec de la terre fertile de 10 cm d’épaisseur ;
- recouvrir le tout par la couche supérieure de la terre initiale pour former un monticule ;
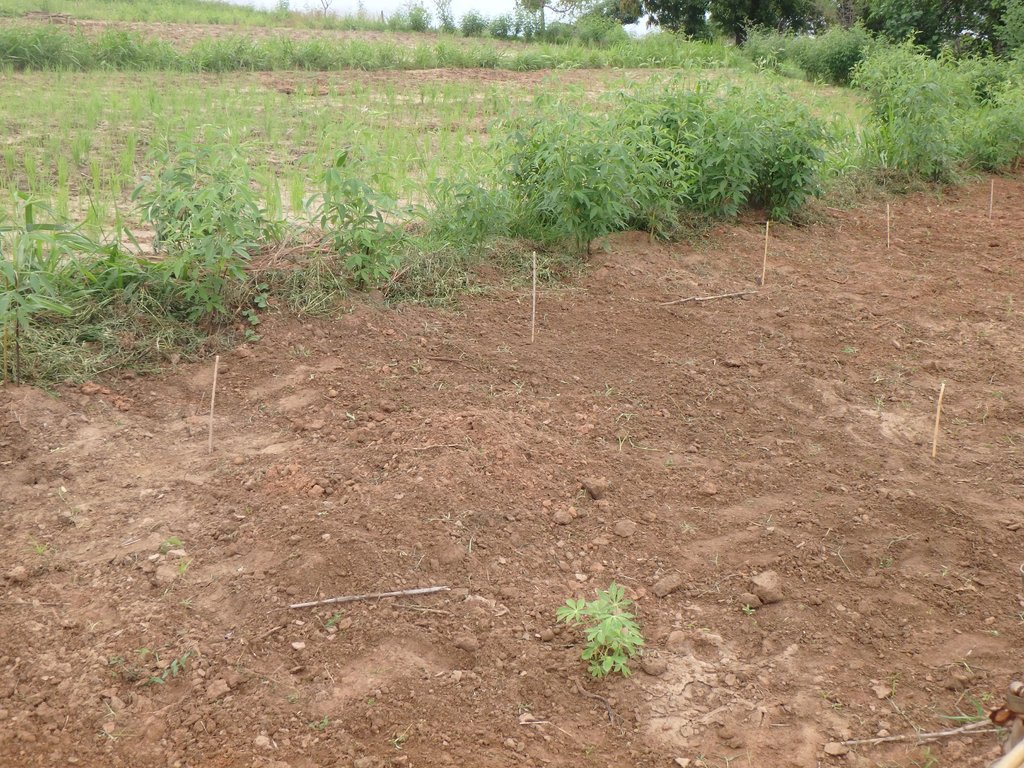
- marquer le centre du trou par une tige et mettre un tas d’engrais et de terre fertile avant de planter la bouture de manioc ;
- laisser le trou pendant 45 jours ;
- mettre en terre la bouture de manioc bien verticalement à la place de la tige initiale en enfonçant 3 bourgeons de la bouture dans la terre ;
- entasser la terre autour de la tige pour permettre la liaison de la terre à la tige.
La tige de manioc à planter doit être en bonne santé, exempt de maladie et en particulier de mosaïque. Elle doit être bien mature, pas trop jeune, ni trop vieille ; sans feuilles, avec 4 à 5 bourgeons ; mesurant au moins 20 cm de longueur. Quand le plant de manioc atteint 30 cm de hauteur, sélectionner la meilleure tige (tige principale) et éliminer les autres tiges (tiges secondaires).
Les principaux intrants nécessaires pour la mise en place du Basket compost sont :
- matières organiques sèches : paille de riz, mauvaises herbes, autres déchets ;
- matières végétales vertes : feuilles d’acacia, feuilles de bananiers, herbes vertes… ;
- terre fertile mélangée avec des déjections animales telles que la poudrette de parc.
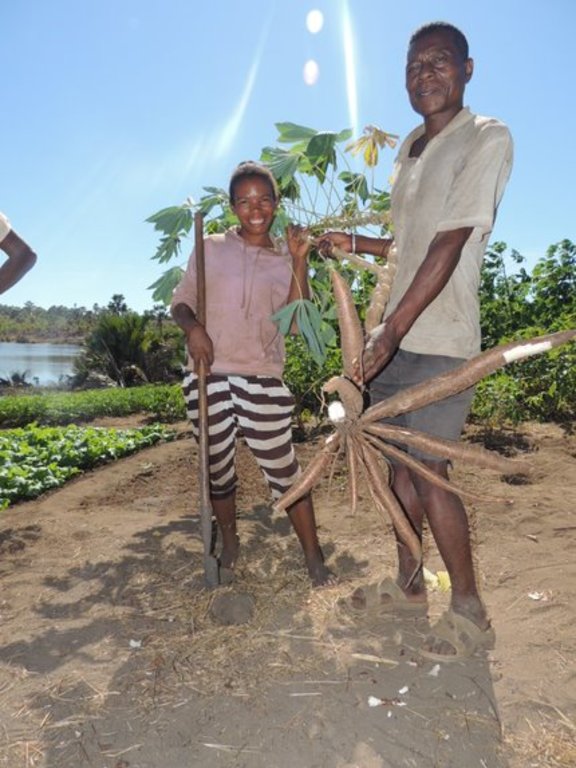
Le Basket compost maximise la production de tubercule pouvant produire 5 à 25 kg de manioc par pied. La récolte se fait après au moins 12 mois de plantation. La difficulté d’application de cette technologie se réfère à la trouaison, au transport et à l’approvisionnement en matières organiques (matières végétales, fumure animale). Cette technologie requiert plus de main d’œuvre et permet d’intensifier la production sur une surface réduite. Elle est donc adaptée aux petits exploitants n'ayant accès qu'à des superficies restreintes. En général, un exploitant peut faire environ 100 trous pour une saison de culture.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
مدغشقر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Boeny
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ambondromamy, Belobaka, Marovoay Banlieue, Manerinerina
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2019
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
GIZ ProSol Madagascar
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - الكسافا
- Vigna radiata
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
manioc/ citrouille, manioc/ maïs
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Les trous de basket compost doivent avoir au moins 40 cm de profondeur avec 50 à 60 cm de largeur et de même pour la longueur.
L'espace entre les trous est de 50 cm à 1 m.
La moitié du trous doit être remplie de matières organiques sèches lesquelles seront ensuite entassées. Une couche de matières vertes bien coupées en morceau sera ensuite déposée suivie d'une couche de déjections animales mélangée aux terres fertiles. Le tout sera couvert de la couche supérieure de la terre initiale pour former un billon. Le trou sera marqué par une tige qui va être remplacée par la bouture de manioc 45 jours après la préparation du basket compost.
المؤلف:
GIZ Prosol Madagascar
التاريخ:
01/02/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 hectare
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
ariary
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4300,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5000
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecte des déchets et débris végétaux | toute l'année |
| 2. | Trouaison | Août - Janvier |
| 3. | Préparation du basket compost | novembre - janvier |
| 4. | Plantation des boutures de manioc | 40 jours après la préparation du basket compost |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Trouaison | jours-personne | 168,0 | 10000,0 | 1680000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Transport et préparation du basket compost | jours-personne | 50,0 | 5000,0 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Brouette | nombre | 1,0 | 110000,0 | 110000,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Boutures de manioc | nombre | 615,0 | 200,0 | 123000,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Poudrette de parc | sac | 350,0 | 1200,0 | 420000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2583000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 600,7 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Le Projet ProSol a octroyé des équipements tels que la brouette, la pelle ainsi que des boutures de manioc.
التعليقات:
Un exploitant peut faire 100 trous de basket compost en moyenne par saison de culture, soit environ 10 ares. Après la récolte de manioc, la parcelle est encore fertile et peut être cultivée avec d'autres cultures. Suivant deux années successives de culture de manioc, il est conseillé de laisser la terre en jachère pendant 3 ans afin d'éviter l'épuisement des sols. La mise en place de basket compost est réitérée après la jachère ou sur sol pauvre pour une nouvelle culture de manioc. Ces prix sont issus des enquêtes sur terrain et validés par les experts GDT.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protection contre le pâturage des bétails. | saison de pluies |
| 2. | Sarclage. | saison de pluies (2 fois, espacés d'un mois) |
| 3. | Traitements phytosanitaires. | à partir de la plantation, une fois par semaine pendant 8 mois |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Sarclage | jours-personne | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 50000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 11,63 | |||||
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1400,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Plusieurs espèces faunistiques et floristiques sont présentes dans cette Région, certaines sont même endémiques. Néanmoins, cette quantité reste moyenne par rapport à d'autres Régions de l'île. Concernant les habitats, environ 20% de la zone peut constituer un habitat pour cette biodiversité (forêts, plan d'eau, mangrove, etc.), ce qui reste assez faible.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
La plupart des villageois reconnaissent les parcelles de chacune des habitants du village
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1 kg/pieds
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2 - 3 kg/pieds
جودة المحاصيل
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Il s'agit des estimations des exploitants enquêtés.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
non pertinent
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Amélioration la fertilité du sol. |
| Augmentation de la production. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Charge de travail très élevée. | Besoin de main d'œuvre extérieure. |
| Disponibilité des matières premières (matières vertes en saison sèche, fumier...). | Collecte de matières premières durant toute l'année. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
5 terrains visités
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
5 exploitants enquêtés
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Fiche technique de GIZ ProSol Madagascar
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
02/02/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Région Boeny, 2016, "Schéma Régional d’Aménagement du Territoire de la Région Boeny"
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Hotel de la Région Boeny
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
GIZ ProSol Madagascar, 2022, "Livret des Paysans Relais"
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
GIZ ProSol Madagascar
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
GIZ ProSol Madagascar, 2022, Poster "Basket compost"
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
GIZ ProSol Madagascar
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
La Technique du basket compost
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://interaide.org/pratiques/content/la-technique-du-basket-compost-en-images
العنوان/الوصف:
Fampiasana basket compost amin'ny kazaha - Bâche de formation Basket compost - Projet Manitatra – Sud Est
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://gsdm-mg.org/wp-content/files/Bche_Basket_compost_-Sud_Est.jpg
العنوان/الوصف:
"Basket compost", site web de l’Université de Mahajanga
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://soatany.org/fiches-techniques/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية