ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ໃສ່ດິນບໍລິເວນຮາບພຽງ ແຄມຫ້ວຍ [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Bounthanom Bouahom
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: viengsavanh phimphachanhvongsod, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2298 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. معلومات عامة
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
SLM specialist:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
لا
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
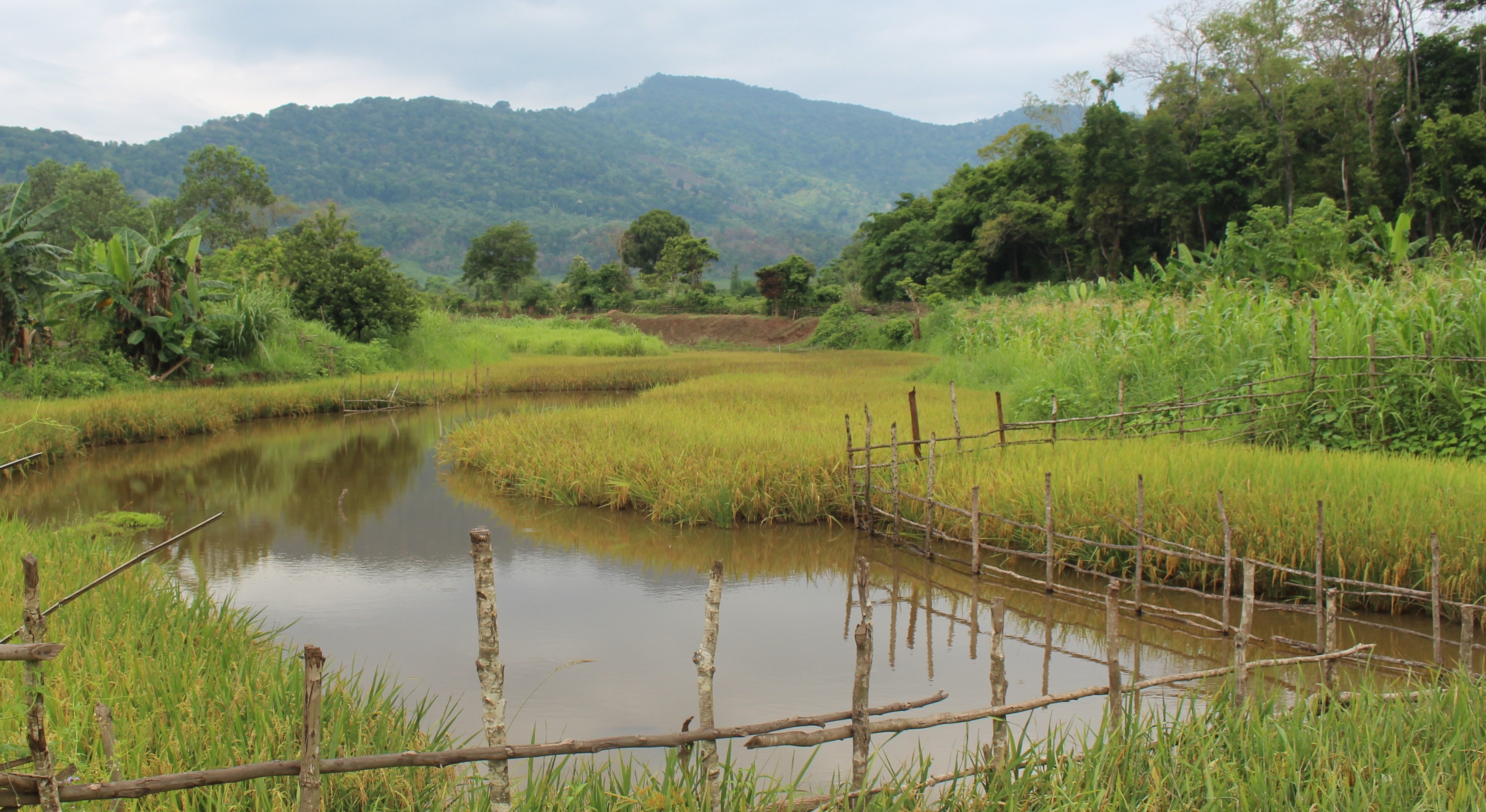
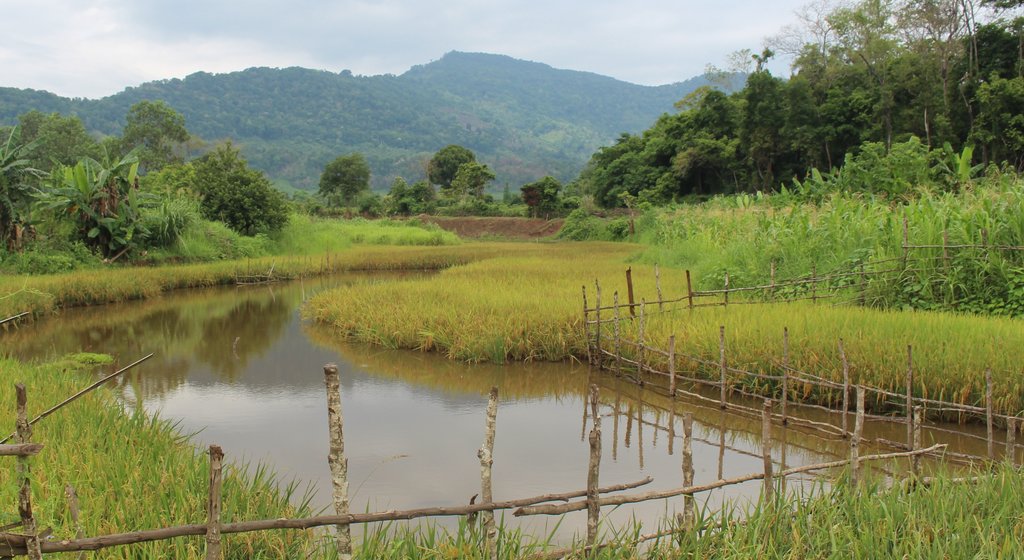
ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ສອງຟາກຫ້ວຍ ມີຈຸດປະສົງ ເພືື່ອແນໃສ່ ຢູດຕິ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ ແບບເລື່ອນລອຍ ໃນເຂດພູດອຍ ທັງເປັນການປັບປຸງ ຊີວິດການເປັນຢູ່ ຂອງປະຊາຊົນທ້ອງຖ່ີນ.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
ເຕັກນິກ ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເປັນແນວຄວາມຄິດ ລິເລ່ີມ ຈາກໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia. ຊ່ຶງໃນເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ປະຊາຊົນ ພາຍໃນທອ້ງຖ່ີນ ເຄີຍຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ເປັນກິດຈະກໍາຫັຼກ ໃນການດໍາລົງຊີວິດ ຂອງປະຊາຊົນ ໃນເຂດພູດອຍ ແລະ ປະຊາຊົນ ກໍ່ບໍ່ເຄີຍເຮັດນາມາກ່ອນ.ຈາກສະພາບ ການດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ, ປະຊາຊົນກ່ໍໄດ້ພົບບັນຫາ ການຂາດເຂົ້າກິນ ແລະ ເນື່ອງຈາກ ຈໍາກັດ ເນ້ືອທ່ີການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຈໍານວນ ຂອງປະຊາກອນເພີ່ມຂ້ຶນ ແລະ ເກີດມີການຍາດແຍ່ງ ພື້ນທ່ີ ທໍາການຜະລິດ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia ໄດ້ລິເລ່ີມເຂົ້າມາເມືອງຕະໂອ້ຍ ໃນຊຸມປີ 1996 ພາຍໃຕ້ ຈຸດປະສົງ ໂຄງການ ເພື່ອຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ການບຸກລຸກ ທໍາມະຊາດ ໃນເຂດທຸລະການດານ ໂດຍໄດ້ມີການສ້າງຕັ້ງ ຄະນະ ກໍາມາທິການ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ໄພພິບັດ ທາງທໍາມະຊາດ ໃນຂັນບາ້ນ. ໂດຍທາງໂຄງການ ໄດ້ເລັງເຫັນຄວາມສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ການຈັດສັນ ອາຊີບຄົງທີ່ ເພື່ອສະເຫນີ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ ໂດຍເລັງເຫັນ ເຕັກນິກ ການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເປັນອີກທາງເລືອກຫນ່ືງ ໃຫ້ແກ່ປະຊາຊົນ ເພື່ືຶ່ອປັບປຸງ ຊີວິດການເປັນຢູ່ ຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ ທັງສາມາດ ຄໍາ້ປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນບັນຫາ ການເຮັດວຽກໜັກຂອງສະມາຊີກ ພາຍ ໃນຄອບຄົວ. ໃນເບ້ືອງຕົ້ນ ທາງໂຄງການ ແມ່ນໄດ້ມີການຝຶກອົບຮົມ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ ຮູ້ຈັກນຳໃຊ້ຄວາຍ ໃນການໄຖນາ ເພາະປະຊາຊົນ ບໍ່ເຄີຍເຮັດນາມາກ່ອນ. ພ້ອມທັງ ການສະໜອງແນວພັນເຂົ້າ, ຈົກ ແລະ ຊວ້ນ ໃນການບຸກເບີກ ແລະ ກະກຽມດິນນາ. ຊ່ືງໃນໄລຍະເບ້ືອງຕົ້ນ ທ່ີທາງໂຄງ ການ ເຂົ້າມາສົ່ງເສີມ ການເຮັດນາ ຢູ່ໃນບາ້ນ ບ່ໍມີຫຼາຍຄອບຄົວ ສົນໃຈເຮັດທົດລອງ ກັບທາງໂຄງການ ເນ່ືອງຈາກເຂົາເຈົ້າ ຢ້ານຜິດຮີດຄອງປະ ເພນີ ເພາະປະຊາຊົນ ເຊ່ືອວ່າ ການປູກເຂົ້າ ແມ່ນຕອ້ງປູກໃສ່ດິນຢູ່ສູງ ແລະ ບ່ໍປູກແຊ່ກັບນໍາ້ ຄືກບັການເຮັດນາ. ແຕ່ເຖິງຢ່າງໃດກ່ໍຕາມ, ໃນເວລານັ້ນ ກໍ່ມີຄອບຄົວ ຈໍານວນຫນ່ືງ ທ່ີຕັດສິນໃຈ ເຂົ້າຮ່ວມທົດລອງ ກັບທາງໂຄງການ ຊຶ່ງທາງໂຄງການ. ຂັ້ນຕອນ ແລະ ວິທີການ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກ ນິກດັ່ງກ່າວ ແມ່ນປະຊາຊົນ ປະກອບສ່ວນ ໂດຍການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ ໃນການຂຸດດິນ, ກະກຽມດິນປັບຫນ້າດິນ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ເປັນດິນຫຸຼບ ຫືຼ ພຽງເທົ່າກັບ ລະດັບ ນໍາ້ຫ້ວຍ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ນໍ້າໃນຫ້ວຍ ສາມາດໄຫຼຍູ້ອອກໄປ ສູ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທ່ີດິນພຽງ ທ່ີປະຊາຊົນ ໄດ້ຂຸດ ແລະ ບຸກເບິກກຽມດິນໄວ້. ໂດຍສ່ວນໃຫ່ຍ ປະຊາຊົນ ຈະເລ່ີມຂຸດດິນ ໃນເດືອນທັນວາ ເຖິງ ເດືອນມັງກອນ ພາຍຫັຼງ ທ່ີນໍາ້ຢູ່ຫ້ວຍລົດລົງ ເນ່ືອງຈາກວ່າ ດິນບໍ ລິເວນດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ ນໍາ້ໄດ້ຖ້ວມທຸກໆປີ ໃນເວລາລະດູຝົນ ຊ່ຶງເຮັດໃຫ້ ດິນເຂດດັ່ງກ່າວນັ້ນ ອຸດົມສົມບູນ ແລະ ຮັບນໍາ້ໄດ້ເປັນຢ່າງດີ. ມາເຖິງປະຈຸ ບັນ, ເຫັນໄດ້ວ່າ ປະຊາຊົນ ພາຍໃນບ້ານມີຄວາມສົນໃຈຫຼາຍ ໃນການເຮັດນາ ລະດູແລ້ງ ຢູ່ສອງຟາກຫ້ວຍ ແລະ ໄດ້ຂະຫຍາຍເນື້ອທີ່ນາອອກ ໃນບ່ອນທ່ີມີເງ່ືອນໄຂ ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນບ່ອນທ່ີມີຫ້ວຍ ພາຍໃນບາ້ນ ແລະ ປະຊາຊົນ ກ່ໍມີຄວາມສຸກຫຼາຍ ທ່ີໄດ້ເຮັດນາ ຊ່ຶງສາມາດ ລົບລ້າງແນວຄວາມຄິດ ເຊ່ືອຖືແບບດັ້ງເດີມ ແລະ ຄວາມເຊ່ືອ ຈາກເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ທ່ີບ່ໍເຄີຍເຮັດນາ ແລະ ຢ້ານຜິດຮີດຄອງ ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ ເຂົາເຈົ້າ ມີເຂົ້ານາ ໄວ້ກິນພາຍ ໃນຄອບຄົວ ເຫັນໄດ້ວ່າເຂົາເຈົ້າ ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ເນ້ືອທ່ີ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ໄດ້ ທັງເປັນການຊ່ວຍປະຢັດ ແຮງງານ ໃນການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ແລະ ນໍາໃຊ້ພື້ນທ່ີ ໃຫ້ເກີດປະໂຫຍດສູງສຸດ. ນອກຈາກນ້ີ, ປະຊາຊົນພາຍໃນບາ້ນ ທ່ີຢູ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ ກໍ່ໄດ້ນາໍເອົາບົດຮຽນດັ່ງກ່າວ ໄປຫມູນໃຊ້ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິ ບັດ ໃນບາ້ນຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າ.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
بلد:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
ແຂວງສາລະວັນ
Further specification of location:
ເມືອງຕະໂອ້ຍ
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
ໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

الأراضي الزراعية
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - rice (wetland)
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- area closure (stop use, support restoration)
- water harvesting
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
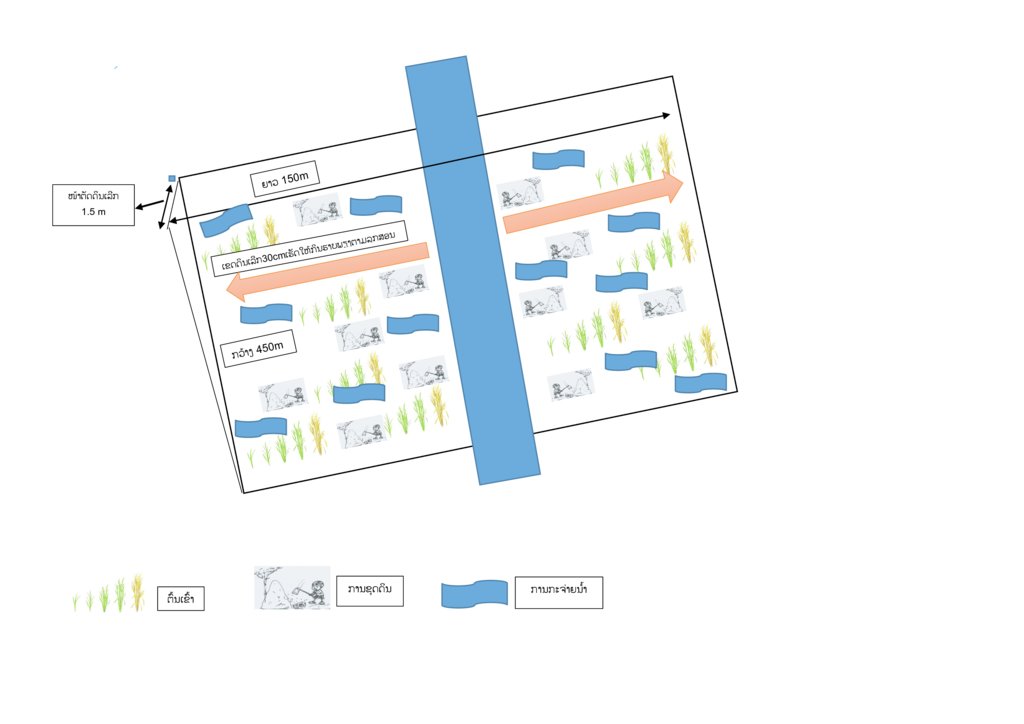
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1. ກະກຽມ ແລະ ຂຸດປັບຫນ້າດິນ ລຽບຕາມແຄມຫ້ວຍ ໃນເດືອນທັນວາ ຫາ ເດືອນມັງກອນ
2. ການຕົກກ້າ (ເດືອນມັງກອນ ຫາ ເດືອນກຸມພາ)
3. ການໄຖດິນ
4. ການດຳນາ
5. ເກັບກ່ຽວເຂົ້າ (ເດືອນເມສາ ຫາ ເດືອນພືດສະພາ)
Author:
ທີມງານ ຈາກຫ້ອງການສົ່ງເສີມ ກະສິກຳ ແລະ ປ່າໄມ້ ເມືອງຕະໂອ້ຍ
Date:
11/08/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
other/ national currency (specify):
ກີບ
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8000,0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
50.000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ການປັບໜ້າດິນ ຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ | ເດືອນທັນວາ ຫາ ເດືອນມັງກອນ |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ປັບໜ້າດີນ | ວັນງານ | 60,0 | 50000,0 | 3000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ອັນ | 2,0 | 30000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | ພ້າ | ອັນ | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | ຄວາຍ | ໂຕ | 1,0 | 7000000,0 | 7000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 10100000,0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1262,5 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ແຮງງານ ໃນການປັບໜ້າດິນ | ເດືອນທັນວາ ຫາ ເດືອນມັງກອນ |
| 2. | ການກະກຽມຕົກຕ້າ | ທ້າຍເດືອນມັງກອນ |
| 3. | ດຳນາ | 1 ເດືອນ ຫຼັງຈາກຕົກກ້າ |
| 4. | ເກັບກ່ຽວຜົນຜະລິດ | ເດືອນພືດສະພາ |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ຕົກກ້າ | ວັນງານ | 2,0 | 50000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ດຳນາ | ວັນງານ | 14,0 | 50000,0 | 700000,0 | 100,0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານ ໃນການເກັບກ່ຽວ | ວັນງານ | 14,0 | 50000,0 | 700000,0 | 100,0 |
| Plant material | ແນວພັນເຂົ້າ | ກິໂລ | 10,0 | 4000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1540000,0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 192,5 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ແຮງງານ ໃນການຂຸດ ປັບດິນນາ ແມ່ນໃຊ້ແຮງງານ ຈໍານວນຫຼາຍ ແລະ ໃຊ້ເວລາດົນ ຊ່ຶງເປັນປັດໃຈ ທ່ີສົ່ງຜົນ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການເຮັດເຕັກນິກນ້ີ.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
لا
Is flooding of the area occurring?
نعم
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
500 ກິໂລ/ເຮັກຕາ
Quantity after SLM:
1200 ກິໂລ/ 0.7 ເຮັກຕາ
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
ສາມາດ ເກັບເອົາເຟືອງ ມາເກືອ ເປັນອາຫານໃຫ້ງົວກິນໄດ້ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ໃນຊ່ວງລະດູແລ້ງ ທ່ີງົວອຶດຫຍາ້ກິນ
animal production
Comments/ specify:
ງົວ ໄດ້ກິນເຟືອງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ແຂງແຮງດີ
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດນາ ສາມາດຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ ສົມທຽບກັບ ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າ ຊ່ຶງມີຄວາມສ່ຽງຫຼາຍ.
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ມີນາທົ່ງພຽງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ມີຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ ເນື່ອງຈາກສາມາດ ນໍາໃຊ້ເຟືອງ ໄປຄຸມໜານປູກຜັກ ເພື່ອປັບປຸງດິນ ເຮັດໃຫ້ມີຜັກໄວ້ກິນ ແລະ ມີນາ ທີ່ສາມາດ ຫາປາໄວ້ກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
production area
Comments/ specify:
ເນື້ອທີ ເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້າຫຸຼດລົງ ແຕ່ມີເນື້ອທີ່ນາແຄມຫ້ວຍເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນ
land management
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm Australia ໄດ້ສະຫນອງຄວາຍ ໃຫ້ຊາວກະສິກອນ ແລະ ຊາວກະສິກອນ ໃຊ້ແນວພັນເຂົ້າ ພື້ນເມືອງ ທ່ີບໍ່ໄດ້ສີ້ນເປືອງລາຍຈ່າຍ.
workload
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນວຽກຫນັກ ສົມທຽບໃສ່ ກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດໄຮ່ເຂົ້ົາທ່ີໃຊ້ແຮງງານຫຼາຍ.
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລີດເຂົ້າ ໄວ້ກິນພຽງພໍ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ
cultural opportunities
Comments/ specify:
ສາມາດ ປ່ຽນແນວຄວາມຄິດ ຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ ທ່ີມີຄວາມເຊ່ືອຖື ບ່ໍໃຫ້ປູກເຂົ້າ ໃສ່ນໍາ້ ເພາະຜິດຮີດຄອງປະເພນີ.
recreational opportunities
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ໃຊທົ່ງນາ ເປັນບ່ອນພັກຜອ່ນ ຊ່ຶງມີອາກາດ ທ່ີບໍລິສັດ
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ເພີ່ມຜົນຜະລິດເຂົ້ານາໄດ້ ທັງເປັນການຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ຄວາມບໍ່ຍຶນຍົງໃນການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ແບບເລ່ືອນລອຍ.
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນບັນຫາ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ ທ່ີດິນ ຈາກກິດຈະກໍາ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ ແບບເລືອນລອຍ
Ecological impacts
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
ເພີ່ມຈໍານວນ ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງພືດ ທ່ີເກີດຢູ່ຕາມແຄມຫ້ວຍ
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
ເພີ່ມຈໍານວນ ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ບ່ອນທ່ີຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສ່ີງທ່ີມີຊີວິດ
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ການປ່ອຍທາດອາຍພິດ ກະຈົກເຮືອນແກ້ວ ໂດຍການຢູດຕິ ການຖາງປ່າ ເຮັດໄຮ່ ໃນເຂດບໍລິເວນ ທ່ີເຮັດເຕັກນິກນ້ີ.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| annual rainfall | increase | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
6.6 التكيف
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
لا
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ການຖາງປ່າ ເຮັດໄຮ່ ໂດຍການ ຈັດສັນອາຊີບຄົງທີ່ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ |
| ເພ່ີ່ມການຄໍາ້ປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ ໂດຍສະເພາະມີເຂົ້າກຸ້ມກິນ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ |
| ສາມາດ ປ່ຽນແປງ ຄວາມເຊ່ືອ ຂອງປະຊາຊົນ ທ່ີໃນເມ່ືອກ່ອນ ທ່ີບ່ໍເຄີຍເຮັດນາ ແລະ ບໍ່ຕອ້ງການ ທ່ີຈະປູກເຂົ້າໃສ່ນໍາ້ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ຊາວກະສິກອນ ສາມາດ ນໍາໃຊ້ເຟືອງ ເປັນອາຫານສັດໄດ້ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ໃນລະດູແລງ້ ທ່ີສັດອຶດຫຍາ້ກິນ. ນອກຈາກນັ້ນ, ເຟືອງ ກໍ່ຍັງມີຄຸນປະໂຫຍດ ຫຼາຍຢ່າງເຊັ່ນ ສາມາດເອົາໄປປົກຄຸມຫນານຜັກ ເພື່ອເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນມີຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ. |
| ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜອ່ນ ເວລາ ແລະ ທັງເປັນການປະຢັດ ແຮງງານ ໃນກິດຈະກໍາ ການເຮັດນາ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ຈໍາກັດ ເນື້ອທີ້ ຮາບພຽງ ທີຢູ່ແຄມຫ້ວຍ ຊຶງບ່ໍພຽງພໍ ກັບ ຄວາມຕອ້ງການຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ ທ່ີຕອ້ງການຢາກເຮັດນາ. | ສາມາດ ນໍາໃຊ້ລົດຈົກ ມາຈົກດິນ ແລະ ຂະຫຍາຍເນ້ືອທ່ີນາ ອອກບ່ອນທີ່ມີເງື່ອນໄຂ |
| ຜົນຜະລິດ ເຂົ້ານາແຊງ ຍັງໄດ້ໜ້ອຍ ເນ່ືອງຈາກ ເນ້ືອທ່ີ ຈໍາກັດ ສົ່ງຜົນ ໃຫ້ມີພຽງແຕ່ບາງຄອບຄົວ ທີ່ມີເຂົ້າບໍກຸ້ມກິນຕະຫຼອດປີ. | |
| ມີບັນຫາ ສັດຕູພືດ ທໍາລາຍເປັນຕົ້ນແມ່ນ ເພ້ຍ, ຕັກແຕນ, ນົກກະປິດ ແລະ ຫນູ. | |
| ປະຊາຊົນ ຂາດເຕັກນິກ ວິຊາການ ໃນການເຮັດນາ ເພື່ອຍົກສະມັດຕະພາບ ຜົນຜະລິດໃຫ້ສູງຂຶ້ນ | ຕ້ອງໄດ້ຮັບການຝຶກອົບຮົມ ຈາກວິຊາການ ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1
- interviews with land users
1
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
17/05/2017
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules