Зимный полив для влагозарядки почвы перед посадкой садов и виноградников в условиясх засушливого зимы. [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Rustam Kalandarov
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, Joana Eichenberger
Усули захира кардани об пеш аз нихолшинони дар шароити замистони хушк.………………………………………………………………
technologies_3687 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
مستخدم الأرض:
Рахимов Тагаймурод
Фермерская хозяйства "Асадулло"
طاجيكستان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Технология природосберегающий противо эрозионный влгонакапляющий система для выращивания садов и виноградников.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
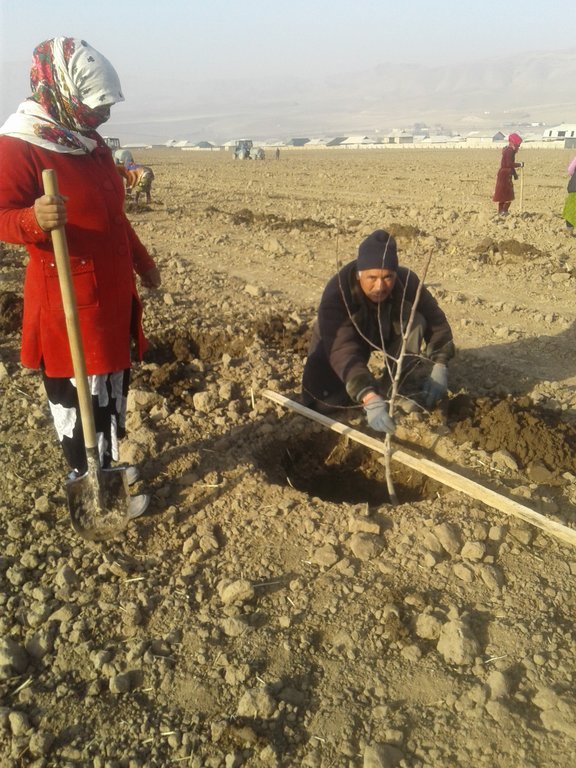
Технология заключается в том, что в некоторые годы зима очень засушливая. Для посадки саженцев почва не готова, по этому после разбивки участка надо копать лунки и заполнять их водой каждую. Через пару дней почва хорошо впитывает воду и уже можно сажать саженцев
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
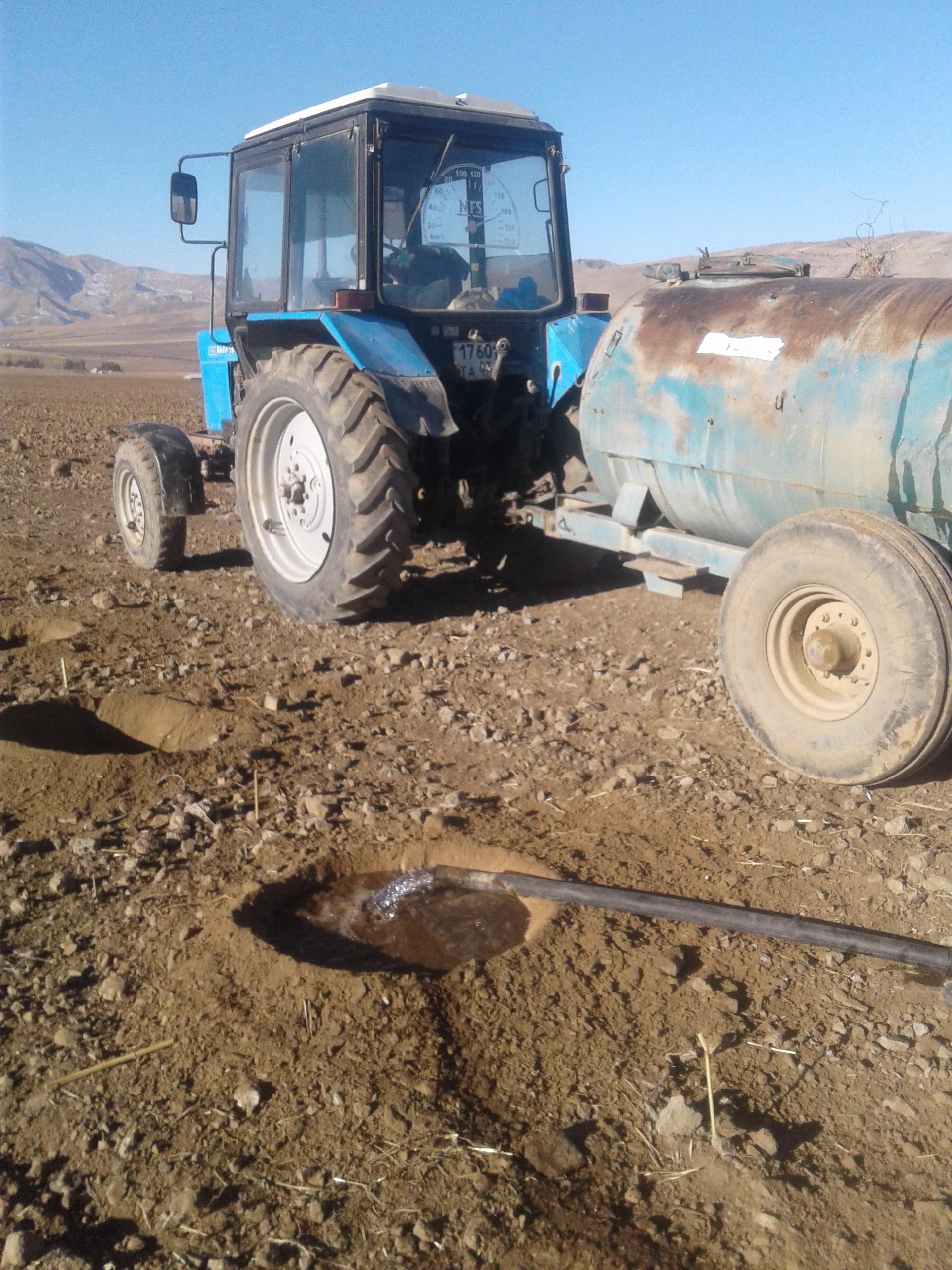
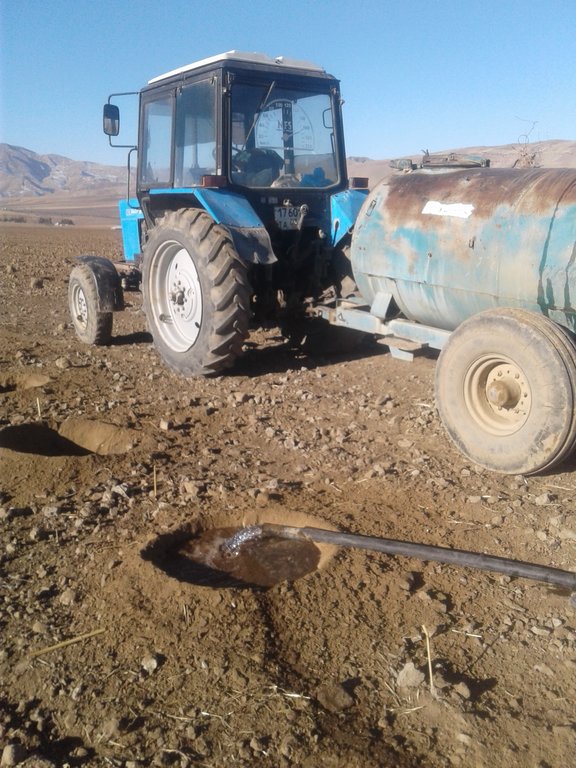
Эта технология в сравнение сплошным поливом на много экономит. Она применяется в дехканском хозяйстве Асадулло на площади боле 40 га. Природное условия в основном богарные, часть условно поливная зона. Часть земель на капельном орошение. Богарные зона здесь засушливая в основном влага есть за счет осадков которые выпадают осенью, зимой и весной. Годовая сумма осадков в последние годы не превышает 450 - 550 мм, это количество для богарного возделывания садов и виноградников недостаточное, считается необеспеченной багарой по этому при возможности проводят поливны. Бывают годы с очень малыми осадками, когда невозможно закладывать молодой сад. Были случай , когда в некоторые хозяйство богарной зоне отложили посадку нового сада из за засушливою периода на другой сезон года. Эта технология больше возможностей для посадки. Отличительные черты технологии в том, что в условиях засушливого (мало осадков) года её применяют в место сплошного полива (зимний полив) ,который раньше не пользовали во всех поливных зонах сельского хозяйства, но для этого необходимы постоянные поливные самотёчные каналы, чтобы поливать зимой. Однако, не всегда бывает такая возможность. По новой технологии можно обеспечить индивидуальный полив для каждой лунки где сажают саженец. После планировки участка на местах производят разбивку и копают лунки, причём копают специальным оборудованием для копки лунок. Каждая лунка глубиной 70-80 см. После выкопки лунки дополна заполняются водой почти по 80 л. Почва насыщается водой через пару днёй и лунка готова, в неё можно сажать саженцы. Основная цель накопление и обогащение почвы влагой, после которого саженцы хорошо приживаются. Обычный полив проводится типу «яхоба» но так как зимние поливы в последние годы из за ограничения электричества затруднены насосы не работают зимняя влагозарядки затруднена. Уже более 20 лет земледельцы «яхоба» не используют. Эта технология часто спасает садоводов в случае если зима проходит без осадков. После посадки во время вегетации можно продолжит обычный полив или капельное орошение в условиях поливного земледелия. Для запуска этой технологии необходимо только выкопать лунки и провести полив. Полив производится специальными тракторами с прицепленным специальным приспособлением поливной бочкой ОВТ, переоборудованной для полива. Во время полива работает один рабочий который держит шланг, если два шланга, то двое рабочих сразу два ряда лунок поливают. За один день можно поливать одним трактором почти 2 га площади сады.
Преимущество в том, что проводится экономный полив и 100% саженцев принимаются. Землепользователям этот способ подходит. Пользуются им те хозяйства, у которых есть возможность доставки горюче смазочных материалов и техники для завоза воды, водовозами для постоянно обеспечения водой поливных тракторов. При зимнем поливе (яхоб) это очень полезнее преимущество в том, что почва получает влагозарядку, уничтожаются зимующие вредители. Но однако в этих зонах вода подается с использованием электроэнергии, по поступление электроэнергии ограничено. Индивидуальный полив можно использовать даже в приусадебных участках.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
На фотографии приведено лунки с политой воды , который подготовливается к просачиванию почвы и вдолнейшем посади саженцев.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Хуросонский район. Хатлон
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Фермерский хозяйства "Асадулло" уч. ка Фахрабад
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Технология находится на Юге в 35 км от столице. Предгорный холмистые зона.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2018
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Технология является как инновация и научного эксперимента.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Урожай один раз за вегетацию.
التعليقات:
Тип землепользование является садоводства.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
Технологию используются в условно поливных землях.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Технология является агрономически с использованием растительности многолетних древесных и кустарниковых пород.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Для предотвращения деградации и эрозии почвы .
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
на 1 га
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
10000 метр квадрат
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
8,9
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.0
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Разбивка участок по схеме посадки. | февраль. |
| 2. | Копать лунки | февраль |
| 3. | Заливка воды | февраль |
| 4. | Посадка саженцы. | февраль |
التعليقات:
Все работы проведено одновременно после покупки лунки сразу заливают водой и через 2 -3 дня можно сажать
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Механизированная работа копка лунки | день | 7,5 | 33,3 | 249,75 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Заливка воды. | день | 7,5 | 33,3 | 249,75 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | посадка саженца | день | 100,0 | 0,4 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 539,5 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 60,62 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Затраты покриваются землепользователем.
التعليقات:
Частная хозяйства каждый землепользователь сами покрывают затраты.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Все затраты покрываются земле пользователем.
التعليقات:
Частная компания каждый землепользователь покрывает сам
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Копка ям и заливка воды.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
ГМС. г.Душанбе
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Технологию можно принимать не зависимо от рельефа .
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
нет дангных
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Зона является условно поливной или богара.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
биоразнообразия местности кустарники полукустарники трявянистые пологи встречаются мендалники Бояришники. и шиповники. Местобитания ландшафт откритого холмистого типа.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Землепользователи постоянно жители местности работа ведется общиной иногда принимают наёмных рабочих сил.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
Хозяйства является крупным
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- شركة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
Компания является частным.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Производства увеличится после применения технологии
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
улучшится после применение технологии
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Технология не влияет за приделами территориям не загрязняет не нарушает экологический баланс.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الشتاء | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الشتاء | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفةبَرَد محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفة رملية/ غبارية محلية | باعتدال |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | جيدا |
| موجة باردة | جيدا |
| ظروف شتاء قاسية | باعتدال |
| جفاف | باعتدال |
التعليقات:
Экстримальные явления для технологии не очень влияет кроме сильных жары и сильных морозов.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Эффективность затраты в краткосрочным и долгосрочным перспективы позитивное.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
домохозяйства это частная компания где принимается технология.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
Технологию кто может те и принимают технологию без никаких доли.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Обеспечивается почва влагой, вырастут саженцы. |
| улучшает роз и развития |
| предотвращает засуху почвы. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Обеспечивается почва влагой, без потерии вырастут саженцы. |
| улучшает роз и развития |
| предотвращает засуху почвы. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Завоз воды. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| завоз воды и заполнят |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
хозяйства
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
хозяйства
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
12/02/2018
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية