Compost for organic waste management and improved crop yields [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: William Akwanyi
- المحررون: George Onyango, Innocent Faith, Noel Templer
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mbolea bora (Kiswahili)
technologies_6648 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Anyanga Matthews George
Welthungerhilfe
كينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Farmers who have implemented the technology have recorded good harvests from their farms. The product of manure has improved their soils.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Composting with on-farm organic solid waste management improves the soil sustainably and raises crop yields.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
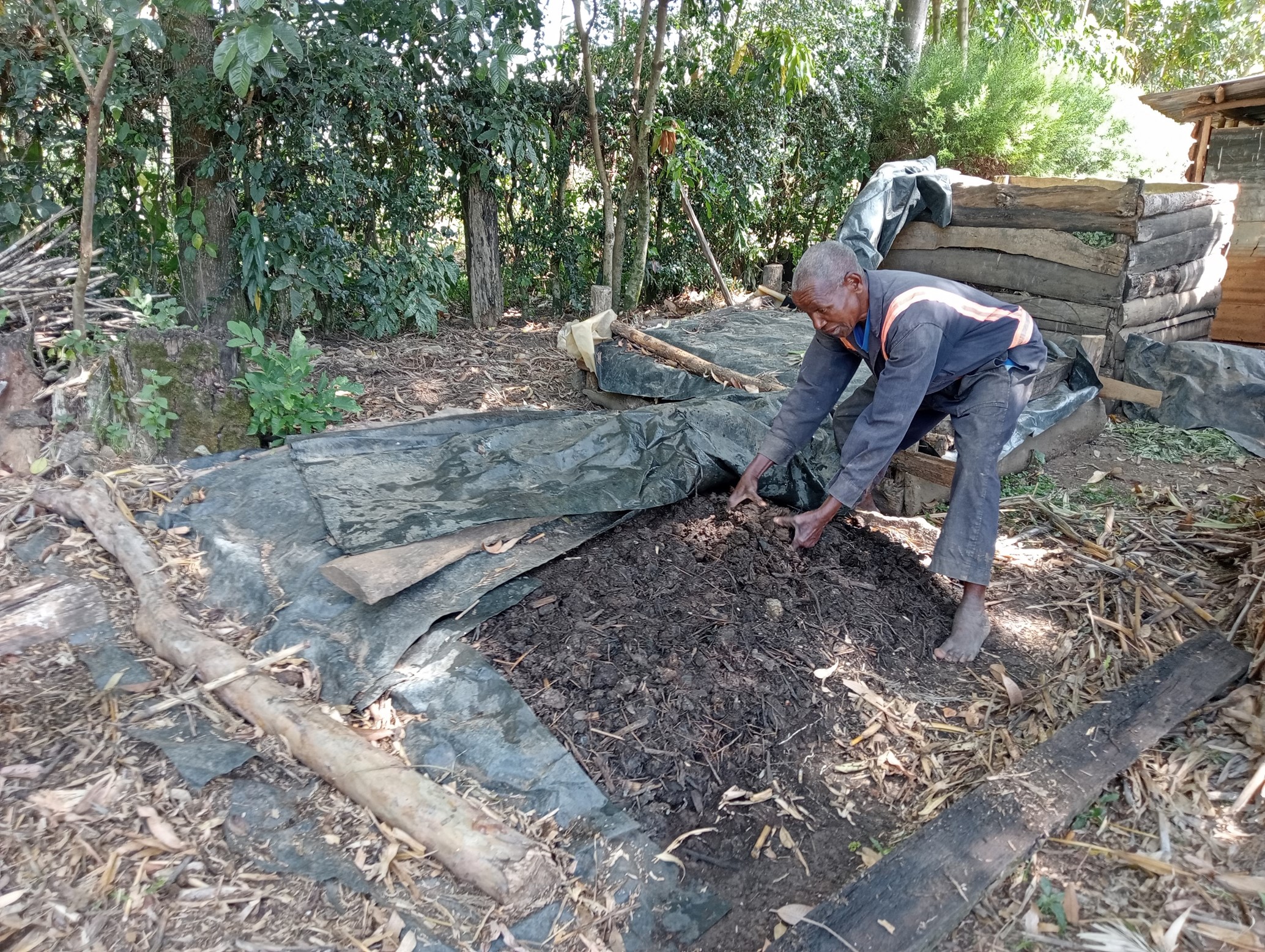
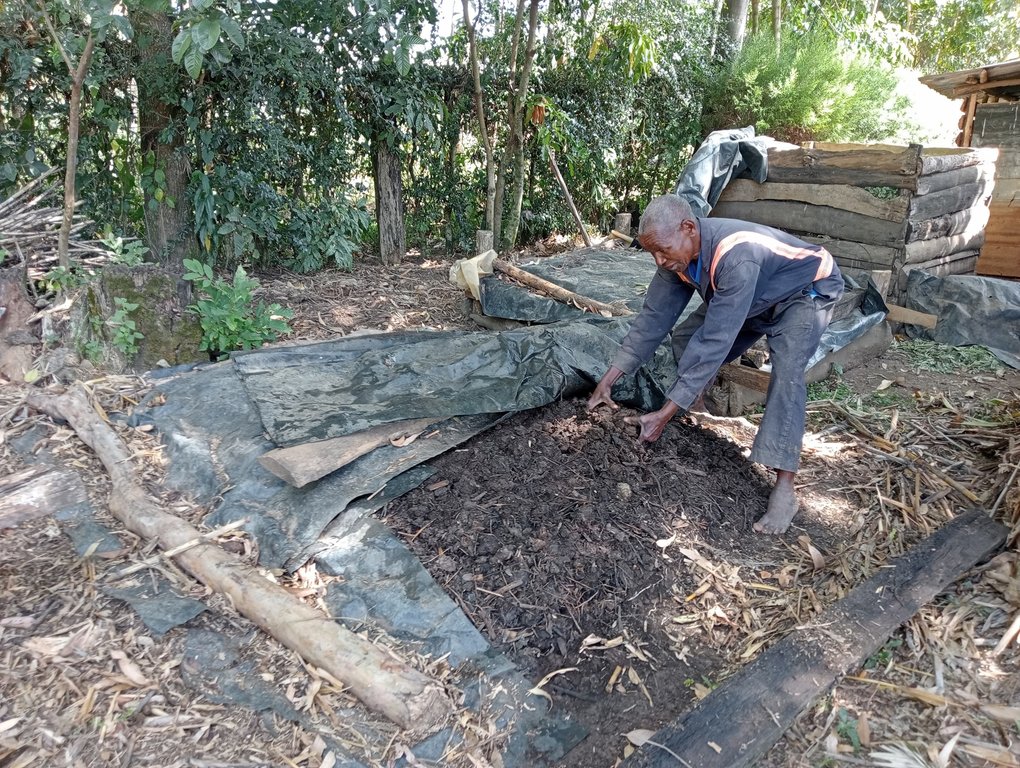
Composting is a natural process of converting organic materials such as plant leaves, and food remains into a nutrient-rich soil-enhancing amendment called compost (if mainly from vegetative matter) or manure (if mainly from animal dung). It involves breaking organic matter down into humus/ compost by aerobic microorganisms - with by-products of water, heat, ammonia (NH3), and carbon dioxide (CO2). Humus is a dark and crumbly natural form of fertilizer applied to the soil to improve crop production. Composting is cost-effective since it can be made from locally available materials such as leaves, plant residues, food remains, cow dung, poultry droppings, animal urine, soil, etc. Composting is thus an on-farm solid waste management measure. When made correctly it can improve carbon sequestration in the soil (compost is carbon-rich) and prevent methane emissions (a greenhouse gas) since methane-producing microbes become inactive in aerobic conditions (in the presence of oxygen).
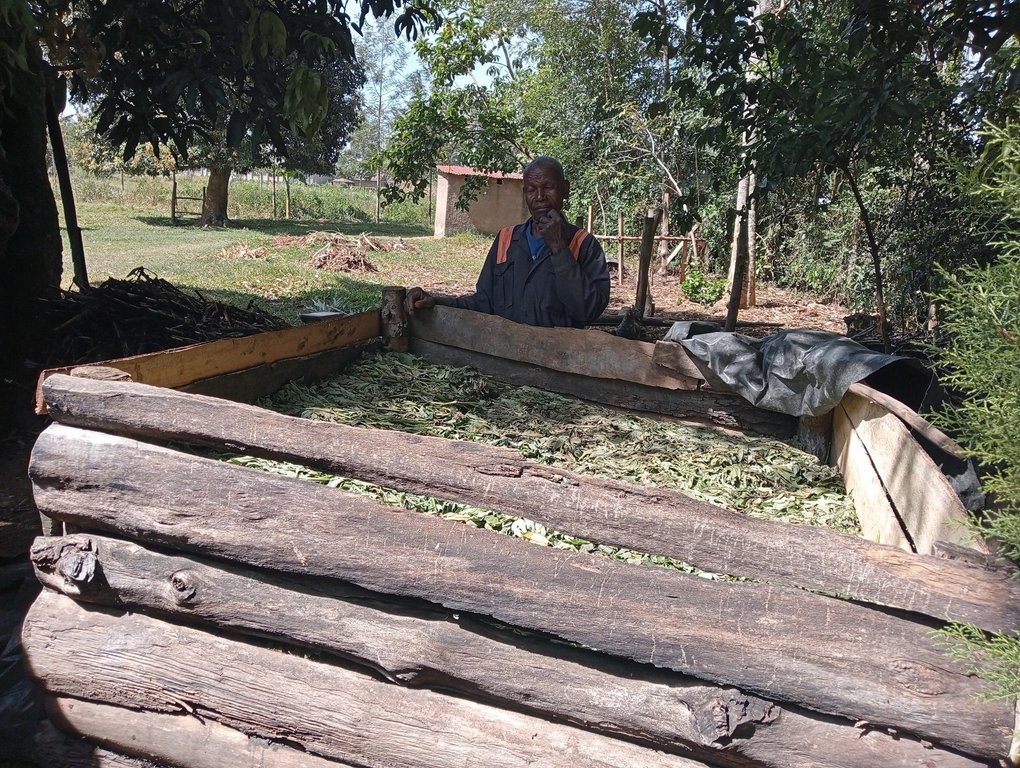
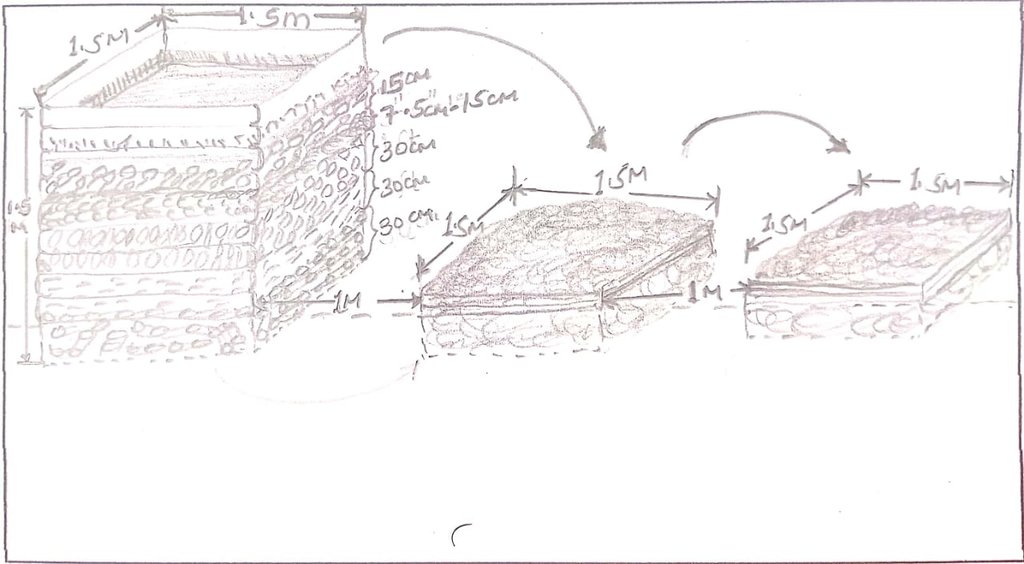
There are many ways of preparing compost. This method involves three key stages; mixing brown organic materials, such as twigs, and green materials, such as fresh leaves that are nitrogen-rich and moist. In the first stage, brown and green materials are layered, beginning with a 30 cm layer of twigs at the bottom, followed by a 30 cm layer of dry matter, such as maize straw chopped to a maximum of 7.5 cm. This is followed by a 30 cm layer of dry grass and dry leaves covered by a 7.5 cm – 15 cm layer of fresh cow dung. The fresh cow dung is covered by a 15 cm layer of fresh tithonia (an exotic plant) that is completely covered by a layer of ash and sprayed uniformly using 10 litres of animal urine and finally completely covered by a layer of soil or manure. All the above inputs except urine are sprayed with 10 – 20 litres of water. The pile is then completely covered with a black polythene sheet to help absorb heat, prevent the entry of rainwater, and prevent volatilization of nitrogen, i.e., the conversion of ammonium into ammonia gas, and left to decompose for 21 to 30 days.
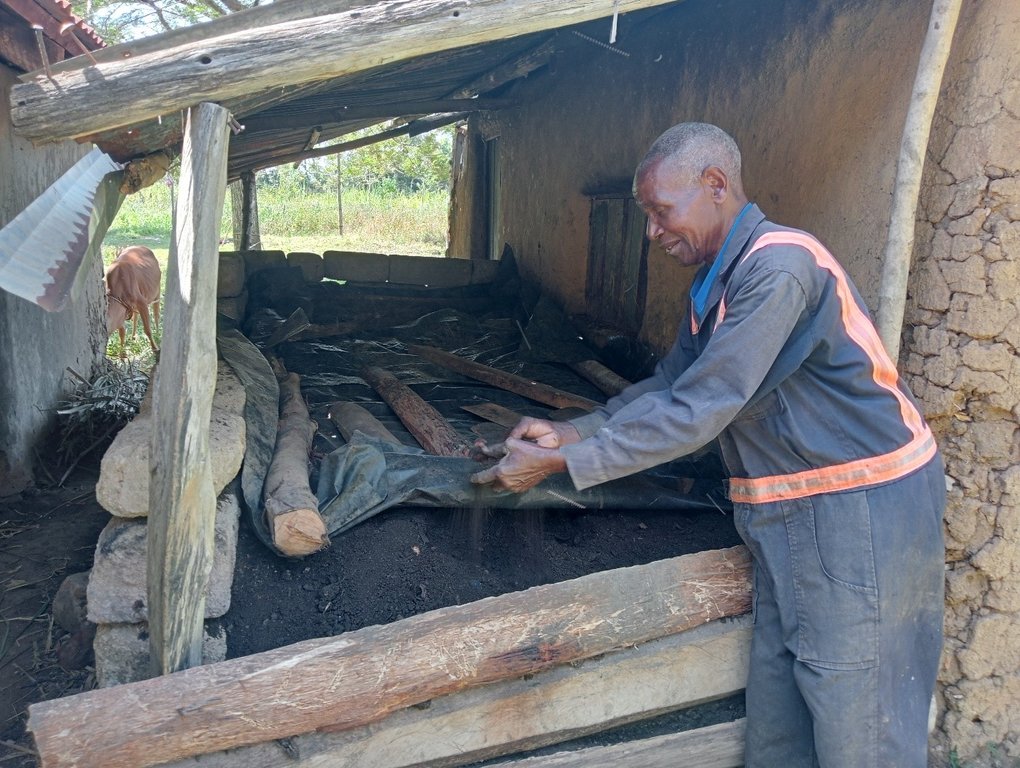
The second stage involves mixing and transferring all the material except the twigs, to another space. The heap is again completely covered with a black polythene sheet to help absorb heat, prevent rainwater entry, and prevent nitrogen volatilization. It is again left to decompose for another 21 to 30 days. The third stage, like the second stage, involves completely mixing and transferring all the material from the second stage to another space and completely covering the heap with a black polythene sheet to help absorb heat and prevent the entry of rainwater. The contents are allowed to decompose for another 21 to 30 days, after which they are ready-to-use compost. The compost is stored under shade and covered with a black polythene sheet again to prevent nitrogen volatilization.
One heap of compost (first stage: 1.5 m by 1.5 m by 1.5 m) produces about 5 tonnes of ready-to-use compost. Composting takes about 90 days; hence, provided that all inputs are available, a farmer can produce compost 4 times each year from the same heaping point, i.e., about 20 tonnes. Normally, a 0.4-hectare farm requires about 20 tonnes of this compost. However, the amount varies from farm to farm depending on the conditions of the soil and the crop(s) to be grown. It is important that soil testing is done to determine the conditions of the soil to ensure that the compost is being used in the most effective manner.
Compost is carried to the farm on wheelbarrows and in buckets and is applied at the farm during planting time where a handful of compost is applied in the planting hole and mixed with soil before planting. It is again applied around the base of the crop and completely covered with soil. Preparation of compost in conservation agriculture situations could pose the problem of competition for plant material since plant material is used in conservation agriculture to cover the soil. To manage this, a farmer implementing both composting and conservation agriculture may have to acquire plant material for composting from other sources such as purchasing stover from other farmer who are not implementing conservation agriculture. In addition, the farmer could also use hedge trimmings as plant material for composting, especially if the farmer has a live fence.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
Composting is a multi-stage process. The inputs/ materials in each stage must be completely covered with a black polythene sheet to help absorb heat, prevent the entry of rainwater, and prevent volatilization of nitrogen. The materials are allowed to decompose for at least 21 days in each stage before they are completely mixed and transferred to the next.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kakamega County in western Kenya
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Elang'ata Village, Bulanda Sub-location, Imanga Location, Marama Central Ward, Butere Sub-county
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The farm where the technology is implemented is not in a protected area.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2018
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
For years, the farmer has been converting farm wastes into manure. However, the Soil Protection and Rehabilitation of Degraded Soil for Food Security (ProSoil) project came in and taught them an improved method of composting that takes a shorter time compared with the traditional method, and prevents loss of nutrients during composting.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- محاصيل الأعلاف - الأعشاب
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - الكسافا
- خضروات - اخرى
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الذرة/الذرة الرفيعة/الدخن في زراعة بينية مع البقوليات
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الافوكادو
- فواكه أخرى
- المانجو، المانغوستين، الجوافة
- البابايا
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Long and short rain seasons
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Maize and beans
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة
نوع الحيوان:
- ماشية - الألبان
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
- الدواجن
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Cattle dung and poultry droppings are used as inputs in composting. Compost is applied on soil where livestock fodder is planted.
المنتجات والخدمات:
- الأمن الاقتصادي، ,وجاهة الاستثمار
- البيض
- روث الحيوانات كسماد/إنتاج الطاقة
- اللحوم
- الحليب
الصنف:
ماشية - الألبان
العدد:
2
الصنف:
الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
العدد:
3
الصنف:
الدواجن
العدد:
10
التعليقات:
There are assorted trees on the farm, and these provide litter which is an input in composting.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Crops are planted only during the rainy seasons since there is no irrigation.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- إدارة النفايات / إدارة مياه الصرف الصحي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A 6.3: تم جمعها
التعليقات:
Plant residues, especially leaves and soft branches are collected and used as input in composting. However, some plant matter is retained in the farm to naturally decompose and turn into manure at the farm. The farmer does not collect plant residues from protected areas. He has planted tithonia at some sections of the hedges at his farm; this provides the main source of tithonia. However, he sometimes harvests tithonia from his neighbours' hedges upon request.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض
- (Cp): تلوث التربة
التعليقات:
Covering of compost-making materials and the final compost reduces loss of nitrogen through volatilization of ammonium into ammonia gas. Compost raises the pH of soils when applied at the farm. Compost contains living organisms (bacteria and fungi) that degrade soil pollutants into non-toxic substances.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Compost improves soil structure and porosity. Compost balances soil pH.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Stage 1: about 30 cm deep under the ground, 1.5 m long by 1.5 m wide by 1.5 m high, including the 30 cm below the ground. Constructed using timber off-cuts (locally known as magogo) supported on posts at corners using nails. From bottom: 30 cm of twigs to extend some few inches above the ground to allow air circulation, 30 cm of dry matter e.g., maize straw chopped to 7.5 cm maximum, 30 cm dry grass and leaves, 7.5 cm - 15 cm layer of fresh cow dung, 15 cm layer of fresh tithonia, layer of ash, layer of soil or manure, black polythene sheet cover.
Stages 2 and 3: about 1-ft deep under the ground, 1.5 m long by 1.5 m wide, height depends on the volume of the material.
Allow space of no more than 1 m from one stage to the other for easy of mixing and transfer of materials from one stage to the next.
المؤلف:
William Onura
التاريخ:
26/01/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Heap of compost
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1.5 m by 1.5 m by 1.5 m
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
KES
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
122,95
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
200
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of pits | At least 3 months before planting time |
| 2. | Framework construction with off cuts | At least 3 months before planting time |
| 3. | Filling stage one with inputs | At least 3 months before planting time |
التعليقات:
Composting takes about 3 months; hence, the farmer should have the structures for composting at least 3 months before the planting time. A farmer can produce 20 tonnes of compost from 1 heap (1.5 m by 1.5 m by 1.5 m).
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Framework construction | Man-days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Filling inputs | Man-days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Jembe (hoe) | No. | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| معدات | Spade | No. | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | |
| معدات | Fork hoe | No. | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | |
| معدات | Wheelbarrow | No. | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | |
| معدات | Hummer | No. | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Handsaw | No. | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Twigs | Wheelbarrow | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Dry matter | Wheelbarrow | 6,0 | 50,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Dry grass and leaves | 90 Kg sack | 3,0 | 50,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Fresh tithonia | 90 Kg sack | 3,0 | 50,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Ash | 90 Kg sack | 0,4 | 200,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Animal urine | 10 litre container | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Soil or manure | Wheelbarrow | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fresh cow dung | Wheelbarrow | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Timber off-cuts | Pieces | 16,0 | 100,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Wooden posts | Pieces | 4,0 | 50,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Nails (assorted sizes) | Kgs | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Water | 20 litres container | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 6265,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 50,96 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
ProSoil project
التعليقات:
The ProSoil project through Welthungerhilfe provided hoes, fork hoes, wheelbarrows, and spades to the farmers. The costs of these implements are KES 400/- for a hoe, KES 350/- for a fork hoe, KES 4,000/- for a wheelbarrow, KES 450/- for a spade, KES 500/- for a hummer, and KES 1,000/- for a handsaw. It is assumed that the farmer will be able to use the hoe, fork hoe, spade, hummer, and handsaw over a period of 5 years, and a wheelbarrow over a period of 10 years before these implements will have depreciated to a point where they will not be useable. The cost is thus spread over the years when the farmer will be able to use the implement.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turning at each stage | 21 - 30 days after start of each stage |
| 2. | Refilling at the first stage | At turning from the first stage |
| 3. | Distribution to the farm | When planting and at first weeding (i.e., 3rd week after planting) |
التعليقات:
Turning involves complete mixing and transfer of the inputs from one stage to the next. Compost is applied at the farm during planting time where a handful of compost is applied in the planting hole and mixed with soil before planting. It is again applied around the base of the crop and completely covered with soil.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Complete mixing and turning from stage one to stage two and from stage two to stage three | Man-days | 4,0 | 200,0 | 800,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Refilling with new materials at the first stage | Man-days | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Transfer to storage | Man-days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Distribution to the farm | Man-days | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hoe | No. | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| معدات | Fork hoe | No. | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | |
| معدات | Spade | No. | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | |
| معدات | Wheelbarrow | No. | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | Dry matter | Wheelbarrow | 6,0 | 50,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Dry grass and leaves | 90Kg sack | 3,0 | 50,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Fresh tithonia | 90Kg sack | 3,0 | 50,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Ash | 90 Kg sack | 0,4 | 200,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Animal urine | 10 litre container | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Soil or manure | Wheelbarrow | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Fresh cowdung | Wheelbarrow | 3,0 | 200,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Water | 20 litres container | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 4165,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 33,88 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
ProSoil project
التعليقات:
The hoes, fork hoes, wheelbarrows, and spades provided by the ProSoil project through Welthungerhilfe are fixed assets and are used for years by the farmer before they can wear out. The farmer can use these implements for other work at the farm. The costs of these implements are KES 400/- for a hoe, KES 350/- for a fork hoe, KES 4,000/- for a wheelbarrow, and KES 450/- for a spade. It is assumed that the farmer will be able to use the hoe, fork hoe, and spade over a period of 5 years, and a wheelbarrow over a period of 10 years before these implements will have depreciated to a point where they will not be useable. The cost is thus spread over the years when the farmer will be able to use the implement. The twigs are reused during the refilling process since they take long to decompose.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another. It is not easy to attach monetary value to some of the input e.g., animal urine, cow dung, and water.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Kakamega Meteorological Station
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
The climate in the area favours most agricultural activities.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The farm is located at an area that is higher in altitude compared to other areas in the larger area. The average altitude for the area is 1,350m above sea level but the farm is at 1,401m above sea level.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil pH of most farms in the area ranges from moderately acid (5.50) to moderately alkaline (7.80).
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
The area has high agrobiodiversity since most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
التعليقات:
The farmer has an official ownership title for his piece of land. He also leases other people's pieces of land for farming. Water in the streams and springs is freely accessed without restrictions. There is a borehole in the neighbourhood, and the managers of this borehole have set rules for accessing the water thereat.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less than 4
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
More than 8
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre. Based on measurement by the farmer.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify. The crops do better compared to how they could do in the past, yet he does not use inorganic fertilizers. Based on estimation by the farmer.
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3 - 4
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to harvesting cycles for nappier grass from the same farm. He applies compost on the pieces of land where he has grown fodder. The fodder does better than how it used to do before when he was not applying compost.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
He applies compost on the pieces of land where he has grown fodder.
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1 - 3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3 - 10
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the amount of milk in litres from one cow. He gets more milk from his cows as compared to what he used to get before the SLM since applying compost on the pieces of land where he has grown fodder makes the fodder to grow faster. Milk production is often at the peak during early lactation months.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Over 50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less than 10
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well. Quote from the farmer, '... it was 50 50 getting any produce before I started using compost ...' meaning that there was high chance that the crop could fail due to poor soils. Compost is a rich source of organic matter; hence, ensure sustainable agricultural production.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Over 5,000
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the amount of money in Kenya shillings spend on inorganic fertilizers in a season. The farmers no longer spend money inorganic fertilizers.
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less than 2,000
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20,000
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the amount of money in Kenya shillings received from the sale of farm produce, including compost in a year. The farmer is able to sell surplus crop and animal products as a result of bumper harvest due to the use of compost on his farm.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1 - 3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
More than 3
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to household income sources, including sale of surplus farm produce and compost. The farmer is able to sell surplus crop and animal products, and other on-farm products such and compost.
عبء العمل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Over 5
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less than 1
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of hours that the farmer can be free in any working day. A lot of work is involved in the preparation and maintenance of compost in order to achieve the desired results.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
About 3 months of purchasing maize
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
No months when there is total lack of food in the house
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house. The soils at the farm have been enhanced; hence, the farmer grows a variety of crops. Food is available in the household to sustain the family from one harvest to the next.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Over 90%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management. Not only is the farmer equipped with skills on how to make compost but also with skills in other SLM technologies such as vermicomposting.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Less than 10
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20 or more
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated soil moisture content during the dry season when soil moisture challenges are expected to be high.
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30 - 50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60 - 80
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated percentage soil cover at the farm.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated percentage of organic matter at the farm. Based on estimation by the farmer.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30 - 50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60 - 80
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated percentage vegetation cover at the farm.
التنوع النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
About 3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
More than 5
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of plants (crops) that the farmer establishes at the farm.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify but the number of earthworms in the farm and bees visiting the farm to look for nectar has increased.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify but the number of earthworms in the farm has increased which is an indication of increased habitats for different animals at the farm.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the probability of the neighbours' farms being burned because of available plant residues. The farmer collects residues from his neighbours' farms for use in composting. The neighbours could have burned the residues leading to death of useful microorganisms (bacteria and fungi).
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify. Composting improves carbon sequestration in the soil and by preventing methane emissions through aerobic decomposition, as methane-producing microbes are not active in aerobic conditions.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| حريق الأرض | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Flammable plant residues are used as inputs in composting and, thus, the risk of fire is reduced.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Use of compost reduces the dependence on inorganic fertilizers.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 11-50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
The project was implemented in the entire ward. Most farmers are preparing compost as advised in the ProSoil project.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
Most farmers are able to implement since the investment cost is not very high.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| With continued use of compost, there is no need for expensive inorganic fertilizers and pesticides that could also contaminate/ degrade the soil. |
| Composting is not capital intensive. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| There is high production in the long run even without use of inorganic fertilizers. |
| Composting is not capital intensive. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Inputs such as tithonia are not easy to find. | Farmers can plant tithonia as hedges on their farms. |
| More labour intensive as compared to the traditional way of composting. | Farmers have to be committed. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| More labour intensive. | Proper planning/ scheduling of farmm activities. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
One visit at one farm
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up questions on phone.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
26/01/2023
التعليقات:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Comparative effectiveness of different composting methods on the stabilization, maturation and sanitization of municipal organic solid wastes and dried faecal sludge mixtures, Mengistu, T., Gebrekidan, H., Kibret, K. et al., 2018, Environ Syst Res 6, 5 (2018)
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free download at https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-017-0079-4
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Composting Recycling Naturally: Simple Steps for Starting at Home
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://scdhec.gov/sites/default/files/Library/OR-1705.pdf
7.4 تعليقات عامة
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية