Reforestación Protectora [Colombia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Luisa F. Vega
- Editors: Javier Otero, Carolina Olivera
- Reviewer: Giacomo Morelli
Reforestación
technologies_4086 - Colombia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. معلومات عامة
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Colombia
land user:
Colombia
co-compiler:
Colombia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
FAO Colombia (FAO Colombia) - ColombiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Unidad de Planificación Rural Agropecuaria - Ministerio de Agricultura y Desarrollo Sostenible - Colombia (UPRA - MINAGRICULTURA) - ColombiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Corporación Autonoma Regional de Sucre (CARSUCRE) - ColombiaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Corporación Ecoambiente (Corporación Ecoambiente) - Colombia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
22/06/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
لا
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Reforestación activa y pasiva gracias a la plantación de especies arbóreas y a la exclusión de pastoreo en el area. Esta tecnología se diseña e implementa con el objetivo de proteger las zonas de recarga del acuífero del Municipio de Morroa, Sucre, Colombia.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
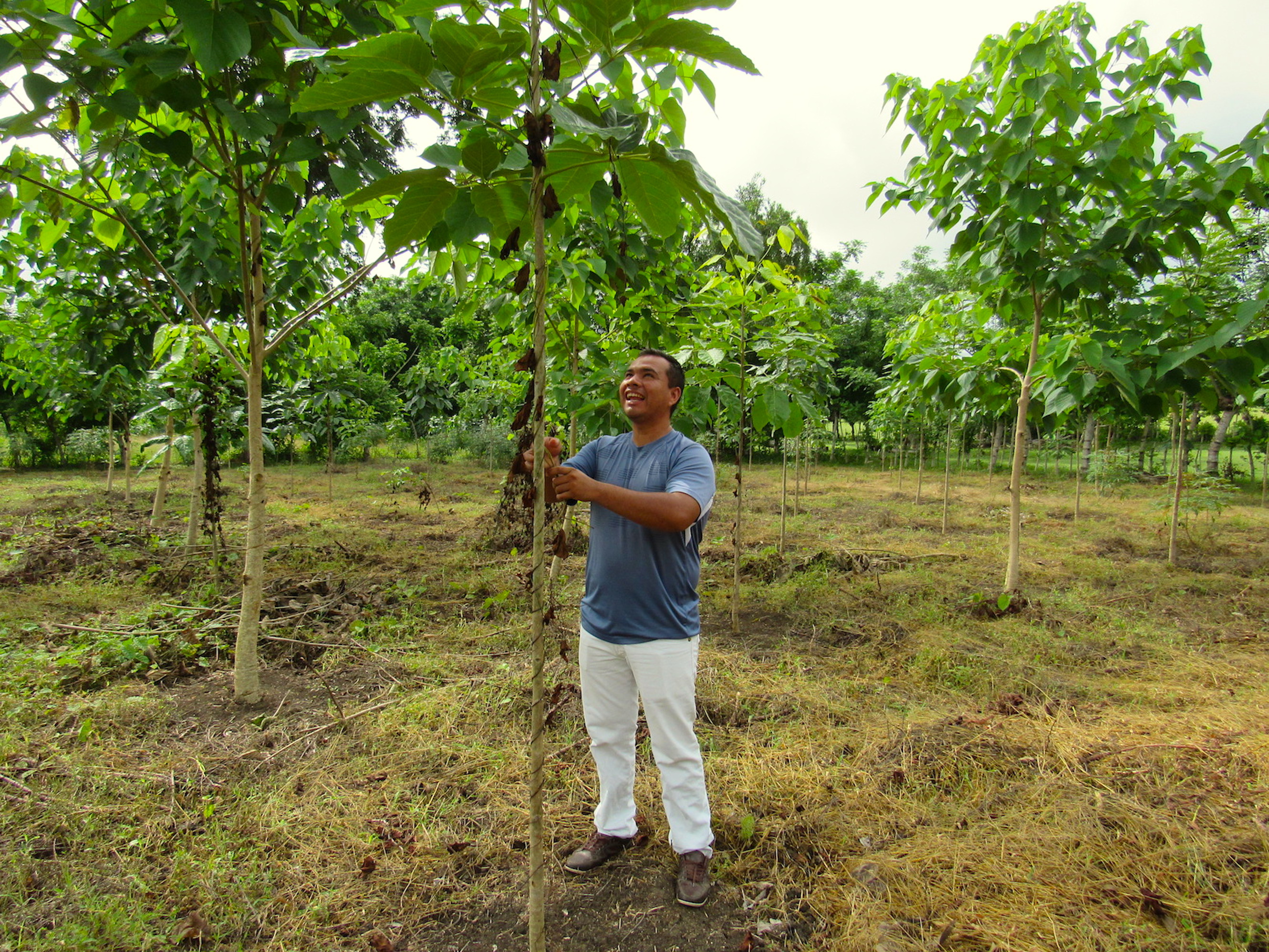
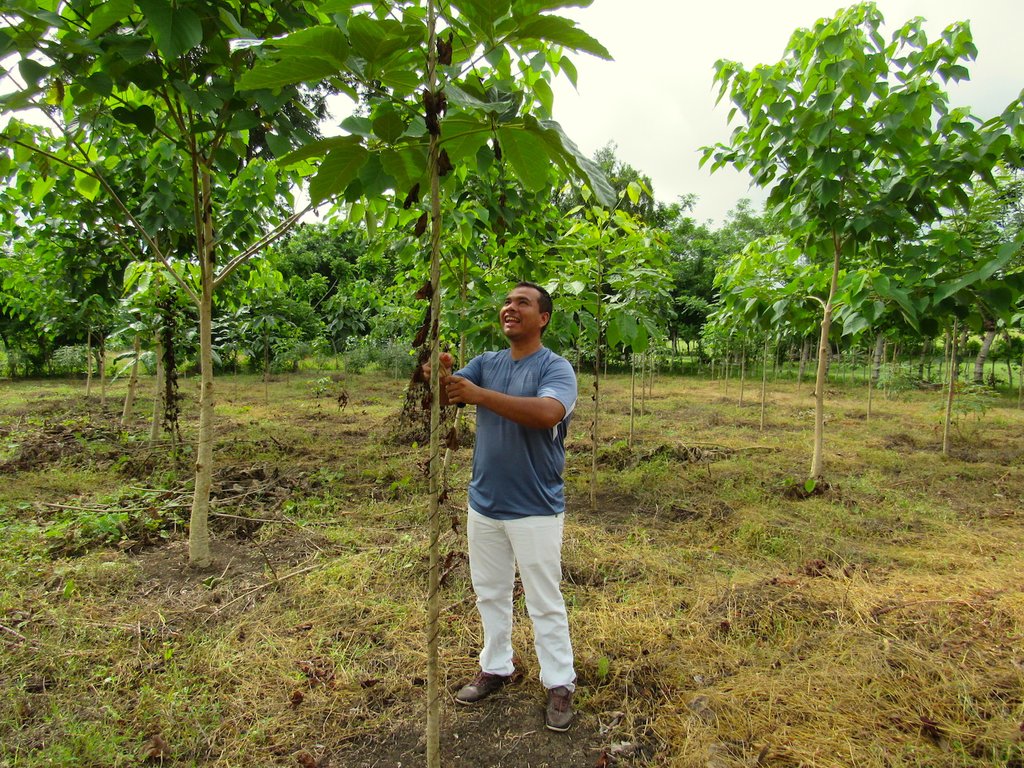
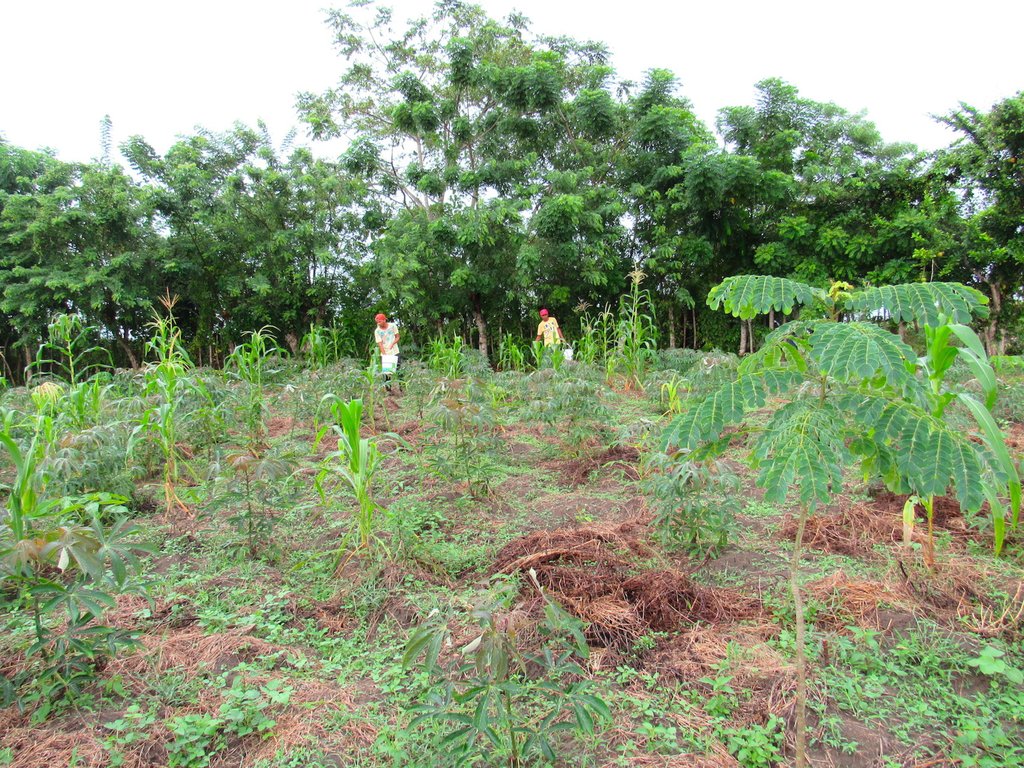
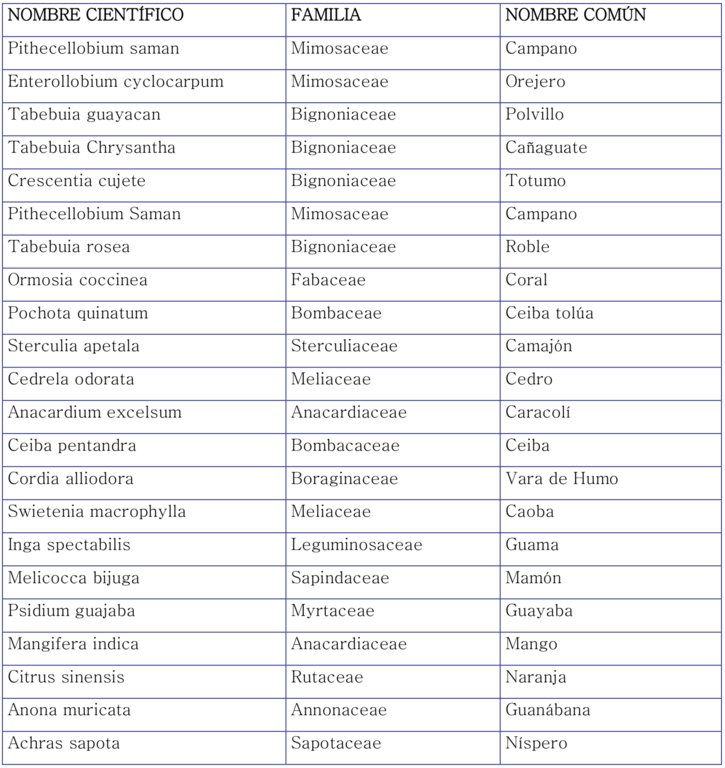
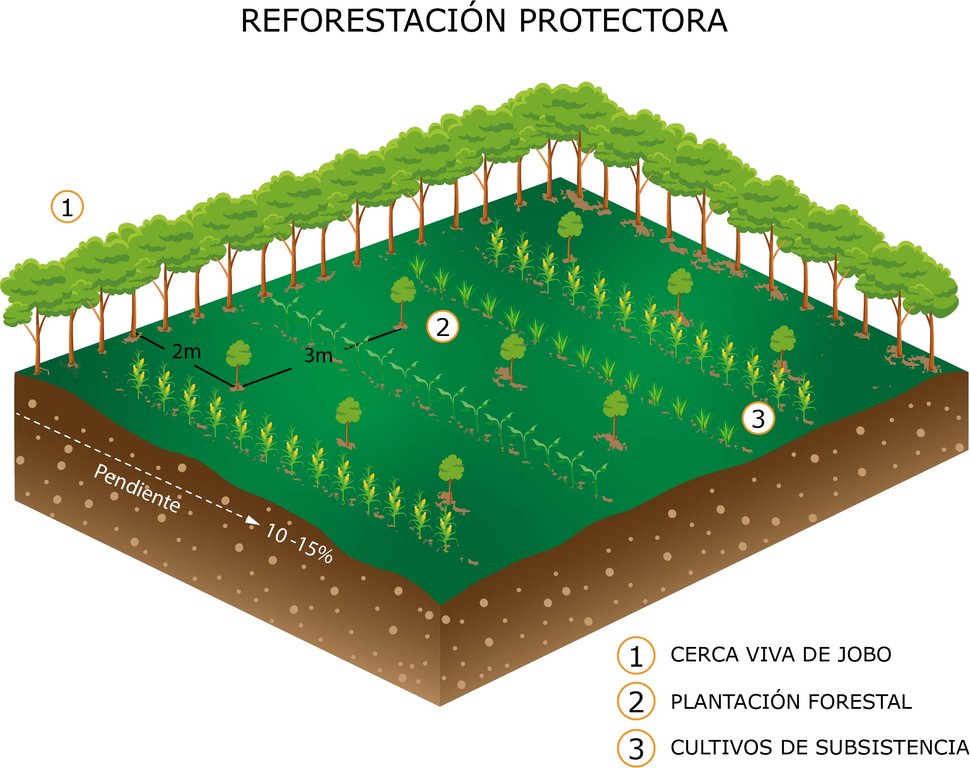
La Reforestación Protectora consiste del diseño, implementación y mantenimiento de 150 ha de plantaciones forestales con exclusión de pastoreo, en areas que se consideran de recarga del acuífero de Municipio de Morroa, Sucre, Colombia. La tecnología fue implementada en los municipios de Morroa, Colosó, Chalán y Toluviejo, donde se generó un cambio en el uso de la tierra de ganadería extensiva a áreas forestales y agroforestales.
Para la evaluación y documentación de esta tecnología se escogió la Finca Pasatedelargo, donde se realizó una siembra con xx arboles de especies forestales nativas en remplazando asi la actividad de ganadería extensiva practicada durante más de 20 años.
Se han implementado las siguientes prácticas de MST.
Siembra de especies forestales.
Instalación de cercas vivas.
Incorporación de abonos y residuos orgánicos.
Reposo total de la tierra, no pastoreo, no labranza.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
Video elaborado por la Corporación Ecoambiente y La Corporación Autónoma Regional de Sucre.
الموقع:
Finca Pasatedelargo, Morroa, Sucre, Colombia (09º21'24".2 W - 75º18'58".0 N)
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
بلد:
Colombia
Region/ State/ Province:
Sucre
Further specification of location:
Municipio de Morroa, Vereda El Rosario.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2017
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Reforestación Protectora implementada en 150 ha por la Corporación Ecoambiente y La Corporación Autónoma Regional de Sucre.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial social impact
- Recarga de acuífero
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Forest/ woodlands
Tree plantation, afforestation:
- Mixed varieties
Products and services:
- Fruits and nuts
- Nature conservation/ protection

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- natural and semi-natural forest management
- agroforestry
- ground water management
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
- M5: Control/ change of species composition
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wr: riverbank erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
- Bh: loss of habitats
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
- Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
- Bl: loss of soil life

water degradation
- Hg: change in groundwater/aquifer level
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
3000,0
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Management | None |
| 2. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 3. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 4. | None | Management | None |
| 5. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 6. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 7. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 8. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 9. | None | Vegetative | None |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 80,0 | 25000,0 | 2000000,0 | |
| Labour | None | None | 12,0 | 25000,0 | 300000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 1,0 | 850000,0 | 850000,0 | |
| Equipment | None | None | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 1100,0 | 800,0 | 880000,0 | |
| Plant material | None | None | 170,0 | 1500,0 | 255000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 50,0 | 1500,0 | 75000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 5,0 | 50000,0 | 250000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 500,0 | 700,0 | 350000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 160,0 | 3000,0 | 480000,0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 12,0 | 7000,0 | 84000,0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 3,0 | 75000,0 | 225000,0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 3,0 | 7000,0 | 21000,0 | |
| Other | None | None | 1,0 | 250000,0 | 250000,0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6330000,0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 2. | None | Vegetative | None |
| 3. | None | Agronomic | None |
| 4. | None | Agronomic | None |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 20,0 | 25000,0 | 500000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 50,0 | 1500,0 | 75000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 500,0 | 700,0 | 350000,0 | |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 955000,0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1134,00
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
pH: 6,27 (ligeramente acido)
Conductividad eléctrica (CE) dS/m: 0,39 (no salino)
Materia Orgánica (Walkley Black) en g/100g: 2,27 (medio)
P disponible (Bray II) en mg/kg: 22,71 (medio)
K intercambiable cmol/kg: 0,31 (medio)
CICE en cmol/kg: 29,72 (alto)
Textura (Boyoucos): Franco arcillo arenoso
Densidad Aparente (DA) g/cc: 1,16
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
لا
Is flooding of the area occurring?
لا
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- group
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
fodder production
fodder quality
animal production
wood production
forest/ woodland quality
risk of production failure
product diversity
production area
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Se unió al proyecto de CARSUCRE y puede estar en contacto con otros productores que participan en el proyecto.
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
Tomó conciencia de las causas e implicaciones de la degradación
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
surface runoff
groundwater table/ aquifer
Soil
soil moisture
Quantity before SLM:
Ha 7,19 g(agua)/g(suelo seco)
Quantity after SLM:
Ha 9,29 g(agua)/g(suelo seco)
Comments/ specify:
La Humedad aprovechable del suelo aumenta considerablemente en el sistema forestal. Este dato se obtiene con el análisis de laboratorio de la retención de humedad del suelo, por la diferencia entre la capacidad de campo y el punto de marchitez. Se comparó la parcela con MST con una parcela de suelo similar, sin MST.
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
La cobertura vegetal favorece la cobertura del suelo.
soil loss
soil compaction
Quantity before SLM:
DA: 1,51 g/cc; porosidad: 35%
Quantity after SLM:
DA: 1,16 g/cc; porosidad: 50%
Comments/ specify:
Según los análisis de laboratorio realizados sobre la parcela con MST en comparación con un terreno similar, sin MST, se observó una menor compactación, traducida por una menor densidad aparente y una mayor porosidad.
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Quantity before SLM:
MO: 2,33 g/100g (medio)
Quantity after SLM:
MO: 2,27 g/100g (medio)
Comments/ specify:
Según los análisis de laboratorio realizados sobre la parcela con MST en comparación con un terreno similar, sin MST, se observó una Materia Orgánica (Walkley Black) equivalente, debido al poco tiempo de implementación del proyecto. La materia orgánica está en un nivel medio pero se ve afectada por las condiciones físicas del suelo.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Quantity before SLM:
30% tierras desnudas
Quantity after SLM:
0% tierras desnudas
Comments/ specify:
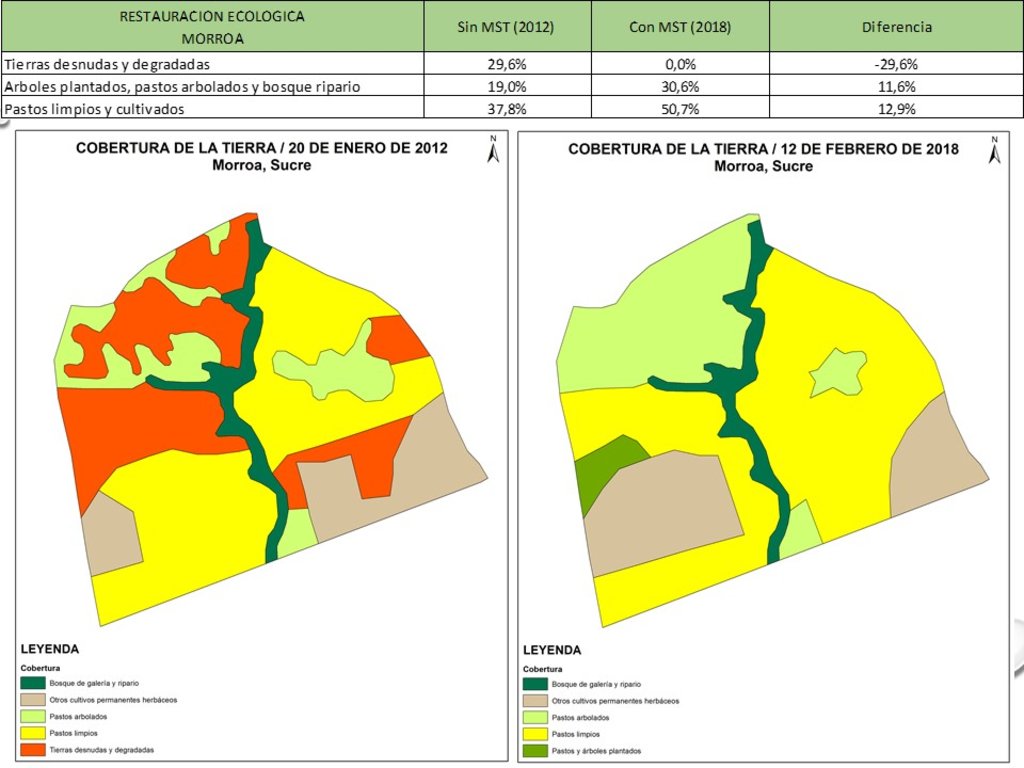
El suelo ya no presenta áreas descubiertas de vegetación en esta parcela. Tomando el dato de las imágenes aéreas del año 2014, en comparación con las del año 2018 en la misma época del año, se midió una disminución de 30% del área de tierras desnudas y degradadas. Se midió igualmente un aumento de 12% de arboles plantados y bosque ripario, así como un aumento de 13% de los pastos limpios. Ver diagrama en las ilustraciones de la tecnología.
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
habitat diversity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
fire risk
micro-climate
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 10-50%
6.6 التكيف
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
نعم
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- climatic change/ extremes
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules