Reconstitution of Soils [إيطاليا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Chiara Cassinari
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ricostituzione
technologies_7346 - إيطاليا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Manfredi Paolo
mcm Ecosistemi
إيطاليا
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
NEW LIFE Project (NEW LIFE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
m.c.m Ecosistemi (m.c.m Ecosistemi)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Reconstitution is a technology that counters land degradation and according to the theory of "Circular Economy" it's a sustainable land management technology
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [إيطاليا]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- جامع المعلومات: Chiara Cassinari
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Reconstitution of soils is a pedotechnique based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials to achieve benefits in areas with barren, degraded, desertified and/ or sealed soils.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
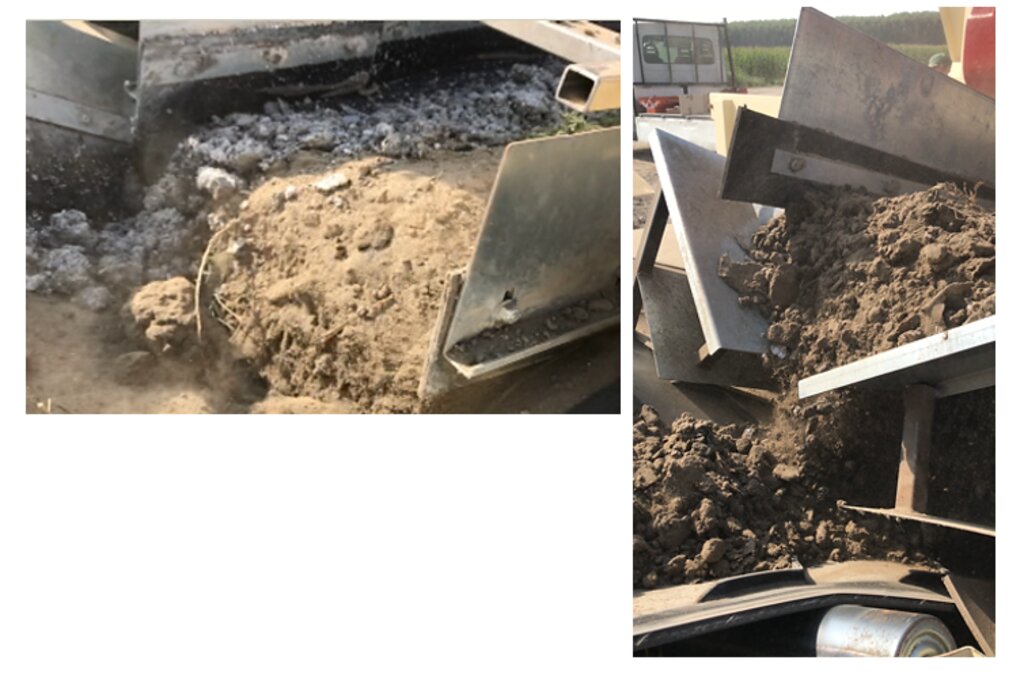
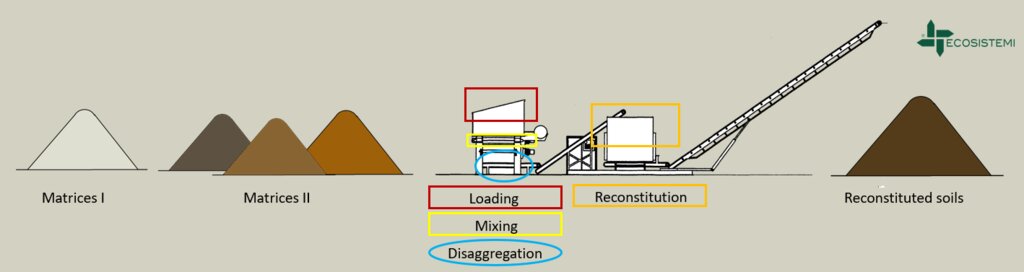
Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
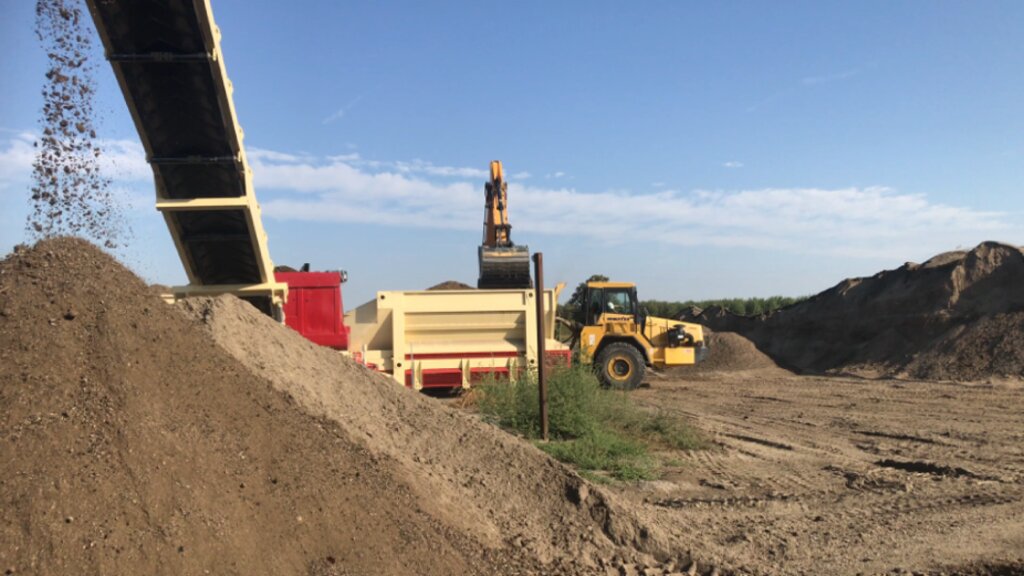
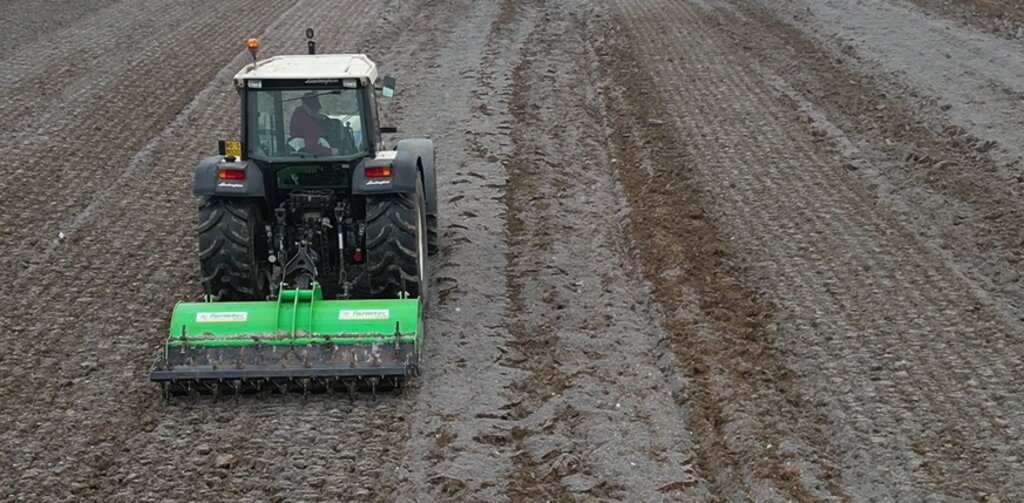
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
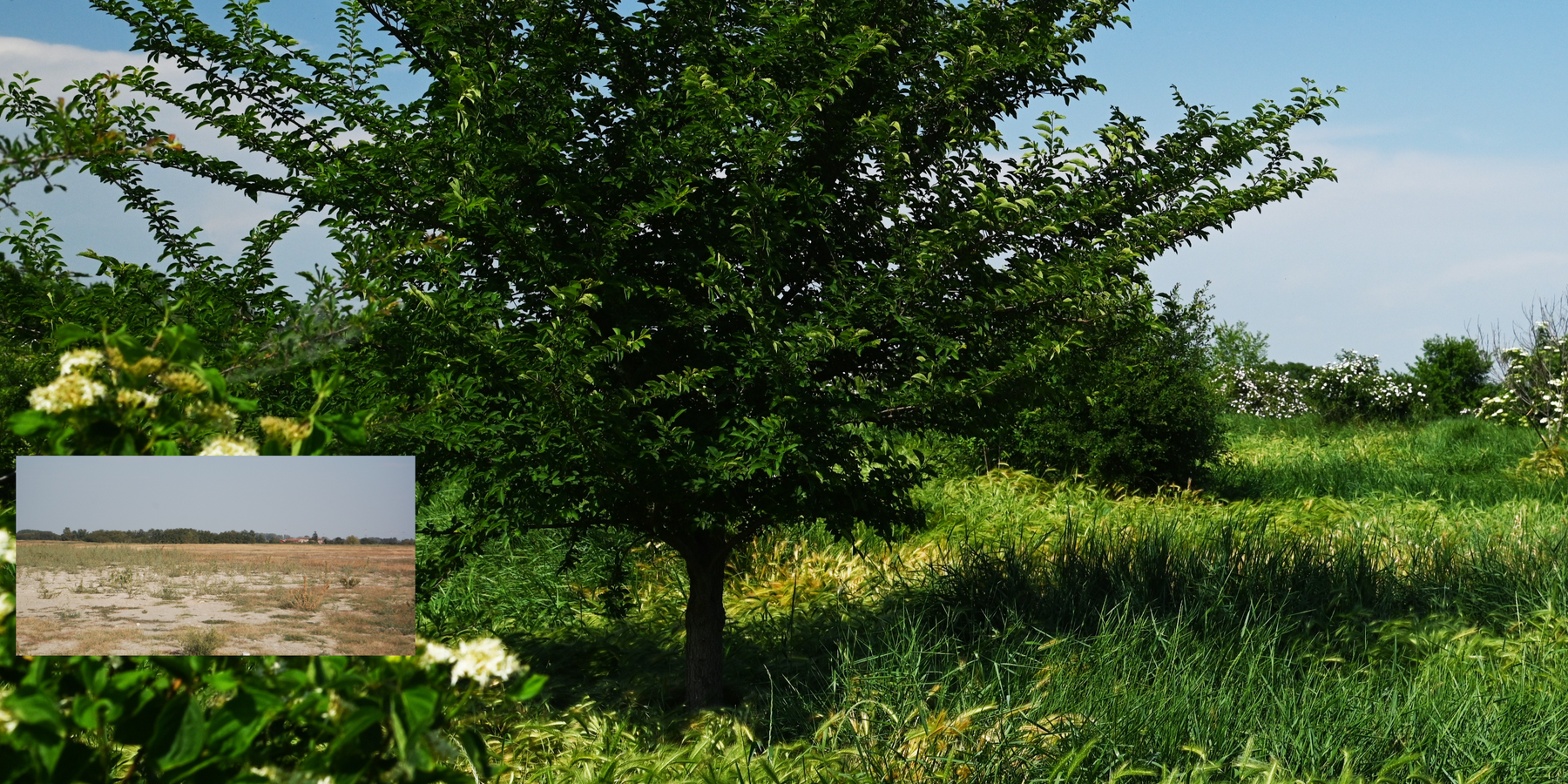
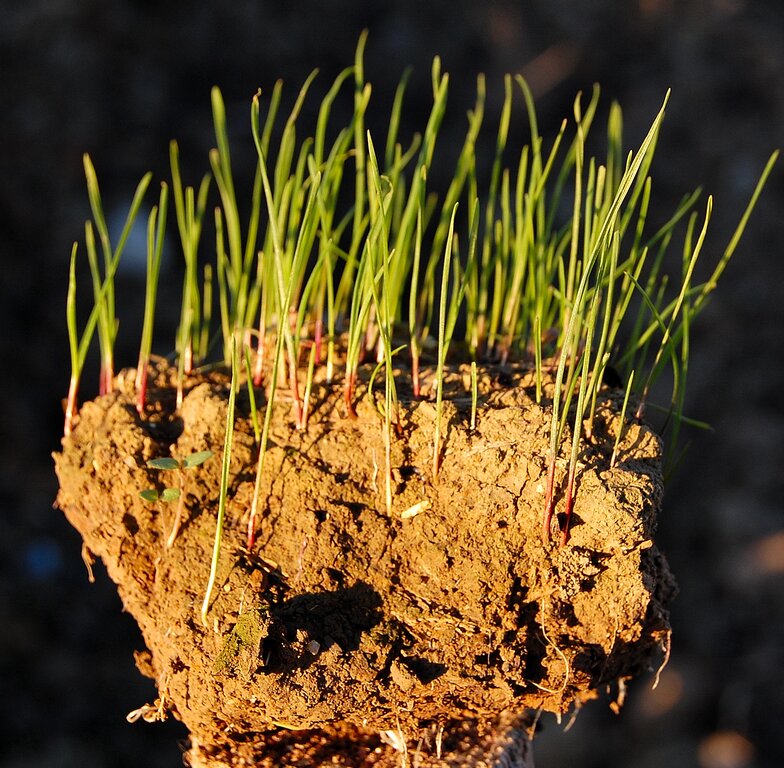
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF3nl4S5X8M
Reconstitution plant
التاريخ:
18/12/2024
الموقع:
Piacenza, Loc. Mortizza
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Paolo Manfredi
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kjy95Kz-e70
Construction site: collection of degraded soil to be reconstituted
التاريخ:
18/12/2018
الموقع:
Piacenza, Gossolengo
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Paolo Manfredi
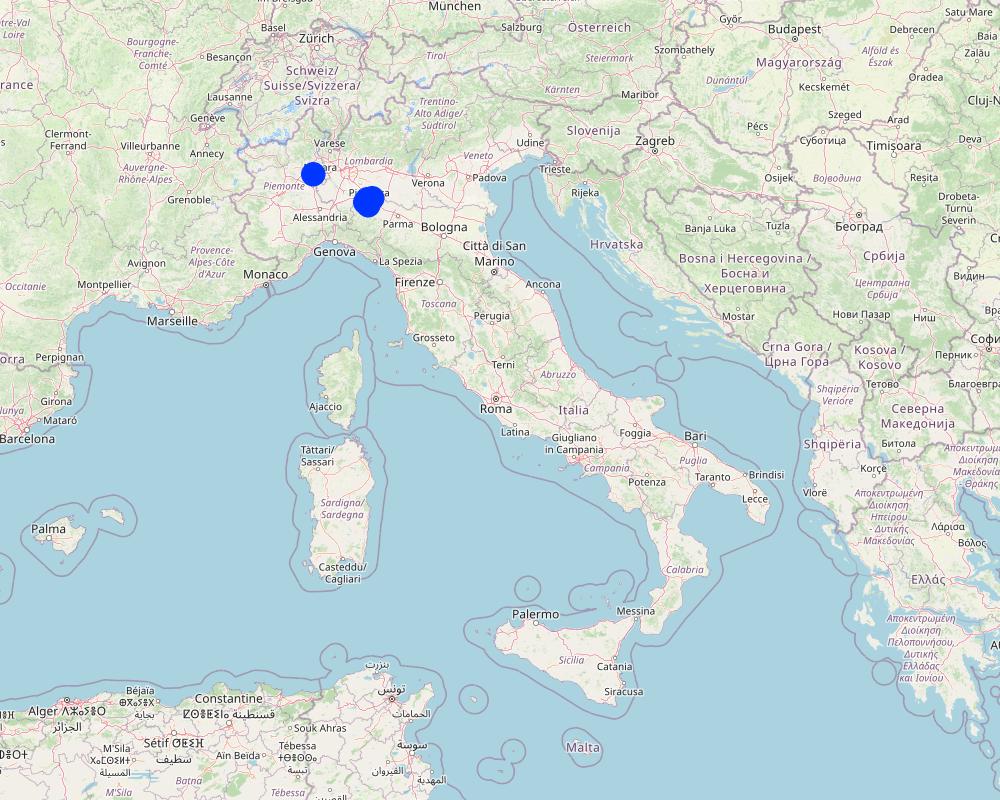
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
إيطاليا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Regional, National and International projects
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- tomato, fodder crops
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
maize - wheat - tomato

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
نوع الغابة الطبيعية /شبه الطبيعية:
- النباتات الطبيعية في الغابات شبه الاستوائيةالجافة
زراعة الأشجار والتشجير: تحديد أصل وتكوين الأنواع:
- أصناف مختلطة
نوع مزارع الأشجار، التشجير:
- مزارع الغابات شبه الاستوائية الجافة
نوع الشجرة:
- أنواع أكاسيا
- أنواع الحور
- أنواع الصفصاف Salix sp
هل الأشجار المذكورة أعلاه ملحاء أم دائمة الخضرة؟:
- مختلطة ملحاء / دائمة الخضرة
منتجات وخدمات:
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
- الترفيه / السياحة
- الحماية من المخاطر الطبيعية
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية
المناجم والصناعات الاستخراجية

أرض غير منتجة
حدد:
degraded, desertified and sealed soils
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- إدارة النفايات / إدارة مياه الصرف الصحي
- ecosystem rehabilitation
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك

التدابير الإدارية
- M6: إدارة النفايات (إعادة التدوير أو إعادة الاستخدام أو التقليل)
- M7: أخرى

تدابير أخرى
حدد:
addition of organic matter, new soil aggregates, increase water holding capacity
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
- انسداد مسام التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
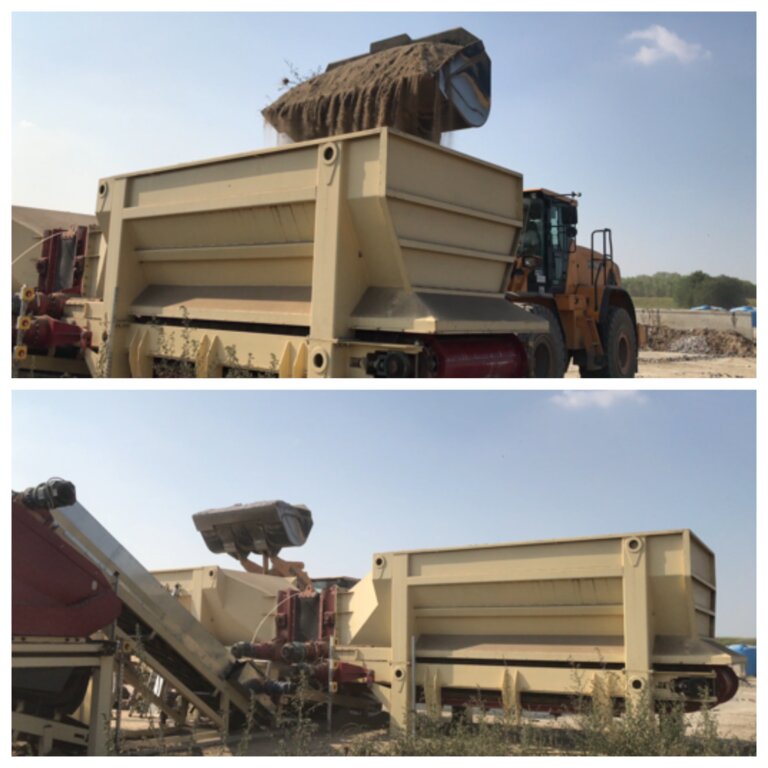
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Reconstituted technology: phases of work:
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected and dosed
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity
3) Disaggregation through rotating movements at variable power
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
المؤلف:
Paolo Manfredi
التاريخ:
12/04/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
10 hectares
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,89
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
123.00, gross income
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | characterization of the intervention site | no timing |
| 2. | morphological planning | no timing |
| 3. | environmental planning | no timing |
| 4. | pedo-agronomic planning | no timing |
| 5. | moving-plant placement only if the area to be restored is distant from the area where the permanent plant is located | no timing |
| 6. | degraded soil removal and collect | after harvest of crops, if there are |
| 7. | reconstitution | no timing |
| 8. | replacement of reconstituted soil | no timing |
| 9. | final soil placement | no timing |
| 10. | site-specific planting to make soil ready for use | dependence of plants species |
| 11. | land use | no timing |
التعليقات:
The reconstitution plants are 2: one is fixed that is located in an area, the other is a moving-plant: that is it can be located near the area to be restored.
According to the distance between the intervention site and the fixed plant it can be more useful using the moving-plant
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | 3 Workers | person/day | 232,0 | 123,0 | 28536,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Earth moving vehicles | number | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000,0 | 15,0 | 1125000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Reconstitution | m3 | 100000,0 | 2,5 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1473536,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 1655658,43 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Costs related to the matrices to be used and transport (1125000.00 EUR) are covered by company producing waste used. The costs to dispose of matrices II are much higher than taking them to the reconstitution plant.
التعليقات:
degraded land value 0 EUR
restored area value 390000 EUR
restoration using allocation of natural soil (8 EUR/m3, cost of natural soil in Piacenza) added to transport costs = 2100000.00 EUR
restoration using reconstituted soil technology = 28536 + 30000 + 40000 + 250000.00 EUR because 1125000.00 EUR are covered by company producing waste and so not spent for restoration.
Cost related to construction area and mobile plant are the costs for the set up of the area where to put the mobile plant and for it' transport to the intervention site.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ordinary plant maintenance | every 6 months or when needed |
| 2. | Reconstituted soil analysis | every 6 months |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | 1 Worker | person/day | 20,0 | 123,0 | 2460,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100,0 | 115,0 | 11500,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 13960,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 15685,39 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most important factor affecting costs could be the transport of degraded soil or matrices I to be used to the restoration site in the case of soil sealed
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
891,02
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
May: average monthly regionally anomaly +230% (heavy rains); October: heavy rains
February 2023 is the month with less rain 27.6 mm; in May is the rainiest 250.7 mm
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Bulletin ARPAE 2023
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
mean annual temperature 14.4 °C Bulletin ARPAE 2023
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Following the soil characterization (data are mean of 30 soil samples) of the last area of intervention with reconstitution; the data describes soil condition before reconstitution.
The soil texture is silty-loam
The aggregate stability index describes soils with poor stability
pH (1:2.5 in H2O) 6.98 ± 0.37
EC (saturated paste) 0.93 ± 0.41 dS m-1
tot CaCO3 10.33 ± 4.36 g kg-1 SS
active CaCO3 3.08 ± 1.24 g kg-1 SS
tot C 10.62 ± 3.68 g kg-1 SS
organic C 10.26 ± 3.44 g kg-1 SS
tot N 1.47 ± 0.43 g kg-1 SS
HA + FA 2.54 ± 1.26 g kg-1 SS
Olsen P 87.83 ± 44.19 mg kg-1 SS
available Fe 74.68 ± 32.97 mg kg-1 SS
available Mn 27.92 ± 15.78 mg kg-1 SS
available Zn 2.30 ± 1.72 mg kg-1 SS
available Cu 4.32 ± 1.34 mg kg-1 SS
soluble B 0.71 ± 0.25 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable K 21.61 ± 34.72 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable Mg 92.68 ± 28.13 mg kg-1 SS
CEC 26.22 ± 4.42 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Mg2+ 2.39 ± 0.50 cmol(+) kg-1
exch K+ 0.42 ± 0.33 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Na+ 0.48 ± 0.22 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Ca2+ 11.82 ± 4.75 cmol(+) kg-1
Chemical fertility is low, intrinsec fertility is poor, global fertility lower-intermidiate
In the link other data about soil analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Hb0PcmSYGY&list=PLXcG4R_rAdFaqGnKCa0qaL6FcrafvU0VE
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
جودة المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
70%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
95%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
65%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
these increment are estimation
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
إدارة الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100
التعليقات/ حدد:
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
الفرص الثقافية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
الفرص الترفيهية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
15%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
تصريف المياه الزائدة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
تراص التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
التنوع النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
الأنواع المفيدة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
تنوع الموائل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
آثار الجفاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
التعليقات/ حدد:
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10%
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| ظروف شتاء قاسية | باعتدال |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The recycle of suitable waste materials used defrays the reconstitution technology in short and long term
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
the Technology is partly modified to face every restoration project
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
design, matrices to be used
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Strengths: to change soil class in Land Capability Classification, to improve soil workability, to create new soil aggregates (the organic matter is covered by fine soil mineral fractions) |
| Advantages: to increase soil fertility, to implement Circular Economy |
| Opportunities: to create a non-renewable resource (soil) and/or to restore it, to implement Circular Economy |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Strengths: to produce the suitable soil for the environment where it will be placed |
| Advantages: to reduce the use of fertilizers |
| Opportunities: to restore soil using suitable waste, Circular Economy |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: demand exceed supply, concerning current number of workers employed in the reconstituted plant | formation of new workers |
| Risks: crisis of industries producing suitable waste | non-stop search for suitable waste to use |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: contamined soils | studies about possibility of using reconstitution to clean soils |
|
Risks: the pedotechniques include all the anthropic activities that determine a growing influence of man on pedogenesis and pedolandscapes; they have to satisfy man needs while avoiding any undesirable environmental consequences (Dazzi et al., 2010). This is the main core of reconstitution of soils, but sometimes, the use of waste material, even if, environmental suitable, isn't understood because of waste are considered materials only for disposal. |
Dissemination concerning the laboratory analysis before the waste use, studies and research projects with University to test environmental suitability of reconstituted soils |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
2 visits/survey a year
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
each land user where technology was adopted
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
15/03/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The reconstitution pedotechnique: Applications, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102246
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The reconstitution: environmental restoration assessment by means of LCC and FCC, 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/8500
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Trees and shrubs monitoring using an ecological approach: the conclusion of the restoration project of Borgotrebbia landfill (Northern Italy), Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Meloni F., Stragliati L., Trevisan M., Giupponi L., 10.31031/EAES.2019.06.000635
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
A new technology to restore soil fertility: Reconstitution, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Francaviglia R., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201933
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Growth and yield response of tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) to soil reconstitution technology, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Gatti M., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201916
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Test on the effects of reconstituted soil on emergency speed and root growth in maize, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Salvi R., Battaglia R., Marocco A., Trevisan M., 10.1515/contagri-2018-0035
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Osservazione di Lycogala terrestre Fr. e Stemonitis axifera (Bull.) T. Macr. su suoli ricostituiti sabbiosi, Manfredi P., Salvi R., Bersan M., Cassinari C., Marocco A., Trevisan M.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Relationship between hydraulic properties and plant coverage of the closed-landfill soils in Piacenza (Po Valley, Italy), Cassinari C., Manfredi P., Giupponi L., Trevisan M., Piccini C., 10.5194/se-6-929-2015
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Soil temperature fluctuations in a degraded and in a reconstituted soil, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., ISBN 20385625
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Confronto tra dati produttivi di mais coltivato su terre ricostituite e terre naturali, Manfredi P., Tassi D., Cassinari C.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Scientific Journal
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Ecosistemi web site
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.mcmecosistemi.com/
العنوان/الوصف:
Paolo Manfredi ResearchGate
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Manfredi-2
العنوان/الوصف:
Chiara Cassinari ResearchGate
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chiara-Cassinari
العنوان/الوصف:
All the publications with DOI mentioned above
العنوان/الوصف:
Ecosistemi YouTube channel
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCOloFv-BLgvIVt9kBZuZyZg
7.4 تعليقات عامة
Very useful questionnaire
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [إيطاليا]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- جامع المعلومات: Chiara Cassinari
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية