Low-Pressure Irrigation System ‘Californian’ [السنغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Julie Zähringer
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_946 - السنغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
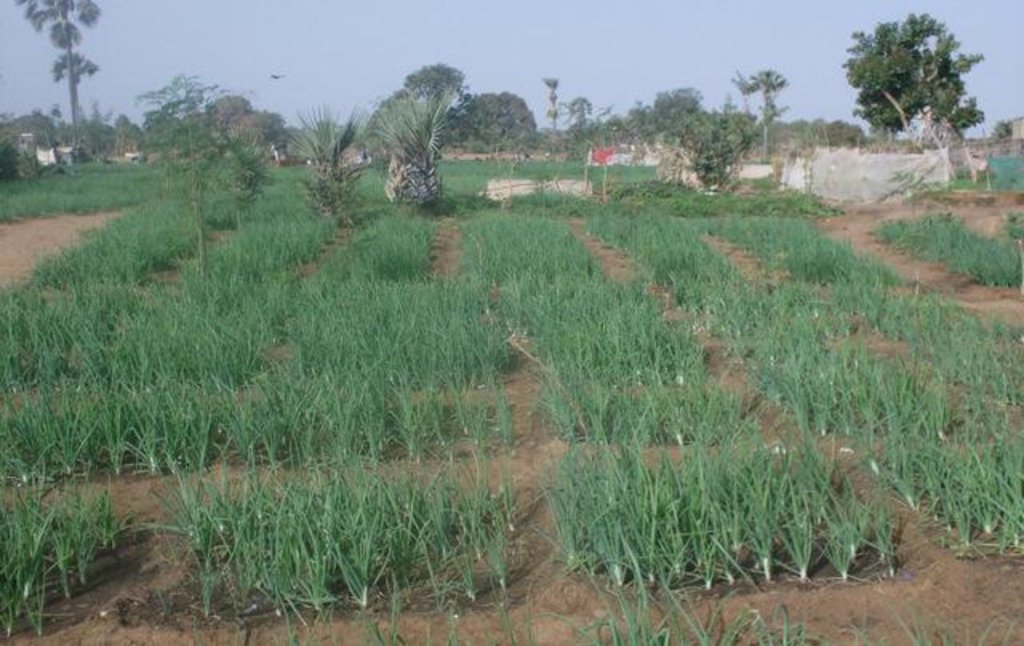
The low pressure pipe distribution system called ‘Californian’ has proven to be a very efficient irrigation system for small-holder farmers group in Africa.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
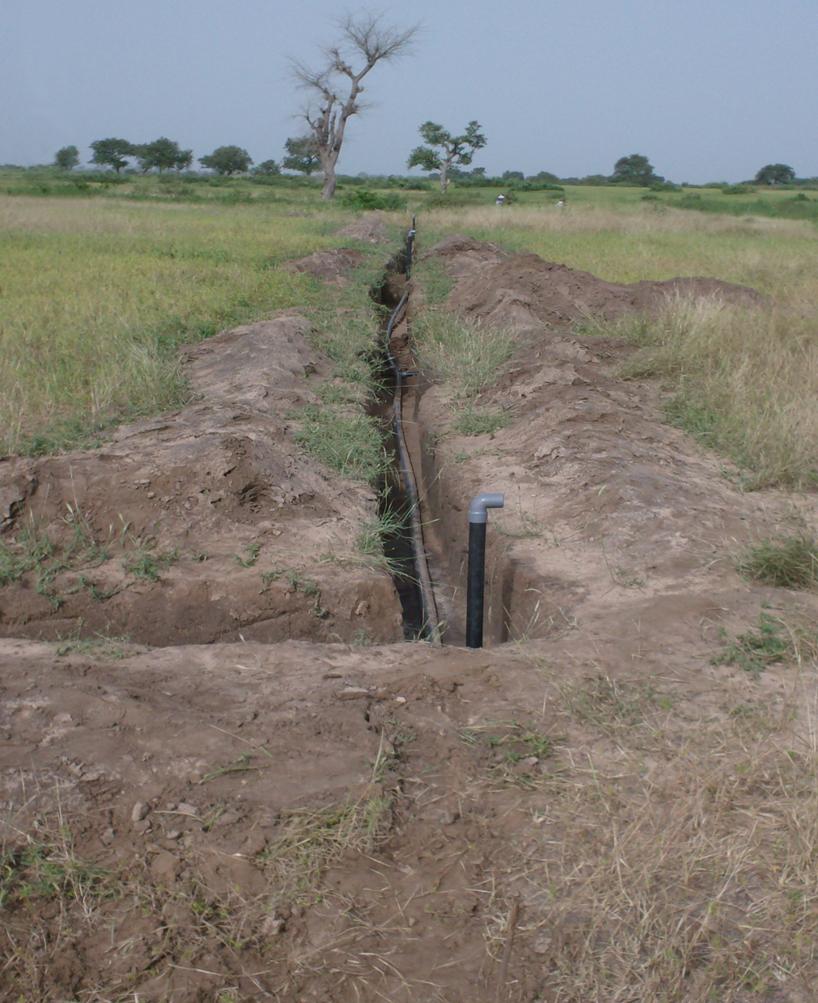
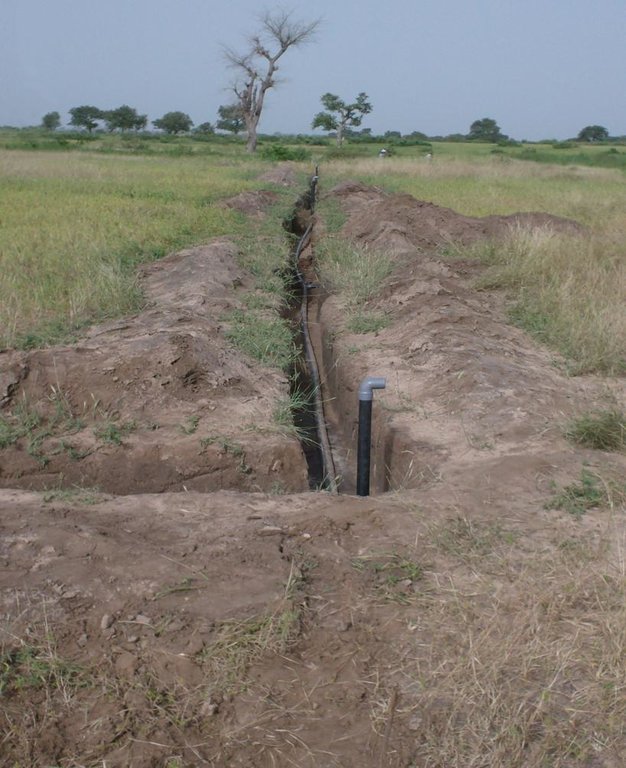
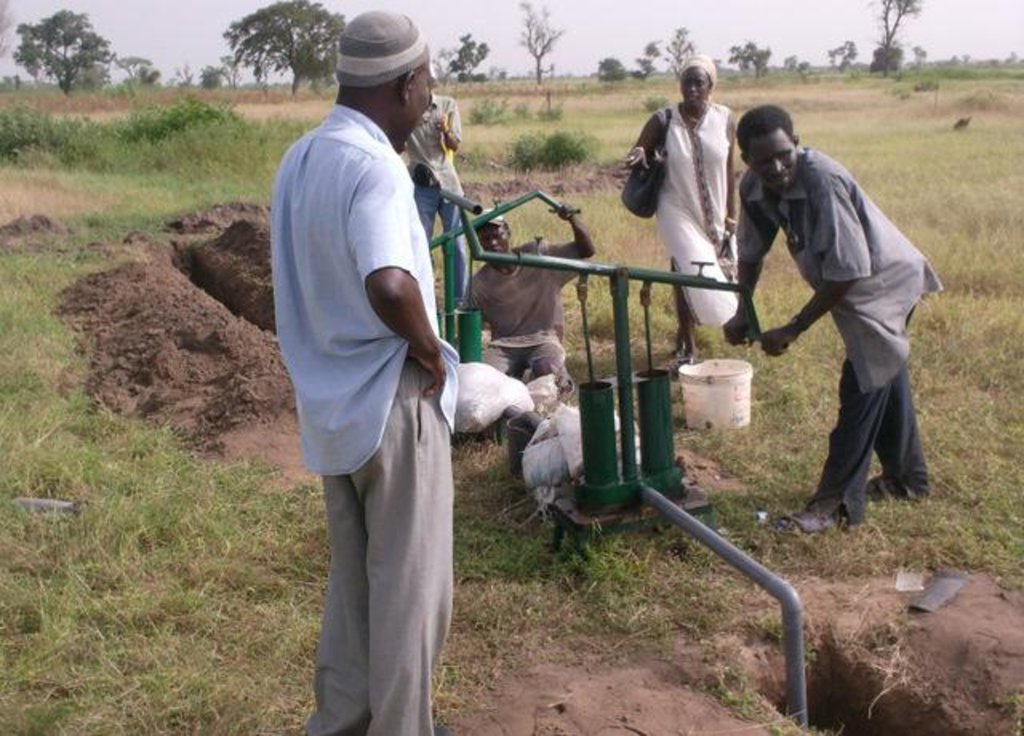
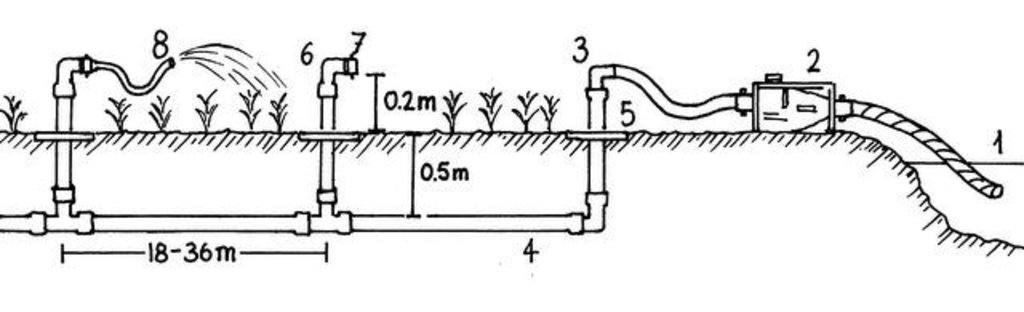
The principle of the Californian system is to convey water to the crops through fixed underground rigid PVC pipes (40–75 mm diameter). The pipe network is buried at 0.50 m depth to avoid deterioration by UV radiation and agricultural practices. Risers with hydrants are fixed to those rigid pipes at regular distance (18-36 m). To each riser a 14 m long flexible hose is attached which can be dragged around to irrigate the individual plots and crops. The installation of the pipe network can be made locally by plumbers. Water is supplied through a pump (manual, pedal or small motor) from a well, a reservoir or a river. From the intake water is conveyed to the highest point of the plot which allows the conveyance to the field’s most distant point (irrespective of topographical conditions - upslope or downslope).
The system is remarkably efficient in sandy or salty soils. It is adapted to small–scale farming especially for vegetable crops, rice and tree crops and is suitable for areas ranging between 0.25 - 1 ha; one riser irrigates an area of 500-1000 m2. The system as such does not require maintenance. In case of deterioration of pipes or fittings, the farmer can easily fix the problem himself or with the assistance of a local plumber. The estimated life expectancy for the Californian system is 6-10 years in West African conditions. Ideal conditions for transfer / adoption of the technology include: (1) Availability of shallow aquifers, and other water sources; (2) Occurrence of sandy soils and sandy clay soils; (3) Clearly defined land legislation and tenure; (4) Access to markets and to microfinance institutions.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment activities for this technology are the following: 1. Layout of pipe network by putting stakes along the line to indicate the orientation of the canal to be dug. 2. Excavate network of canals (0.2 m wide, 0.5 m deep; straight and regular). In sandy soil the interval between risers is 30m x 18m or 36m x 18m (intervals are multiples of 6 m = PVC pipe unit length). Density of risers is 10 -15 risers / ha.
3. Install the pipes into the open canals, fittings are assembled by sticking. 4. Install hydrants composed by a 0.2 m high riser, a PVC elbow and a locally made flow control device (plug); the risers are anchored in the soil through a small concrete slab.
5. Put the pipe under flow condition to verify the water tightness of the system. 6. Bury the canals. 7. Protect risers from sun. Regarding maintenance of the system the following is important: 1. Before starting to pump it is recommended to let open one of the hydrants in order to avoid excessive pressure and blasting of pipes. 2. In case of deterioration of the pipes or fittings, land users can easily fx the problem themselves or request the intervention of a local plumber.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
السنغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Diourbel
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Diourbel, Baba garage village
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A6:أخرى
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Dimensions and main components of the low-pressure irrigation system: (1) water source; (2) manual or motor pump; (3) input hydrant; (4) rigid PVC pipes; (5) small concrete slab; (6) elbow; (7) plug; (8) flexible hose for irrigation
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Technical assistance needed for design, installation and operation of the system; installation of pipes is quick and easy; no need for topographical survey)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Agronomic measure: low pressure irrigation
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Before starting to pump it is recommended to let open one of the hydrants in order to avoid excessive pressure and blasting of pipes | زراعية | |
| 2. | In case of deterioration of the pipes or fittings, land users can easily fix the problem themselves or request the intervention of a local plumber | زراعية |
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
If soil is not sandy labour input for establishment increases. Hand or treadle pumps are provided by the project. Motor pumps (with pump capacity 2 HP) increase costs for establishment and maintenance (fuel) but reduce labour inputs for operation.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
التعليقات:
Strong local leadership, long term land use rights and external funding or access to microfinance institutions are preconditions
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0.1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
< 10
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
الفرص الثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
الملوحة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
High tolerance as long as water source is not depleted
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The estimated life expectancy for the Californian system is 6-10 years in the West African conditions
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
468 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is high demand for the technology. Full participation of stakeholders in the whole project process and the involvement of local leaders, local NGOs and private companies are pre¬requisites for successful implementation
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Initial investment cost of construction material and equipments | |
| Breakage of riser pipes | |
| Scarcity of surface water resources, poor water quality due to salinity, low water discharge from the shallow wells and boreholes limit the applicability of the technology | |
| Lack of farmers knowledge on irrigation techniques and lack of qualified personnel for training and supervision hinder successful implementation |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية