Strip mine rehabilitation [جنوب أفريقيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Kirsten Mahood
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_970 - جنوب أفريقيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Stellenbosch (University of Stellenbosch) - جنوب أفريقيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
06/12/2001
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Rehabilitation of areas degraded by strip mining, through returning stockpiled topsoil and transplanting of indigenous species, to promote revegetation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In contrast to the land degradation commonly caused when ‘strip mining’ is carried out, a land rehabilitation technology, which was first developed experimentally, is now routinely applied by mining companies on the west coast of South Africa. Indeed it is now a legal requirement in South Africa for mining companies to rehabilitate mined areas to a condition and productivity equivalent to the pre-mining situation.
The primary purpose of the technology described here is to achieve this result – thus allowing the site to be used again for extensive grazing by sheep and wild animals. Revegetation also reduces wind erosion. The technology further contributes to increasing biodiversity, as particular attention is given to planting a range of locally endemic and other indigenous species.
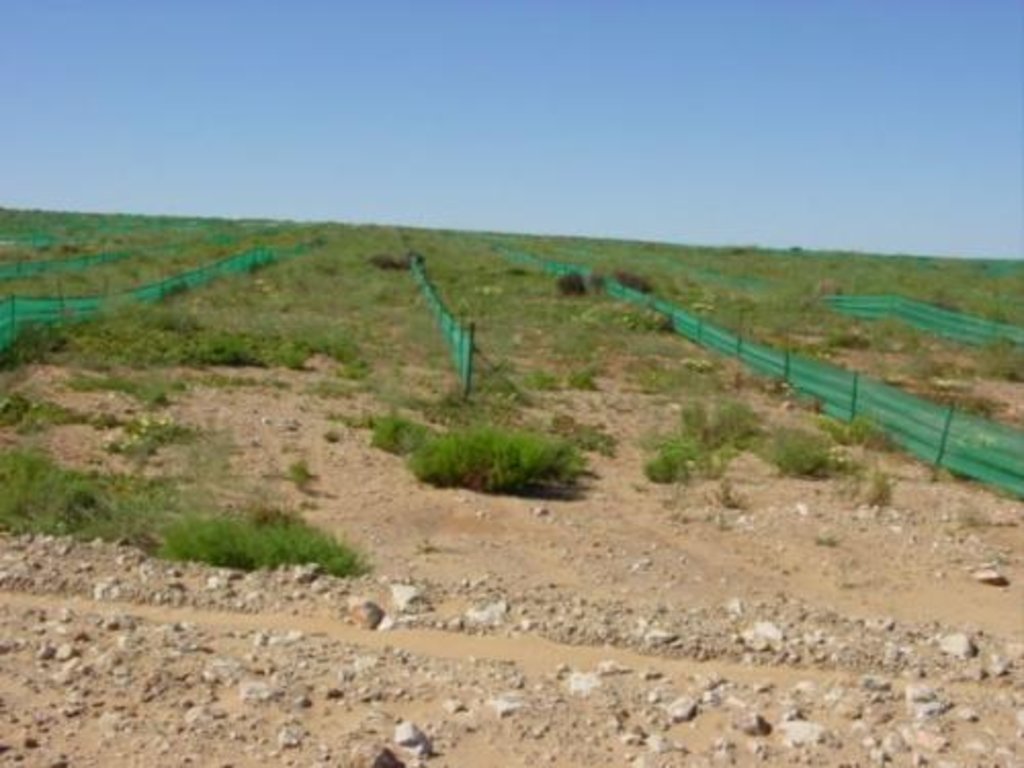
The sequence of operations is as follows: during strip mining operations the topsoil is pushed to one side by bulldozer, and stockpiled. The substrata is then excavated mechanically, removed by tipper truck, and processed to extract the heavy metals. The tailings (waste materials) are returned by tipper truck to the area from which they were mined, and then levelled by bulldozer. The stockpiled topsoil is returned and spread by bulldozer over the levelled tailings. Indigenous succulents and other plant species are dug out by hand, with a spade, from either the surrounding areas of natural vegetation, or from the piles of topsoil (where plants may have naturally established) and transplanted manually into the newly spread topsoil. The planted areas are protected from wind erosion by erecting fine mesh nylon netting as windbreaks. These are 0.8 metre high and 5 metres apart. The nets are usually installed for a period of up to 2-3 years. Subsequently they are removed, once the vegetation has successfully become re-established, and they may be re-used at the next rehabilitation site. Maintenance activities continue for a few years – until the site is rehabilitated. An individual mine strip is usually about 1 km long and some 100 m wide.
This form of strip mine rehabilitation has been in operation since 1990, and costs on average just over US$ 200 per hectare, with all expenses met by the mining company. This particular approach was developed for the Anglo-American subsidiary – ‘Namaqua Sands’. A similar approach was adopted by ‘PBGypsum Mines’ located further inland, where rehabilitation is also conducted on several hundreds hectares of mined land. Not all mining companies use the same technology, however.
Purpose of the Technology: Establishment activities:
Mining activities (not part of technology)
1.Removal and stock piling of topsoil
2.Excavation, removal and processing of substrata to extract heavy minerals
3.Return and levelling of the mine tailings
4.Return and spreading of topsoil Technology activities
5.Collection/digging up of indigenous plants
6.Transplanting into returned topsoil
7.Erection of fine mesh nylon net windbreaks Activities 1-4 are a continuous process associated with the speed of mining activities and involve the use of heavy earth moving machinery (bulldozers, front end loaders, tipper trucks). Activities 5&6 take place immediately prior to the onset of the rainy season and involve hand labour for collection and transplanting and tractor and trailer for transporting collected plants. Activity 7 can take place at any time of the year involving hand labour for erection of the nets and tractor and trailer for transport.
Maintenance / recurrent activities per year:
Maintenance activities restricted to:
1.Ensuring the nylon nets remain upright
2.Supplementary watering during the winter months, when rainfall inadequate, to support plant growth
2.3 صور التقنية
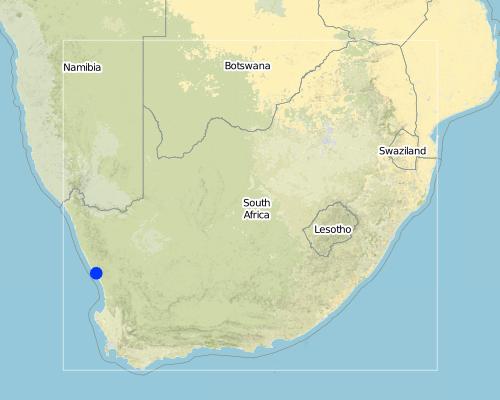
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جنوب أفريقيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Western Cape
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Brand-se-Baai, Western Cape
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Developed at University of Stellenbosch
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- مربى ماشية محدد
المناجم والصناعات الاستخراجية
حدد:
Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Aridness and climate change. Erratic rainfall/climate. Frequent drought.
Ranching: Yes
Constraints of mines and extractive industries: Stockpiling of topsoil; processing of subsoil
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Aug
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Specification of other vegetative measures: translocation of indigenous plants
Specification of other structural measures: land levelling, artificial windbreaks
Type of agronomic measures: zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pu): فقدان الوظيفة الإنتاجية الحيوية بسبب أنشطة أخرى
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 2000
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Other species: Succulent plants
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
Structural measure: silt fence
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Construction material (other): nylon net - small grid size
Silt fence: all 5m and height of 0.8m
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Rand
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
9,07
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
12.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of plants from natural vegetation | نباتية | Pre-rainy season |
| 2. | Collection of plants from topsoil stockpiles | نباتية | Pre-rainy season |
| 3. | Transport plants to rehabilitation area | نباتية | Pre-rainy season |
| 4. | Plant all plants | نباتية | Pre-rainy season |
| 5. | Insert droppers into net pockets | بنيوية أو هيكلية | all year |
| 6. | Spread nets over topsoil areas | بنيوية أو هيكلية | all year |
| 7. | Erect nets and hammer in droppers | بنيوية أو هيكلية | all year |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | hectare | 3,0 | 75,0 | 225,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | machine | hectare | 67,0 | 100,0 | ||
| المواد النباتية | seedling | hectare | 100,0 | |||
| مواد البناء | nylon netting | hectare | 70,0 | 100,0 | ||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 225,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Topsoil pushed into stockpile | زراعية | all seasons / continuous |
| 2. | Subsoil removed and processed | زراعية | all seasons / continuous |
| 3. | Processed subsoil returned to mined area and levelled | زراعية | all seasons / continuous |
| 4. | Stockpiled topsoil spread over processed subsoil | زراعية | all seasons / continuous |
| 5. | Plants transplanted onto spread topsoil | زراعية | just before rainy season / late autumn/winter |
| 6. | Ensure nets remain upright | بنيوية أو هيكلية | all year/continuous |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | hectare | 37,0 |
التعليقات:
Per hectare
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour costs
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
soil fertility: very low, soil drainage / infiltration = low, soil water storage capacity = low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Most of income from mining
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
vegetation, establishment
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land can be used again for extensive grazing after mining
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
improved conservation / erosion knowledge
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
restoration of bio-productive function
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
biodiversity enhancement
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
reduced wind velocity
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Low establishment costs and very low maintenance costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make use of whatever resources and potentials are naturally available (such as micro-catchments to trap rainwater and improve soil moisture conditions for plants) to lower establishment costs. |
|
Costs are met by the mining company – no costs are transferred to those who subsequently use the land for grazing How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular monitoring of soil and vegetation conditions. |
|
Land productivity is restored and biodiversity increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Seeding as well as transplanting. |
| Wind erosion minimized. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Rehabilitation is an extra cost for the mining company. | Ensure mining company meets the costs through enforcing legislation. |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية