ICT2Scale – supporting smallholder farmers with cellphone-based services via SMS [تونس]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7002 - تونس
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
Agricultural Innovation Specialist:
Rudiger Udo
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
تونس
Agricultural Economist:
Frija Aymen
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Economics and Participatory Methods:
Idoudi Zied
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Agricultural and Resource Economist:
Dhebibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
PhD Candidate:
Oueghemmi H
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - لبنان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
The ICT2Scale project contributes to better land management by supplying smallholder farmers with targeted SMS messages on diverse agricultural practices. This enables them to optimize resources and adopt more sustainable methods, consequently improving livelihoods in remote areas.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
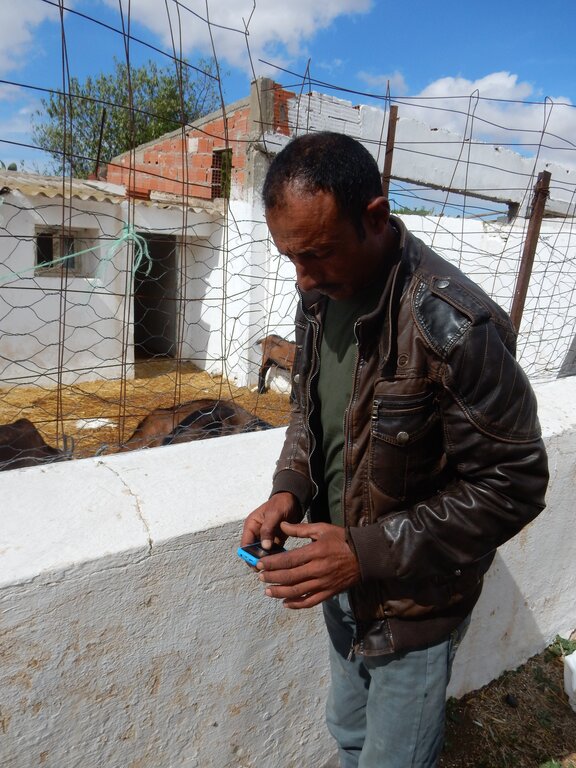
In Tunisia, smallholder farmers rely heavily on extension services for information regarding new and sustainable agricultural practices, improved varieties, and market prices. Unfortunately, these services often fall short, particularly in remote areas, due to inadequate financial, human, and logistical resources. Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) can play a crucial role in filling this void. This can strongly contribute to developing the agricultural sector and reducing or preventing land degradation.
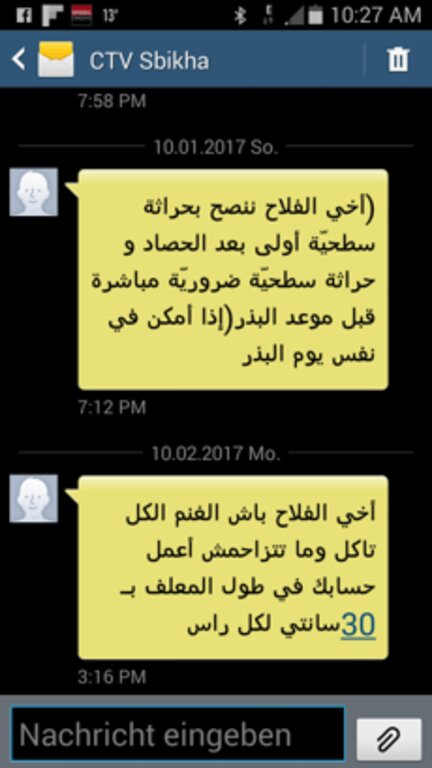
The ICT2Scale project aims to address these issues and reach these substantial group of farmers. The project was led by the International Center of Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA). It was initiated in 2019 with a survey to identify the information needs of smallholder farmers. Tunisian farming experts crafted 101 technical SMS messages, disseminating them to approximately 1,000 smallholder farmers in Kairouan, Zaghouan, and Jendouba. These messages covered diverse commodities such as cereals, olives, citrus, honey, and livestock, simultaneously aiding farmers in sustainable land management and resource optimization.
A one-day workshop was organized to compile the advisory messages. Thirty specialists from various disciplines gathered, including different National Agricultural Research and Extension Services (NARES) centres. The workshop's estimated cost (including food and per diem) was around $1000 USD. Each SMS “unit” - of one message to one farmer - costs approximately $0.01 USD, totalling $1010 USD to make the 101 SMS available to 1000 farmers. Although the data services were provided free-of-charge by network companies, the overall project cost is still estimated at $3000 USD per year. Similar infrastructure with similar cost was implemented in the projects “Mind the Gap” and "Crop-Livestock and Conservation Agriculture (CLCA)".
A follow-up survey conducted by phone in May and June 2021 involved 421 SMS recipients, revealed that 60% found the messages useful, with 54% claiming to have learned something new. However, only 15% agreed that the messages arrived at the right time. Notably, 41% of farmers expressed a willingness to pay $0.01 USD per message after the project, indicating a potential avenue for the sustainability of this SMS technology. Farmers recommended using SMS for weather alerts and disease outbreaks; employing phone calls or Interactive Voice Responses (IVR); sending messages at the right time; and incorporating information on marketing, training, and livestock vaccination programmes.
Key advantages of an SMS service are:
-More cost-effective than in-person advice via public extension agents
-Particularly effective during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the lack of personal contact
-Immediate reach to thousands of farmers in case of emergencies or opportunities
-Flexible and adaptable for quick information updates
-Useful when extension resources, such as vehicles and funds, are limited or unavailable
-Effective in disseminating information about events like training and seed distribution
However, some weaknesses persist, including a lack of interaction (i.e. a top-down approach), less convincing than personal exchange, and ongoing funding challenges, with the Tunisian government hesitant to invest in the project without more dialogue and convincing arguments.
In summary, the ICT2Scale project has proved the viability and cost-effectiveness of employing SMS technology to reach smallholder farmers in remote areas. Consequently, this has the potential to enhance more sustainable and efficient use of land and natural resources, leading to an improvement in rural livelihoods. However, securing sustainable funding remains challenging in order to scale up and maximize impact.
Acknowledgement:
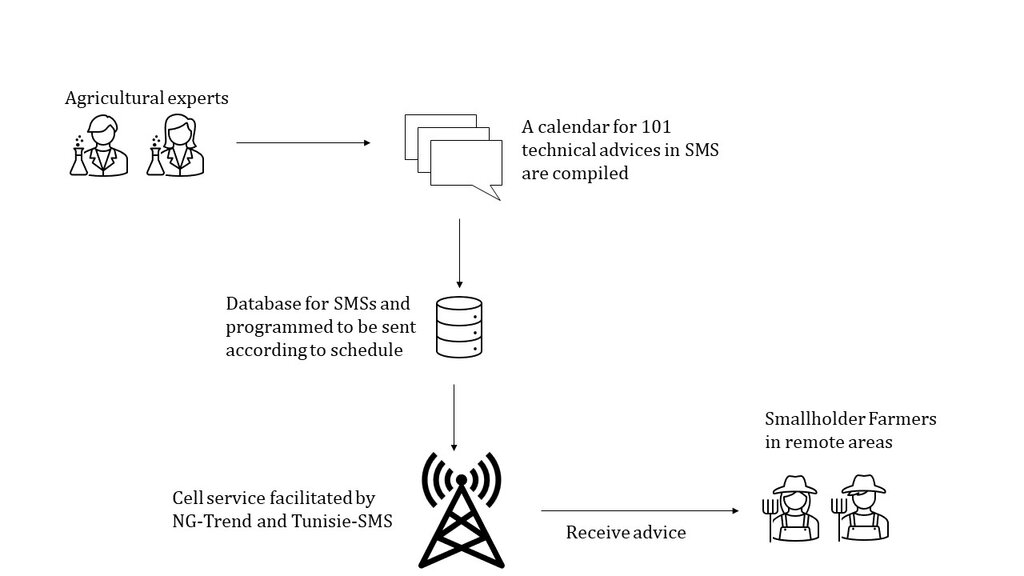
ICARDA’s work on Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) for agricultural development is supported by the German Agency for International Development (GIZ) in Collaboration with National Public Partners (AVFA, OEP, INRAT,ONAGRI, and CRDA) and Private Partners (NG Trend, Tunisie SMS) in Tunisia.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
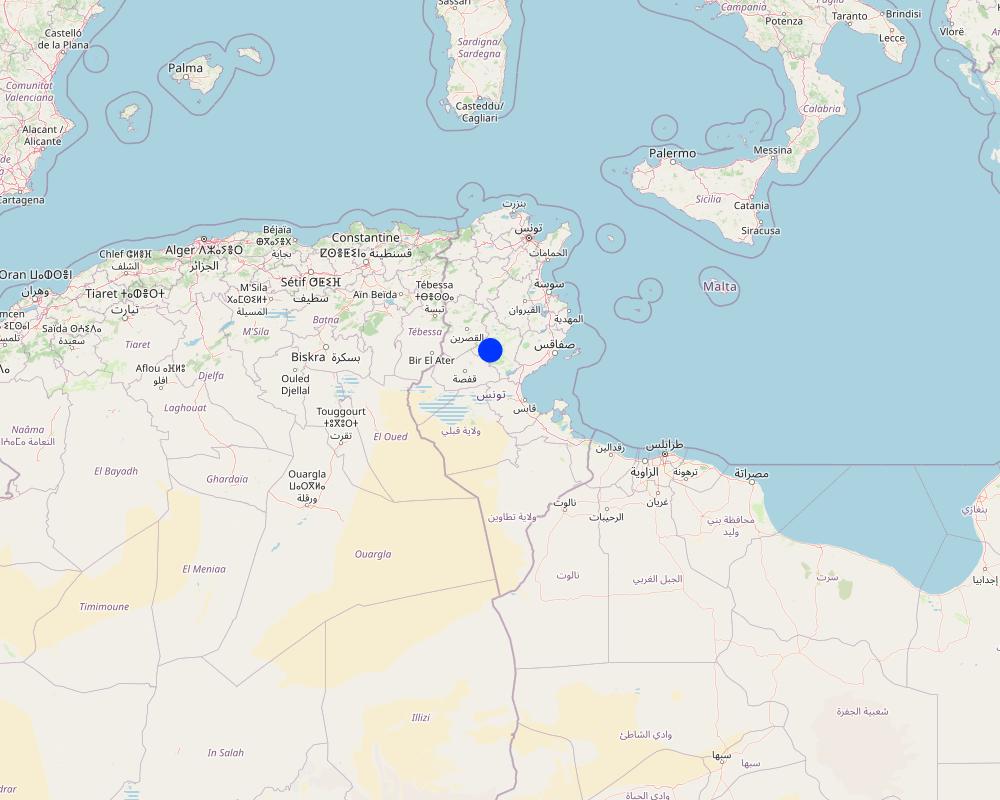
تونس
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kairouan, Zaghouan, and Jendouba
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2019
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الشعير

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- الأغنام
التعليقات:
The SMS messages were directed to different land use and land management such as barley cultivation, livestock herding, and olive production.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- Digital agriculture
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

تدابير أخرى
حدد:
Digital
التعليقات:
Most SMS messages were about agronomic and management measures.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
By informing farmers with technical advice, farmers can manage their land more sustainably.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Agricultural experts from different National Agricultural Research and Extension Services (NARES), lead farmers and ICARDA scientists formulated 101 technical advises in SMS following an elaborated "agricultural" calendar. This way farmers receive technical advice when needed. This is facilitated by NG-Trend and Tunisie-SMS
المؤلف:
Joren Verbist & Udo Rudiger
التاريخ:
2024
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Whole project / infrastructure
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Workshop to compile technical advice | |
| 2. | Setting up network |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Workshop to compile 101 SMS advice messages | workshop | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | |
| معدات | SMS unit (101 SMSs to 1000 farmers) | unit | 101000,0 | 0,01 | 1010,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Remaining | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | ||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 3010,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 3010,0 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
...
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the production increases.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the quality of production increases.
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers with technical advise, it is expected that the production increases.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers with technical advise and current prices, so they can lower their expenses.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers with technical advise and current prices, it is expected they can increase their selling prices.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
By informing farmers when the best moment is to plough the field, soil loss through erosion is reduced.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Informing farmers about management operations and their timing, drought impact decrease
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدة جدا |
التعليقات:
Farmers can receive various advice that allows them to cope with a wide range of climate-change induced issues and disasters.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
Around 1000 smallholder farmers
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The system in SMS-based which does require a smartphone, making it more accessible. |
| The technical advises allow to improve production practices. |
| The technical advice gives good reference for current practices |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| More cost-effective than in-person advice via public extension agents |
| Particularly effective during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the lack of personal contact |
| Immediate reach to thousands of farmers in case of emergencies or opportunities |
| Flexible and adaptable for quick information updates |
| Useful when extension resources, such as vehicles and funds, are limited or unavailable |
| Effective in disseminating information about upcoming events like training and seed distribution |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| SMS is often received at wrong timing. | |
| SMS messages did not include advice on animal vaccination programs. | Include this in the technical advice |
| SMS messages did not include early warnings for (weather) hazards. | Include this as well in the infrastructure and adding underpinning (weather) forecast models for this. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| SMS is not useful for illiterate farmers | Education in the rural areas should be improved in general. |
| Lack of dialogue (a top-down approach) | Include farmers when writing the advice and consider their needs beforehand, which was also done during the project. |
| Less convincing than personal exchanges | |
| Challenging to have ongoing investment | By showing to donors and national government that using SMS services is a viable and cost-effective way to improve rural livelihoods and make better use of the land and natural resources. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Udo Rudiger. (20/9/2021). Lesson learned from the study on "Impact of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) on Agricultural Development in Tunisia". Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/66236
العنوان/الوصف:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mohamed Zied Dhraief, Aymen Frija, Hassen Ouerghemmi, Barbara Rischkowsky, Udo Rudiger. (26/10/2023). A contextual ICT model to explain adoption of mobile applications in developing countries: A case study of Tunisia. PLoS ONE, 18 (10).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68779
العنوان/الوصف:
List of SMS messages to be send to farmers.
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/10637
العنوان/الوصف:
Udo Rudiger, Boubaker Dhehibi. (5/11/2021). General project "ICT2Scale" presentation.
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/66426
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية