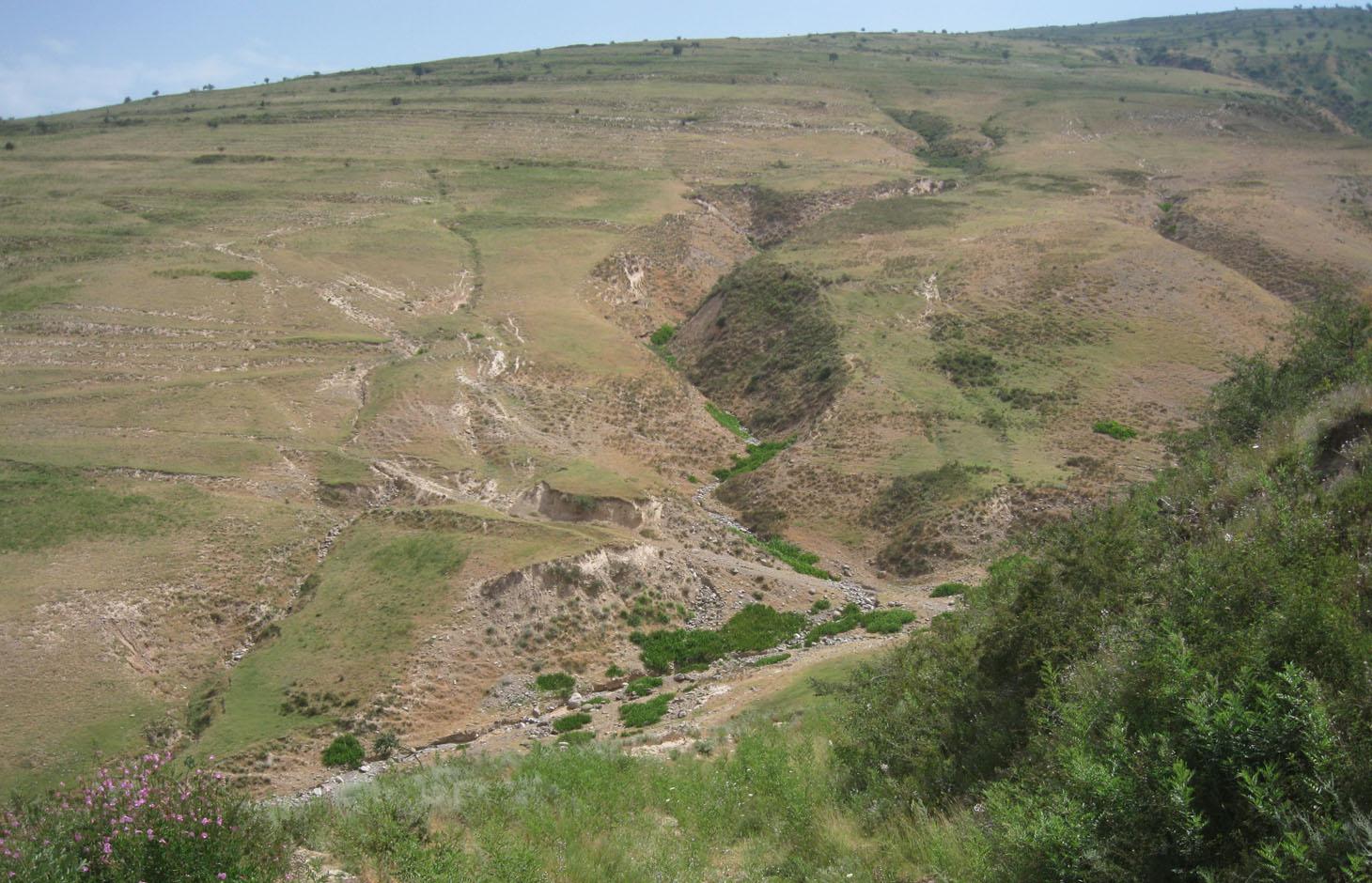
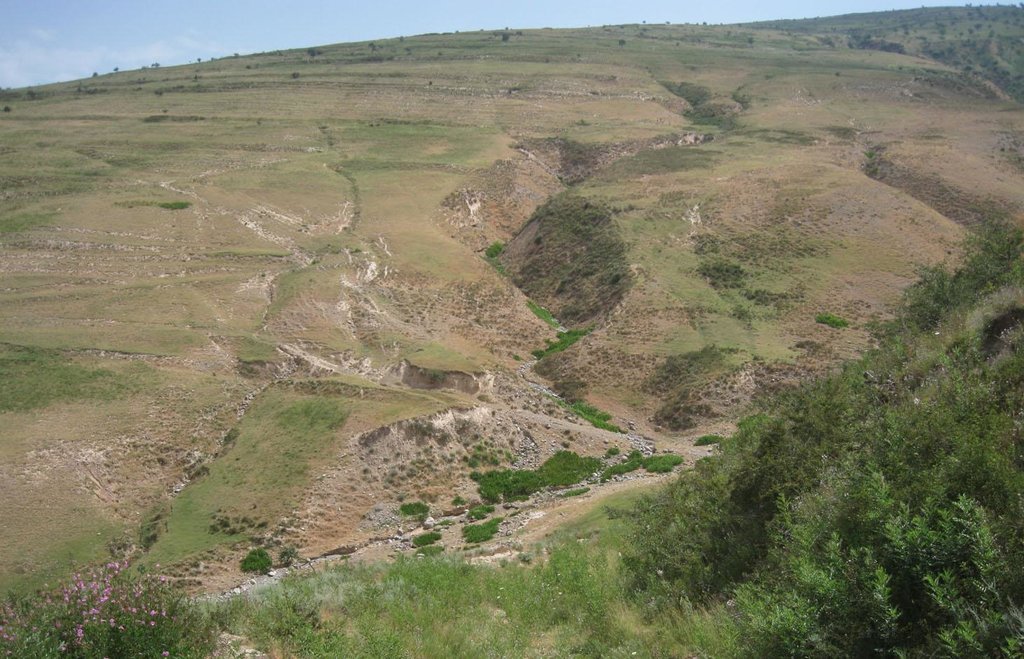
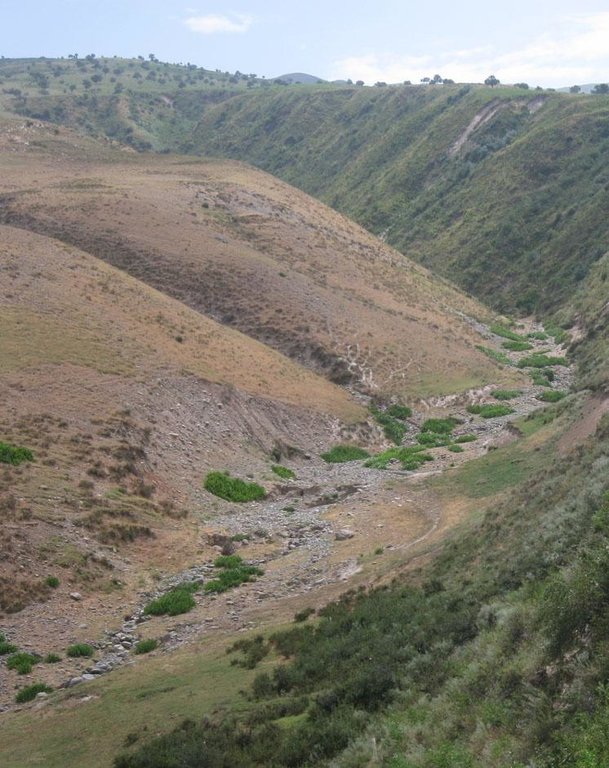
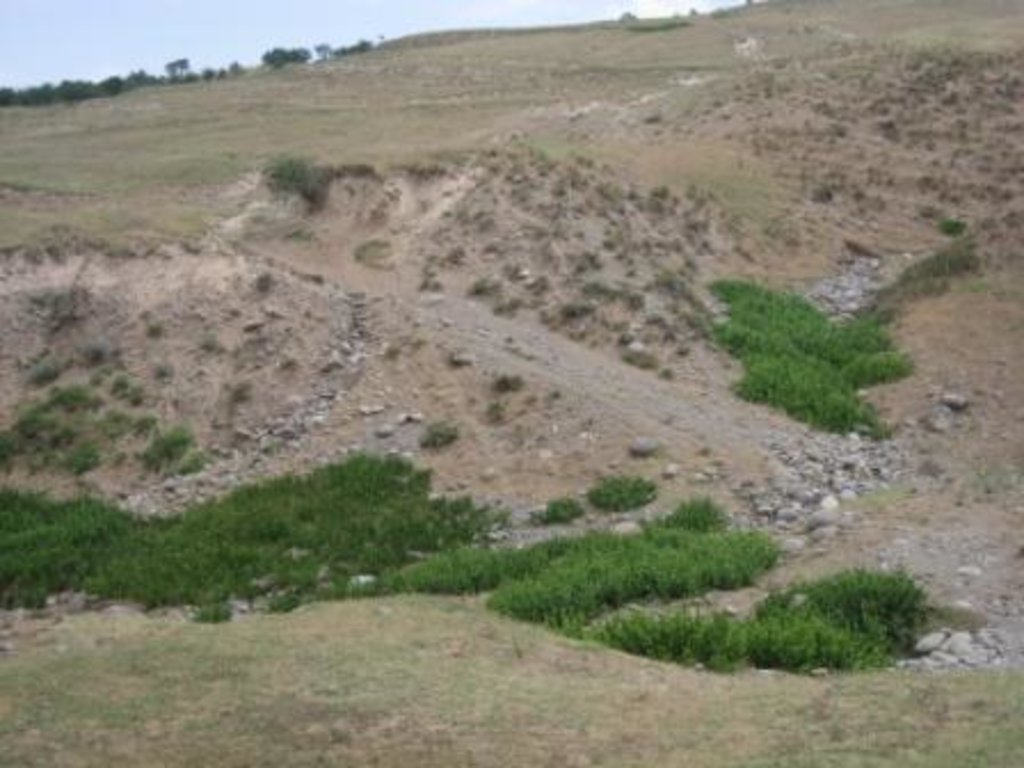
Degraded communal pasture Chukurak [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Malgorzata Conder
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1548 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - قرغيزستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Degraded communal pastureland without grazing management and sufficient waterpoints
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A communal pastureland of 150 -200 hectares is located at the foothill and the riverbank. Around 60 households let their livestock of totally 100 cows and some 400 sheep and goats graze there. The livestock is divided into three groups. Each group is meant to graze at different places in the pastureland. As there is no water point higher up in the pasture area, livestock graze near the village where a water point is installed. Due to this the riverbed, which is already poor in vegetation, is totally overgrazed. Every family is looking after a herd for a day every two month.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim is to install more water points higher up in the pastureland to decrease pressure on soil and vegetation cover by improving rotation within the pastureland. The whole land is overgrazed and livestock numbers are increasing, which is why controlled pasture management could be expected to decrease the degradation process. Nevertheless, more vegetation would be available for feeding livestock and the journey to the next water point shortened thus saving the heard’s energy. As nobody feels responsible for the pasture, nobody is responsible for pasture. No controlled grazing or rotation plan exists at Jamoat level. The farmers do not organise which parts have been grazed and could be grazed next. The livestock owners pay very small rent so they do not value the pastureland and no money is available to implement projects (like installing water points).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Each of the 60 households is paying 10-12 Somoni per year for grazing their cattle on the communal grazing land. Rent is paid per household not per amount of livestock. The total amount of pasture fees collect in Chukurak village is 600-700 Somoni per year. Neither establishment costs, nor investment or maintenance activities are done.
Natural / human environment: Pastureland extends from the village in the valley, to the foothills. Half of the grazing area is on the riverbed and fan with very poor vegetation cover. The foothills show a high percentage of overgrazed, trampled, eroded area. Except for the water point near the village, no water and shady points exist for resting livestock. Three small water sources existed before, two of them where covered by the floods in spring of the current year. The other source produces a negligible amount of drinking water. 60 households graze their livestock, which totals 100 cows and 400 small livestock. Every household is responsible to graze the herd one day every two month. Except that, no management exists between the families and Jamoat.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Muminabad
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2 km2.
Between 150 - 200 ha
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
No technology is developed, 2.3.2 is hypothetical
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- الأغنام
- cow
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing, soil compaction, soil and gully erosion, increasing vegetation cover and hence lower resilience for disaster risks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decreasing vegetation cover, increasing disaster risk, decreasing flood and drought resilience, rill and gully formation
No water acces in the upper part of the pastureland
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cow, sheep, goat
Grazingland comments: semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
Area is of some 200 ha, but livestock is mostly in lower part of the area because of no available water in the higher zone
Type of grazing system comments: semi-nomadism within an delimited communal area, intensive pastoralism due to overgrazing
Area is of some 200 ha, but livestock is mostly in lower part of the area because of no available water in the higher zone
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: March-Sept
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- Rotational grazing
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Bare vegetation cover, no trees, soil erosion, trampled paths, rill building, no waterpoints are all calling for pasture management among the villages.
Location: Above Sarmaydon village, Chukurak watershed. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For managed and controlled grazing)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Technical knowledge required for Ingineers: high (Waterpoint installation)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
المؤلف:
Malgorzata Conder
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Somoni
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,83
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.00
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Rehabilitation labour (regarding structural measures for DDR for riverbed stabilisation or trees planting) is more cost intensive than preventive measures as pasture management.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Footslopes (ranked 1, possible Technologies: riverbed protection, gabions, rotational grazing ) and hill slopes (ranked 2, possible Technologies: rotational grazing, trees planting)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1, hills between 18 and 28%), rolling (ranked 2, fan) and moderate (ranked 3, fan near settlements)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
Soil water storage capacity: Very low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
غير صالحة للإستعمال
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (in spring timemore water available)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Around 3 ha, if 7.7 pers/household counted. In total 2350 ha pasture
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Land ownership is based on Land user certificates
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
less forage available for livestock due to reduce vegetation cover
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
important clear-cutting in the past
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
no organizational task without pasture management
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
التعليقات/ حدد:
lack of water points for livestock
نوعية المياه للماشية
التعليقات/ حدد:
lack of water points for livestock
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
more fodder has to be bought, because grazing is insufficient
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less forage for livestock
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
no organizational task without pasture management
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
More difficult to feed livestock
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
Improved vegetation cover, improved infiltration, slope stabilization and natural disaster resilience
Install water points higher up, rotate within the grazing land and less energy needed by livestock, which leads also to less overgrazing
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Establish rotational grazing, which would not be expensive and does not require further equipment except of organizational tasks. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Empower communication and decision-making between the farmers by regular meetings or round tables on community level |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Importance of rotational grazing depends on Jamoat and farmers level | Strengthen communication between Jamoat and Farmer through consultancy, meetings etc. Farmers, as tenants, should also get a voice. |
| Pastureland rent is too cheap and it is not valued. There is no incentive to change, because nobody feels responsible for that area. | Increase the rent and discuss communally where the money should be spent (e.g. for water points). |
| Pasture management does not show benefits immediately, which makes it difficult to evidence good management. | Awareness raising and increasing knowledge of the short and long-term benefits. |
| Installation of water points is crucial, but very costly and hard work. | Awareness rising and find alternatives of investing in livestock. |
| Livestock number should decrease, but it is socioeconomically very important and demands a lot of time to change this attitude. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية