Pâturage temporaire (4-5 ans) de Gay-Grass et Trèfle blanc [France]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Julie Lemesle
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_3160 - France
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. معلومات عامة
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
لا
Comments:
Il n'y a pas de dégradation des terres.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Pâturage, zone dans laquelle les vaches vont prélever l'herbe de ray-grass (anglais) et trèfle blanc.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
1. Le pâturage est installé de manière artificielle par l'exploitant ici tout autour des bâtiments de l'exploitation proche de la salle de traite (ou stabulation). Nous sommes sur des parcelles situées à proximité des bâtiments de manière à favoriser le pâturage par les vaches laitières dans le but de produire un lait biologique. Comme sur l'ensemble de l'exploitation, nous profitons d'un climat de type tempéré océanique. Les prairies sont installées pour plusieurs années (minimum 5 ans)
2. Les principales caractéristiques sont :
-réaliser l'autonomie fourragère pour produire du lait biologique : le ray-grass anglais est la graminée d'excellence pour le pâturage sur notre exploitation. Elle est intéressante sur le plan nutritif, résiste très bien au pâturage répété des animaux, et est parfaitement adapté au climat local. Le trèfle blanc est lui aussi adapté au pâturage répétitif; par ailleurs, il permet un apport d'azote dans le sol (grâce aux nodosités qui fixe le N2 atmosphérique) qui favorise le développement du ray-grass. Enfin, même si l'été est sec, le trèfle blanc garde une bonne croissance estivale. Afin de maximiser la production fourragère et donc l'autonomie, les vaches changent de parcelles régulièrement afin de laisser un temps de repousse entre deux passages, c'est le pâturage tournant.
-structurer le sol et préparer une culture suivante qui aura un bon potentiel de production
-Permettre de produire beaucoup de matière organique ( en agriculture biologique il n'y a pas d'intrant chimique) donc résultat économique avantageux pour l'exploitant
-Préparer le sol pour une future culture tête d'assolement
3. Les objectifs du pâturage sont :
- diminuer les coûts de production du lait (l'herbe paturée = aliment faible en coût, aliment le moins cher)
- rechercher et atteindre l'autonomie fourragère
- permettre aux animaux un meilleur bien être ( meilleure santé)
- Épandre des déjections de manière naturelle et uniforme, comme les vaches se déplacent en autonomie, ( sans coût donc moins de travail pour l'éleveur)
4. Au départ il faut une bonne implantation au semis. La pâture peut durer 5 ans ou plus si elle est bien entretenue.
Il est nécessaire de faire une fauche régulière au minimum une à deux fois par ans pour maintenir une pâture appétissante et appétante pour les animaux.
5. C'est une technologie économe, son impact pour l’éleveur est de mieux gagner sa vie. Aussi, au niveau technique il y a un meilleur développement racinaire, donc travail du sol grâce aux vers de terre et à la non utilisation des engrais chimiques et donc un meilleur PH. La prairie permet un stockage de carbone sous forme de matière organique (puit de carbone).
6. Ici ils aiment bien la pâture, rotation longue, alimentation riche équilibré sans supplémentation, coût de l'aliment faible, bien être animal, bien être sociétal (les consommateurs apprécient de voir les vaches dans les champs et de consommer des produits issus des champs).
Inconvénients: Entretien et fauche des mauvaises herbes du type: chardons, rumex
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
بلد:
France
Region/ State/ Province:
Bretagne/France/Ille et Vilaine
Further specification of location:
Argentré du Plessis
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Le pâturage est une culture qui existe de manière traditionnelle depuis plus de 50 ans au moins. Cette culture a été remise au goût du jour par le fait d'associer le ray-grass anglais (graminée) et le trèfle blanc (légumineuse).
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

أراضي الرعي
Intensive grazing/ fodder production:
- Improved pastures
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
Comments:
Vaches laitières Prim'Holstein
Nombre de période de croissance par an: 3 (Plusieurs pâturages dans la même pâture et minimun une coupe d'herbe)
Densité d'élevage/ chargement: 1 UGB (Unité gros bovins) par hectares
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated crop-livestock management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

management measures
- M2: Change of management/ intensity level

other measures
Comments:
Couverture végétale tout au long de l'année donc limitation du ruissellement des nitrates vers les cours d'eau et la nappe phréatique notamment en période hivernale.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
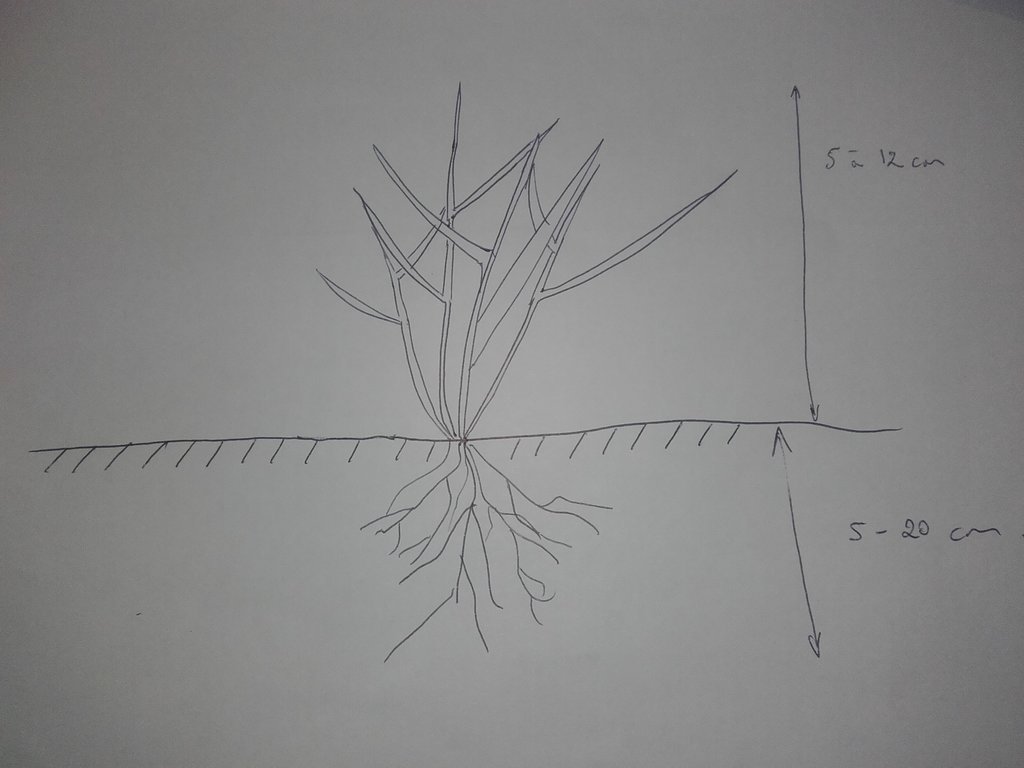
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Les prairies de Ray Grass anglais se développent de manière à couvrir rapidement le sol. La prairie est pâturée lorsqu'elle atteint 15 cm de hauteur en moyenne. L'enracinement important permet un redémarrage de la végétation et un maintien de la structure du sol.
Author:
Renier Mélanie
Date:
12/12/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
5 hectares
other/ national currency (specify):
euro
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
115 euros
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tracteur et charrue | après la récolte de la culture soit en octobre pour l'automne suite à la récolte d'un maïs. Ou au printemps ou l'été après la récolte du blé d'une céréale |
| 2. | Semis de la pâture | après la récolte de la culture soit en octobre pour l'automne suite à la récolte d'un maïs. Ou au printemps ou l'été après la récolte du blé d'une céréale |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 1 personne | 1 demie journée par hectare | 1,0 | 57,0 | 57,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | une charrue pour tourner la terre | 1,0 | ||||
| Equipment | un tracteur | 1,0 | ||||
| Equipment | tracteur et charrue pour 5 hectares | heures-maschines | 1,5 | 30,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | Tracteur et semeuse pour 5 hectares | heures-maschines | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Plant material | 200 Euros par hectares (coût de la semence) | 200,0 | ||||
| Plant material | Mélange de semence (biologique) pour 5 hectares | kg | 200,0 | 1,5 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 432,0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 432,0 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | coupe ou fauchage | 1 à 2 fois au printemps |
| 2. | pâturage tournant | récurrent de mai à juin |
Comments:
lien http://saperfel.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/P--LE-cout-des-fourrages.pdf
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizers and biocides | 4,0 |
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
- Implantation semis
- la fauche d'entretien
-le temps travail personnel salarié
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
650,00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
faible pluie estivale
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
http://www.linternaute.com/voyage/climat/ille-et-vilaine/departement-35/2017-2016
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
climat océanique influencé par le gulf stream, hivers doux et humides, étés tempérés et frais
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
لا
Is flooding of the area occurring?
لا
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder quality
Comments/ specify:
le pâturage des prairies de type Ray Grass anglais - trèfle blanc assure une alimentation de bonne qualité nutritionnelle pour les bovins (apport d'énergie, de protéine et de cellulose équilibrés)
Water availability and quality
drinking water quality
Comments/ specify:
de part la structure racinaire et la couverture du sol, la prairie assure une bonne filtration de l'eau
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
ces prairies ne demandent pas d'irrigation et sont adaptées au climat local, les ressource en eau de l'exploitation seront donc réservées à l'élevage
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
les prairies étant installées pour un minimum de 5 ans, la couverture du sol est assurée pendant ce temps
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
le système racinaire des variétés fourragères permet à la biodiversité du sol d'en améliorer la structure et donc de ne pas compacter le sol
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
De part son développement, la prairie constitue un puits à carbone. L'implantation de fabacées (trèfle blanc) permet d'enrichir le sol en azote
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
rôle puits de carbone
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
ne nécessite pas d'irrigation + couverture du sol permettant bon cycle de l'eau
groundwater/ river pollution
Comments/ specify:
rôle de filtration du couvert végétal
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
de part l'absence de traitement phytosanitaire, cette pratique est sans dommage sur les champs voisins
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
puits de carbone
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| annual rainfall | decrease | moderately |
Comments:
C'est compliqué de répondre à cette question
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
Comments:
C'est difficile à évaluer
6.6 التكيف
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
لا
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| économique : apport en quantité de fourrage de qualité |
| écologique : couverture des sol ; vie du sol |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Economique: Pâturage faible coût à mettre en place Sociétal: bien être des animaux et lait de bonne qualité pour les consommateurs Ecologique: La pâturage piège le carbonne grâce aux trèfles |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Pas de point faible pour l'exploitant |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
2 informateurs, agriculteurs
Jean Pierre et Christophe Lemesle
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
18/10/2016
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules