Calliandra contour hedges [اوغندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
Orugo rwa Calliandra (Rukiga)
technologies_1178 - اوغندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Kabale District Local Government (Kabale District Local Government) - اوغندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
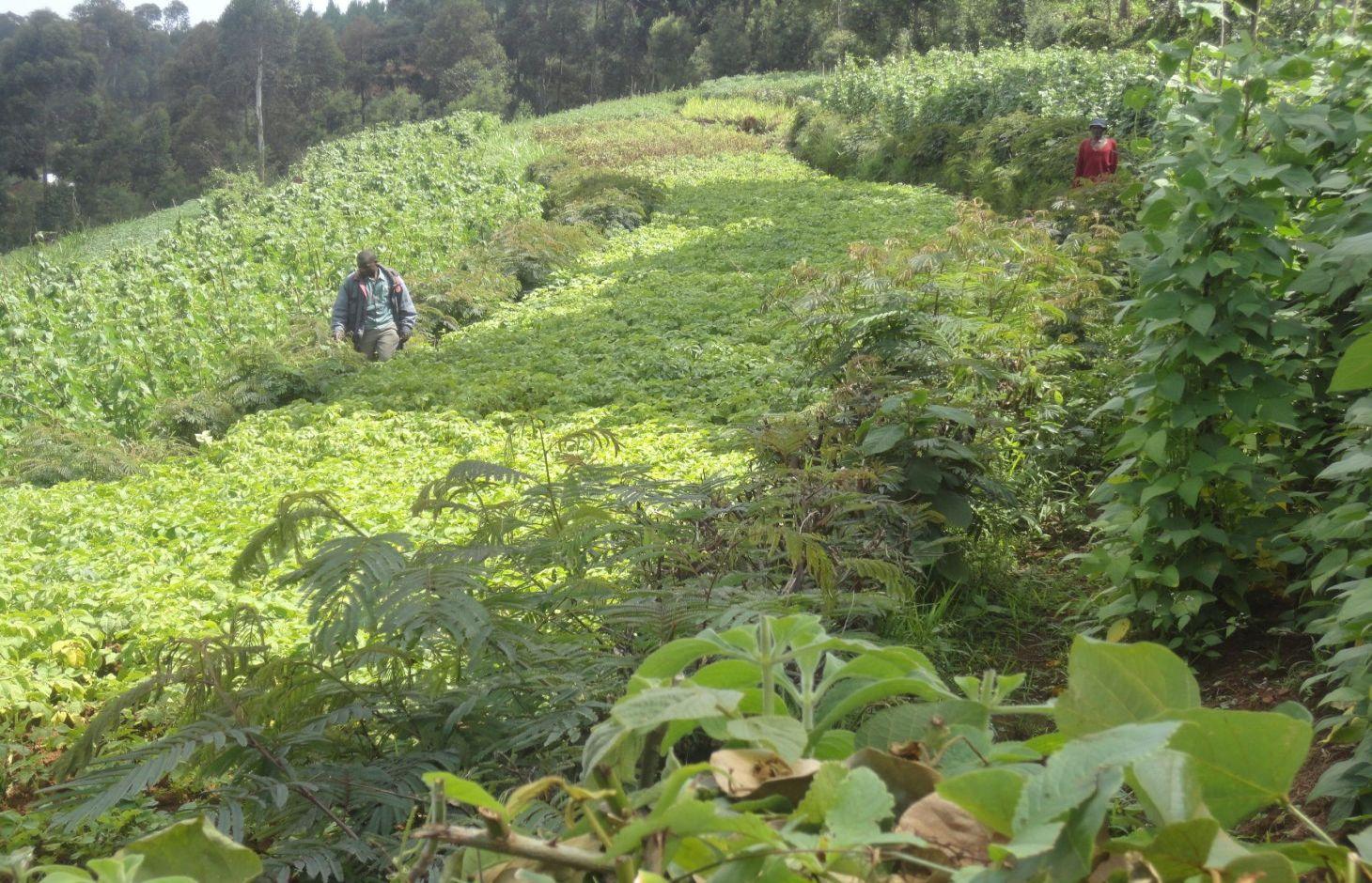
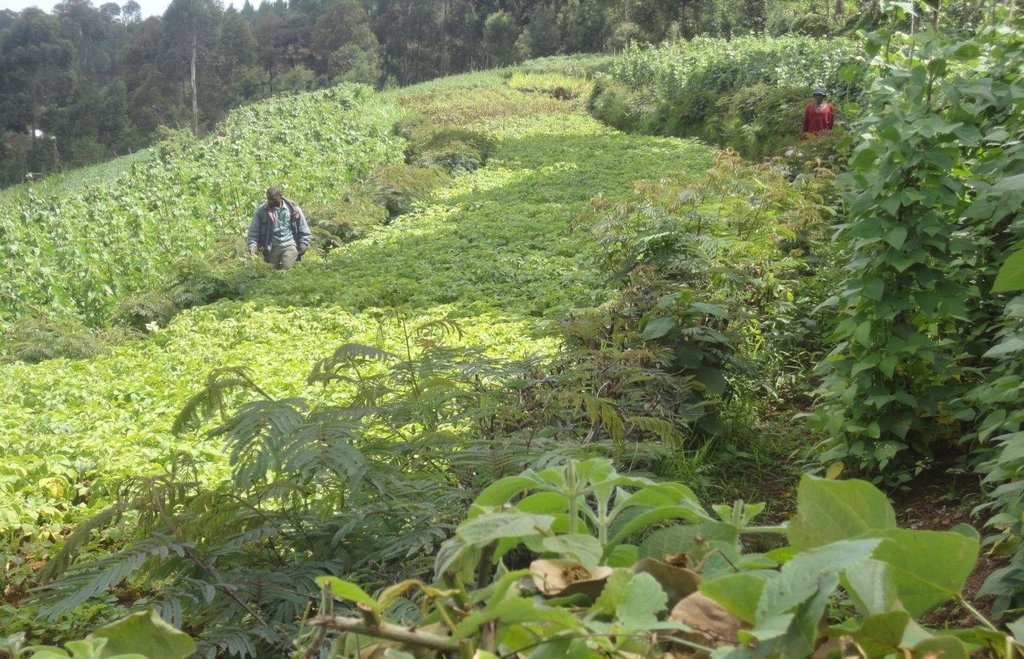
Contour hedges of Calliandra planted on very steep slopes to combat soil erosion by decreasing surface runoff and increasing infiltration.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Calliandra Calothyrsus trees are closely planted along the contours on hilly and steep slopes to create natural and effective barriers for reduction of the surface runoff and retention of eroded sediment. Calliandra hedge barriers are a fairly cheap, effective, and sustainable way of controlling soil erosion and landslides on vulnerable steep slopes, especially where trash lines and Napier grass strips were inadequate to mitigate dispersed and concentrated soil and water runoff. Once established, the living barrier is durable with minimal additional maintenance cost to the farmer apart from pruning. The average length of a hedgerow is 50 to 70 m, corresponding to the width of a single terrace. The height varies according to intended use of the mature shoots. To use the stems as stakes, the hedgerow is allowed to reach a height of 4 to 6 m at maturity while a height of 1 to 2 m is sufficient for harvesting foliage as livestock fodder. The hedge barrier reaches its mature, maintenance level after 12 to 18 months.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the Calliandra hedge barrier is to reduce soil and water runoff.Calliandra is a leguminous shrub with deep roots that provids additional benefits such as soil stabilization and soil fertility improvement through nitrogen fixing. Calliandra is a source of fodder and its flowers attract bees.
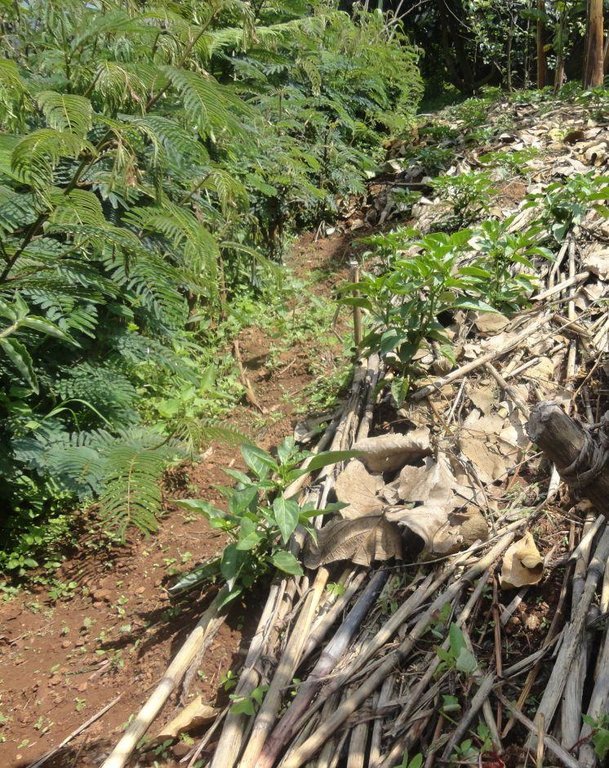
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: At the beginning of the rainy season, calliandra seedlings are transplanted from the nursery (0.2m to 0.3m height) and planted in a row (0.3m spacing). In the early stages, gap-filling with more seedlings may be necessary as some fail to get established. A mixture of top soil and manure is applied in the spaces between the seedlings and watering is done to improve the seedling survival rate. The distance between rows is 10 to 15 m and depends on the gradient of the slope. Establishment of hedges starts with construction of an earth banked terrace, creating a trench at the lower end of the terrace. Calliandra seedlings are planted on the higher side of the trench. Measuring off 10 m lengths upwards into the terrace, other rows of Calliandra seedlings are planted along the contour in order to achieve the inter-row spacing. Establishment is manual labor intensive and therefore the community, organized as Farmer Field Schools, participates in the planting, one field at a time. Simple tools such as hand hoes, sokajembe (pick-axe) and shovels are used. Maintenance is achieved by weeding, mulching and cutting back. For it to establish well, Calliandra needs to be weeded to minimize competition with weeds for water and nutrients . The weeds also harbour pests. It may also be necessary to mulch the area around each seedling during the dry season. Where mulching is done, the mulch is placed at least 0.05m away from the plant to reduce pest attacks. Calliandra calothyrsus trees are cut back at a height of 2m to between 0.15m and 1m to improve foliage which is used as fodder for livestock. The hedge is then maintained at a height of 1 to 6 m depending on the intended additional uses. The branches removed can be used as fuel wood or stakes, while leaves can be used as fodder.
Natural / human environment: The hedge barrier may be attacked by pests. Scales are white, powdery insects that attack Calliandra stems. Scales can be controlled using washing detergents such as ‘Omo’ dissolved in water and sprinkled on affected plants using leafy branches or a knapsack sprayer. Black ants can seriously damage trees. They can be controlled by spraying. Other likely pests are crickets and grass hoppers which affect seedlings in nurseries, and Armillaria mellea, a fungus that attacks roots of Calliandra plant causing root rot and eventual death. Affected plants are uprooted and burnt. In addition, calliandra is affected by hot, dry weather. During the hot, dry weather, the hedge barrier becomes weak. However during the wet season it sprouts again, and, if well managed, becomes healthy again. A well-maintained hedge barriers can last well over 20 years.
2.3 صور التقنية
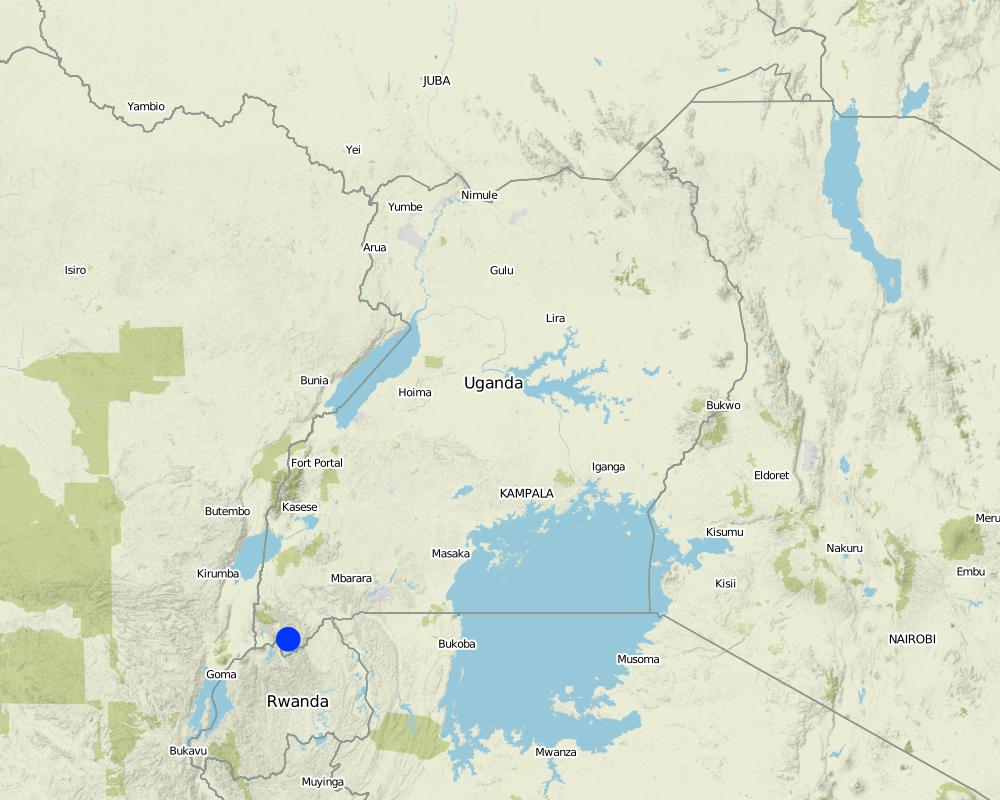
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اوغندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Uganda
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kabale District
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.29294, 29.96006
-1.29336, 29.96027
-1.29327, 29.96084
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.03 km2.
The documented case study area is around 3ha
-1.29371, 29.96095
-1.29345, 29.96091
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology was introduced by ICRAF in 2006 and scaled-up Kagera TAMP project 2 years ago.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- محاصيل الأعلاف - أخرى
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- أشجار العلف (كالياندرا، لوسينا، المسكيت، إلخ.)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: February to MaySecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- مراعي محسنة
- Livestock is grazing on crop residues
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The slopes are steep >30% to very steep >60%), with very high precipitation (>1440 mm). Severe surface erosion and landslides may occur at the beginning of the rains, before sufficient vegetation covers the soil. Continuous cultivation with little external inputs and nutrient transfer affects negatively soil fertility and in results reduces crops growth/vegetation cover, leading to erosion on steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Floods are common in the valleys over the past ten years.
Improved pasture: Diary hiefers,pigs(largewhite and layers)pasture include calliandra,stellia and elephant grass.
Constraints of settlement / urban: floods invade houses
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): transport problem
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wm): مجموعة كبيرة من الحركات الأرضية/انزلاقات أرضية
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor vegetative cover/no trees to bind soil particles.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rainfall intensifying in september and April.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (steep slopes (extreme topography)), population pressure (Population increase/no of people increased per sq km), poverty / wealth (lack of resources to implement known natural resources degradation mitigation measures)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
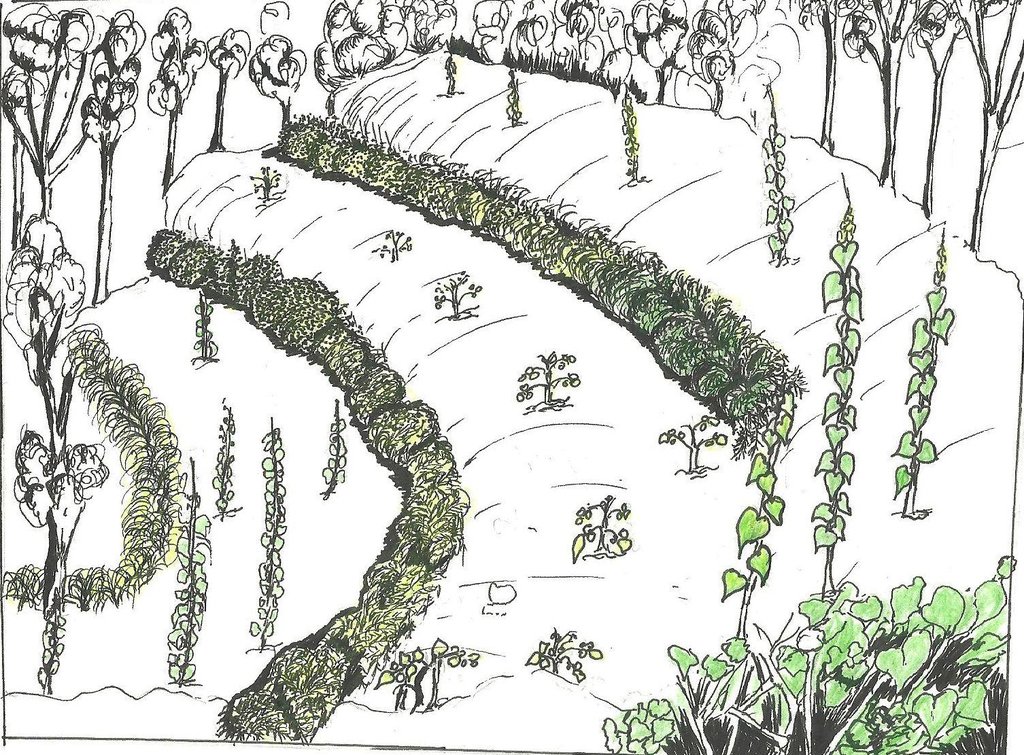
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Calliandra trees are planted in rows along the contour. Cutting back is done between 12 and 18 months to a height of 0.5 m. The trees are allowed to grow to between 1 and 6 m and the hedge is maintained at that height. Gap-filling, weeding and trimming are critical for a productive hedge.
Location: Bukoora, Kabale. Kabale/Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Such knowledge as is required to manage the Calliandra nursery, transplant and maintain the plants especially until the first coppice.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user is responsible for maintaining the technology on his or her land and a good hedge requires diligence)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 670 to 720
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Calliandra was planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: n/a
Perennial crops species: n/a
Grass species: n/a
Other species: n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 40%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): n/a%
Gradient along the rows / strips: <3%
المؤلف:
Byonabye, Prossy, Kagera TAMP, Kabale, Uganda
التاريخ:
2013-11-29
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
UGX
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
2602,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.80
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of Calliandra nursery | Dry season |
| 2. | Plantation of Calliandra seedling on the higher side of the trench | Wet season |
| 3. | Weeding |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | 1,0 | 44,6 | 44,6 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | tools | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | 1,0 | 30,4 | 30,4 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | 1,0 | 9,6 | 9,6 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 100,8 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,04 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 18 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prunning and triming the hedge barriers | wet/dry season |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 20,8 | 20,8 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | tools | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 | |
| غير ذلك | 100,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 38,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,01 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: I panga,1 watering can, 1hoe.
The cost assesment above refers to steep slopes.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The cost of seedlings (0.20 US$ each) and their transport up along steep slopes are the key factors affecting costs and hindering spontaneous adoption of the technology. Otherwise, the technology is acceptable to farmers as benefits are easily visible in the short run.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. at the Equator
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Maintenance such as pruning trimming is mostly done by the men, but the other activities are done by both men and women.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (meets basic needs/necesities).
45% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Crop and animal production greatly increased for land users implementing conservation measures , compared to those who do not implement.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
التعليقات:
The land belongs to an individual with no title but has all the rights over it.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
n/an/an/an/a:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
150
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
700
جودة العلف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25
منطقة الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.5 million
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3.5million
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
increased pests
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
-
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
| n/a |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Benefits are high compared to establishment and maintenance cost
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
45 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is appreciated by most farmers but adoption is limited by cost of seedlings and transportation up steep slopes
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Calliandra binds the soil, thus reduces landslides. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It should be maintained through proper management |
|
Adds scenic beauty on a plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? By regular trimming |
|
Calliandra is good and attractive to bees How can they be sustained / enhanced? Leave every second or third row to flower |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
It is easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote education campaign and spread information |
|
It has helped to increase crop and animal production How can they be sustained / enhanced? By proper management and not overgrazing animals |
|
Stabilize the soil and strenghtening resistance to intensive rainfall and fast runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology through increased community mobilization |
|
Very effective to reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other practicies e.g. mulching |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The hedge barrier is ineffective before 12 months | Combine with trash lines before establishment |
| Technology harbors nesting birds | Ensure regular trimming of Calliandra to reasonable height and use scarecrows |
| Needs at least 2 seasons to establish | Apply manure and water to the seedlings to ensure accelerated growth |
| May reduce the amount of sunlight available to young crops if left untrimmed | Trim regularly |
| Extra cost in protecting from damage by livestock | Inter-crop with other fodder species to act as alternative fodder for livestock |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP Project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية