Leaf Litter Collection for FYM Production [بوتان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Karma Wangdi
- المحرر: Tashi Wangdi
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sochhag Tey Nor Lue Zhoni (གསོ་འཕྱག་སྟེ་ནོར་ལུད་བཟོ་ནི།)
technologies_6818 - بوتان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Norbu Dawa
Lingmukha Chiwog (Community), Lingmukha Gewog (Block), Punakha Dzongkhag (District)
بوتان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - بوتان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
This technology is practiced for decades without any problems regarding land degradation. While leaf litter collection can have positive effects when managed sustainably, there are also potential negative impacts associated with excessive or improper leaf litter collection
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
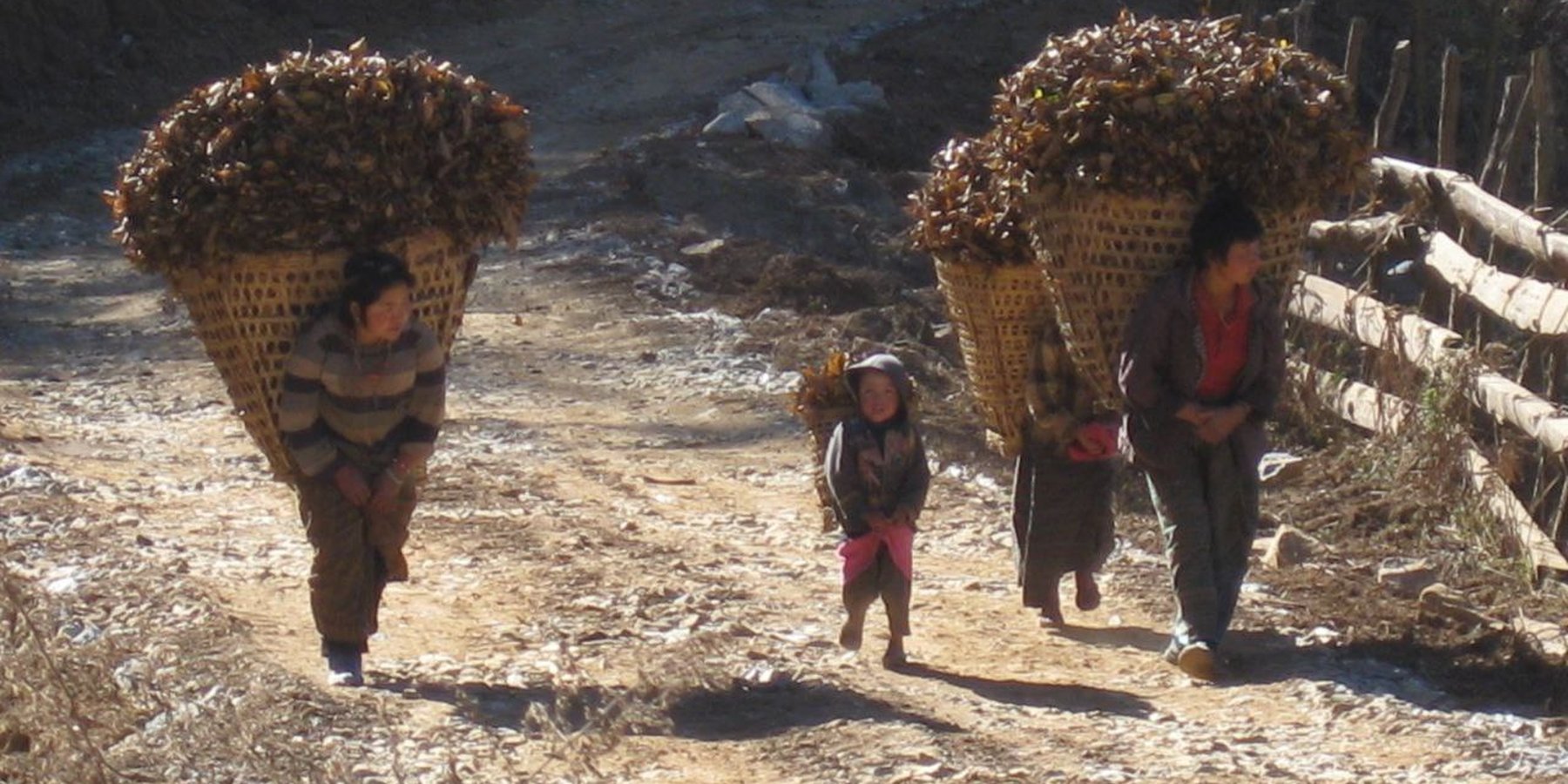
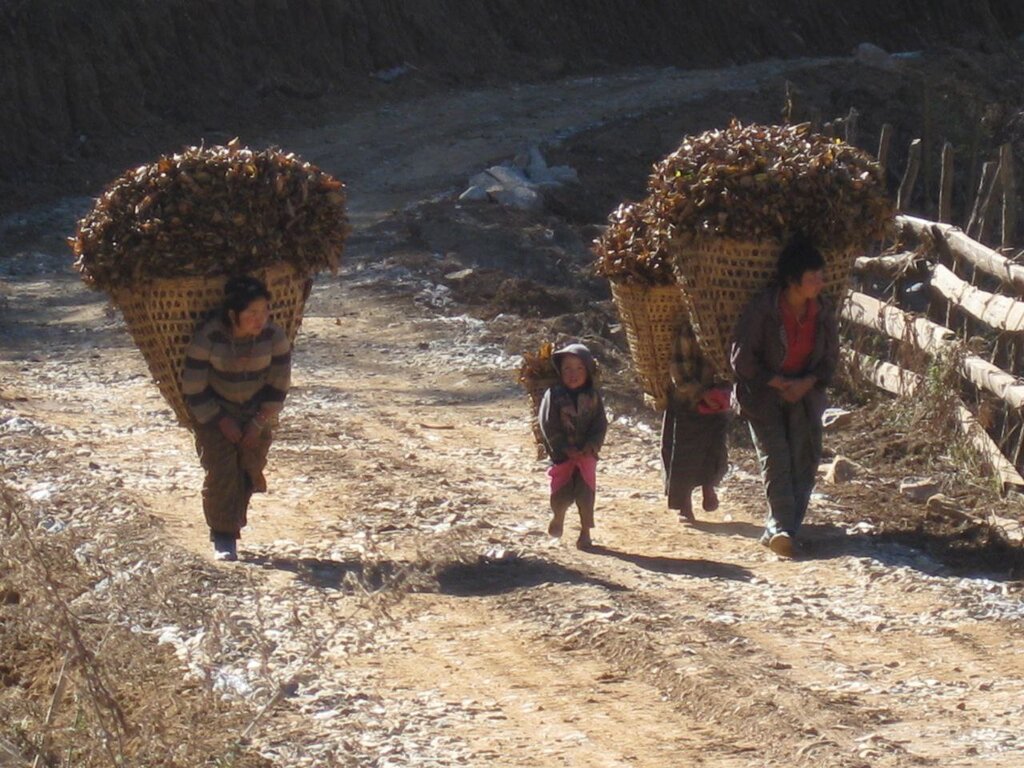
Leaf litter collection is the practice of collecting leaf litter from a designated forest area called sokshing and using it as bedding material for cattle. It then forms a constituent of farmyard manure which is applied to farmland.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Leaf litter collection, is the practice of collecting leaf litter from a designated forest area called sokshing and using it as bedding material for cattle. It then forms a constituent of farmyard manure which is applied to farmland. The term 'sokshing' comes from 'sok' meaning leaf litter and 'shing' meaning tree. The tradition of harvesting leaf litter from a designated forest area for agricultural use has been in practice for decades in the life of Bhutanese farmer (Chettri et al., 2012). According to BHUCAT, 2012, the use of sokshing is a widely used traditional farming practice in Bhutan with dominance in temperate regions but spreading into more humid subtropical areas. Leaf litter from the forests is used for the purpose of livestock bedding and then farmyard manure (FYM) production. Leaf litter as animal bedding is kept for a few months to almost a year. In Bhutanese society leaf litter is an important component of agriculture because of its contribution to manure production with most communities having designated specific forest management units for its production and collection for individuals or for communities. Sokshing is an important and highly relevant system and it continues to be important for villagers, even in the face of changing livelihood and institutional orientations. The government recognises sokshing and its institutions as a relevant mechanism for community forest management (Dorji et al., 2003).
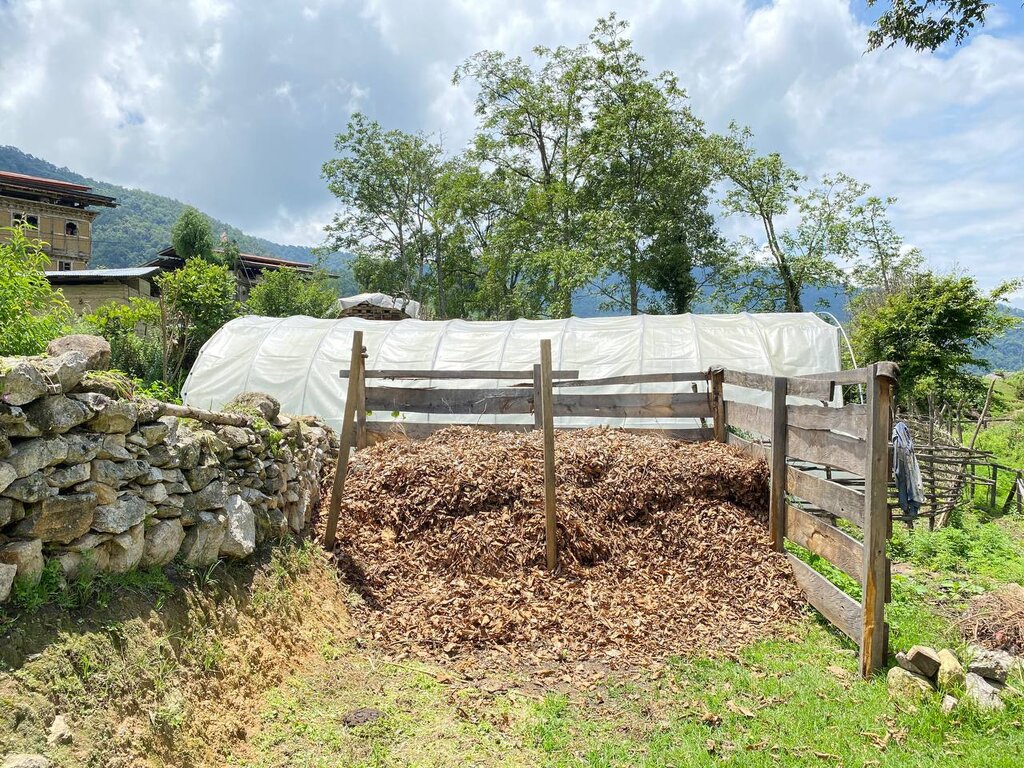
Leaf litter, predominantly gathered during the winter when the leaves have fallen, is collected from the forest floor by cleaning the entire understorey. It is carried to the farm and stored before being used as bedding material for cattle, providing comfort and insulation from cold. It is then mixed with cattle manure to form farmyard manure (FYM), (BHUCAT, 2012). FYM and mineral fertilizers are the two main sources of plant nutrients in Bhutan. Farmers not only depend on forests for leaf litter but also for livestock feed and construction materials (Gautam, 2009). FYM is a mixture of animal dung, crop residues, and other organic materials and plays a vital role in enhancing soil fertility and improving crop productivity. Its application to agricultural fields provides numerous benefits. Recent research by Gupta et al. (2022) demonstrated the positive impact of FYM on soil health and crop yields. The study found that FYM application significantly increased soil organic carbon content, which is essential for soil structure, water holding capacity, and nutrient retention. Furthermore, FYM enhanced the availability of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting optimal plant growth and development. Additionally, FYM improved soil microbial activity, leading to enhanced nutrient cycling and improved nutrient uptake by plants.
Leaf litter collection plays a role in ecosystem health and functioning. The accumulation of fallen leaves on the forest floor contributes to nutrient cycling, soil health, and moisture retention. Despite its benefits, the sokshing process exposes the forest's soil to erosion because all the leaves, debris, and undergrowth are removed. Nutrient mining occurs over time as a result of the annual removal of leaf litter, and many sokshing forests exhibit stunted growth and other signs of forest degradation. However, on balance, when used in conjunction with dairy production, sokshing offers a low-cost, readily available supply of bedding and then organic fertilizer, although it is labour-intensive.
In some situations, there may be specific benefits in removing the litter. A recent study by Jiang et al. (2021) emphasized the importance of leaf litter collection for mitigating the negative impacts of invasive species. The research found that invasive plants can alter the decomposition rates of leaf litter, disrupting nutrient cycling and leading to changes in soil properties. By collecting leaf litter, especially in areas where invasive species are prevalent, we can minimize their detrimental effects and help preserve the ecological balance.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
التاريخ:
06/07/2023
الموقع:
Proper Lingmukha
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Niki Rai
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بوتان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bhutan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Punakha, Lingmukha
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The end product, FYM, is located in the farmer's own field.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Traditional farming practices in Bhutan
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
- Bedding materials for cattle
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الشعير
- الحبوب - أخرى
- potatoes, chili and beans
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الخضروات - القمح / الشعير / الشوفان / أرز الأراضي المرتفعة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
once a year
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Cereals-Vegetables
التعليقات:
Owner grows all the cereal crops (Locally known as 'Dru na gu'). The farm is the focus for the FYM application so that is described here.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - أخرى
- خضروات - اخرى
- Beans, Chili, potatoes
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الخضروات - القمح / الشعير / الشوفان / أرز الأراضي المرتفعة
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
cereals- Vegetables
التعليقات:
Owner grows all the cereal crops (Locally known as 'Dru na gu'). The farm is the focus for the FYM application so that is described here.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
Irrigation is relied upon for crops like chili and cole crops when rainfed conditions are insufficient.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
- A7: أخرى
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A 6.3: تم جمعها

التدابير الإدارية
- M6: إدارة النفايات (إعادة التدوير أو إعادة الاستخدام أو التقليل)
التعليقات:
They are collecting leaf litter from forest
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
التعليقات:
that farmland is protected against degradation because FYM application however, Forest land are left barren after collecting the residues exposing the area to natural calamities such as erosion, destroying natural habitats of microorganisms.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- غير قابل للتطبيق
التعليقات:
While this technology may not directly address land degradation, it involves utilizing forest residues to produce farmyard manure (FYM) for crop cultivation, leading to improved fertility of the cultivated land. however there are also potential negative impacts associated with excessive or improper leaf litter collection to the forest area.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
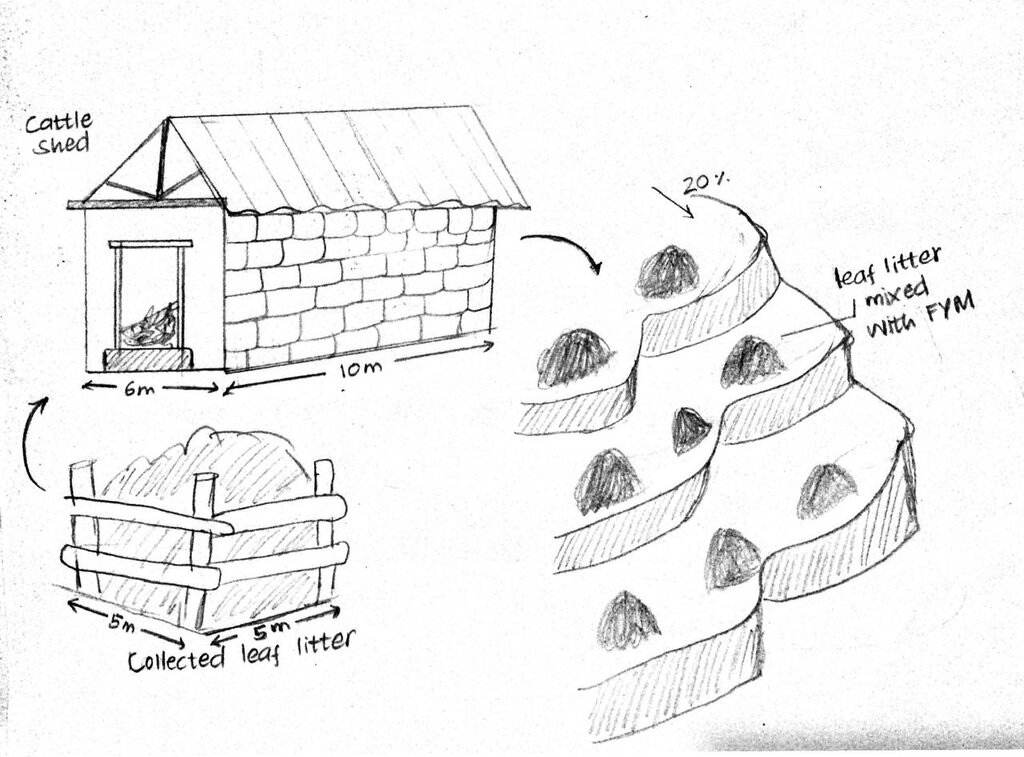
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical specifications as given above
المؤلف:
karma Wangdi
التاريخ:
06/07/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Cattle shed area
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
15/10
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ngultrum
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
82,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
800
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site selection | Winter |
| 2. | Collection of cosnstruction materials | Before on set of rain |
| 3. | hiring of labors | Before the cultivation |
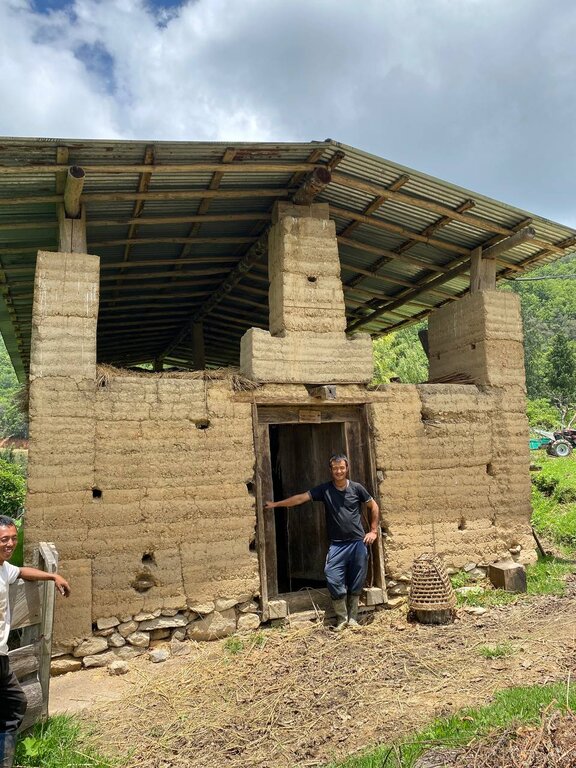
| 4. | Construction of the cow shed | winter |
| 5. | collection of leaf litters from the forest | winter |
| 6. | Stocking and use of leaf litter as bedding materials in the cow shed | winter |
| 7. | Let the leaf litter decompose for a month or more | anytime |
| 8. | Application of FYM during the field preparation | Before the cultivation of crops |
التعليقات:
Establishment is done based at his own convenience and he has to bear all the establishment cost
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | person days | 15,0 | 800,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | Spade | no. | 6,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | crowbar | no. | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | pickaxe | no. | 2,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | sickle | no. | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | wire | metre | 50,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | knife | no. | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | Power chain | no. | 1,0 | 98,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | nail | kg | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Timber | nos. | 150,0 | 350,0 | 52500,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | CGI sheet | nos. | 20,0 | 780,0 | 15600,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Working Lunch and Refreshment | person day | 15,0 | 410,0 | 6150,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 86750,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1057,93 | |||||
التعليقات:
All the cost for construction including labor charge and food are all covered by the owner
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Timber/wood change after damage caused by rain and heat | |
| 2. | CGI sheet replacement | |
| 3. | Leaf litter collection | |
| 4. | FYM production |
التعليقات:
Repairment and repayment of construction materials are done when ever there is damage caused.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | person | 10,0 | 800,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | spade | nos | 5,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | crowbar | nos | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | pickaxe | nos | 2,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | sickle | nos | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | wire | metre | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| معدات | knife | nos | 3,0 | 100,0 | ||
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Urea | packets | 2,0 | 1300,0 | 2600,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Nail | kg | 0,5 | 250,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Timber change | nos. | 30,0 | 150,0 | 4500,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | CGI sheet change | nos. | 8,0 | 780,0 | 6240,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Working lunch and Refreshment | Per Person | 10,0 | 410,0 | 4100,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 25565,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 311,77 | |||||
التعليقات:
Maintenance cost are all borne by the owner
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
There are no additional off-farm income-generating activities besides vegetable production, which has an impact on the overall costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1000,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Annual rainfall ranges from 500 mm to 1500 mm
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
National center for hydrology and metrology
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
This area probably falls under warm temperate zone which is one of the Bhutan's agro-climatic zone.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitude:
slope angles: 3%
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil Type: Sandy clay loam
MC (%): 6.84
OM (%): 7.98
OC (%): 4.64
pH (H20): 5.98
EC (µs/cm): 250.20
N (%):0.23
P (ppm):0.33
K (mg/100ml):140.07
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
The region comprises a mixture of forest, shrub-land, wetlands, alpine habitats, agricultural land, and areas around human habitation
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Owner is a native of Lingmukha
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
He owns 5 acres of land where by he cultivates cereals, vegetables and some fruit trees
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
- Family
- Family
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
Water User Group and bylaws
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
Many of the household are average earned farmers so they are accessible to good infrastructure facilities.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
After the SLM technology, crop production doubled in case of chili and cole crops.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The introduction of hybrid crops has enhanced crop quality, but it is challenging to quantify this improvement in terms of specific quantities.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Enhanced bedding materials and improved living conditions for livestock animals have led to increased product production.
well this is professional estimates.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
They are continuing the traditional farming practices
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farm production costs are minimal as they can produce their own organic manure directly from the field
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The integration of livestock and agriculture production provides farmers with various sources of income, including earnings from animal products
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The impact of technology on food security or self sufficiency cannot be quantified however in their opinion there is increase in food production after the technology. Now they can commercialized their product as well as adequate for self consumption.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil moisture has been improved in the applied field where they are practising from olden days
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The forest's land cover has reduced because of leaf litter collection.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Soil fertility and crop production improvement after technology.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Disturbance to microorganisms and soil vegetation of forest. There may be downstream siltation if too much forest is denuded.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
29 households
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
They have been using this technology for more than 5 decades without receiving materials, incentives and payments
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Soil fertility improvement |
| Improved crop production. |
| Minimise the cost for buying chemical fertilizers. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Enhance soil structure |
| Sustainable nutrient recycling |
| Cost effective option or low cost technology |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Habitat alteration | Reforestation and one alternative can be use of kitchen waste |
| Labor intensive | Labor exchange and power tillers for transportation |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Depletion of forest recourses | Strong policy on leaf litter collection |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
1
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
1
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
1
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
06/07/2023
التعليقات:
Data were collected based on field visits and face to face interactions with the land user.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
NSSC Bhutan catalogue of soil and water conservation approaches and technologies, 2012
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Website
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Traditional practice of leaf litter harvesting and utilization by farmers in west-central Bhutan: Paving the way for sustainable management
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://ag2.kku.ac.th/kaj/PDF.cfm?filename=07-Rekha.pdf&id=825&keeptrack=8
7.4 تعليقات عامة
This technology doesn't fit easily into the form because it has three components (litter collection/ FYM production from bedding/ application to the field
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية