Contour trenches and contour strips [أوزبكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Joren Verbist
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7557 - أوزبكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
Research Associate - Spatio-temporal assessment:
Senior Scientist Sustainable Land Management:
Akramkhanov Akmal
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
أوزبكستان
Crop Specialist:
Fayzullayev Abdulla
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
أوزبكستان
Water Harvesting Expert:
Muddaber Mohammad Ali
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
الأردن
Water Harvesting Expert:
Jafar Alwidyan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
الأردن
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiative1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Contour trenches for the cultivation of almond trees, and contour strips for cereals are types of rainwater harvesting structures. They are designed to capture runoff, reduce erosion, and enhance soil moisture—thereby improving land productivity and supporting climate-resilient agriculture in lowland dry areas.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Qashqadaryo Province in southern Uzbekistan experiences a hot, dry summer and a mild winter. Combined with unsustainable land management practices, climatic stresses have exacerbated land degradation and made local livelihoods increasingly vulnerable.
As part of the Food Systems, Land Use and Restoration (FOLUR) project, the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) designed and tested rainwater harvesting (RWH) structures to combat land degradation and enhance rural livelihoods. These RWH structures support vegetation growth, reduce surface runoff, prevent erosion, and restore soil health—thereby reversing degradation and improving agricultural productivity.
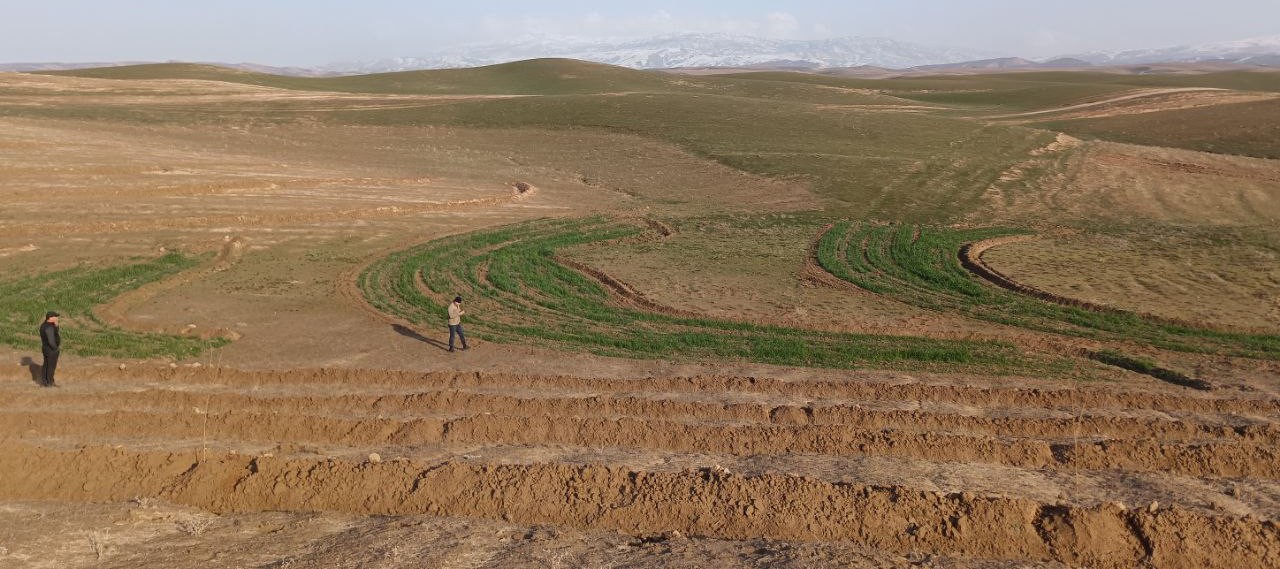
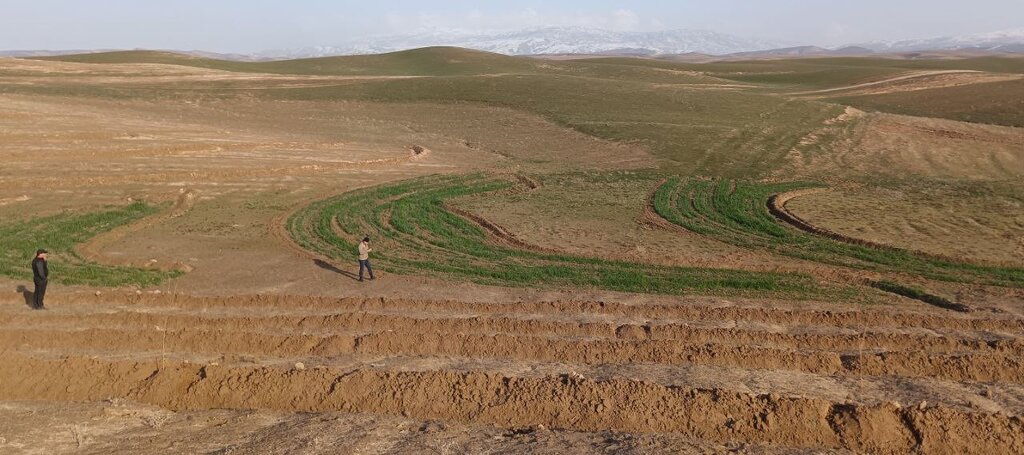
Based on slope gradients and hydrological characteristics, two RWH techniques were selected: modified contour trenches for the slightly sloping upper areas, and modified contour strips for the flatter zones.
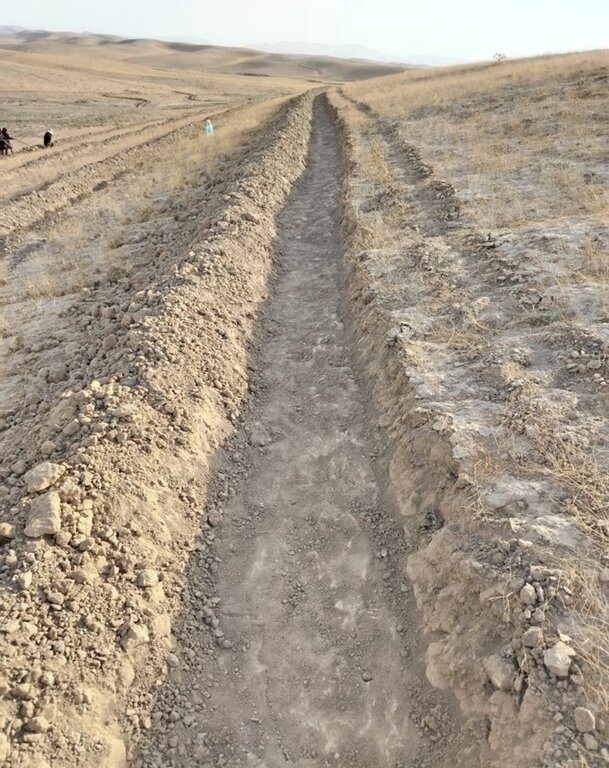
In the upper portion of the site, which spans 1.54 hectares, modified contour trenches were implemented for perennial tree crops. Design calculations suggested a spacing of 8 metres between trenches, and 7 metres between almond trees along each trench.
Implementation began with the marking of contour lines using a laser level: two labourers worked for two days. Then a tractor fitted with a three-mouldboard plough dug the trenches. While the tractor generally performed well, work had to be completed manually at sharp bends and gully crossings. Eight labourers then spent two days shaping and stabilizing the trenches. In total, approximately 1,300 metres of trench lines were created.
Costs were relatively modest. The tractor, hired from a farmer, cost $150 per day. Manual labour amounted to 24 person-days at $10 per day. 100 almond trees were planted, and 85 tamarix trees were added as a protective windbreak.
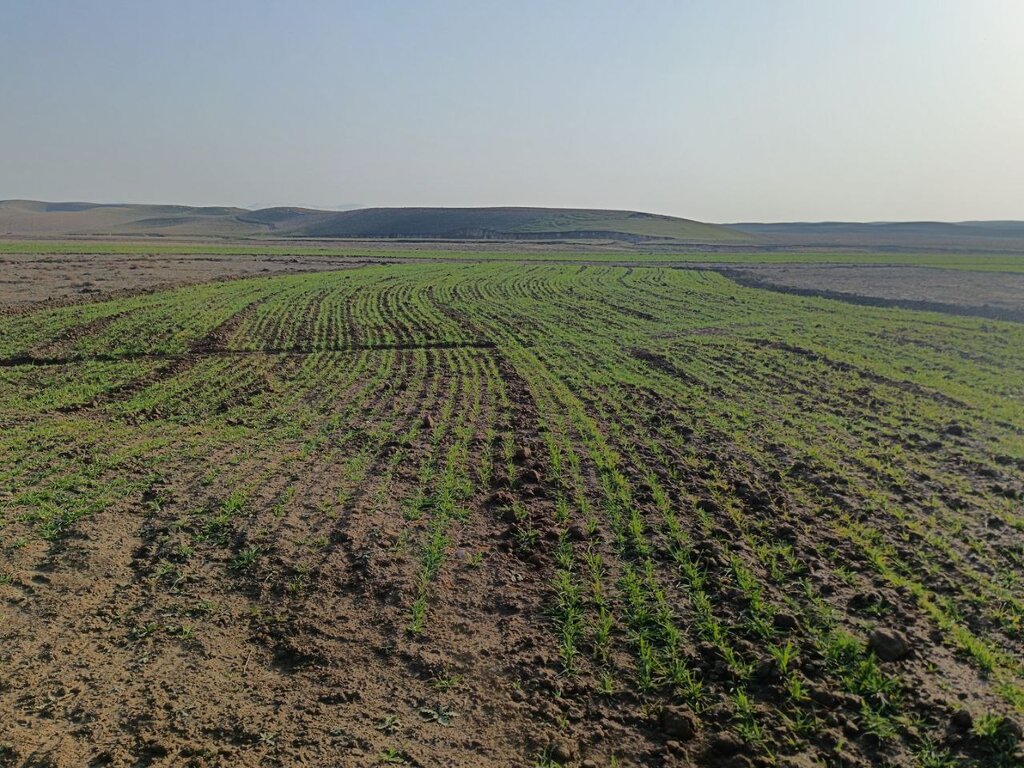
In the lower, flatter part of the site—about 1.68 hectares—standard contour strips were unsuitable due to the very low slope, which would not generate enough runoff. Instead, a modified version was implemented. Low ridges along contour at a vertical interval of 30 cm, allowed rainwater to pool and infiltrate. The same tractor was used with a single mouldboard plough to form nine contour ridges, shaped by two passes.
Afterwards, ten local women labourers finalized the ridges manually. The total length of the contour strips reached 500 metres, and the ratio of catchment to cultivated area varied from 5:1 in the upper sections to 1:1 in the lower zones, based on expected runoff.
The cost of this phase included one day of tractor use and 15 person-days of labour, totalling approximately $300. This site is intended for rainfed cultivation, and will follow a crop rotation system including barley, legumes and fallow periods. Over time, farmers are encouraged to adopt no-till practices to improve soil health.
Following implementation, light rainfall provided a test of the structures. Both the contour trenches and strips performed as intended, with no damage observed.
The interventions demonstrate how a tailored combination of RWH structures and cropping systems can rehabilitate degraded land. Local involvement helped to build community ownership. The result is a more productive and climate-resilient landscape that offers long-term benefits for soil conservation and rural livelihoods.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أوزبكستان
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
8°43'14.26"N, 66°41'51.87"E
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2024
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الشعير
- Nuts/ fruits including almonds
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Barley, legumes etc
التعليقات:
Note fruits/ nuts on one part of the land and cereals/ legumes/ fodder on another section (see 2.2)
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
- Mixed
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- حصاد المياه
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
- A4: المعالجة تحت السطحية

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
- الحواجز والضفاف
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية
- (Ed): الانكماش والترسب
- (Eo): تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
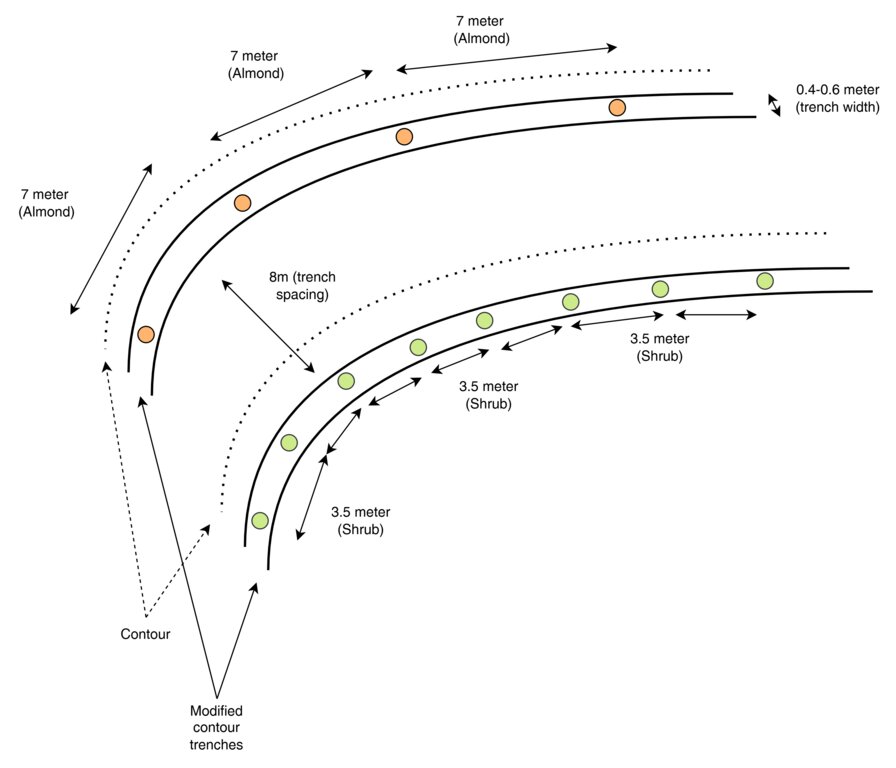
This top-view diagram shows the layout of modified contour trenches along contour lines, spaced 8 meters apart vertically. Each trench supports either:
Almond trees, spaced 7 meters apart, or
Shrubs, spaced 3.5 meters apart.
Each trench is aligned to follow the natural contour of the land to intercept runoff and enhance infiltration. Shrubs and trees are planted separately in designated trenches, not mixed.
المؤلف:
ICARDA
التاريخ:
2025
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
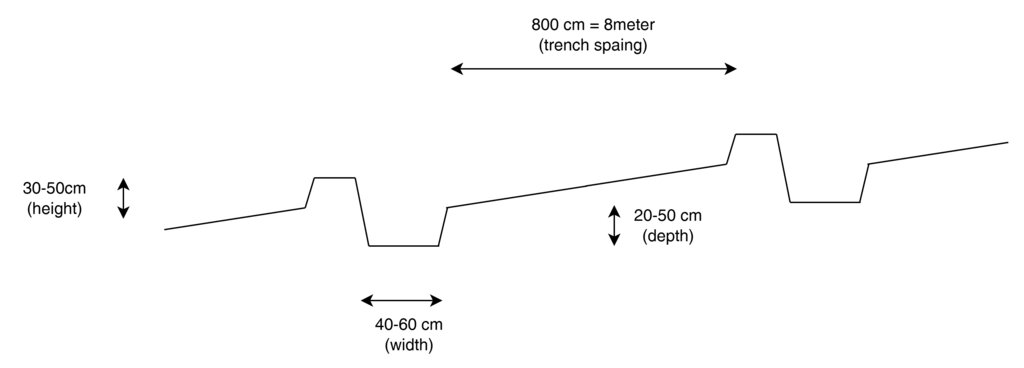
This cross-sectional profile illustrates the physical dimensions of a modified contour trench:
Width: 40–60 cm
Depth: 20–50 cm
Bund height (upslope side): 30–50 cm
Trench spacing: 8 meters
These dimensions are designed to retain and slow down surface runoff on slopes of 10–20%, enhancing water infiltration for tree or shrub growth.
المؤلف:
ICARDA
التاريخ:
2025
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
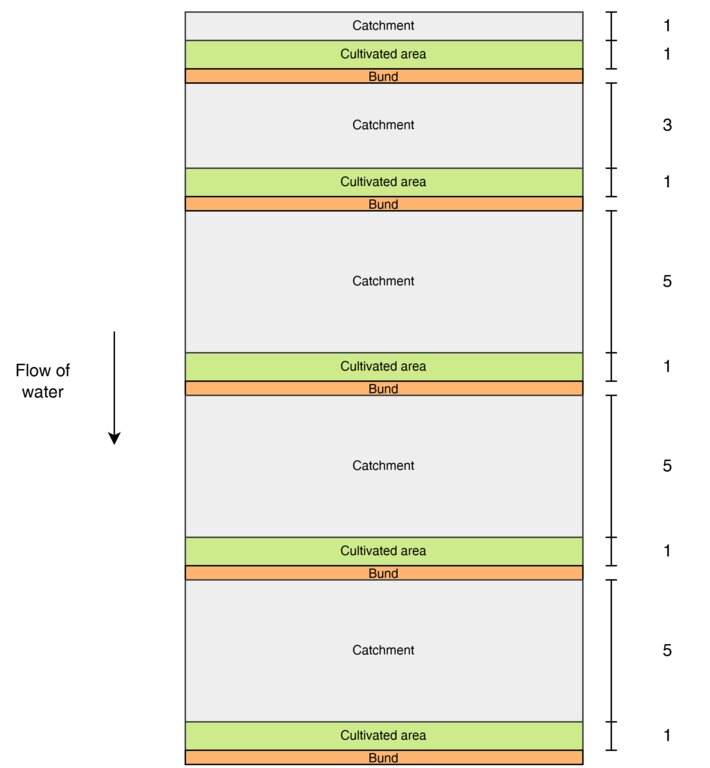
This diagram shows the layout of modified contour strips designed to enhance rainwater harvesting and crop productivity on sloped land. Each unit consists of a cultivated strip supported by a bund, located just downslope of a catchment area that concentrates surface runoff toward the crops.
Water flows downslope through the system.
The catchment-to-cultivated area ratio increases downslope to account for the growing volume and force of accumulated runoff, as well as differences in slope and infiltration capacity:
1:1 in the upper strips, where the steeper slope generates stronger runoff, and only limited water is desired to avoid erosion or damage.
3:1 in the middle strips, where moderate runoff accumulates.
5:1 in the lower strips, where the gentler slope allows more infiltration and where the lower kinetic energy of the runoff poses less risk to the structures.
المؤلف:
ICARDA
التاريخ:
2025
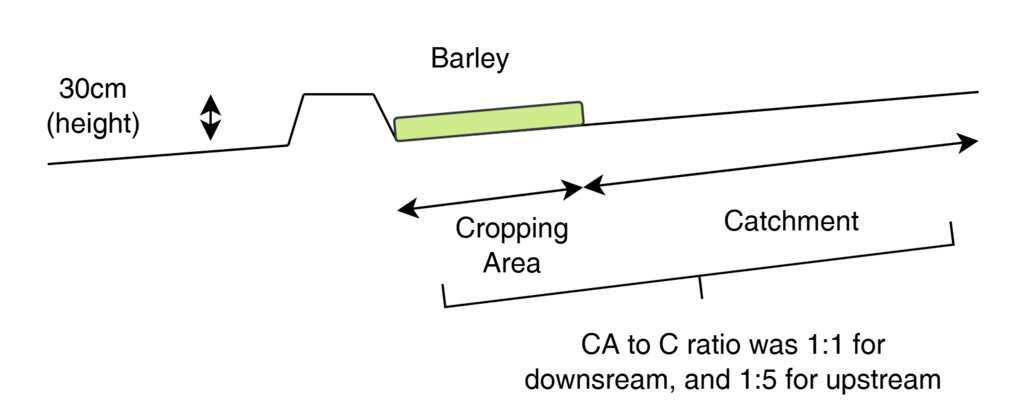
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
This cross-sectional view illustrates a modified contour strip:
A 30 cm high earth bund holds runoff upslope.
The cropping area (e.g., barley) is placed directly upstream (behind) the bund.
A catchment area lies upslope, sloped to direct water into the cultivated zone.
The catchment-to-cultivated ratio ranges from 5:1 (upper strips) to 1:1 (lower strips) depending on expected runoff volume, ensuring efficient water use and soil conservation.
المؤلف:
ICARDA
التاريخ:
2025
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
3 ha (with half: half of each RWH technology)
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
10
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour marking | 22–23 September |
| 2. | Tractor ploughing | 24–25 September |
| 3. | Manual shaping/finishing | 25–26 September |
| 4. | Tree/shrub planting | 26–27 September |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Contour trench construction | Person-days | 24,0 | |||
| العمالة | Bunds for contour strips | Person-days | 15,0 | |||
| العمالة | Marking contours | Person-days | 4,0 | |||
| معدات | Ploughing (contour trenches) | Machine-days | 3,0 | |||
| معدات | Ploughing (contour strips) | Machine-days | 2,0 | |||
| المواد النباتية | Almond seedlings | 100,0 | ||||
| المواد النباتية | Shrubs | 85,0 | ||||
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Manure | kg | 600,0 | |||
| غير ذلك | Lumpsum contour strips | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | ||
| غير ذلك | Lumpsum contour trenches | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | ||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 2000,0 | |||||
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
2000,0
التعليقات:
Total implementation costs are around 2k USD. 50/50 between the two designs.
We have spent around 310 for tractor
300 for loader for levelling
270 labour for shaping the pits (after tractor)
400 for ploughing prior of planting the barley
340 for no till planter services for planting the barley
250 labour for applying fertilizer
100 for fertilizer (inc transport)
Estimation 20-50 for labour for plating the seedlings
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inspection and incidental repairs | |
| 2. | Potentially sediment cleaning |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
No numbers have been recorded yet as the structures are new. An estimate of the maintenance costs would be 10-25% of the establishment costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
325,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The strips are better suited for the flatter areas and the trenches on the higher sloping areas.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- أطفال
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
- Water not available
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
At first relatively unproductive land, with rwh techniques, production is increase is expected
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
More water is retained in the land and in the soil hence less drought vulnerable
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Trees, shrubs, and crops
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Structures require some maintenance
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in more stable yield is positive for farm income
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less dependent on external food during dry periods
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Implementation was together with local land users, enhancing their knowledge in SLM
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water is much better retained as consequence of the rwh structures.
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Run-off (damage) poses less because the ability to accumale is limited because water is now trapped by trenches and bunds
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراكم التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Expert estimates
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
More water is retained in the catchment, hence less flood risk downstream
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
The RWH structures can trap sediments
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Because of improved vegetation cover, soil is better held together, becoming less susceptible for being lifted up the wind
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Expert estimates
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان مفاجئ | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Expectations
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Income diversification through forest nut and fodder production: Modified contour trenches enable the planting of both almond trees and fodder shrubs, supporting a mix of high-value cash crops and livestock-based livelihoods while restoring degraded sloped land. |
| Higher and more stable yields in flat rainfed systems: Modified contour strips improve water use efficiency and infiltration in cereal fields (e.g., barley), leading to better germination, stronger crop stands, and increased yields—especially valuable in low-rainfall zones where productivity is otherwise constrained. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Improved erosion control and landscape stability: Both techniques reduce surface runoff, limit gully formation, and prevent soil loss—thereby rehabilitating degraded land and protecting long-term soil productivity. |
| Enhanced soil moisture and drought resilience: By capturing and infiltrating rainwater along the contour, both methods improve water availability in the root zone, boosting the performance of crops and vegetation under arid and increasingly variable climate conditions. |
| Cost-effective and locally scalable: Constructed with accessible tools like mouldboard ploughs and finished by manual labour, both structures are affordable, require minimal inputs, and are suitable for community-based, participatory land restoration efforts. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| One challenge with modified contour trenches is that their effectiveness can be reduced over time due to sediment accumulation inside the trenches, which may reduce their water storage capacity and redirect runoff flow, especially during intense rainfall events. In addition, the bunds can weaken or collapse if the soil is loosely compacted or livestock walk over them. | Periodic maintenance is required every 4–5 years to remove sediment, re-shape trenches, and recompact or reinforce bunds, especially in sensitive segments. Involving local land users in routine inspection and light seasonal upkeep helps sustain long-term functionality. Introducing controlled grazing or fencing can prevent trampling by animals. |
| Modified contour strips are relatively low structures and therefore vulnerable to damage or overtopping if catchment-to-cultivated ratios are misjudged, or if bunds are not compacted well—especially during unexpected intense rainfall. Another limitation is that the strips rely on proper elevation spacing and contour accuracy, which requires some technical skill. | Ensuring accurate layout using a laser level and proper training of local staff during implementation is key. Adjusting catchment ratios downslope (e.g., from 5:1 to 1:1) helps avoid overloading. Annual visual checks and minor repairs after each rainy season are usually sufficient to maintain bund height and integrity. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Oweis, T. and Haddad, M. 2023. Rainwater Harvesting Design Manual: Micro-catchment Systems for Drylands Agriculture. Lebanon, Beirut: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hdl.handle.net/10568/169777
العنوان/الوصف:
Mekdaschi Studer, R. & Liniger H. (2013). Water Harvesting: Guidelines to Good Practice. WOCAT, Bern, Switzerland
عنوان الرابط URL:
wocat.net/documents/85/WaterHarvesting_lowresolution.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Critchley, W. & Siegert, K., (1991). Water Harvesting: A Manual for the Design and Construction of Water Harvesting Schemes for Plant Production. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organisation, Rome
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.fao.org/3/U3160E/U3160E00.htm
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية