Water Spreading Weirs [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
- المحررون: Torben Helbig, Noel Templer
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Biye Baahiwe
technologies_6715 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mohamed Badal
Natural Resource Development Protection and Utilization Department of Somali Region Bureau of Agriculture.
أثيوبيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
It is soil and water conservation and degraded land rehabilitation technology. Furthermore, the water harvested can be used for spate irrigation and growing food crops and livestock feed.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Water Spreading Weirs are designed to protect the degradation of agricultural fields and rangelands. They contribute to soil and water conservation and enhance the productive use of dry valleys for food crops and livestock fodder production via the harvest and spread of runoff water and fertile soils.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
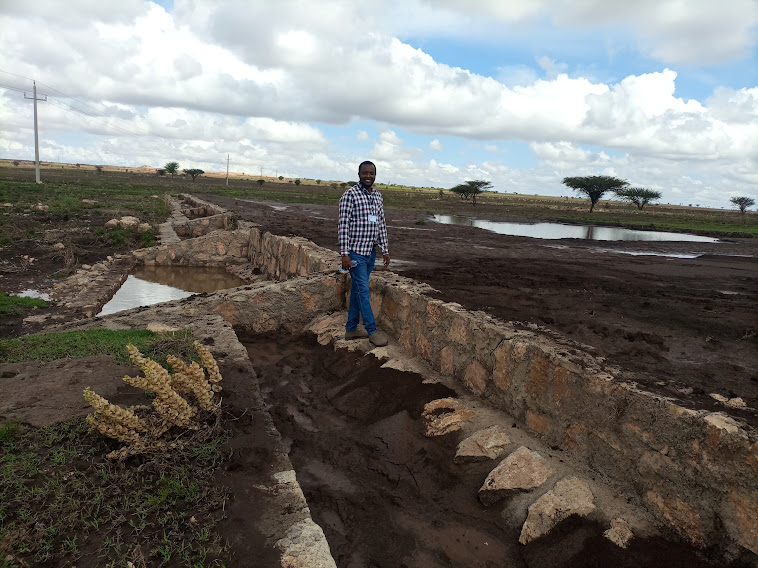
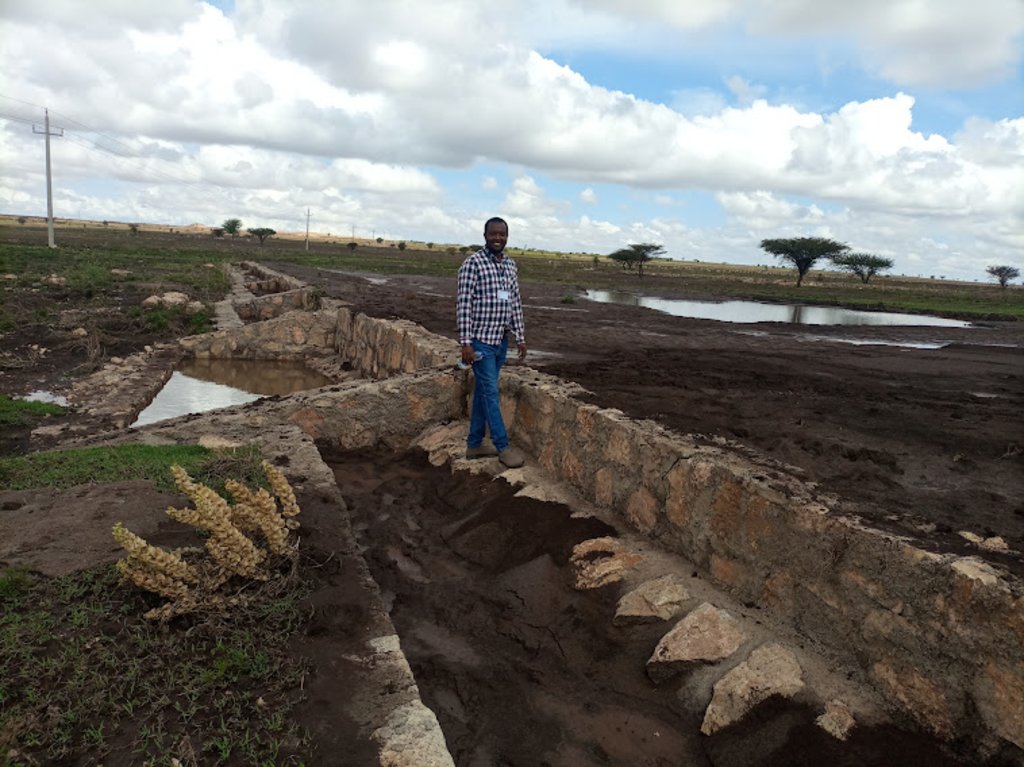
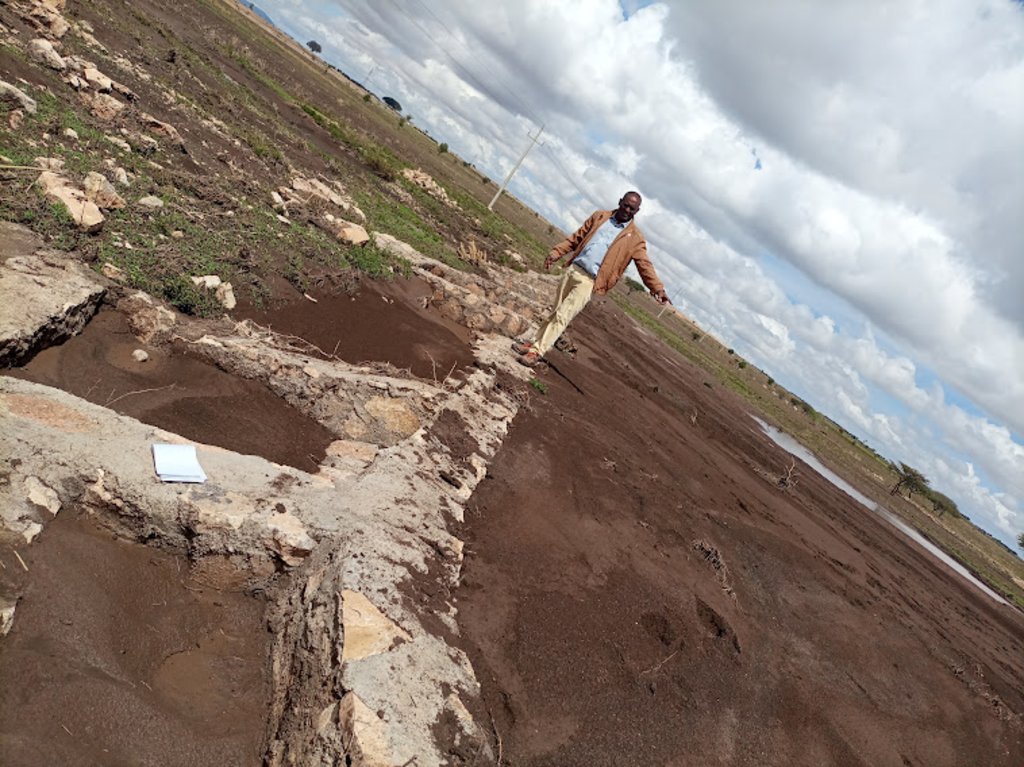
Water Spreading Weirs (WSWs) spread runoff water to the tips of the structure's wings, slowing down the speed of runoff and arresting the sediment pouring downstream. WSWs are applicable both on farmland and rangelands to improve the productive use of the land’s resources. They protect soil erosion and control gully development as well as increasing surface and sub-surface water availability. Activities such as mobilization of the community through awareness creation are among the numerous tasks implemented to put the technology in place. The community participates in site selection and participatory planning. Other stakeholders assist in area delineation, profiling the implementation area, and design. Labour and inputs such as surveying and construction materials, notably stone, sand, water, and cement, and equipment such as line levels, theodolites, spades, hoes, forks, string and measuring tapes etc. are required. On top of these, implementing the technology is supported by satellite images and ground validation exercises.
The main purpose of the technology is to reduce land degradation, harvest and use runoff water for spate irrigation and household uses, improve environmental resilience to the risks of drought, increase the depth and fertility of land behind the structure by capturing sediment washed away, allow infiltration of water and increase overall production of food and fodder crops. Also, the contribution to groundwater recharge is immense. Furthermore, it allows the agropastoral community to grow both cash and food crops which helps to ensure food security. Above all, the water harvested means people can remain in the area and that their livestock have access to drinking water for about three months after interception of rainfall. However, the agropastoralists may be discouraged by the size of the WSWs which can be from one hundred to over two hundred meters across. Care also must be taken that the structures do not cross livestock migration routes.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
The photo is trying to portray the water and soil harvested/stopped from running downstream. The detachment and removal of the topsoil without cover and fragile soil types are easily removed and transported to a long distance beyond the regional territory. The trends denied the productive use of land resources. In contradiction, the structure mitigates the loss of water and soil.
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Somali
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
It is located on the farmland used by the extended family and beyond.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2022
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology was put in place in partnership with the government bureau of agriculture and line office with the Capacity Development and Strengthening Drought Resilience (CDSDR) Project of the GIZ in the Somali Region.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول -فول الصويا
- خضروات - اخرى
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
The legume crop is chickpea. Whereas, the vegetables are tomato and onion.
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Maize is intercropped with chickpeas.
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Cereal crop sorghum rotates with maize and chickpeas. Essentially, crop production suffers from a lack of adequate rainfall. For example, during the last two to three years the area experienced drought. Mainly livestock supports the livelihoods of the inhabitants.

أراضي الرعي
- Agro-pastoralist
نوع الحيوان:
- الجمال
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
- الماعز
- الأغنام
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Essentially, the farming operation is practiced by oxen-plow in which case the animals provide traction force whereas crop residue supply feed to the animals.
المنتجات والخدمات:
- روث الحيوانات كسماد/إنتاج الطاقة
- اللحوم
- الحليب
- النقل/الجر
التعليقات:
Agro-pastoralism is the common practices in Amadle kebele of south Jijiga district.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
The rainfall distribution is erratic with violent erosive feature flooding the plain with severe damage when flowing downstream.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
التعليقات:
The technology is Water Spreading Weirs, stop the run-off and distribute the water across the farmland.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wm): مجموعة كبيرة من الحركات الأرضية/انزلاقات أرضية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- انسداد مسام التربة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
التعليقات:
The technology/structure contributes strongly to soil and water management. The tremendous loss of both resources is immensely reduced by the application of water spreading weirs.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
The technology reduces the speed of runoff, stores the sediments, and distributes the water across the structure which creates an opportunity for spate irrigation and the use of residual moisture as supplemental sources of irrigation for growing early maturing crops.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
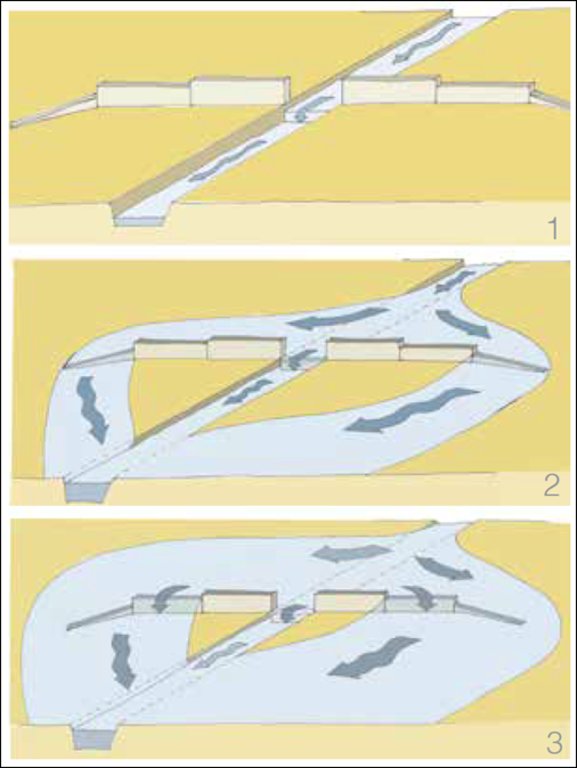
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Spate schemes depending on the increase supply flow:
Part i: The flow of small flood rested channel in the river bed
Part ii: A small or medium flood and overflows pours on the lower wings, &
Part iii: A large flood also pours on high wings.
المؤلف:
Anonymous consultant
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
1 WSW
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
Variable ( could be from 100m to over 200m depending on the steepness and width of the farmland.
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
8.414 USD
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assessing the field (observation) | |
| 2. | Consult the local community along with agricultural partners at different levels | |
| 3. | Surveying and profile data collection | |
| 4. | Develop design and get approval | |
| 5. | Outsource the engineering/masonry works | |
| 6. | Train the masonry workers | |
| 7. | Supply materials | |
| 8. | Implement (execute the excavation and the masonry work) | |
| 9. | Monitor the development (construction supervision) |
التعليقات:
Note: 1 USD = 53.481 Ethiopian birr (ETB) when this data is collected.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
27490,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
So far, the project entirely cover the investment and maintenance costs.
التعليقات:
According to the project and regional bureau of agriculture experts, a single structure costs 27, 490 USD. However, in one cascade (dry valley treatment unit) about 8-10 structures are necessary to successfully address the objective of the technology (Soil and Water Management) and ensure productive use of the land from soil arrest and residue of moisture captured in the area. It also enables the use of runoff for spate irrigation.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assess and identify the damage | During the off-season for ease of access to the sites |
| 2. | Estimate the level and cost of damage | During the off-season |
| 3. | Supply materials | |
| 4. | Employ the masonry worker | |
| 5. | Construct /maintain the damaged parts | Before the short/long rainy season. |
التعليقات:
Maintenance costs are largely associated with the degree of damage and cost of materials and masonry worker or labor costs that consistently changing in current Ethiopia.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
12154,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The cost is borne by the project.
التعليقات:
The technical experts give only an estimate of both initial investment and maintenance costs. Variations in materials and labor costs are frequent beyond the imagination. However, maintenance depends on the degree of damage. It seems that maintenance cost estimation takes the highest sides which may dishearten the adoption of the technology in the absence of projects.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Economic crisis and frequently escalating material costs along with rising financial inflation.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
750,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall is erratic and erosive. The project site receives rainfall twice a year (Belg- short rain from March to April and Meher- long rain from June to September). However, the number of days on which rain is intercepted is fewer than the ranges stated over here.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Jijiga Meteorology station
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
South Jigjiga district is characterized by hot weather.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The topography where WSW technology/structures are put in place is mostly on gentle slopes across the dry valley drainage line.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
The soil ranges from black silty loam to brown silty and fragile soils that are highly vulnerable to flood. It easily detached and moved away with runoff.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
حدد:
As the weather of the area is often too hot salinity is not uncommon in the aquifer.
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Rainfall is characterized by erratic and erosive nature. Therefore, flooding is common when heavy rain is intercepted.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Less biodiversity of plant species. Acacias are the common trees, and opuntia and euphorbia species are also common plants in the area. A wild species that may be considered invasive is common in the area. The lower growing weed (wild species) locally known as Weylowed is suggested introduced from Yemen to the Somali part with onion.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
It is the community who are benefiting from the technology. Furthermore, this respondent is a regional SLM specialist. Therefore, specific information on age and gender is not given here though the community was also consulted.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Extended family groups of four households are using the land where the WSW is put in place.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
Land use right is based on clan and extended family.
التعليقات:
The land is also owned by individuals. However, there is no land measurement and certification in this region.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is the expert's conviction that crop production in the area increased with water harvest and spread over the farm for use as spate or supplementary irrigation to the seasonal rainfall.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the moisture harvested by the structure is believed to add grain filling period, the crop quality is also expected to increase.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Fodder production also increases with the availability of good soil and moisture conserved in the farm behind the structure.
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increases with increasing availability of feed or fodder from either crop residue, natural grass or browse.
إنتاج الخشب
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
It rather improves crop resilience because of improved soil moisture.
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Opportunities can be created to increase the size of land under farming with increasing availability of moisture and fertile soils.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Moisture availability eases the management operation.
توليد الطاقة
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
نوعية مياه الشرب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Basically, quality is not a priority issue for agro pastoralists in dry valley areas.
توافر المياه للماشية
نوعية المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
نوعية مياه الري
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the structure reduces the degree of degradation, expense on agricultural inputs is believed to be reduced.
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
It promotes land users' understanding of SLM through training and exposure to the actual structure and soil and water harvested behind the structure.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
They may manage to access water for livestock drink and/or household consumption.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The structure harvests soil moisture on the farm. It reduces the speed of runoff, stops, and spread over the farm.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased through production of more biomass.
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The physical barriers stops the soil and water loss.
تراكم التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الملوحة
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is related to a warm climate that triggers evaporation and salinity development in the long run.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الحموضة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
آثار الجفاف
آثار السيكلون والعواصف المطرية
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
سرعة الرياح
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
As the intervention is in its early phase, it is difficult to give an assumption before and after the application of SLM (technology or physical structure). However, a 40 years old woman known as Run Muhamed gave us her insight into the productivity of the land by comparing the hindsight vs the current harvest under highly erratic and erosive rainfall distribution. Accordingly, over the years the harvest per hectare diminished from 0.75 ton/ha to 0.1 ton/ha. This signals the effect of climate change/climate variability and land degradation on crop production. Her household is one of the owners of the land among the other four members of the extended family where the WSW was put in place.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the structure is recently constructed, it is dire to envisage the off-site impacts of the technology at this juncture. However, it has a positive contribution to the availability of groundwater in the adjacent farms.
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Streams are less common in the dry valley.
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
It reduces the speed and volume of downstream flooding.
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
Need an investigation of its impact on the groundwater.
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Believed to reduce it in the long run.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The intervention believed to improve the existing negative consequences of degradation through promoting soil and water management and reducing risks of crop failure.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفة رملية/ غبارية محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان مفاجئ | باعتدال |
التعليقات:
After an extended dry year, like this season, the technology is overloaded with a flash flood. The soil was frequently exposed to the sun and the prevailing heat waves in the area were easily detached by torrential rain. Then the soil and water were partly arrested whereas an immense amount washed away. It seldom could topple the structure if not the cascade comprises eight to ten structures with relatively short intervals to support one another. Furthermore, the dry valley soil is very fragile let alone exposed to a long-term drought that is associated with a heavy shower at the beginning of a short season like this season.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
التعليقات:
It is a technology implemented at the community or extended family level. It is too early to evaluate the adoption trend at this particular time.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The technology/structure reduce soil and water erosion. |
| Harvest water and make the people and livestock beneficiaries from the still water for crop production, drinking, and household uses. |
| Increase soil moisture and risks of crop failure because of shortage of rainfall. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Rehabilitate both degraded agricultural and grazing lands. |
| Improve agropastoralist access to livestock feed and benefit from the positive impact caused by the technology. |
| Eventually, contributes to the improvement of ecology and overall ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High initial investment cost. | Enhance the in-kind contribution of the land users, and increase matching funds from the government as cost-sharing with other projects. |
| Agropastoralist complains about the space it occupies in their farmland regardless of the benefit they accrue over a long period. | Increase the awareness of the community on the productive uses of the degrading land based on the evidence. |
| The structure may fall over the livestock migration/travel routes that are not acknowledged by some members of the community. | During masonry work, precaution is essential to calm down the possible complaints that could emerge because of the raised structure by leveling the crossover roads/paths. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| An inadequate number of structures in a cascade subjected to ineffective soil and water management and distribution of rainwater to support as supplementary sources of moisture for crop production. | Increase the number of structures per conceptual statement and standardize the intervals between the structures. |
| Excessive land users' desire that is unassociated with a tangible contribution to the development of the technology from their side. | Further building land users understanding of SLM technologies and their benefits so that they can build a sense of ownership and accountability to contribute and complement the external efforts. |
| Land users give emphasis mainly on the immediate benefits of the technology (harvesting water for livestock drinking and household use) than the objectives of rehabilitating the dry valley for productive use of it such as crop and livestock feed production. | Acknowledging the immediate benefits, and the mainstreaming work regarding the pillar objectives of the project intervention. |
| The initial investment, as well as maintenance costs, are either expensive or overestimated by local actors. Such a higher cost may discourage land users in the absence of projects or SLM funds. | It would be good to be pragmatic in cost estimation. Furthermore, adapting the technology using local materials may promote the adoption and sustainability of the structure for widespread use. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Three individuals.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
One person.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Four individuals.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
23/03/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Mekdaschi & Linger, 2013. Freie Universitat Berlin
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://www.geo.fu-berlin.de/en/v/iwrm/Introduction/Principles/index.html
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Water-spreading weirs
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.unccd.int/best-practice/water-spreading-weirs
العنوان/الوصف:
Water Spreading Weir - NATURAL RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://nrmdblog.wordpress.com/2016/12/12/water-spreading-weir/
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The questionnaire is inclusive and more relevant to evaluate such physical structures as a technology. However, successive drought seasons experienced in the area subject the fragile soil to be easily detached and immensely moved by the early rains past the structure. This may affect the valuation of the efficiency of the technology since dry areas are also characterized by a flash flood that could certainly mask the benefits of such a good technology.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية