Vetiver grass soil conservation system [جنوب أفريقيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Vetiver system
technologies_938 - جنوب أفريقيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
03/09/1999
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
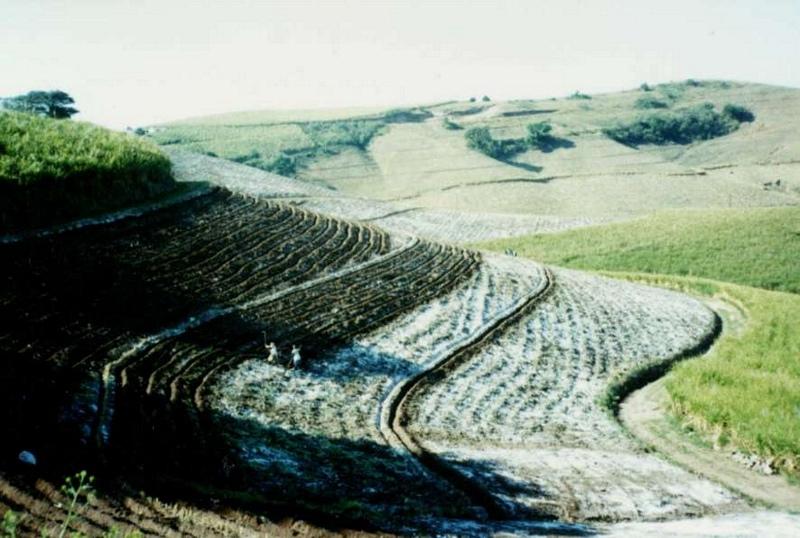
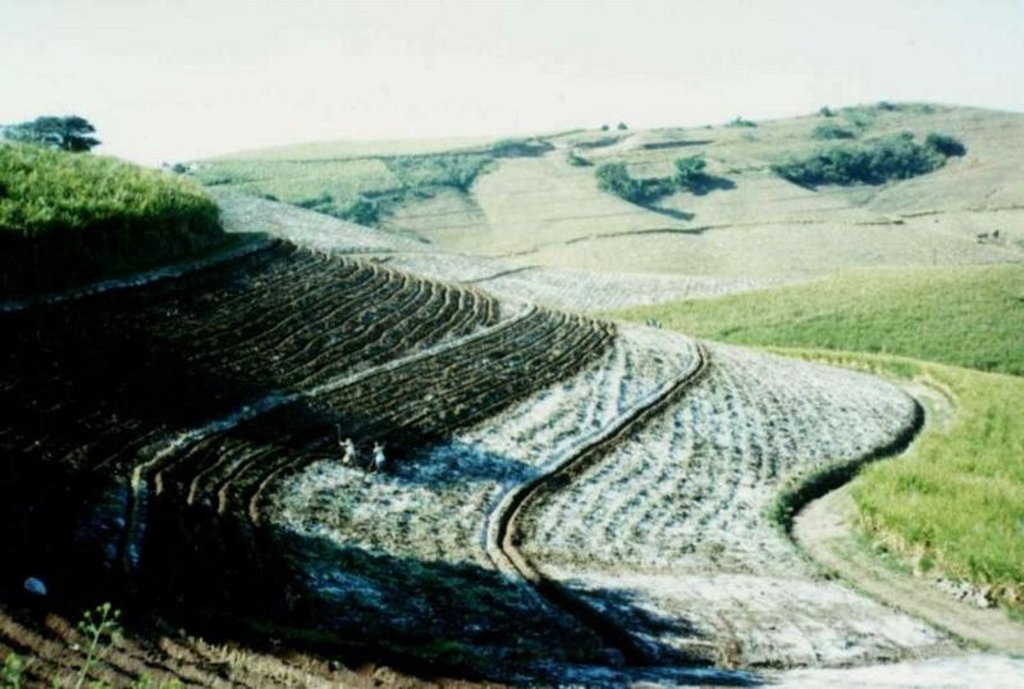
Contour lines of vetiver grass planted within fields of sugar cane, on stream banks and roadsides, to act as ‘hedges against erosion’.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
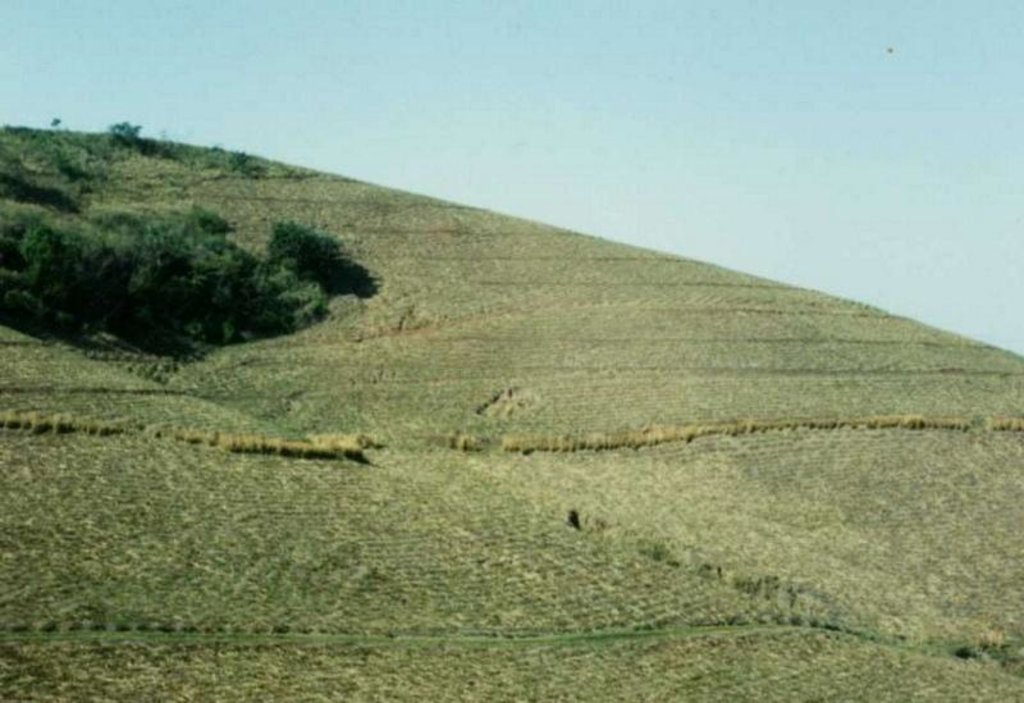
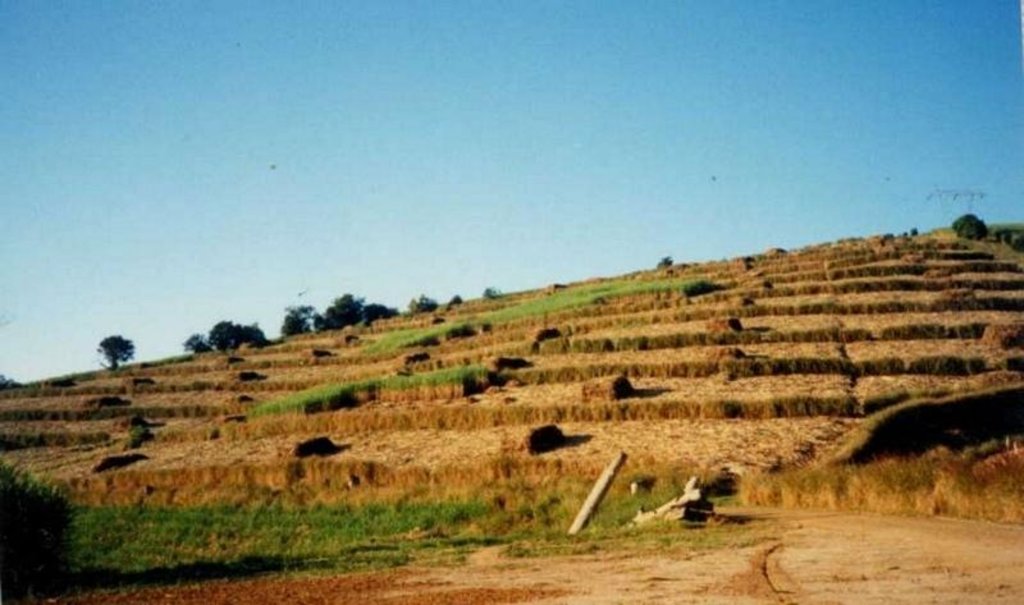
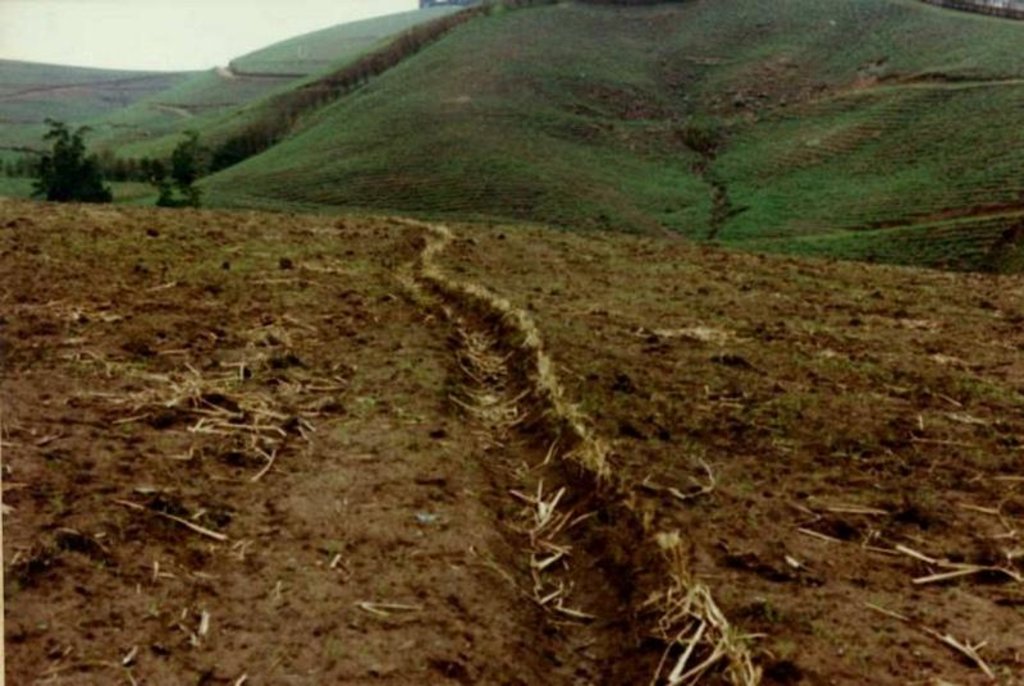
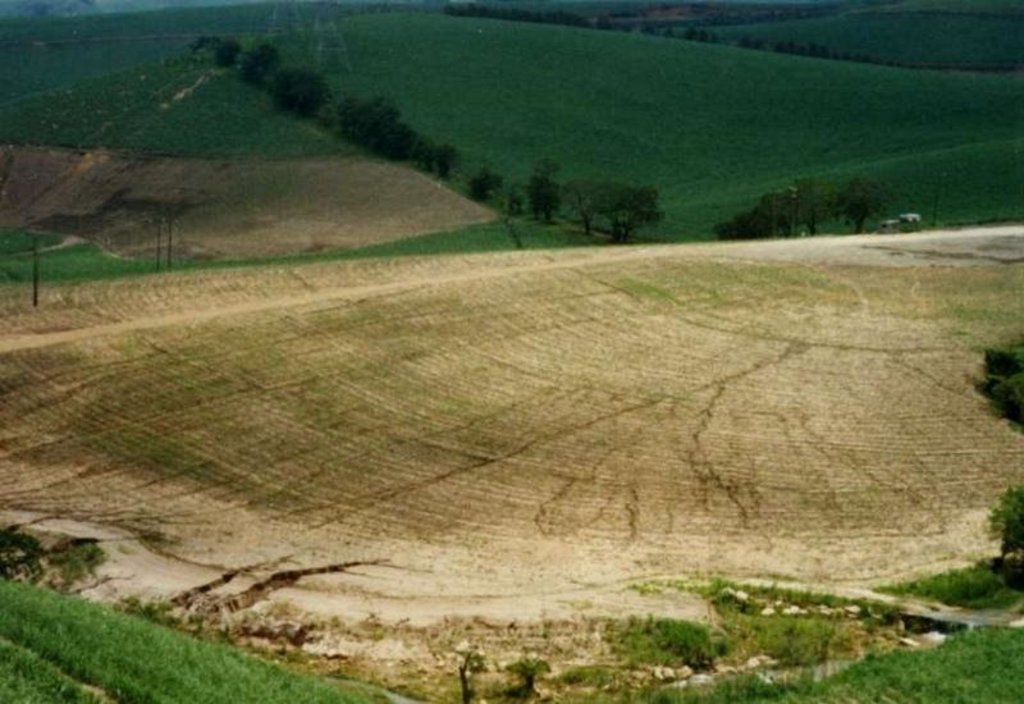
This example of vetiver grass barriers comes from a commercial farm in Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa, where sugar cane is grown on a large scale under a rainfall regime of around 1,000 mm per year. Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides), which had been growing naturally on the farm for years in isolated clumps, began to be used in 1989 to form vegetative hedges along the contour.
The purpose of these hedges is to protect the land from surface erosion by creating semi-permeable barriers, allowing excess runoff to filter through but holding back sediment. Infiltration is thus increased and moisture conserved in-situ. Although sugar cane in itself protects the soil quite well when the canopy is closed, after harvest on the moderate to steep slopes (10% to >30%) and erodible soils of the north coast of Kwa-Zulu Natal, extra protection is required. The vetiver system is supplemented by other soil conservation measures such as strip cropping, terraces, mulching and minimum tillage – all of which are used to some extent on this farm. Vetiver also helps by permanently marking the contour line, which then guides land preparation. In common with other vegetative barriers, vetiver lines lead to the formation of terraces over time, through the effect of tillage and water erosion between the strips.
Vetiver clumps are dug up and separated into slips (tillers), cut to a length of 10 cm and then planted 10–15 cm apart along the contour, also by stream banks, and by roadsides, just before the rains. This ensures good establishment. Single lines are used in this farm, though double lines are more effective at creating a hedge, and are the normal recommendation. Work starts at the top of the slope, and continues downwards. The cross-slope grass hedges are sited at 5 m vertical intervals on slopes of more than 10%, in lines about 200 m long. The cost of vetiver grass planting depends very much on slope (and thus the number of lines to be planted), availability of materials and labour.
Maintenance is very important, as vetiver often requires ‘gapping-up’ to keep the barrier dense, and it needs also to be cut back before the dry season to prevent it burning. The cut material can be used for mulching. Vetiver is poorly palatable, and therefore not useful as fodder. The maximum height of a vetiver hedge is kept down to approximately 50 cm. This minimises shading and competition, keeps the fire risk low, increases tillering (for production of vegetative splits) and ensures adequate density.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جنوب أفريقيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
KwaZulu/Natal
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Lower Tugela district
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The grass originally came to this country from Mauritius.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The steep topography and shallow soils limit the types of land use possible e.g.. perennial grass cover (sugarcane or grazing) or commercial timber production. Annual cropping is not possible without major alteration to the landscape e.g. terracing.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 200
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - April
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 8 m2.
The vetiver system has been applied on my own properties. Neighbouring farms have adopted other methods of conserving the soil. i.e. vegetative, agronomic and structural in various combinations (= farm)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, structural measures, management measures
Specification of other vegetative measures: grass strip as hedges
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, minimum tillage, contour ridging
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Et: loss of topsoil, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
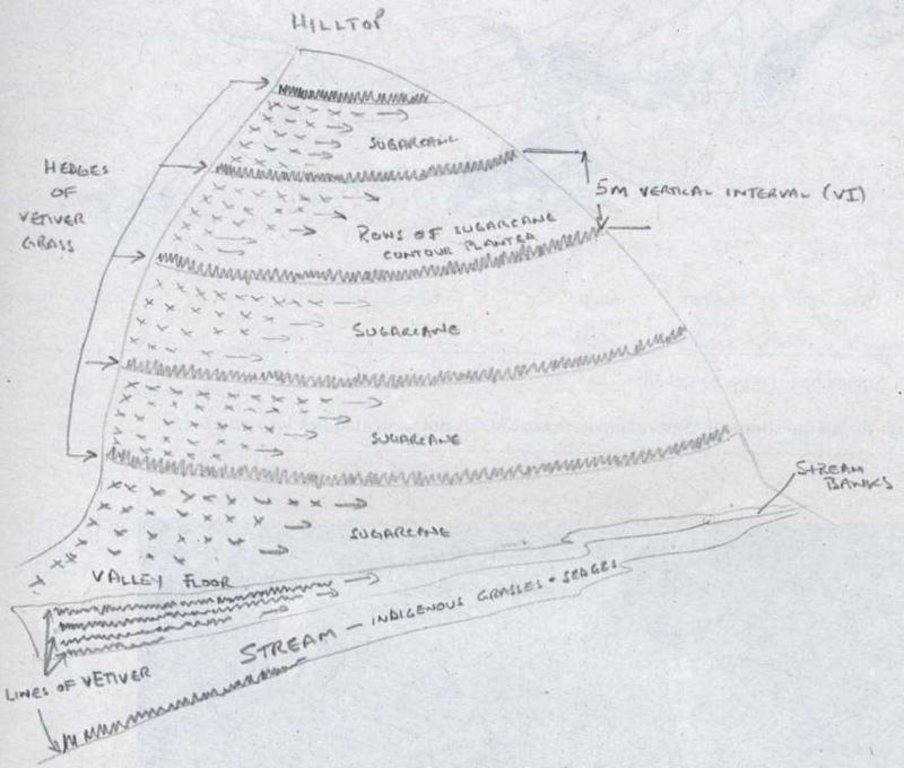
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Vetiver grass is planted as a vegetative barrier (hedge), on the contour at 5 metre vertical intervals within fields of sugarcane.
Location: Lower Tugela district. KwaZulu/Natal
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: Sugarcane
Remarks: Full ground cover
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Chemical crop eradication
Contour ridging
Material/ species: Planting lines ridged on contour
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vetiver grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 20.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Other type of management: Cane is planted on suitability (slope, soil depth)
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
rand
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
6.00
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant with fertilizer & water | نباتية | Rainy season (Sept - Mrch) |
| 2. | Weed & gap plant | نباتية | |
| 3. | Cut back to promote tillering | نباتية | |
| 4. | Crop gradication | إدارية | Nov-Jan |
| 5. | Ridging of planting furrows | إدارية | +- 1-2 months before |
| 6. | Planting of sugarcane - fertiliser in furrow | إدارية | |
| 7. | Top dress fertiliser | إدارية | 9 week after planting |
| 8. | Herbicide application | إدارية | Anytime necessary after planting |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | minimum tillage | زراعية | mulching at harvest |
| 2. | minimum tillage | زراعية | |
| 3. | mulching at harvest | زراعية | April-Dec / Every year |
| 4. | Weed | نباتية | /3 times |
| 5. | Gap plant | نباتية | /Once |
| 6. | Weed | نباتية | /When required |
| 7. | Spray for creeper grasses | نباتية | /When required |
| 8. | Plaint unwanted trees etc. | نباتية | /When required |
| 9. | Harvest sugarcane | إدارية | / Annual |
| 10. | Trash management (mulch spreading) | إدارية | After harvest completed / Annual |
| 11. | Fertiliser application | إدارية | 1-2 months after harvest / Annual |
| 12. | Herbicide application | إدارية | Required / Annual |
| 13. | Hand weeding | إدارية | / Annual & when required |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: 1 hoe
1) Labour,
2) Transport,
3) Price of grass,
4) Fertiliser,
5) Equipment
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
1) Labour,
2) Transport from nursery to field,
3) The steeper the gradient the more contour lines of vetiver grass will be used,
4) Fertiliser
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- عالية (>3%)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
منطقة الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some local growers are experimenting with the vetiver system or with vetiver grass used in other applications (gullies, road embankments, etc.)
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The author is the land user |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
When planted correctly, vetiver forms a dense, permanent hedge which retains soil and water so increases crop yield How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make sure there are no gaps between slips in order to maintain a dense vegetative barrier. |
|
It has a strong fibrous root system that penetrates and binds the soil to a depth of up to 3 meters and can withstand the effects of tunnelling and cracking. Its many uses e.g.. Thatching, mulching etc. |
| Vetiver grass seed is sterile so it doesn’t spread. |
| Not very competitive to crops growing alongside. |
|
The cut material can be used for mulching and has multiple secondary uses (thatching, basket making, etc). Once established it can withstand periods of drought and waterlogging. It is also resistant to grazing and to most pests and diseases. Adaptability: can be planted in various environments and grows well in most soil types. Depending on the availability of planting materials and the spacing adopted, can be relatively cheap and easy to establish and – once well established – vetiver requires minimal maintenance. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The author is the land user |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Sugarcane residue is often blown against the hedges & this can form a thick blanket thus preventing ratooning of crop | Strategic/controlled burning at end of growing season or trimming back |
| The grass burns very easily when mature, due to its density | Keep chemicals off vetiver. |
| Susceptible to certain chemicals used in sugar cane | Establish own nursery. |
| Planting material expensive to buy: therefore costs increase considerably unless farmer has own nursery | |
| Takes time to plant a large area (in this case 2.5 ha per year). |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية