Integrating native trees in rubber monocultures [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Gerhard Langenberger
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
减缓单一橡胶种植的负面环境影响:关于橡胶与当地树种混种并结合杂草管理的生态种植研究 (Chinese)
technologies_1717 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Blagodatsky Sergey
University of Hohenheim
ألمانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Universität Hohenheim - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
China Agricultural University (China Agricultural University) - الصين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
The technology combines the integration of native tree species into rubber monocultures with changed weed management to mitigate negative environmental impacts and to provide alternative income options for farmers.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
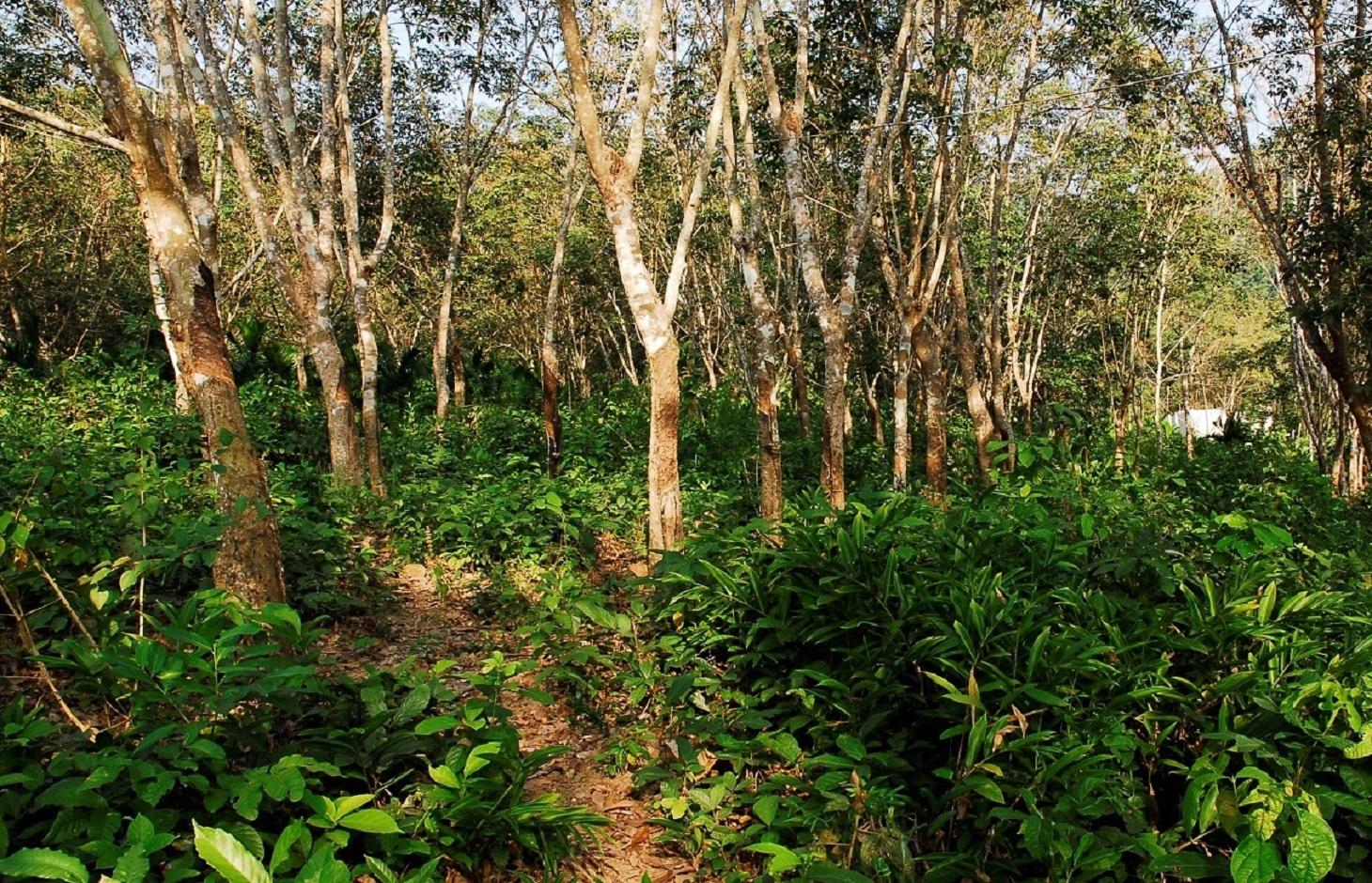
Natural rubber is a crucial renewable resource produced from the tree Hevea brasiliensis. Production is largely based on monoculture, often associated with chemical-based clean-weeding. This causes environmental problems such as loss of biodiversity, pesticide pollution and erosion of topsoil. The SLM-technology aims at mitigating negative impacts by interplanting the rubber with native tree species which have economic potential of their own. Changes in weed management are part of the package also.
Native (indigenous) tree species are integrated into mature rubber plantations. Criteria for species selection are: a) adapted to environmental conditions; b) shade tolerant; c) vertical growth not affected by light; d) conservation value; e) economic potential; f) easy to manage. Rubber trees are usually planted in rows at a spacing of 6-8 m, and an intra-row distance of 2.5 to 3 m. The native trees are planted between the rubber rows. The plantation should be mature as the canopy will have reached its highest density, and weed competition is naturally suppressed. The spacing of the native trees needs to be adapted to their growth potential and intended usage. After planting, regular monitoring is necessary to identify pests or diseases. The following species were selected for demonstration sites: 1) Parashorea chinensis, a valuable timber tree, 2) Taxus mairei, a multi-purpose tree, providing good timber but also an anti-cancer drug, taxol, and 3) Nyssa yunnanensis, selected for its conservation value. At the end of the economic life span of the rubber trees (about 30 years) there will be several options, but there are three main ones. First the rubber plantation can be replanted, although the harvest of the Parashorea chinensis trees would be premature. The Taxus mairei trees could be maintained through a new plantation cycle. Second, both, the rubber and the intercropped trees could be maintained for future timber and taxol production. Third, the plantation could be transformed into a sustainable forest managed scheme where the rubber trees are extracted step by step and the intercropped trees maintained for their intrinsic value.
Procedures for the selection and planting of the indigenous tree species are crucial. Identification should be based on suitability for the climate and soil as well as economic potential. The raising of tree seedlings requires experience and nursery propagation by experts might be required. Only healthy seedlings should be used. Planting should take place during rainy periods. Potted seedlings are better than bare-rooted seedlings since they establish better. Generally, weed management (if necessary) should shift from herbicide application to mechanical weeding. Grass competition needs to be avoided in any case! Controlled cover of natural undergrowth will reduce erosion and promote water infiltration.
The implementation site for the trials is located in Xishuangbanna Prefecture, Yunnan Province, SW China. The original vegetation was tropical rain and monsoon forest, but now there is a rich mosaic of different land-use and vegetation types. The whole region is exceptionally species rich and part of the Indo-Burma-Biodiversity Hotspot.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province, PR China
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Naban River Watershed National Nature Reserve
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
0,03
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.03 km2.
The technology is currently tested on three trial sites coveríng 3 ha. Some farmers started to adopt and also planted trees in rubber. But no figures are available so far.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- review on available knowledge on rubber management and history
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology is a result of the synthesis of research findings of the SURUMER-project and a review of available publications on rubber management.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- المطاط
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 270, Longest growing period from month to month: April - December
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Large-scale expansion of rubber monocultures results in the loss of topsoil and siltation of streams with respective consequences for CO2 emissions (increased), soil degradation, water quality and stream ecology. The excessive application of agrochemicals adds to these problems. The monoculture practice combined with clean weeding results in plant biodiversity loss. The related simplification of habitat structures also leads to a considerable decline in animal biodiversity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The focus of land users is primarily on sustainable income, and their environmental concerns mainly relate to water provisioning (land user's point of view). In the farmers view: “The biggest environmental problem is water quantity. Rubber sucks out a lot of water, therefore we do have a water scarcity problem”. Farmers are aware of the contamination of drinking water due to the use of pesticides and herbicides in the rubber plantations.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: The majority of farmers shifted to pure rubber growing, although many villages still have paddy rice fields.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Replacement of forests by monocultures.), poverty / wealth (Older people still have the memory of extreme poverty. Rubber was the main driver to reduce poverty; high profit gained by rubber encouraged people in pursuit of large scale monoculture.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (A tremendously improved infrastructure allows the establishment of plantations even in previously remote areas.), governance / institutional (Strong support from government in terms of subsidy and other incentives from 1980s to 2000s; subsidies are more recently reduced)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Clear-weeding, mainly with herbicides.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Removal of natural vegetation leads to higher runoff), land tenure (Introduction of Household Responsibility System in 1980s gave use-right to farmers. This pushed decisions on transformating natural forests to monocultures. No full property rights could hinder could), labour availability (Compared to the traditional agricultural system, rubber monocultures require less labour. Recently, there is even less labour available due to the relatively low income gained by rubber), education, access to knowledge and support services (The awareness about ecosystem services and functions is still poorly developed.), war and conflicts (Chinese government´s objective to be independent on important strategic resources such as rubber)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
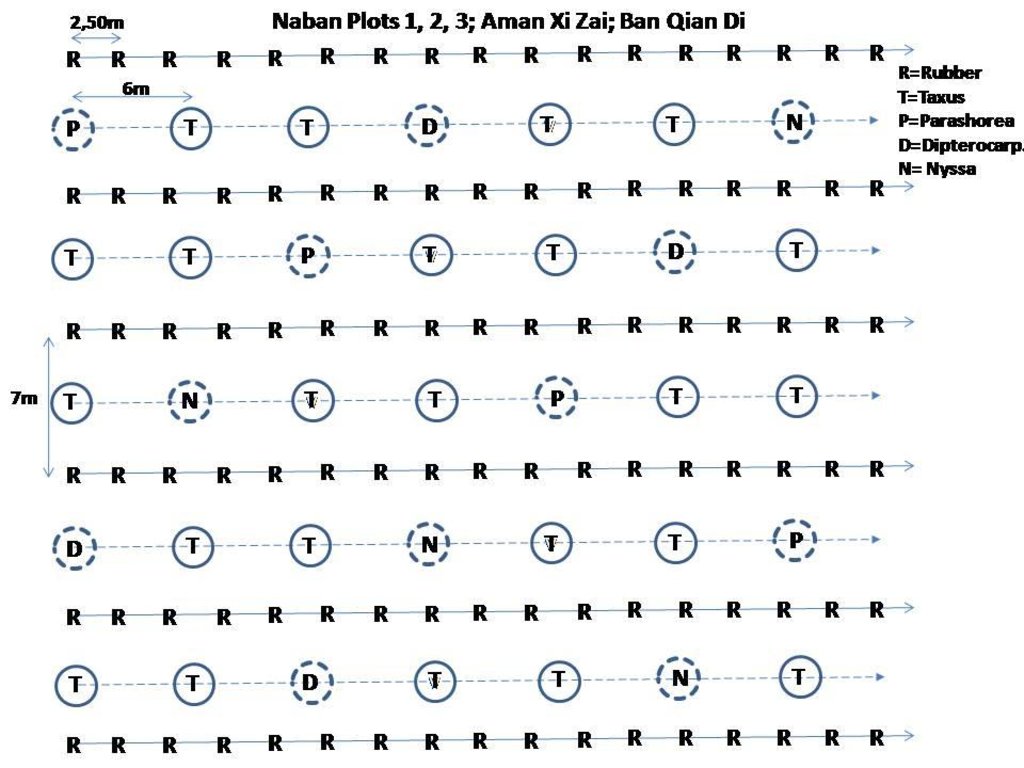
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
The concept is based on the commonly suggested planting scheme of rubber with a row distance of ca. 7 m and a spacing of trees within the rows of ca. 2.5 to 3 m, resulting in ca. 450 to 500 trees/ha. The intercropping will take place between the rubber rows, on terraced slopes between the rubber terraces. Planting takes place after the plantations have reached half of their economic life span, which is ca. 15 years. It is important to consider that farmers often plant much denser than suggested by official guidelines, which needs an assessment of the light / shade conditions. With a too high rubber density the resulting light conditions might be too poor for intercropping even for forest trees. In our case the distance within a row of the intercropped trees has been set at 6 m, due to the (known) ecological characteristics of the selected 4 tree species. But the decision needs to be taken specifically for each new site, the potential tree species and the intentions of the land-user. Thus, in our case, we opted for a higher density of Taxus (bold circles) which is well known for its slow growth. and integrated the two other tree species at a wider distance (dotted circles).
Location: Yunnan Province, SW China. Xishuangbanna Prefecture
Date: September 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The selection and management of native tree species requires a very good ecological as well as dendrological knowledge and understanding.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (If species selection has been successful and management is supported by a knowledgeable extension service.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Intercropping of native tree species
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 240
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6 m
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Parashorea chinensis, Taxus mairei, Nyssa yunnanensis: all planted (container-planting)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0-80%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Shift from herbicide-based weed management to mechanical weeding with machine tools. This has not yet been implemented due lack of experience and proper tools.
المؤلف:
G. Langenberger, Institute of Agricultural Sciences in the Tropics (490), University of Hohenheim, Germany
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
RMB
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
6,3
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
16.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1.Seedling acquisition and transport | before or during rainy season |
| 2. | 2.Planting of seedlings in rainy season | rainy season |
| 3. | Weed management with brush cutters. | ? no experience |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | |
| معدات | animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 2400,0 | 2400,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 2568,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 407,62 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.07 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1.Control of pests and diseases | monthly |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 96,0 | 96,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 96,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 15,24 | |||||
التعليقات:
The costs are based on the establishment of 3 demonstration plots of ca. 1 ha each. It should be possible to considerably reduce the costs by producing seedlings on site.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Seedling costs are by far the major cost factor. Since the selected species are very unusual and don't have a considerable market they were extremely expensive. Since Taxus is also a reputed medicinal plant, it might also have influenced the price. All other costs are actually negligible compared to the costs of the seedlings. In this case the establishment of an own nursery might considerably reduce the costs, since propagation at least of Taxus and Parashorea is easy if the seeds can be acquired.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: So far, the number of persons applying the technology is still too low to draw any meaningful conclusion.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5% (farmers have been well off in the past, currently they are under pressure due to the very low rubber).
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
التعليقات:
Water use rights seem to be an issue.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
considerably, but no experience
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
no practical experience, yet
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
less erosion
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
cf. Hongxi
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
compared to clear-weeding
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
cf. Xueqing
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
| cold spells | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
The above assessment is based on the fact that we are actually dealing with plants adapted to tropical conditions. Therefore, the species should be less affected by high temperatures and increasing rainfall, but might be sensitive to droughts. Nevertheless, there is no experience!
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The establishment costs for the demo-sites have been very high, but could be considerably reduced if adopted by more farmers. The assessment above therefore needs verification!
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Comments on adoption trend: We experienced interest in the technology by farmers, but due to the lack of experience and the lack of affordable and accessible seedlings they are hesitant.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Additional income options. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The technology offers considerable long-term advantageous to farmers. It diversifies the product portfolio and good options for additional income in the future. Beyond the establishment it doesn't require much labour. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High investment costs. | Government subsidies. |
| Time until first returns can be expected. 5-10 years for taxol production |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The technology is based on a long-term perspective and thus favours farmers who have a such an outlook. But farmers with little land usually think short-term. | The current trend of rural-urban migration will support the technology since it can be easily combined with off-farm work. According to SURUMER findings off-farm income already contributes about one third of the overall household income in the rubber growing areas. |
| Current establishment costs are very high due to the lack of a seedling market. | If the technology becomes known and popular, more nurseries will produce seedlings which will reduce costs. Alternatively, farmers might establish their individual (or community) nurseries. |
| The technology requires considerable knowledge about tree ecology and tree breeding. | There should be extension officers at the local agricultural or forestry bureaus supporting farmers. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
12/02/2016
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ahrends, A. et al. (2015) Current trends of rubber plantation expansion may threaten biodiversity and livelihoods
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Global Environ Change, 34, 48-58.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Langenberger, G. et al. (2016) Rubber intercropping: a viable concept for the 21st century?
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Agrofor Syst, 1-20.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Liu, H. et al. (2016) Impact of herbicide application on soil erosion and induced carbon loss in a rubber plantation of Southwest China
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
CATENA, 145, 180-192.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية