Vermicomposting [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
- المحررون: Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Likissa Kurmana Dufera
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Komposti Ramo
technologies_6643 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Dinqa Degu
Farmer
أثيوبيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The technology restores degraded soil and reduces investment costs on chemical fertilizers.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
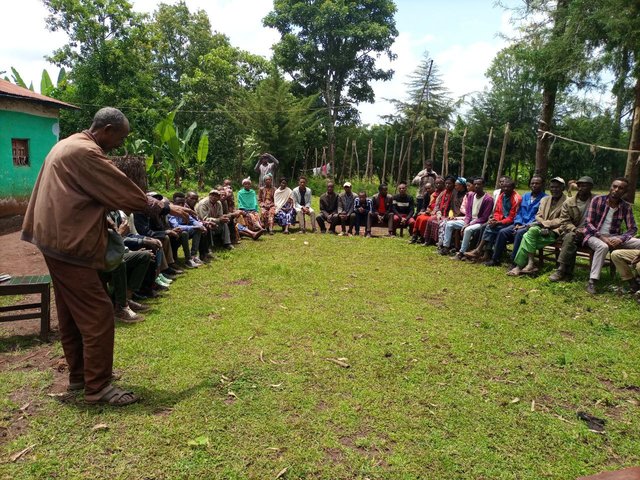

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [أثيوبيا]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
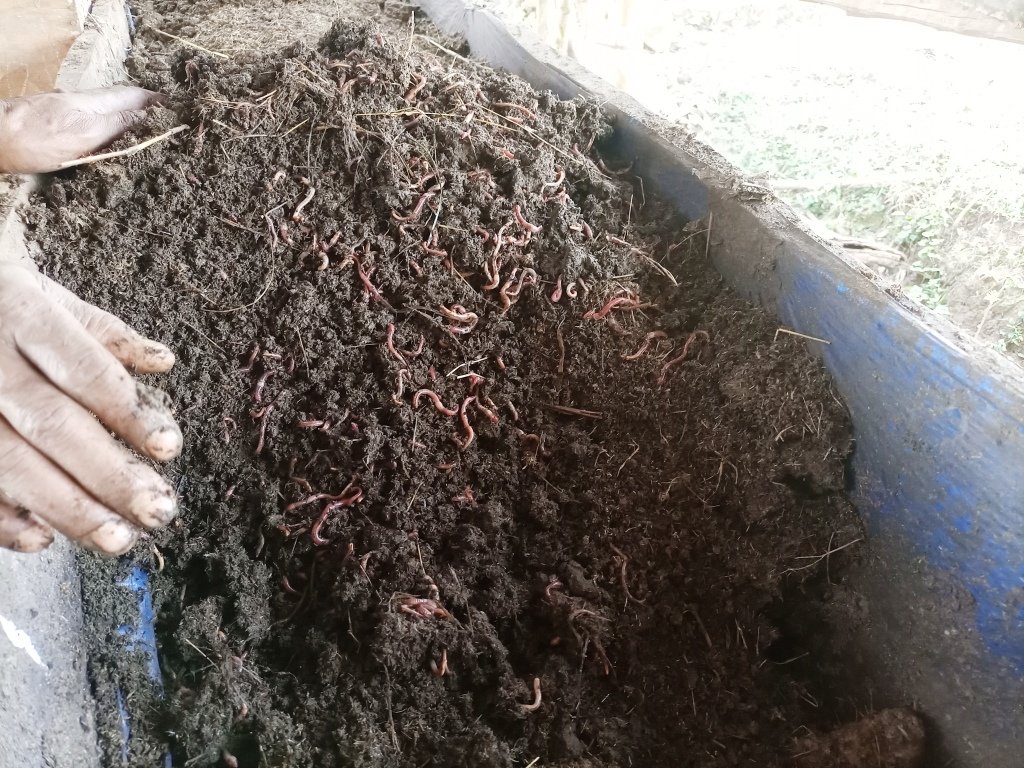
Vermicompost is the product of the decomposition process using various species of earthworms. It is a form of humus and is produced through worms digesting and excreting organic in their casts. Vermicompost has been shown to be an effective organic soil amendment, reducing the need for inorganic fertilizers.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
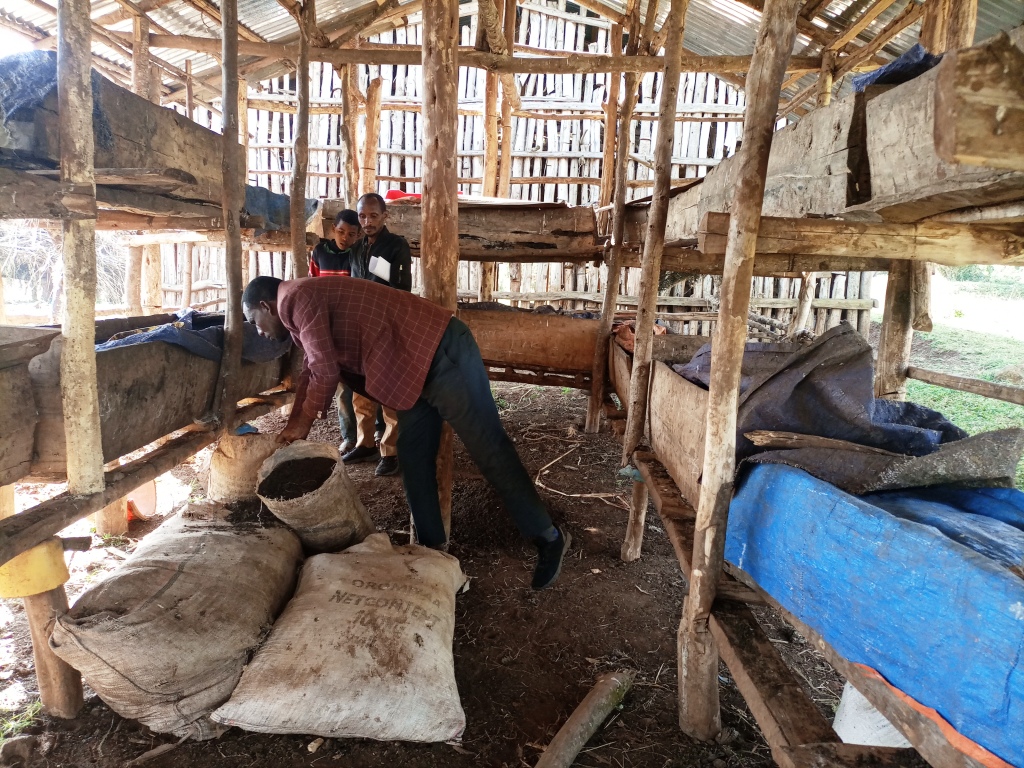
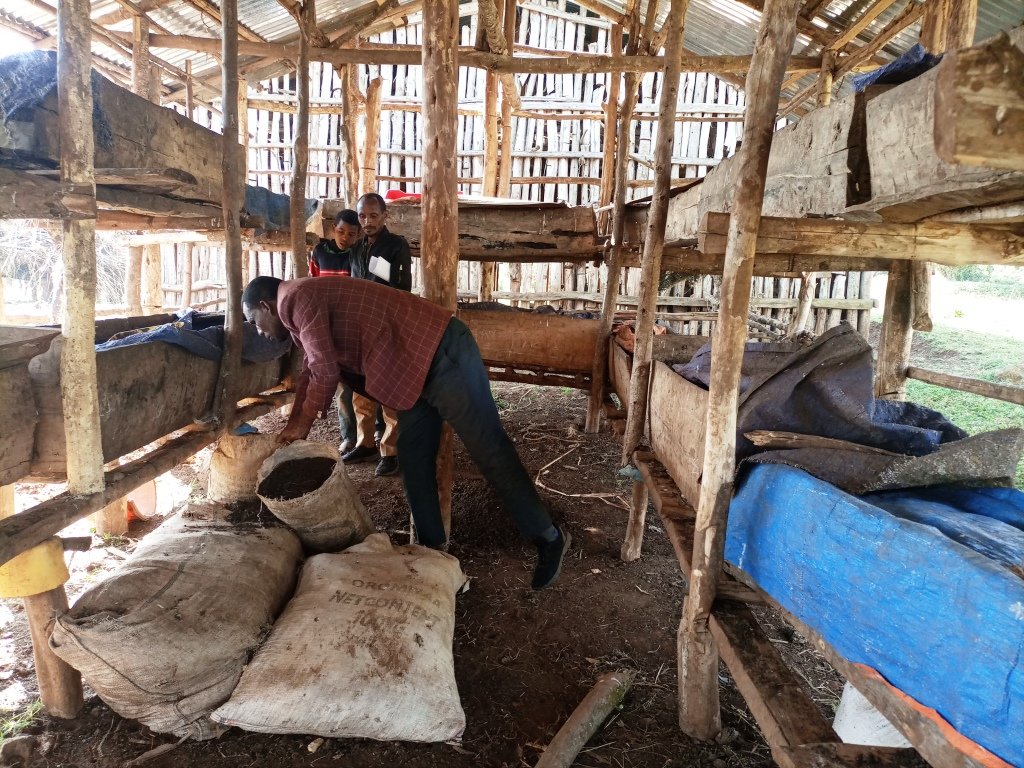
Vermicomposting is the process by which worms convert organic materials (usually wastes) into a humus-like material known as vermicompost. The process is an aerobic, bio-oxidation, non-thermophilic process of organic decomposition that depends upon earthworms to fragment, mix and promote microbial activity. In making vermicompost, earthworms are very good at transforming dead plant material, and livestock droppings into excellent manure. The excrement of the worms has high nutrient levels and a growth‐promoting effect on plants. Earthworms are very sensitive to changes in moisture and temperature. They need a continuous food supply and protection from ants, birds, and chickens. Compared to ordinary compost making, it needs maximum care. For optimum management practices, vermicompost production must be located close to the homestead where livestock barns are usually located. Livestock droppings (especially those of horses and donkeys) are the best sources of feed in addition to plant biomass and other household refuses. Vermicompost production needs a bin in which the worms live. This holds the bedding and food scraps, regulates the amount of moisture and temperature in the bedding, and blocks light which is harmful to the nocturnal worms. Worm bins can be made from plastic or wooden materials. In Ethiopia, wooden boxes are preferred because they are more absorbent and provide better insulation.
Vermicompost reduces farmers’ investment costs on chemical fertilizers. It also has a sustainable role in restoring soil fertility, ameliorating soil acidity and rehabilitating degraded farmland – all of which are problems in the southwestern part of Ethiopia. In the farm where vermicompost is applied, newly transplanted seedlings, in the case of vegetables, remain green and resilient as the compost improves not only the nutrients but also the moisture content of the soil. According to the land users, annual and perennial crops such as horse beans (Vicia faba), wheat, cabbages and avocados grown under vermicompost do very well. Under ideal conditions, 1,000 earthworms can convert 45kg of wet biomass per week into about 25kg of vermicompost. Therefore, the size of production depends on the number of worms, supply of foods, availability of boxes, and associated management practices. In rows and spot application of vermicompost during planting the crop allows efficient and effective uses of the products.
Currently (2023) the government in the southwestern zones of Oromia Region is promoting vermicompost as a vital organic fertilizer. This signals a change in the public sector's and end-users’ mindset in the use of organic fertilizer as a reliable soil amendment, particularly in acid-prone areas. In general, compost restores soil fertility, increases crop production and improves the livelihood of the end users. While the initial cost of constructing the house and installing bins and worms is high, there is potential for the use of local materials. However, it demands considerable household labour for upkeep.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Video of the technology was not taken.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Oromia, Buno-Bedele Zone
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Gechi district
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The technology is located close to the home.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2020
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
ISFM+ project (Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project of the GIZ).
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - قمح (ربيعي)
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- الخضروات - الخضروات الجذرية (الجزر والبصل والشمندر وغيرها)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Cereals with legumes (wheat with faba beans/horse beans).
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
Vermicompost was applied to produce Faba beans under rainfed and vegetable production under irrigated conditions.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة
- (Pu): فقدان الوظيفة الإنتاجية الحيوية بسبب أنشطة أخرى

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Chemical fertilizers trigger the soil to dry compared to vermicompost, which keeps the soil moist and the structure firm and coherent. This indicates relieving the degraded soil by changing its color and properties. Also, it allows an increase in the biodiversity of flora and fauna.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
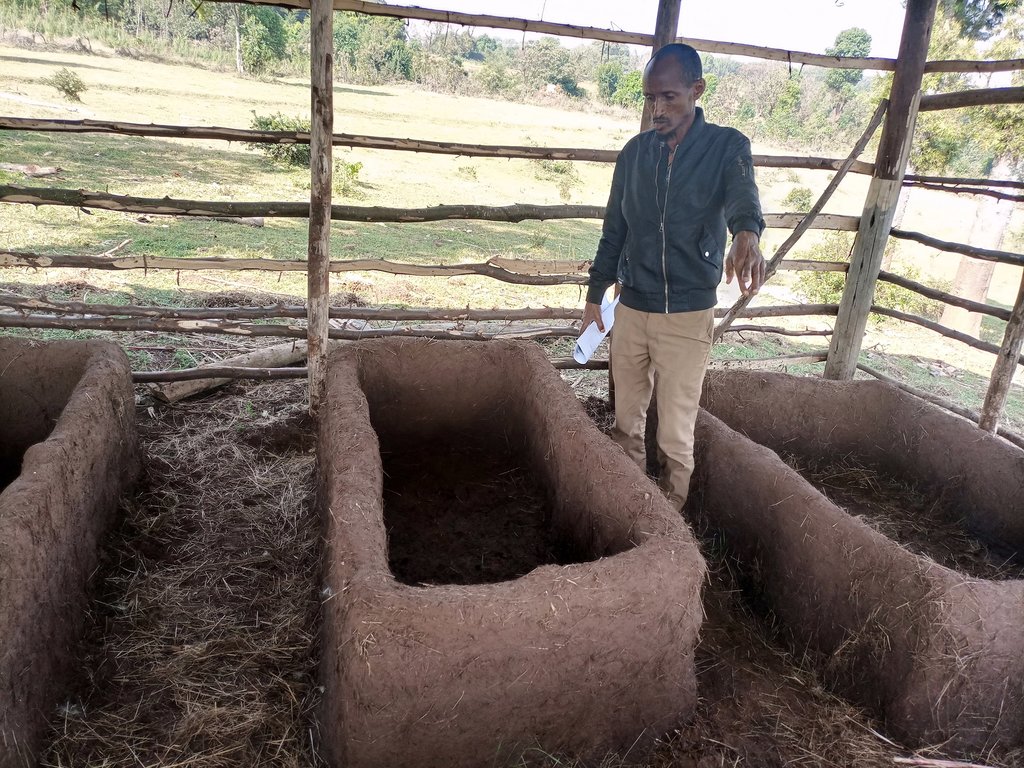
The box is also made with wooden pegs supported with thin horizontal bars and plastered by mud made of soil and water mixed with straw of teff (Eragrostis tef). The box is usually 3 meters long, 60 cm wide, and 50 cm deep, with a total capacity of carrying 0.9 m3 of worms and feedstock at a time. This is a manageable size with 50 cm wide between the structure to allow mobility of the caregivers for effective management of vermicompost.
المؤلف:
Gerba Leta
التاريخ:
04/02/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
House, boxes, worms, labor...
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
The preferred box size is 3m (L) x 50cm (W) x 30cm (H) with holes (0.5cm diameter).
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
ETB
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
53,12
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
200
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Constructing house or huts. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 2. | Build or purchase the worm bin/ boxes/structure with same function. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 3. | Purchase and/or introduce the worms. | Anytime, preferable before the main cropping season. |
| 4. | Add the food and water to the box/structure. | Regularly, through monitoring the status of the worms in the bin/box. |
| 5. | Monitor the surround from the predators and aerate the structure. | Regular monitoring is commendable. |
| 6. | Harvest and dry the vermicompost for use. | When the worms feed on the feedstock and cast the compost (brown humus). |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labor | PDs | 183,0 | 200,0 | 36600,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Boxes | number | 14,0 | 250,0 | 3500,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | House with corrugated iron sheet | Lump sum | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Worms | kg | 12,0 | 500,0 | 6000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 71100,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1338,48 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
ISFM+ project of the GIZ covered some minor costs of a farmer.
التعليقات:
Labour cost is estimated for a year, each with half a day for follow-up and care. The establishment price is just an estimation. A farmer can start with a few boxes: a couple or more boxes made of local materials that are less costly. Therefore, the estimation is based on the model farmer's approach since he used corrugated iron sheet roofed house and wooden boxes to establish the vermiculture/ vermicompost production center. Otherwise, locally available materials can be used to build hats and wooden structure with plastic lining to serve as boxes. Once established, the recurrent cost is limited to labor and some pesticides.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labour to supply feedstock and provision of other related management practices. | It needs follow-up and supplying the feedstock throughout the year. |
التعليقات:
It demands supplying feedstock and water, protecting the worms from predators, and providing other management practices.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labor for follow-up and related practices | PDs | 183,0 | 200,0 | 36600,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 36600,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 689,01 | |||||
التعليقات:
Family must sources free labour at least for half a day throughout the year.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The cost is consistently changing. It might be attributed to the economic crisis and the growing inflation.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Bedele
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The altitude is also descending as one travel from highland to lowland agroecology.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Species diversity has been improved with the application of compost to the farm.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري جدا
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
Land use right is half inherited, and the other half is self-appropriated but got approval from the local administration.
التعليقات:
The land user appropriated some parts of his possession and has changed the marshy land to a farm where irrigation water is accessible.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Abandoned for faba beans
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.2 tons/ha
التعليقات/ حدد:
The yield of Faba bean increased from negligible yield where a farmer abandoned it to over 1 ton per hectare.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
It was not scientifically measured but the farmer communicated the harvest of good seed size with better tastes as compared to the harvest without using vermicompost.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is an assumption and evidence that validate that compost favors the growth of diverse wild species. Also, it increases biomass production that associates with fodder or feed production.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
The use of vermicompost enables to regain of the lost crop species because of soil degradation.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
As it added organic matter to the soil, it improves soil structure and other attributes of the soil that improve the land.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
It reduces investment on synthetic fertilizers and allows to harvest organic products.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
As most of the distinctions between the treatments with SLM technology vs without technology are not properly documented by the land users, it is difficult to quantify them. However, the evidence from the demonstration plots shows the yield increments by more than quadruple per unit of land. Since then the technology is applied recently, and promoting documentation of the yield difference by the land users themselves is commendable to ensure access to reliable data.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Generally, it added value to the efforts of ensuring food as well as nutrition security.
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Health situation is converging with ensured food and nutrition security.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased through exchange visit and participatory learning of the effect of the technology on the farm.
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Slightly improved with access and use of the technology.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
This is with the assumption that vermicompost improve soil structure via the addition of organic matter and improves water infiltration than favoring runoff.
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراكم التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الحموضة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Vermicompost improves soil properties and related attributes to crop and the environment. Most of the assumptions made here are based on the knowledge and skills of SLM experts and land users than the empirical analysis because there is no such detailed data documented and available either by the land users or the project itself.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
As the application of the technology is on a plot basis, assessing its off-site effects necessitates widespread adoption and application of the technology. This may need long terms and intensive follow-up.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
As the technology is recently introduced, the level of awareness is low and it is in the pilot phase.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
Produced the boxes from local materials such as mud and posts.
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
The land users and the district ISFM+ project focal person modified the boxes by building with a bunch of sticks plastered with mud to replace the priceless boxes made up of timbers.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Reduce investment costs on chemical fertilizers. |
| Partly replace the role of chemical fertilizers. |
| Improve soil fertility and reduces soil acidity. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Rehabilitate the degraded land and improve the biodiversity of flora and fauna. |
| Reduce risks of crop failure. |
| Creat employment opportunity |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Labor demanding. | Engage family labor. |
| Shortage of biomass to supply feedstock. | Improve access to biomass supply and improve practical uses of crop residue and animal excreta. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of proper documentation by the land users inline with such comprehensive questions. | Promote the capacity of land users to document the various facets of the technology on land management, production, and other multiple pros and cons. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Two
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
One
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
One
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
05/02/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Organic Exchange. 2009. Soil Fertility Management: An introductory Fact-Sheet for Farmers and Projects.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free online
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
MoA. 2016. Technical Manual: Integrated Soil Fertility Management. SLMP Training Series 14. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free online
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Vermicomposting
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://composting.ces.ncsu.edu/vermicomposting-2/
7.4 تعليقات عامة
Similar to the other integrated soil fertility management practices /technologies, in this questionnaire, there are clearly irrelevant questions to this particular technology or too comprehensive to be addressed by the land users.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [أثيوبيا]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية