Silvo-pastoralism: Orchard with integrated grazing and fodder production [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Malgorzata Conder
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1554 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - قرغيزستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Increased productivity of the land by planting fruit trees and conserving the land by restricting the access of livestock resulting in improved runoff retention
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
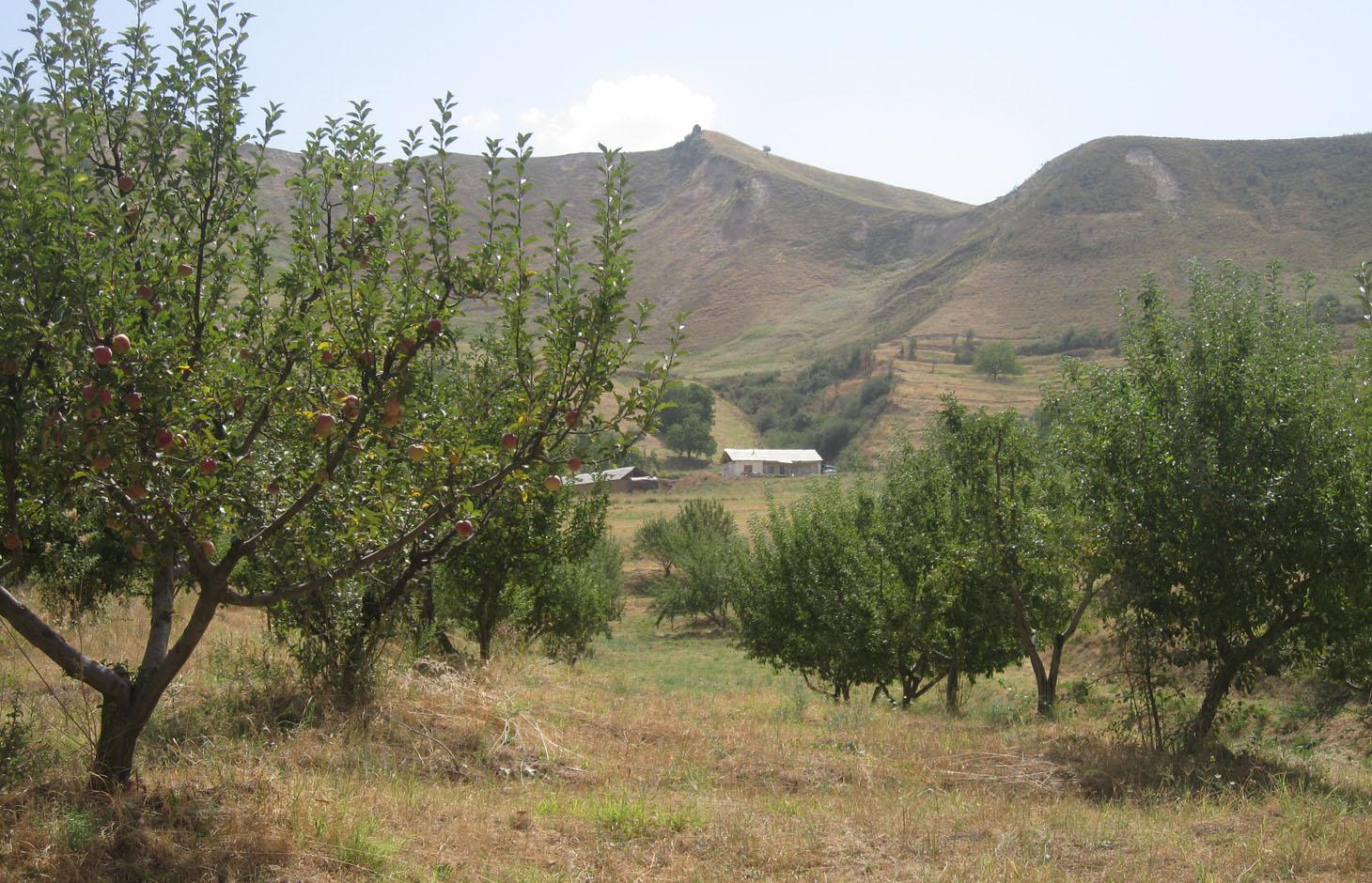
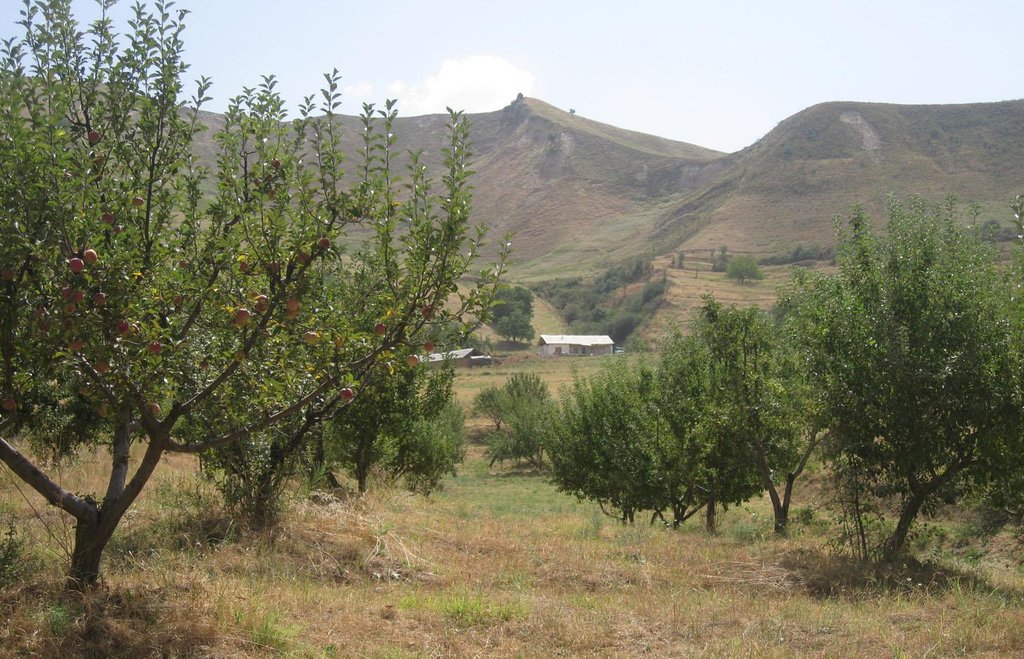
In Soviet times, this area of totally 40 ha comprised terraces and walnut trees in the steep foothills and pastures in the lower and flatter part. After the collapse of the Soviet Era, many similar areas got degraded due to uncontrolled grazing and overuse of natural resources. The area described in this documentation, in contrast, was taken over by a family in 1991. Within the whole area of 40 ha, roads were built to improve the access and 6000 trees were planted, whereof 1200 fruit trees were planted on the pasture, conversing it into an orchard.
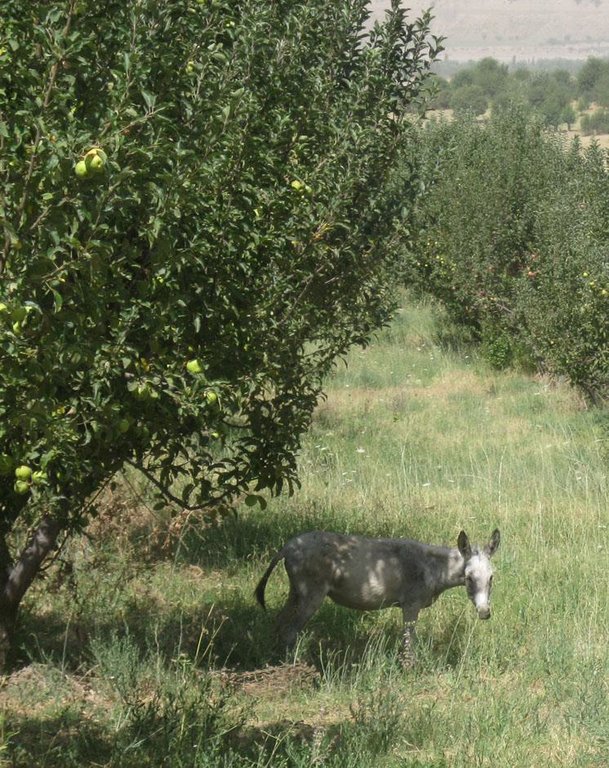
At present, the 6 ha of orchard are mainly consisting of three types of apple (white, golden and red), some pear and cherry trees. Several trees must have dried out or have been cut, as the farmer counts currently around 1000 fruit trees. The whole orchard is combined with pasture land. The farmer let his livestock graze in the orchard, and cuts the remaining grass in autumn, if there is still left.
The integrated orchard with pastureland and fodder production is partially fenced to hinder livestock entering his property. Furthermore, the orchard is within the range of vision which allows the farmer`s family to guard it.
The farmer who is managing the orchard today obtained the property of his father in order to continue the family project by his own initiative. By farming he ensures the livelihood of his family. Hence, he felt responsible to progress and improve the quality of life of his own family. The main reason for establishing the orchard within the grassland and to install fences, was to increase productivity of the land, bringin along beneficial effects on soil quality. According to his land users certificate, the main purpose of this land is to provide the local market with food products.
After planting, some of the seedlings were stolen or eaten by livestock from neighbouring farms. Initial labour input in the newly established orchard consisted of getting and planting the seedlings and applying pesticides. The trees are being maintained by pruning. Soil is loosened and drainage provided to increase water infiltration and to protect the trees additionally from parasites. The pasture is grazed by the livestock of the farmer. As the family only has a small number of livestock, grass is cut afterwards and used as fodder. Half of the fodder harvest belongs to the hired worker, the other half belongs to the farmer. The other tasks are executed by the farmer and his family.
The climate is semi-arid with precipitation (800mm totally) mainly during winter and spring time. Altitude is around 1380 m asl. The plot is located at the foothill, with the wider riverbed and fan downstream and overgrazed hills upstream. Bordering with the property from above, a steep slope with a dense vegetation of grafted fruit trees and walnut trees stabilizes the soil.The farmer is living with the family on the property, near the village of Momandion. In the past many livestock from nearby entered the property and grazed there. Through better control and fences less livestock is entering. The property is located directly on the road to Muminabad, the center of the District with a market- 2 km away.Considering the establishment costs of the orchard, the farmer is a fairly whealthy man, nevertheless he had to rely on his family and friends in terms of the working input.The establishment phase was a time and money consuming
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Muminabad
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 km2.
Orchard is within the farmer's land property of totally 40 ha
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
22 years ago
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الثمار التفاحية (التفاح، الكمثرى، السفرجل، الخ)
- الفواكه ذات النواة (الخوخ، المشمش، الكرز، البرقوق، الخ)

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): No major problems because of the early implementation of the technology which prevented the area of being (over)grazed without control
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The farmer is afraid of a possible landslide on his property. Another issue is the lack of a continuous fence, because still some unwanted livestock is able to enter the orchard. He installed a water point next to his house recently.
Other grazingland: agropastoralism: first grazing and if grass is left, then cut
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
التعليقات:
Grazing land: Extensive grazing land
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (uncontrolled)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (increased livestock), governance / institutional (no or undeveloped pasture management after Soviet collapse)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
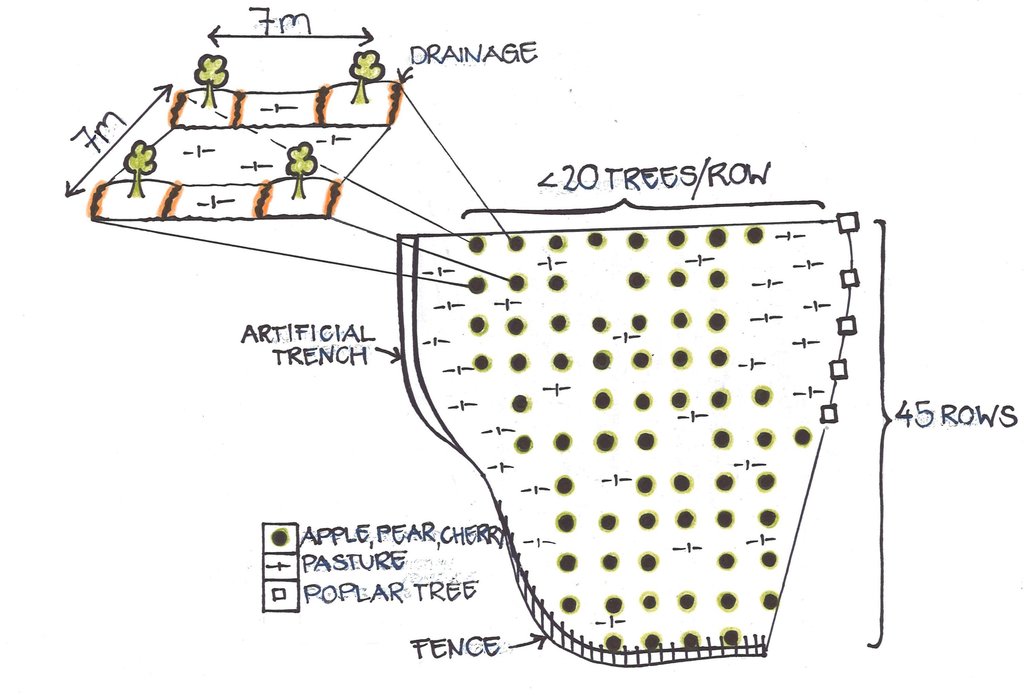
The orchard is situated within the farmers' property which is almost completely fenced by an artificial trench, thornbush fences, poplar trees and a natural steep slope. The orchard is 6 ha in size and consists of around 45 rows, with some 20 trees per row on average. In some places trees are missing due to drying out or cutting. Currently approximately 1000 fruit trees are growing. In between the tree rows and at the borders of the orchard, grass is growing and grazed by animals, and if not entirely grazed cut for haymaking in autumn.
The fruit trees grow at a distance of 7 meters. Around the trees the soil is loosened and a tiny trench is dug, the latter serving as a rainwater drainage.
Location: Momandion. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Date: 14.09.2012
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Good knowledge for planting required, knowledge about maintenance activities is probably more widespread amongst farmers, idea of fencing is lacking)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, pear, cherry
Change of land use type: change of pasture land into an orchard with integrated pasture land and fodder production (Silvopastoralism)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Fencing hence more extensive and controlled grazing
المؤلف:
Conder Malgorzata
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Somoni
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,83
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
12.40
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying and transport of fruit seedlings (totally 6000 seedling, whereof 1200 seedlings on for the orchard of 6 ha) | once |
| 2. | Planting fruit tree seedlings (totally 6000 seedlings, whereof 1200 seedlings for the orchard), cost according to planted trees (3 TJS per tree) | once |
| 3. | Partial fencing (of around 200m) along the property, 10.5 days, 3-4 persons | 1991 |
| 4. | Building roads for access to the house | 1991 |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 194,9 | 194,9 | 100,0 |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 0,7 | 0,7 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 207,0 | 207,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | fence | ha | 1,0 | 124,2 | 124,2 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 526,8 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 109,07 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning of 400 trees, ca. 40 days, 1 person, 3 TJS per tree (all trees pruned every 3 years) | spring/ once a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around 1000 fruit trees, ca. 25 days (5 h/day), 1 person | spring/ once a year |
| 3. | Pesticides spraying once (should be done 2-3 times), 4 days (ca.5 h/d), 1 person | End of May/ once a year |
| 4. | After several years: Harvesting fruits (mainly apples) | September/every year |
| 5. | Cutting grass, by 10 people, one month, hours per day unknown. Half of straw harvest for owner, other half for the mowers as salary (4-5 Somoni/bundle). Total salary: 1000 bandles | End of summer |
| 6. | Guarding the orchard | all the time |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 383,3 | 383,3 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | pesticides | ha | 1,0 | 7,8 | 7,8 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 391,1 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 80,97 | |||||
التعليقات:
The structural fencing is adapted from T_TAJ047. Working hours are approximate as the work was done a long time ago, with the help of many relatives with different work times. No overview over the exact work and cost input exists, tools were mainly borrowed, prices unknown. Road building done in the past was not included, because current costs were difficult to estimate. Work as guardening is not monetarised. Apple harvesting as recurrent activity (vegetative measure) is derived from T_TAJ013. In the cost summary, the fencing was calculated proportionally to one ha.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Apart from the orchard, the whole property was rebuilt with roads, fences and tree planting which caused high initial costs during the establishment phase.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200m asl, weather station Muminabad)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
التعليقات:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the area of the orchard with pasture is fenced it is not an communal pasture anymore as it was before
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
From pruning
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Products for market leading to higher income, sharing of some knowledge about management of private land enhances dissemination and exchange of information/knowledge.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Family project to improve the quality of life of the family. Costs were high at the beginning with little outcomes, now there is less labour required and the outcome is high.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Even though they neighbours see the whealty orchard, the farmer din not see any other farmers adapting this Technology. Reasons are unknwon.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Giving good yield and "cash crop" hence having success in the project of the family |
| Better quality of fodder and less damages due to intrusive livestock |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Thanks to the establishment time, right after the collapse of the Soviet Union, when land was generally well conserved, the technology worked as a preventive measure. |
| Silvopastoralism not only raises productivity of the same plot as an orchard and pasture is combined, but also enables mutual benefits (p.e.rooting system raises soil moisture, which is again improving vegetation cover). |
| The technology might work as exemplary model for other farmers |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There is always work to do, without input no (good) output. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| For the farmer, the economic benefit is more important than the ecologic benefit. Especially, there is missing sensibility of the farmer concerning the application of pesticides (quantity, type). | A workshop which provides guidelines on optimal use of pesticides (type and quantities of pesticides, timing and frequency of application etc.) |
| The establishment of orchards is more efficient on big plots of land, which often prevents poor farmers with small plots from establishing orchards. | Creating incentives to change land use, by combining plots from different land owners, which will allow to share costs for establishment and maintenance. Yields should be clearly attributed to the individual farmers. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
19/07/2012
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية