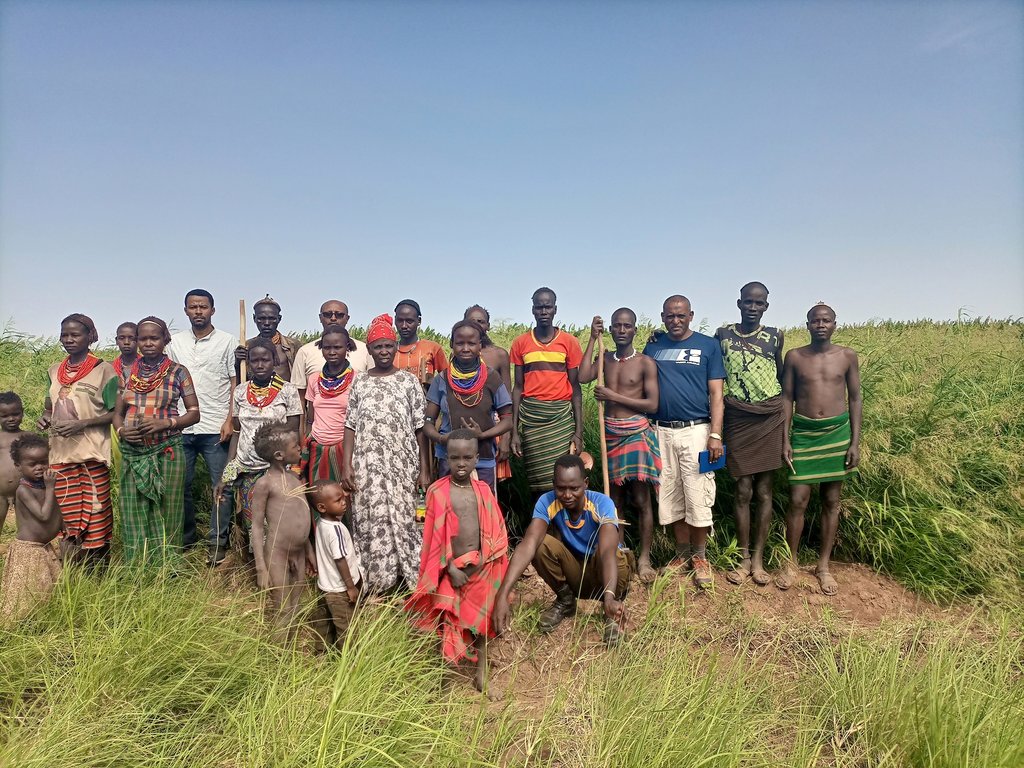
Panicum coloratum for irrigated fodder [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Panicum
technologies_6563 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Lutulya Abebe
Agro-pastoralist (fodder producers group leader)
أثيوبيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Resilient in Pastoralist Areas (RIPA)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Development Enterprises - Ethiopia (iDE-Ethiopia) - الولايات المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The technology is a regenerative practice friendly to the environment.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
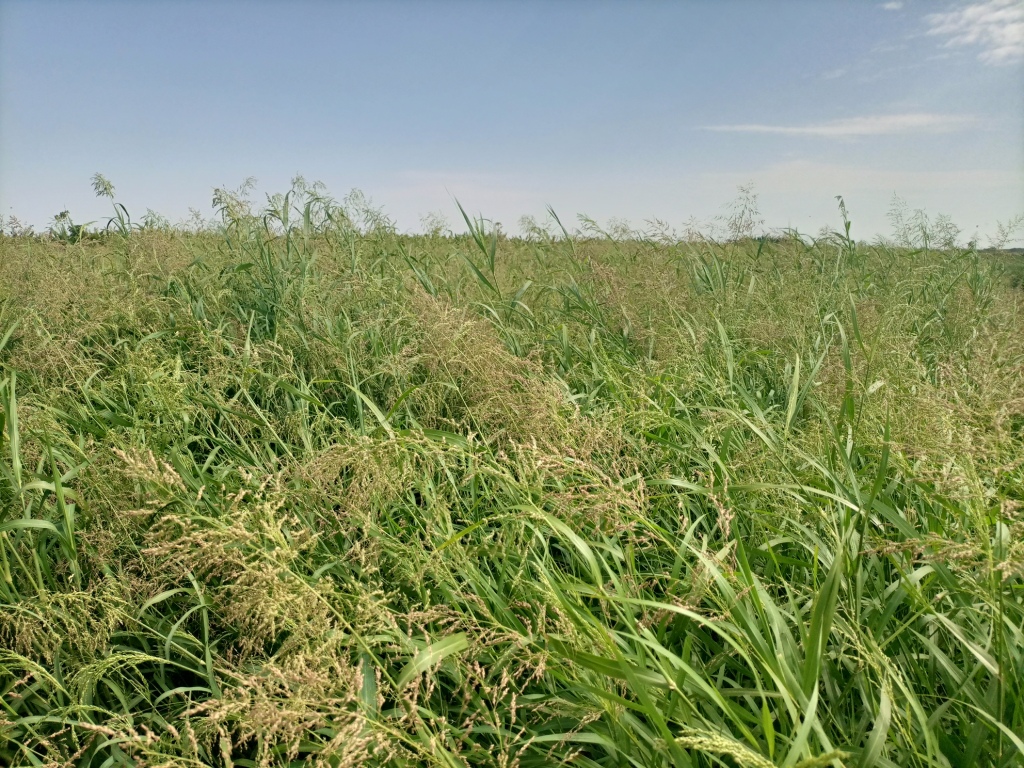
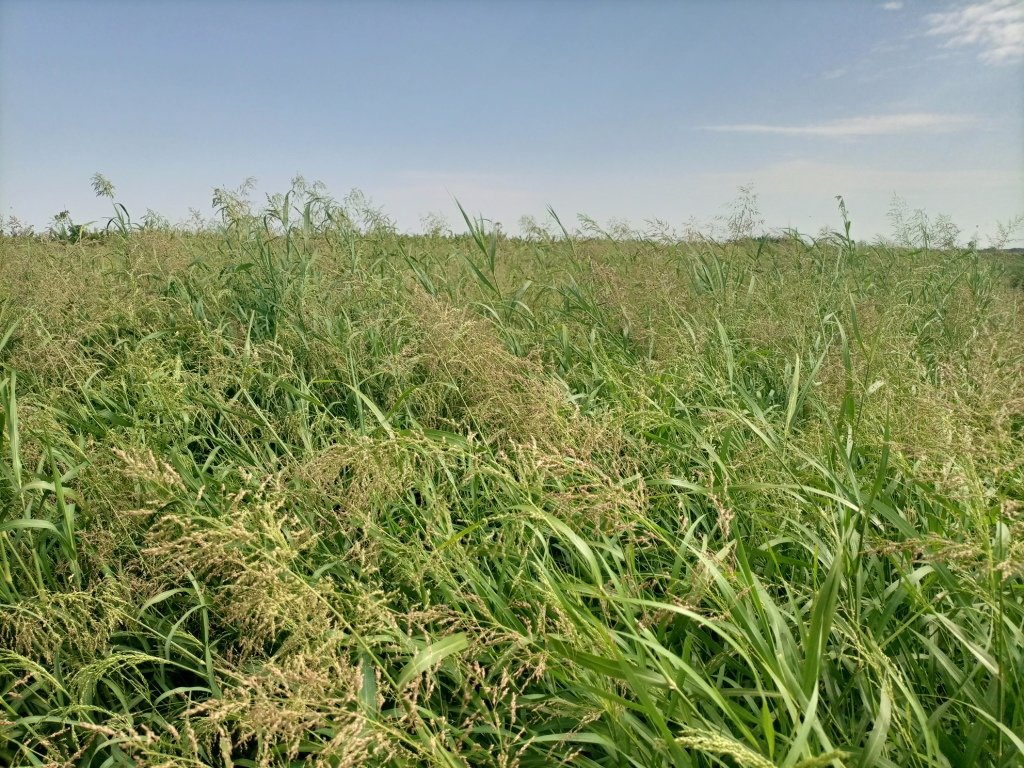
Panicum coloratum is a palatable tropical grass with high biomass production potential. It is grown in the irrigated fodder development areas of Dassenech district. Panicum is a fast-growing perennial which can be repeatedly harvested once it reaches maturity. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortage in dry periods – which are becoming worse with climate change.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Irrigated fodder production is carried out by pastoralist groups in arid areas of South Omo. Among a number of fodder grasses, Panicum coloratum is a fast-growing species. Panicum is grown as livestock fodder, particularly for the dry season when feed availability is in short supply. It mitigates the issues of recurrent livestock feed shortages which are becoming worse with climate change. Also, growing fodder grass allows resource-poor pastoralist communities to generate income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Irrigating at least twice a week, good weed management, and fertilization ensure sustained production.
In Dassenech district of Southwest Ethiopia, Panicum’s annual fresh biomass and dry matter production potential is over 63 and 18 tons/ha, respectively. It can reach its first harvest after about 60 days and subsequently can be harvested every 45 days. Panicum germinates and establishes readily on any soil type under both irrigated and rainfed conditions. It is also drought tolerant and resilient to climate variability, and does particularly well on alluvial soils with high fertility. Panicum is mainly used for grazing, but it is also suitable for cut-and-carry feeding systems. Each member of the pastoralist group grows panicum on 0.04 ha of land. In the flood lowlands of the Omo River basin, panicum is known for tolerating periodic flooding, salinity, & disease.
Previously, the land users were unfamiliar with this particular grass and its associated management practices. Also, irrigating on a regular schedule and keeping the grass free from roaming animals adds a work burden to the pastoralist community. However, the Resilience in Pastoral Areas (RIPA) project has introduced and familiarized the community with fodder production and management practices. The project also assists in linking the output to sustainable market. In this regard, the contribution of the RIPA project of the International Development Enterprises (iDE) is immense. The pastoralists appreciate their livestock’s access to year-round feed, as well as the generation of income from the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. Fodder production also creates year-round employment opportunity. However, the community's reliance on government and civic organization support for land preparation and access to irrigation water (conveyance services) might be considered a threat to ensuring sustainability of fodder development by the pastoralist groups.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Videos of the technology is not documented.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Southern Nations, Nationalities and People Region (SNNPR).
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Omorate, Dassenech.
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Panicum production site is closer to the mouth of the Omo river. The technology is piloted in two sites and scaling up sites have been increasing around the irrigable areas.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2021
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Resilient Initiatives in Pastoralist Areas project of the International Development Enterprises has implemented fodder development along with other perennial crops such as banana as part of promoting resilient agriculture in the dry areas of South Omo Zone of SNNPRS.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- أعشاب، فلفل تشيلي الحر، فلفل
- أعشاب نجيلية طبيعية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
The area receive bimodal rainfall but not reliable to grow crops.
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
نوع الحيوان:
- الجمال
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
- الماعز
- الأغنام
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
كلا
المنتجات والخدمات:
- الأمن الاقتصادي، ,وجاهة الاستثمار
- الحليب
- جلود الجاموس الخام
الصنف:
الماعز
العدد:
12
الصنف:
الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
العدد:
8
الصنف:
الجمال
العدد:
1
الصنف:
الأغنام
العدد:
9
التعليقات:
The site is pastoralist area who used to rely on flood retreat agriculture in the past. However, due to the construction of Gibe III hydroelectric power dam, the spill over during plenty of rain remain still as artificial lake over thousands of hectare for long period of time. As a result, the conventional agriculture practices abandoned. Thus, a shift to irrigation agriculture is in the process at least to produce fodder crops and other perennial crops such as banana for consumption and market.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- أعشاب، فلفل تشيلي الحر، فلفل
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة
التعليقات:
The area used to receive short rain twice a year. However, rainfall distribution is unreliable. So, the introduced perennial fodder and banana production persist throughout the year using irrigation.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
التعليقات:
Fodder and tropical fruit crop production is entirely practiced using full irrigation from Omo river.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
التعليقات:
Perennial fodder production contributes to SLM through permanent soil cover.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
As a perennial crop, the grass covers the ground permanently and reduces moisture loss to excessive evaporation in the dry areas.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
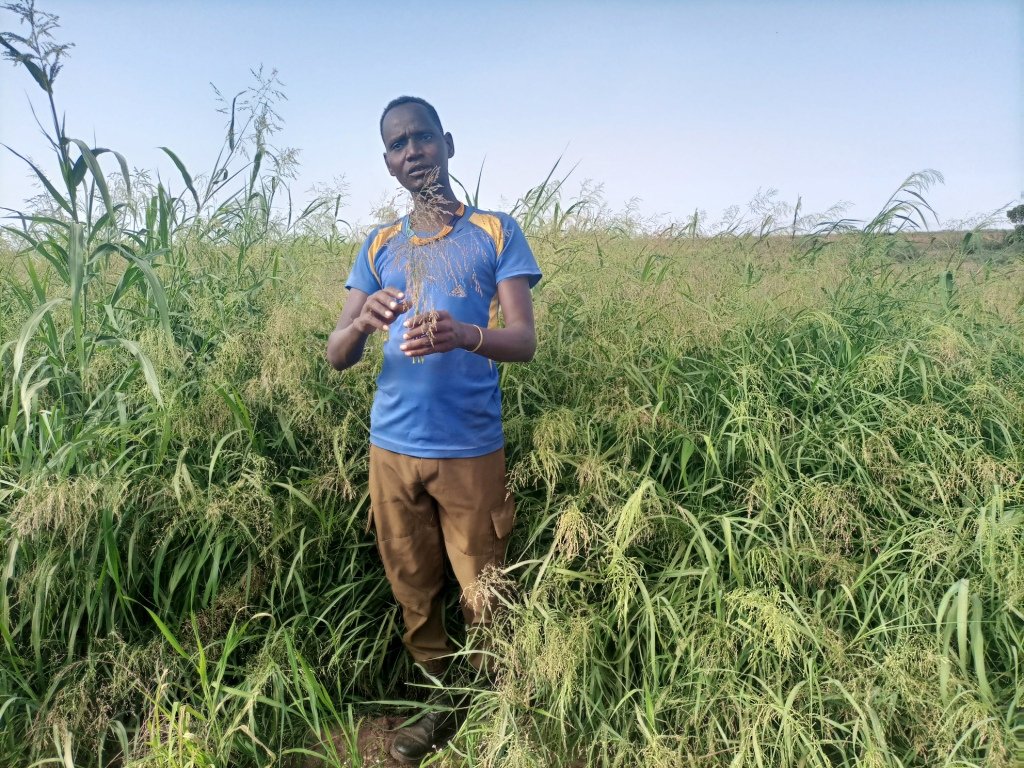
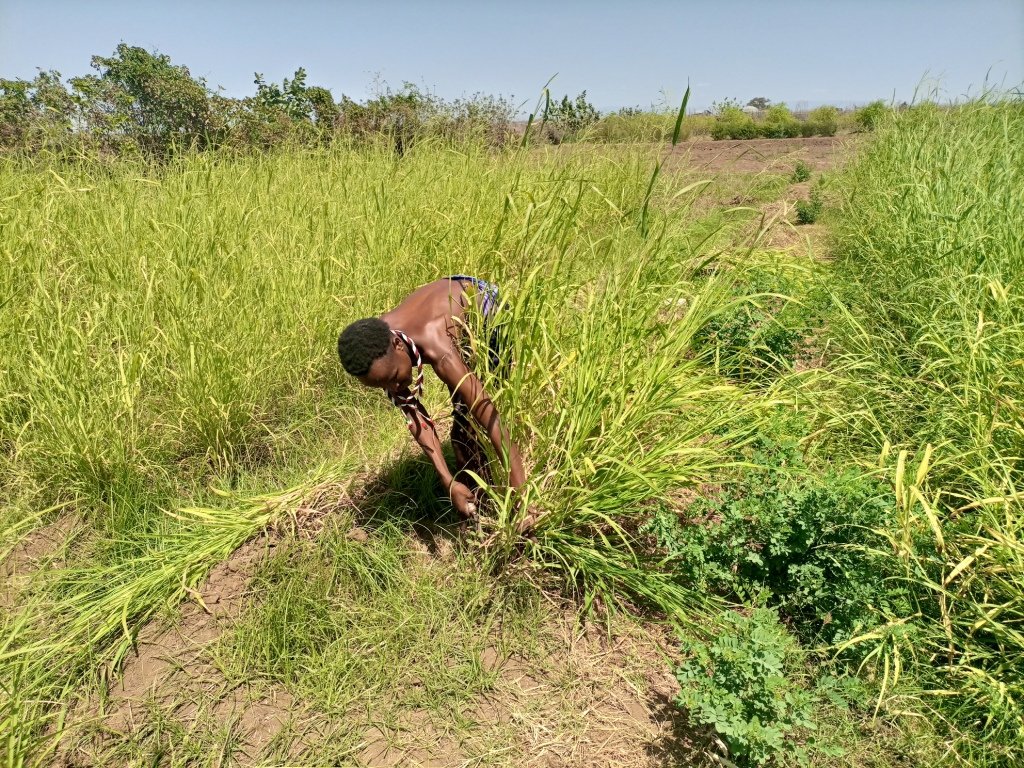
This is the photo of the pastoralist group. There is no specific sketching that portrays the technology but the following points provide tips for adopters of the technology:
- The land is tilled and harrowed by a tractor for two to three rounds.
- On the third-round ridge and furrow are formed using tractor or hand tools.
- The seeds or splits are planted in rows along the ridge.
- Spacing between ridges varies with the purpose: for haymaking 25 -30 cm and for seed production 50-60 cm to simplify the application of intensive management practice for the latter one.
- The farm/crop should be irrigated twice a week for better production.
- Need Fertilization to ensure good production/harvest.
المؤلف:
Gerba Leta
التاريخ:
19/08/2022
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 timad
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
0.25 ha
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ethiopian Birr (ETB)
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
53,438
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
It is variable based on the types of work (from 50 birr to 100) for half day before the sun gets too hot. That is equivalent to one day in dry lowland areas.
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing and land preparation | Any season for irrigated fodder production, |
| 2. | Planting/sowing | During the start of season for irrigation fodder production. |
| 3. | Fertilizing | At planting and at boot height. |
| 4. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 5. | Weeding | Twice starting 3- 4 weeks post planting. |
| 6. | Harvesting the grass (fodder) | During harvest maturity. |
| 7. | Hay making (bailing) | Post harvest. |
| 8. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | Harvesting season and post harvest. |
التعليقات:
As fodder development is based on irrigation, it can be started any time/season of the year.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Clearing and land preparation | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 50,0 |
| العمالة | Planting/sowing | PDs | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 14,0 | 200,0 | 2800,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Weeding (twice a season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Spade | Pcs | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| معدات | Hoes | Pcs | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seed | kg | 4,0 | 300,0 | 1200,0 | |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | NSP | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 15200,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 284,44 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Other than cost of labor, some inputs and material costs are covered by the RIPA project of the iDE.
التعليقات:
Irrigation-based fodder development is in the pilot phase. There is growing interest among the government organization (Woreda Office of Agriculture) to adopt and scale up the promising development. Please note, the cost is estimated only for a season or one round of production. Once reaches its first harvest, Panicum can be harvested every other 45 days onward. Of course, it needs the application of necessary management practices, every season.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning irrigation ditch | During off-season or before the start of next growing season. |
| 2. | Fertilizer (NSP) | Twice: at the beginning of the season & when the fodder reaches boots height. |
| 3. | Irrigating the farm | Twice a week. |
| 4. | Weeding (2x) | Based on the density or prevalence of weeds. |
| 5. | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | When the seed reaches harvest maturity. |
| 6. | Harvesting and hay making | At harvest and post harvest. |
التعليقات:
As there is no structure such as fodder banks, maintenance cost is not documented.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Cleaning irrigation ditch | PDs | 5,0 | 200,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Irrigating the farm | PDs | 12,0 | 200,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Weeding (at least twice during the growing season) | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Seed collection, drying and cleaning | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Harvesting and hay making | PDs | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | NSP Fertilizers | kg | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 10900,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 203,97 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
NA
التعليقات:
The cost estimation is only for one irrigation season that may range from 45 days to 60 days or some more including the harvesting and drying of the outputs. Once established, the cost of production is gradually declining.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Economic crisis and increasing Inflation rate affect the establishment as well as maintenance costs. Particularly, fuel, fertilizer, and labor costs are consistently changing.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Erratic and unpredictable.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Rainfall distribution is unreliable to produce crops under rainfed conditions.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The site is in the lowland around the mouth of Omo River basin.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil pH is over 7 and the soil is slightly saline alluvial.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Diversion/river water is used for irrigation. There is ample water provide that there is pump to convey the water to the nearby farm. In the rainy season, the river is turbid and full of eroded soil from the upstream catchments. However, the depth of the water table is variable based on the distance of the farm from the edge of the river. Around the main river basin, the water table is shallow but too deep as one go away from the river basin.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Around the farmland, diversity of crops and vegetation is limited. Away from the farmland, there are a few lowland shrub species and faunas common to the dryland.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The water pump is used to convey water and the tractor for land preparation. Therefore, a mix of mechanization and manual systems are employed in the area. Irrigation land was allocated to the group but they partitioned and distributed to each member of the group.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
As their animal is freely roaming, only small size of land is permantantly owned around the river side and homestead.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- لمجموعة
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
The pastoralist, still freely move and settle where they think appropriate and shift after certain years.
التعليقات:
Apart from the irrigable land which are located around the river basin, land is openly accessible to the pastoralist community.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
Access to facility and the services is mainly to those pastoralist community who are residing closer to the Omorate, the woreda capital.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Access to irrigation water increase the fodder production throughout the year.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the alluvial soil around the river bank is suitable for Panicum, it increases the quality of fodder.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in livestock production is related to the availability of feed/fodder.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Access to irrigation water highly reduced risk of production failure.
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
التعليقات/ حدد:
The land that used to be ideal is now converted to farming.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Panicum as perennial fodder increases ground cover throughout the year and contributes to land management from wind erosion in the dry land areas.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
توافر المياه للماشية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
نوعية المياه للماشية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
توافر مياه الري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
نوعية مياه الري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الطلب على مياه الري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-1
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
As Panicum is harvested at least six times a year post reaching the first maturity, farm income is significantly increases.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Income can be generated from the sale of fresh fodder, hay and seeds.
فروقات اقتصادية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Irrigated fodder production needs intensive management practices. Panicum is perennial fodder that remain on the field all year round. So, irrigating, weeding and looking after the farm... increases the workload.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
الوضع الصحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الفرص الثقافية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
الفرص الترفيهية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
المؤسسات الوطنية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
As it permanently covers the ground, it has high likelihoods of reducing surface runoff.
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improve water drainage.
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Decreases surface evaporation but not transpiration.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farm remains covered by perennial grass. Irrigating the farm also favor the regrowth of other wild species.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Above ground biomass is highly increased as described in the description section.
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced with increased management practices. Invasive alien species such as Prosopis juliflora is less common in this part of the River basin.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Animal diversity correlates with fodder availability.
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
It reduces the impacts of drought on livestock by providing access to adequate feeds throughout the year.
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
As Panicum increase ground cover and store the carbon above and below the soil surface, it reduces the emission of the carbon.
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
It breaks the velocity of wind in the lowland, one of the main issues.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
Slightly ameliorate the micro-climate of the area.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is expected that downstream flooding is reduced as the perennial fodder crop cover the ground throughout the year.
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Permanent ground cover expected to increase the filtering capacity.
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
It has expected positive effects of reducing wind transportation.
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
As perennial crops cover the ground and absorb the carbon, it has an inevitable positive effects on reducing carbon emission.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The fodder development is a pilot practice. Its up scaling will have a positive off-site effects to the surrounding areas.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | باعتدال |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | باعتدال |
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدة جدا |
| فيضان مفاجئ | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدا |
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Panicum has drought, flood and disease tolerating feature.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The technology was piloted two years ago. The cost of establishing it is partly supported by the RIPA project. Land preparation and conveying irrigation water covered by the local government.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
التعليقات:
So far, the pastoralist piloted the technology through government and NGO support.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Supply year round feed for the land users' livestock. |
| Allow pastoralists/agro-pastoralists to generate income from the collection and sale of fresh fodder, hay and seed. |
| The technology supplies feed that can be reserved for the emergency time through hay making. |
| Introduction of fodder production technology enables the pastoralist group access usufructs to irrigable land that promotes the changing in farming practices from entirely pastoralist to agro-pastoralist on a gradual basis. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The technology considered as one of the regenerative agricultural practices that have positive contribution to carbon sequestration. |
| It reduces risks of feed shortage during the extended dry season. |
| A prompt sources of income for the pastoralist community via the sale of fresh fodder, hay, and seed. |
| Feeding livestock on grass reduces methane production as compared to feeding them on processed feeds. |
| The onsite shattering of the seed increases the density of grass every other season. Thus, it improves the ground cover and production of huge biomass per unit of land. |
| Panicum harvested 15 cm high that simplify regrowth/tillering and propagation of the grass from the ratoon. The practice stimulates prompt ground cover and year-round sequestration of carbon. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Access to irrigation facility and service is via government and project support. | Try to secure multiple sources of finance, and encourage market oriented production to enhance the pastoralist groups develop reliance on their own. |
| Smaller size of land is accessible to irrigation. | Increase intensification of fodder development and diversify sources of income via production and marketing of fresh fodder, hay, and the seed. |
| Shortage of baling machine to fasten the hay for simplicity of storage and transportation | Improve pastoralist access to the facility and services so that their resilience to feed shortage and associated issues are promptly increases. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Shortage of storage structure or fodder bank to store/ reserve the harvest for market and/or later uses. | To promote the establishment of storage or fodder bank by the land users group themselves, and try to find sources of finance to support them in this regard. |
| Lack of sustainable market links for Panicum seed. | Establish reliable market value chain with private suppliers/distributors to the other part of the country. |
| Lack of legume fodder species to improve the dietary value of the grass family. | Introduces important legume species with high biomass production potential or other leguminous tree species with multiple uses such as windbreak or as buffer plants around the periphery of the fodder farm. |
| Panicum needs longer time to reach harvest if intended for seed production that may dishearten the pastoralist to wait longer time. | Allocate separate plots for seed production, or else, make the right choice for the types of outputs that suits the pastoralist's urgent needs. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Over 20 members of the pastoralists group are met.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
One knowledgeable land user who is representative of the pastoralists group.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Three
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Published articles and locally developed guideline for growing Panicum.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/08/2022
التعليقات:
Field visit was made from 17 August to 19, 2022.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
ILRI. 2013. Colored Guinea grass (Panicum coloratum) for livestock feed on small-scale farm. ILRI Forage Factsheet.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free online
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Hitiso, W. & Guyo, M. 2017. Biomass Production of different grass species available at irrigated lowland of Dassench woreda in Southwestern Ethiopia. Bangladesh Journal of Animal Science, 46 (3): 188-191.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free online
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hidosa, D., Adicha, A., Sultan, M., 2022. Production and Commercialization Status of Improved Panicum Grass Cultivation in the Lowland Livestock Production System of South Omo South-Western Ethiopia. Research on World Agricultural Economy, 3 (4): 694. DOI:10.36956/rwae.v3i4.694
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free online
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Tropical Forage. 2020. Panicum coloratum
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.tropicalforages.info/text/entities/panicum_coloratum.htm
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The questionnaire is very comprehensive and inclusive to socio-economic and environmental benefits, and the effects of a specific SLM technology.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية