Post-fire Forest Residue Mulch [البرتغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Sergio Prats Alegre Prats
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
acolchoado, aplicação de restos vegetais
technologies_1186 - البرتغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Keizer Jan Jacob
Universidade de Aveiro-CESAM
البرتغال
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - البرتغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
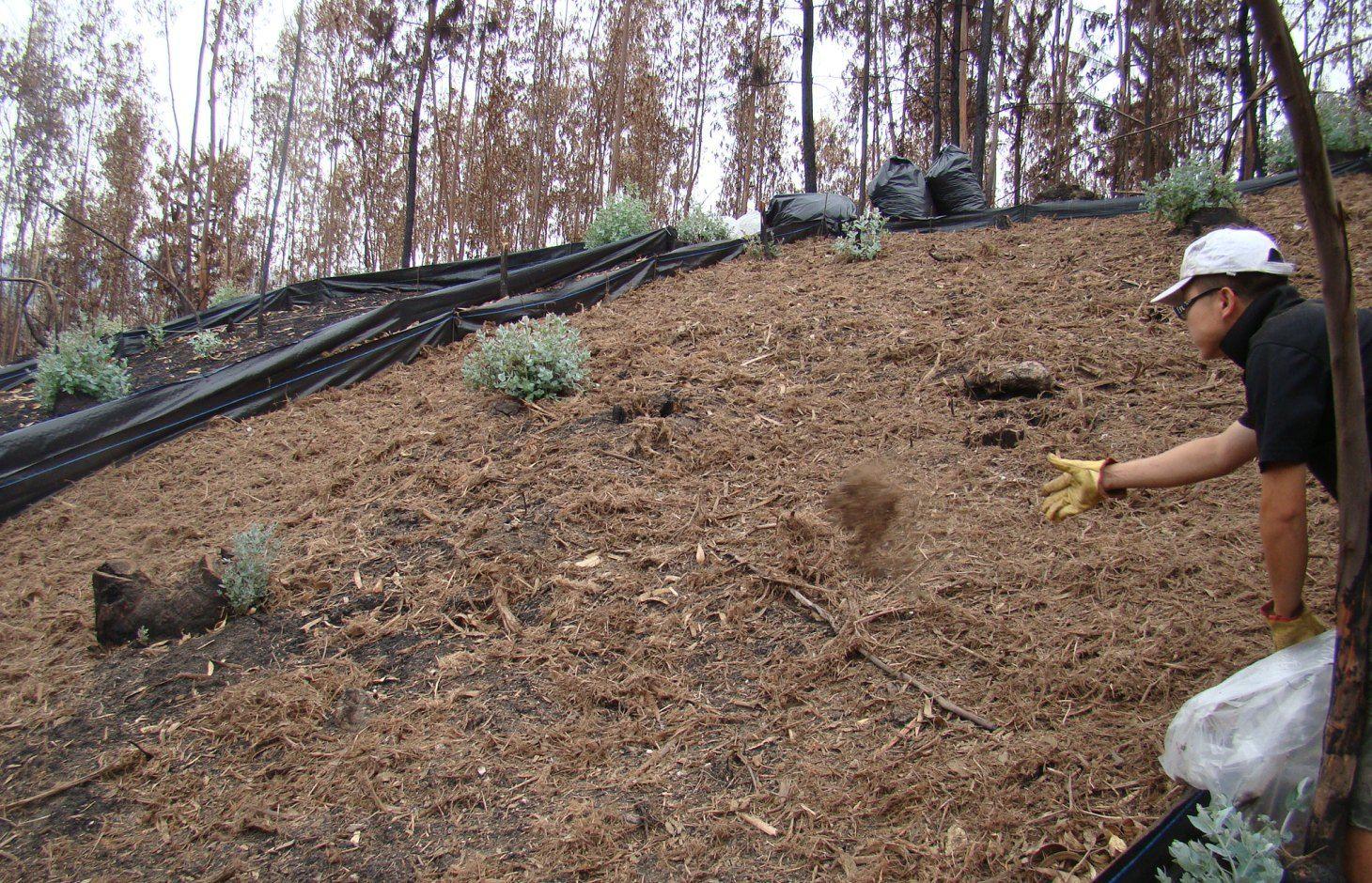
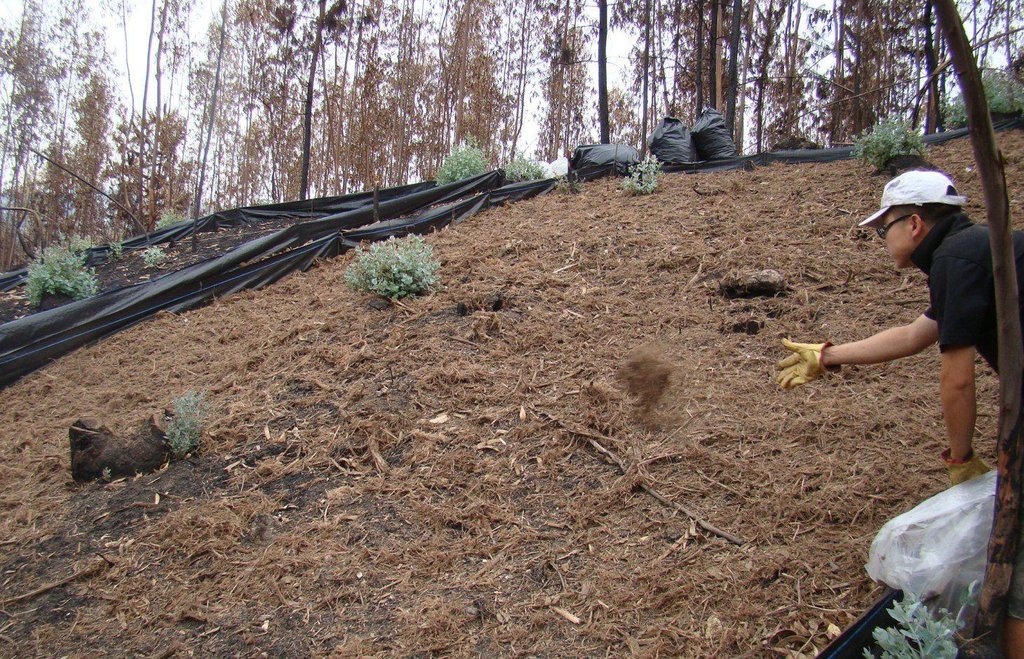
Forest residue mulch is spread immediately after a wildfire in order to prevent soil erosion and reduce overland flow.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In two areas of eucalypt plantations affected by wildfires in central Portugal in 2007 and 2010, the research team of the University of Aveiro set up two experiments in order to test the effect of forest residue mulching as a soil erosion mitigation technique. Forest residues such as chopped eucalypt bark mulch was spread over a group of erosion plots, and was compared to an untreated group of plots.
The mulching was applied at ratios of 8.7 and 10.8 Mg ha-1 provided an initial ground cover of 70 to 80%, and was found to reduce post-fire runoff by 40-50% and soil erosion by 85-90%, respectively.
Purpose of the Technology: The increase in ground cover will decrease post-fire soil erosion by reducing raindrop impact over the ashes and bare soil, and decrease the runoff amount by increasing water surface storage, decreasing runoff velocity, and increase infiltration.
Ideally, post-fire mulching must be carried out immediately after the fire, in order to prevent that the first autumn rainfall events fall over the bare and unprotected burnt soils. It is intended for places in which burnt severity was moderate to high and where there are important values at risk, such as water reservoirs, populations, industries, human and wild life.
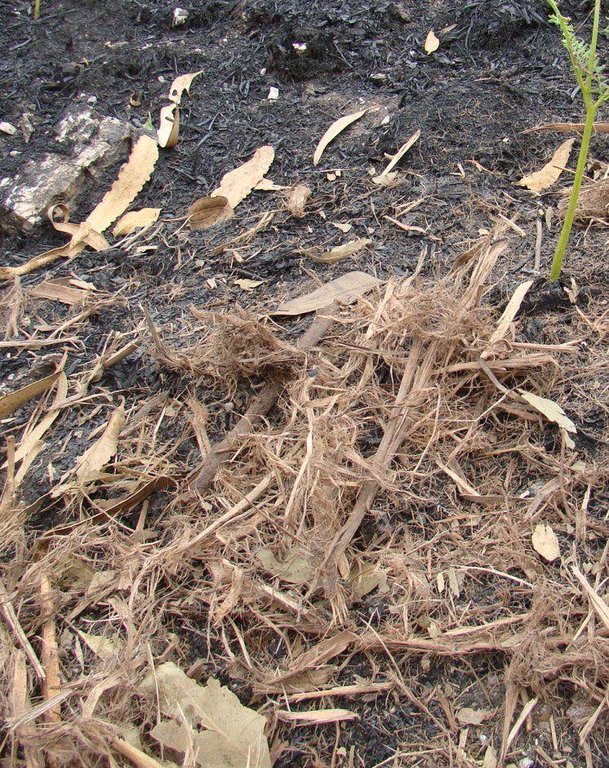
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The chopped bark mulch was obtained at a depot 20 km from the burnt area, where eucalypt logs are debarked and then transported to a paper pulp factory. The bark is chopped into fibers and are typically transported to a biomass energy plant. We used these 10–15 cm wide 2–5 cm long bark fibers as the source for our mulching experiment. The chopped bark mulch decays very slowly (around 20% less ground cover per year) which was very useful in cases of low re-growth of natural vegetation.
Natural / human environment: The eucalypt trees in the region are typically planted as monocultures for paper pulp production, and harvested every 7-14 years. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-)natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. Since the 1980´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, aided by a general warming and drying trend but driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
البرتغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Portugal/Beira Litoral
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Sever do vouga/ Pessegueiro do Vouga, Ermida
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.0E-5 m2.
The experiment was carried out in grous of small bounded plots of 0.25, 16 and 100 m2.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The first experiment was carried out in 2007.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
نوع الشجرة:
- أنواع الكينا أو الاوكاليبتوس
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Increased runoff and soil erosion, resulting in a decrease of on-site fertility and derived off-site effects such as loss of water quality, reservoirs water volume storage, higher risk of flooding and human beings damage.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of wood resources and productivity.
Plantation forestry: eucalypt are logged and left to regrow from stumps each 7-10 years
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Eucalypt monocultures are prone to suffer wildfires), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Increased runoff is observed after wildfires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Burnt areas are very sensitive to high intensity events), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sediment deposition can decrease the storage volume of reservoirs.)
Secondary causes of degradation: floods (Overland flow can be extremely high after forest fires), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Roads concentrated the runoff and are greatly degraded.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
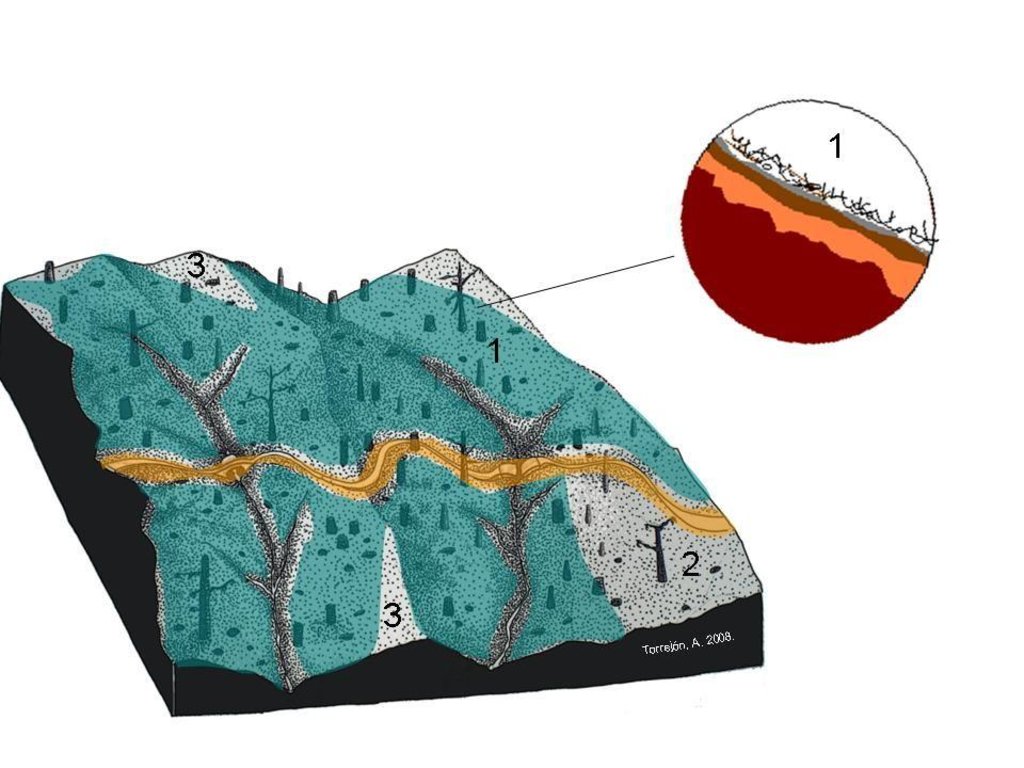
Forest residue mulch is spread as homogeneous as possible over steep areas (steeper than 15º) burnt at high fire severity (represented in green and 1). Other areas which are flat (2) and burnt at low severity or only partially burnt (3) must be avoided.
Location: Ermida. Sever do Vouga/ Portugal
Date: 15 9 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (forest residue mulching is highly effective in all situations, but applications using short fibres mulching as well as low intensity burning should be avoided.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Mulching
Material/ species: chopped bark, cork, stems, leaves, straw/eucalypt, pine, oaks, shrubs
Quantity/ density: 2-10t/ha
Remarks: material with low density (straw) need less weight for achieving the final goal: 70% ground cover.
المؤلف:
Departamento de Ambiente e Ordenamento. Universidade de Aveiro.
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Euro
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,78
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
64.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labour | |
| 2. | Transportation (small truck for carrying persons and material) | |
| 3. | Eucalypt chopped bark mulch | |
| 4. | Others |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 192,0 | 192,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 51,2 | 51,2 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Forest residue mulch | ha | 1,0 | 307,6 | 307,6 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Others | ha | 1,0 | 64,1 | 64,1 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 614,9 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 788,33 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
The prices were determined in winter 2012 for central Portugal. It is intended that mulch is applied only once, and thus maintenance is not needed. In other regions other forest residues can have a higher availability. Straw, needles, deciduous leaves or chopped shrubs are lighter compared to eucalypt chopped bark, slash stems or wood chips, and thus, can be easier to apply and transport. However, the lighter the material, the easier it can be blown away in windy areas.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Accessibility and steepness will raise the costs, but selecting forest residues with lower densities as well as applying them in horizontal strips along the slope can reduce the application rates and the costs.
For large and inaccessible areas some researchers indicated that helicopters can reduce the costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (300m)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Topsoil organic matter is high (Around 10 % between 0 to 5 cm of soil depth)
Soil fertility is high-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (Dependent on the soil water repellence cycles, characteristics of eucalypt and pine plantations on the area.)
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Eucalypt chopped bark mulch increases expenses if not funded by the Government
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less damage to off-site neighbouring properties
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Public awareness of the technology is very limited. It is necessary to show it to landowners and stakeholders and increase dissemination.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Hazard towards adverse events
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
If applied in large areas
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الرواسب المنقولة بواسطة الرياح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
If applied in large areas upslope
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology has been tested by scientific researchers and it is very effective, but not broadly implemented.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology has been tested by scientific researchers researchers and it is very effective, but not broadly implemented.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| It will prevent sediment movement and accumulation over roads and downslope properties |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
It is a technology very easy to apply, with low failure possibilities and a strong soil erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Some researchers found better performance by grinding the mulch and selecting only the longest fibres. |
| The material is readily available (residues from the main forest specie affected by the wildfire) |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The costs are not very high, but enough to discourage the landowners to cover the expenses. | Look for Government funding, educate land owners about soil erosion conservation techniques. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| When applying high density mulches the application labour requirements and costs will be higher | Distribute the mulch in strips, use lighter mulches, grind to remove the fine fibres or maybe try to reduce the application rate. It is also possible to use in-situ chopping tree machines or to use aerial application methods, such as helicopters to reduce the application costs. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Prats S. A., Macdonald L.H., Monteiro M.S.V., Ferreira A.J.D., Coelho C.O.A., Keizer J.J.,2012. Effectiveness of forest residue mulching in reducing post-fire runoff and erosionin a pine and a eucalypt plantation in north-central Portugal. Geoderma 191, 115-124.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Internet
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Shakesby R.A., Boakes D.J., Coelho C.O.A., Gonçalves A.J.B., Walsh R.P.D., 1996. Limitingthe soil degradational impacts of wildfire in pine and eucalyptus forests in Portugal.Applied Geography 16, 337-335.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Internet
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Robichaud, P.R., Lewis, S.A., Ashmun, L.E., Wagenbrenner, J.W., Brown, R.E., 2013a.Postfire mulching for runoff and erosion mitigation Part I: Effectiveness at reducinghillslope erosion rates. Catena 105, 75–92.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Internet
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية