Compost Production Pits for Crop Production [Uganda] [اوغندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Sarah Babirye
- المحرر: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- المراجعون: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel, Donia Mühlematter
Olwezo lwakasasilo
technologies_3303 - اوغندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Baguma Innocent
0706385387
None
اوغندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - اوغندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
17/10/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
It is a good sustainable land management technology that enables farmers locally to make cheap organic manure to increase food production while improving the degraded areas.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Compost manure production is a sustainable land management practice promoted by small scale farmers by using banana, cassava, sweet potato peelings, jack fruit residues and food left overs. The aim is to improve soil fertility, increase agricultural production and household income. The technology makes nutrients more readily available to plants in a short period of time through composting. During composting, raw organic matter is transformed into stable humus which is absorbed by plants thus enabling increased production.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Compost manure application is an integrated pest, disease and soil fertility management technology that cheaply avails organic matter to increase crop/land productivity among local farmers. Farmers use locally available inputs like weeds, kitchen refuse, crop residues (maize, sorghum, millet, wheat among others) at less or no cost. These nutrients are thus made available to plants through transforming raw organic matter into stable humus, which is readily absorbed by plants. This increases agricultural and vegetable production. However, the nitrogen content in the compost can be further increased if waste plant materials such as Lantana Camara, Sesbania are integrated. Procedures to make compost manure include the following steps:
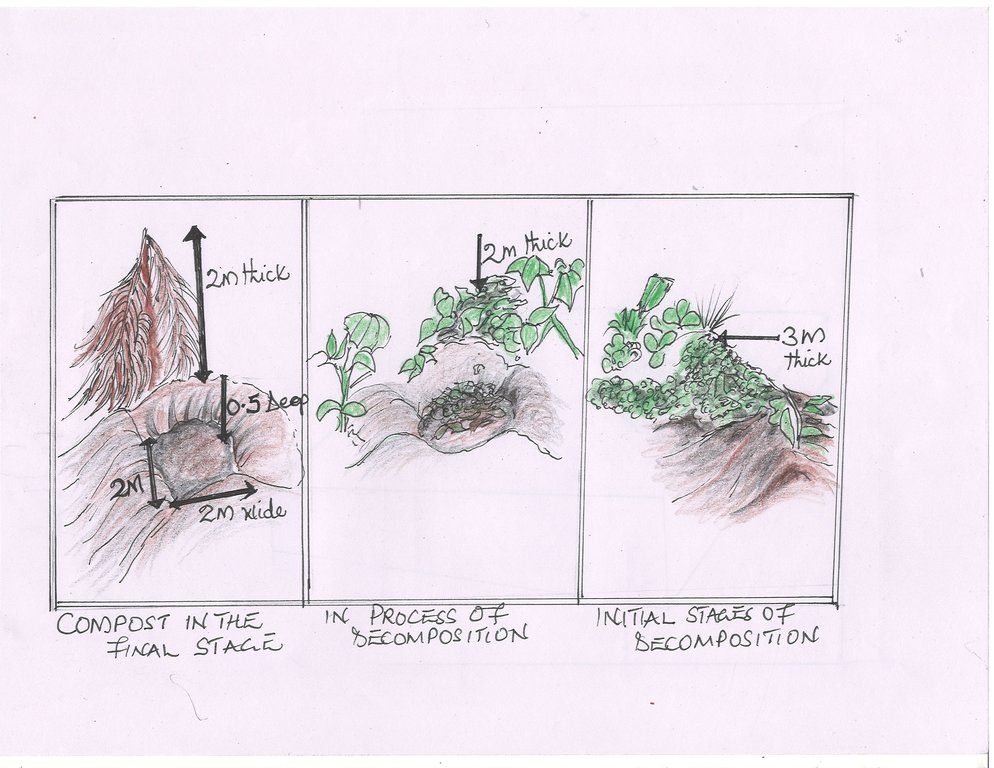
• Digging pits of about 2m length, 2 m width and 0.75 m depth.
• Placing the assorted organic materials in pit no. 1 and covering it with soil in a dome shape to prevent water from seeping into the decomposing materials. Residues so assembled should be in their raw form collected from either the kitchen, weeds from gardens, peelings and crop residues like maize and sugarcane husks. As a rule of thumb, the compost pile should be build by beginning with a bottom layer of bigger sized materials, such as maize stovers, of about 15cm height. This should also include a layer of dry vegetation, hedge or grass cuttings to about 15cm height. Sprinkling top soil and adding water by using a watering can will to moisten the whole layer. In this pit, the degradation process will take a period of 1-2 months.
• In the third month, the materials are then transferred to pit no. 2, arranged and compressed in layers and covered with soil in a dome shaped manner.
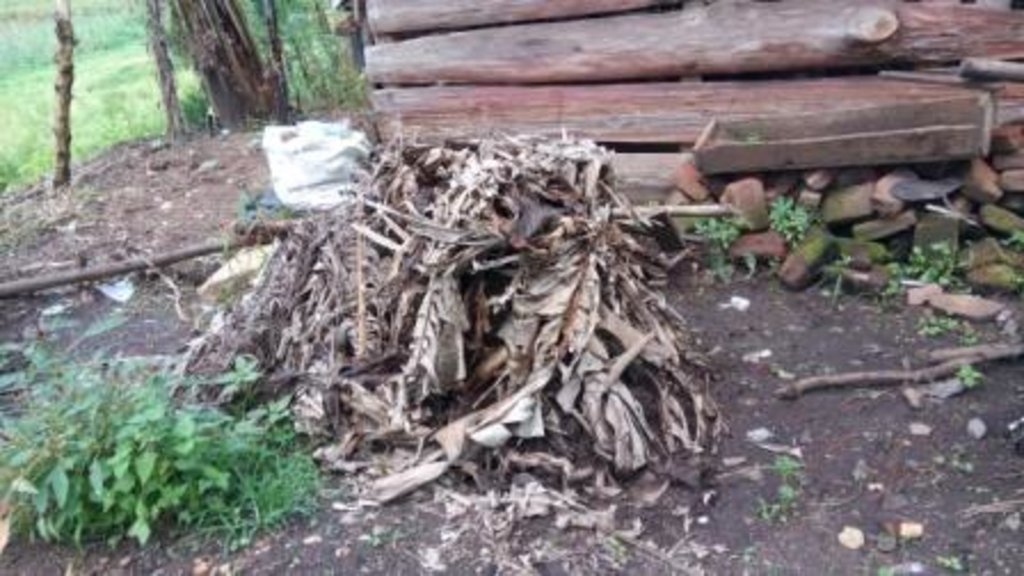
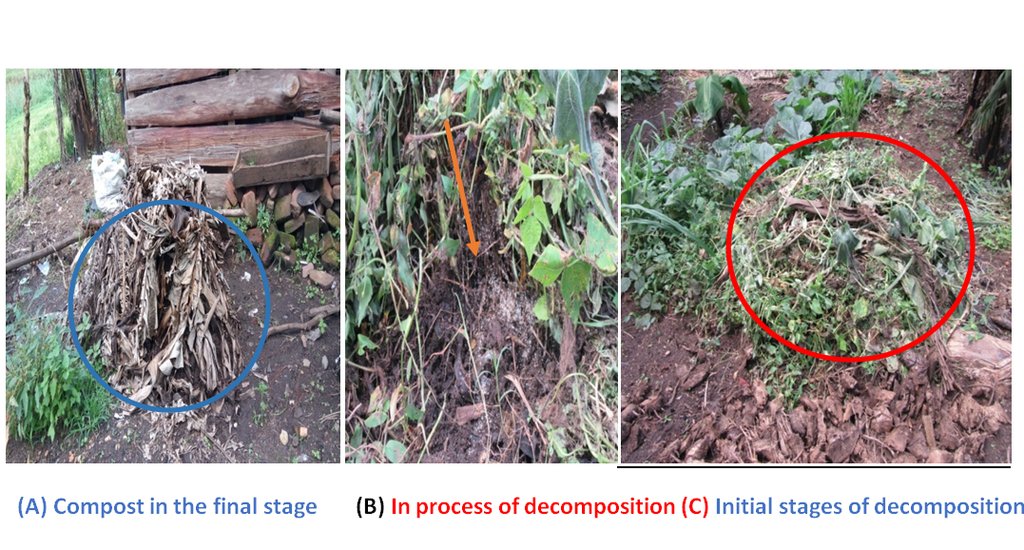
• After another spell of 4-5 months, these decomposed materials are then transferred to pit no. 3. This comprises of decomposed matter ready for use. In this last pit, manure in the final stage is always cold, dark and most importantly, less bulky. It produces a pleasant smell when spread.
In case of a banana plantation, ready compost is applied around the banana hills or in trenches between 4 banana plants. Soils with compost cannot easily be washed away by water or blown by wind as the soil particles are held tightly together with the sticky substance secreted in the process of decomposition. This glue-like structure also helps to hold moisture in the soil hence improving the structure.
The farmer selects a suitable and convenient place for the compost pit system preferably near the garden and home stead where he digs three pits. The cost of digging a compost pit depends on where the pits are to be located. If the place is easy to dig, each pit costs about UGX 5,000/=. Other costs include, hiring a spade at UGX 1,000/=, a hoe at UGX 1,000/=, a pan at UGX 1,000/= and a watering can at UGX 1,000/=, all summing up to UGX 9000/= for the whole activity. The technology improves production in both annual and perennial plants such as fodder grasses and crops through restoring degraded soils by improving soil structure, soil moisture and micro organism content. As the technology provides nutrients to plants it also reduces environmental pollution associated with inorganic fertilizer use. Nutrients are released gradually, enabling the following year’s crops to benefit as well. Weeding is done easily in areas applied with compost manure as the soil has a soft texture. Through this technology, home hygiene is improved by utilising wastes. Plant diseases and pests like banana weevils are suppressed.
However, making compost manure is challenging. It requires a lot of commitment and serious efforts to collect the kitchen and garden residues all the time. Digging a pit is quite laborious and farmers with little land find it hard to reserve land for compost pits.
This technology is an agronomic measure that helps in waste management through recycling, re-use or reduction of wastes, thereby improving sustainable land management. Maintenance is always by ensuring that compost pits are not under permanent shade and properly covered. Pits should be emptied after the process is done in preparation for the next cycle.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
التاريخ:
17/10/2017
الموقع:
FORTPORTAL, KABAROLE DIST
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Aine Amon
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اوغندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
KABAROLE
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
FORTPORTAL MUNICIPALITY
التعليقات:
Coordinate points where the technology was captured were E 03017319 (Longitude) and Latitude N 004014.4
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Bananas, vegetables (cabbage, amarathus among others)
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Land use has not changed due to the technology applied.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- حدائق منزلية
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
التعليقات:
In case of banana plantation, the compost is applied around banana heaps and in trenches between 4 banana heap.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر

التدابير الإدارية
- M6: إدارة النفايات (إعادة التدوير أو إعادة الاستخدام أو التقليل)
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Compost manure application reduces /restores degraded soils. This is throug improving soil structure, soil moisture and micro organism content.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The dimensions for the compost pits are:
Width 2 m
Length 2 m
Depth 0.5 m
Slope: Gentle slope
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
UGX
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
3224,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1 Pit costs 2500/= (i.e Labour to construct a pit where the residues are deposited).
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a suitable place near the garden and near the home stead | تدابير أخرى | Once |
| 2. | Site should not be under permanent shade | تدابير أخرى | Once |
| 3. | Put top soil in between different layers to quicken decomposition | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once |
| 4. | After filling with materials,cover with soil and make it dome shaped | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Once |
| 5. | leave it to settle for 4-5 months when it is fully decomposed | تدابير أخرى | Once |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Digging 3 Pits | man pit | 3,0 | 2500,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a hoe | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a spade | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a watering can | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a pan | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 11500,0 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
All costs are covered by the land user (100%)
التعليقات:
The technology is cost efficient to low income farmers.
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | By covering the manure under decomposition | إدارية | Every 5 months |
| 2. | By empying the pits when manure is ready | إدارية | Every 5 months |
التعليقات:
The technology has few activities on the maintenance side.
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Emptying pits | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | Hiring a hoe | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a spade | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hiring a pan | pic | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 5500,0 | |||||
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour. Despite the fact that the technology is highly cost effective, most farmers lack money to hire people to dig pits for them and buy the few necessary inputs like spade, hoes for the activity to take place.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8Kg of bananas in 1 acre
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
25kg of banana in 1 acre
جودة المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers are able with the use of this technology to harvest high yields for both home consumption and commercial purposes.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Moisture increases to 75%
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soils with composts cannot easily be blown by water and wind as the soil particles are held tightly together with the sticky substance secreted in the process. This glue-like structure also helps to hold moisture in the soil hence improving the soil texture and structure and therefore wind and rains cannot blow away the soils.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Nutrients can be recycled in the soil over and over again in the process of applying this manure to the soil.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Breaking down of matter like weeds, shrubs, kitchen residues (banana, cassava, sweet potato peelings) into humus by the micro-organisms improve on the soil organic matter.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
High fertility levels of the soils from theses decomposed composts increase the vegetation cover as a result of humus generated.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
The quantity of annelids like earth worms increased. This is because they feed on both live and dead organic matter. Earthworms help in the breaking down of organic matter into humus and improve on soil aeration.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Besides enriching the soil with fertility, the compost manure has the ability to suppress diseases and pests in the garden like the banana weevil.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تعليقات بشأن تقييم الأثر:
The technology has no off site impacts.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Manure made on farm is cheaper than when it is brought from off farm. Organic manure improves on soil structure. |
|
Manure is readily available. Increases water holding capacity. |
| The technology improves on home hygiene. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| It is a very cheap technology that avails manure to farmers using locally available materials. |
| Poor farmers who cannot afford buying in organic fertilizers can improve on their yields using this technology. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The technology requires a garden that is so close to the homestead since the materials are bulky to carry. | Make pits closer to the home. |
| Need to control the rainfall run off from the decomposing area. | Advisable to construct pits under shades. |
| Microbes required to release nutrients require moisture so seasonal variations may affect the system. | Farmers should always utilize the seasons' conditions to enable best microbial action. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Few farmers have adopted the technology since it demands commitment. | Sensitization to farmers on the importance of organic manure. |
| There is always a bad smell before the materials are covered up hence may result to conflicts from neighbours. | Collecting the wastes faster and cover them immediately. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
1
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
1
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
1
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The Effects Of Various Organic Fertilizers On Growth Biology Essay,PASCHALIS BARLAS,2013
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://www.uniassignment.com/essay-samples/biology/the-effects-of-various-organic-fertilizers-on-growth-biology-essay.php
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Climate change mitigation potential of agricultural practices supported by IFAD investments by Mery Richards,Aslihan Arslan,Romina Cavatassi Todd Rosenstock
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.academia.edu/38512422/IFAD_RESEARCH_SERIES_35_-_Climate_change_mitigation_potential_of_agricultural_practices_supported_by_IFAD_investments_An_ex_ante_analysis
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية