Pitcher irrigation for the management of moderately saline soils [بنغلاديش]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Md Babul Hossain
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Udo Höggel
Kalash shesh podhothi
technologies_4112 - بنغلاديش
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Biswas Sachindranath
+8801718691666
Soil Resource Development Institute
Principal scientific officer, Soil Resource Development Institute, Regional office, khulna
بنغلاديش
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Biswas Amarendra Nath
+8801718732843
Soil Resource Development Institute
Senior Scientific Officer, Soil Resource Development Institute, Regional Office, Khulna.
بنغلاديش
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
Zahid Ameer M.D.
8801552409934
zahidsrdi@yahoo.com
Soil Resource Development Institute
Soil Resource Development Institute, Head Office, Farmgate,Dhaka-1215
بنغلاديش
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI) (Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI)) - بنغلاديش1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
14/2/2017
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Pitcher irrigation technique is very effective to check the salinity development on the soil surface through capillary pores in dry season ( November to May ) in salt affected coastal area of Bangladesh.
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
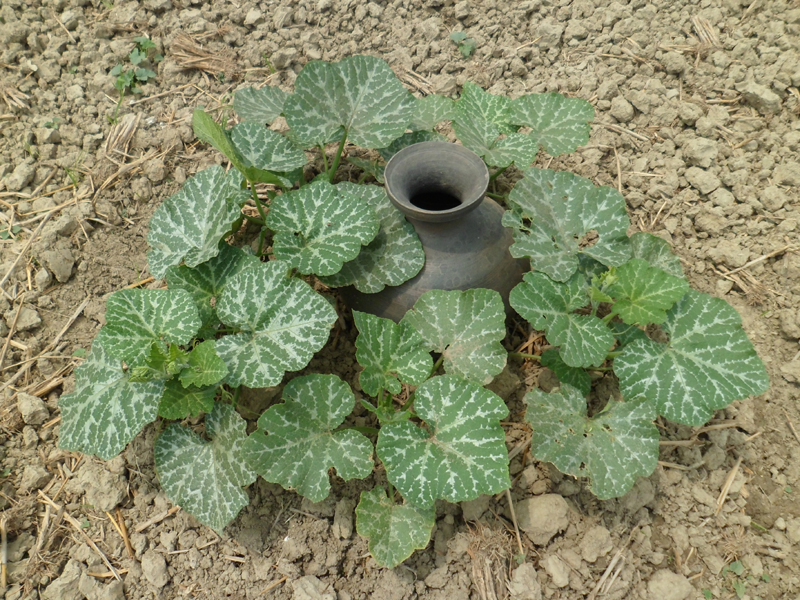
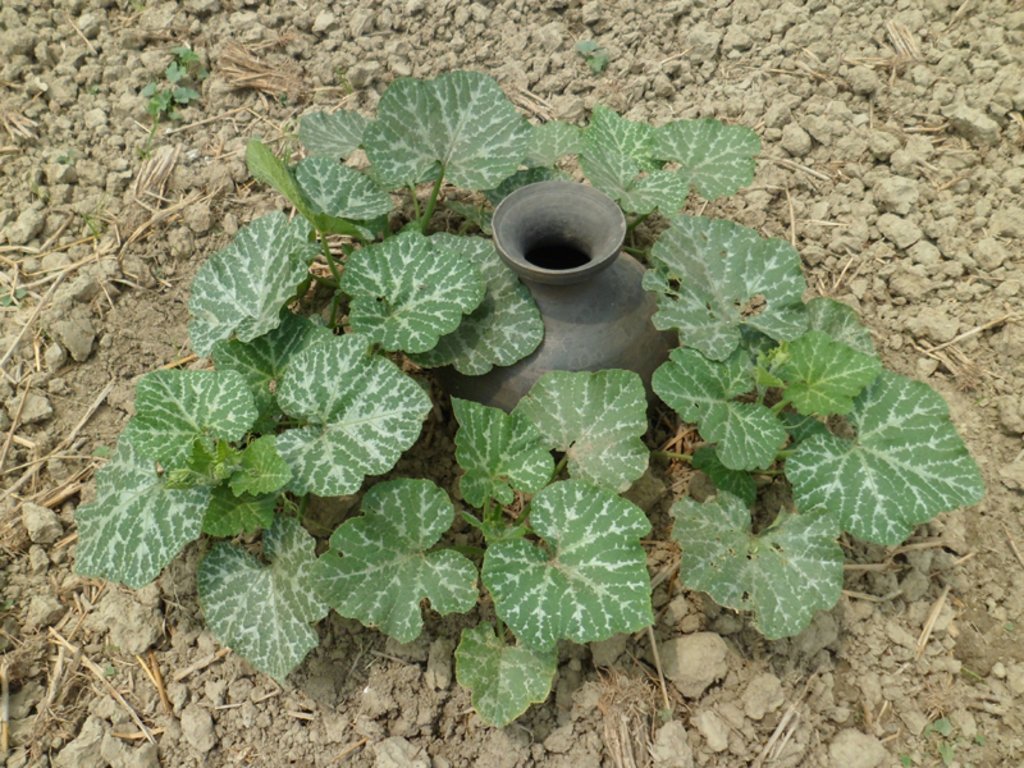
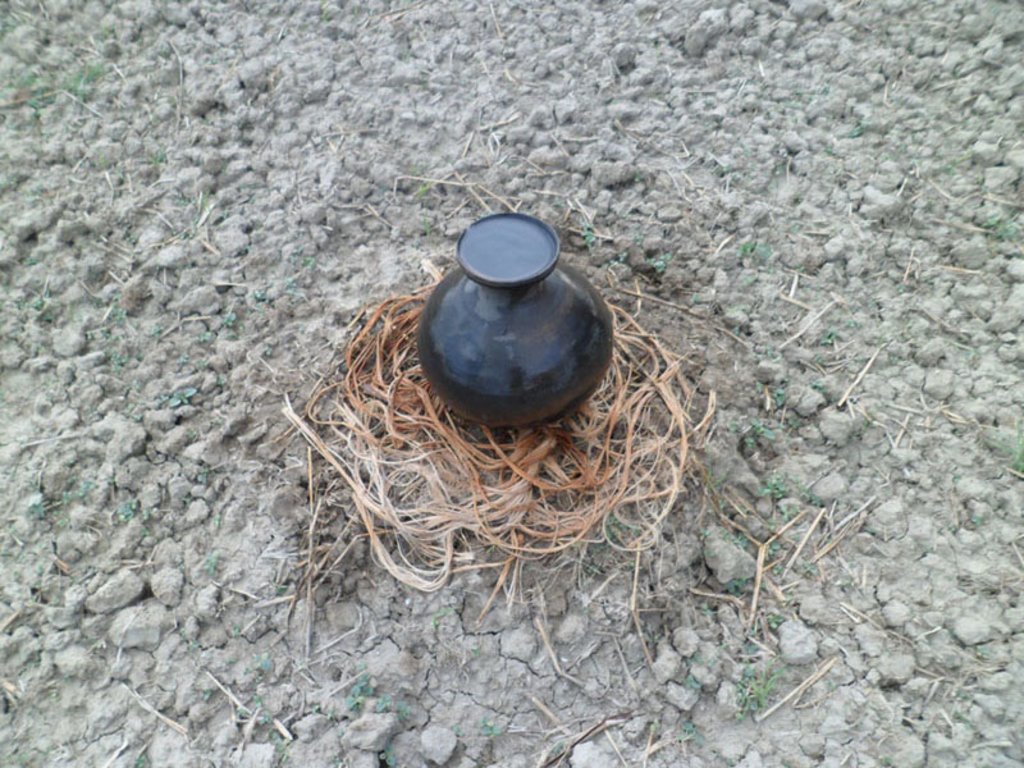
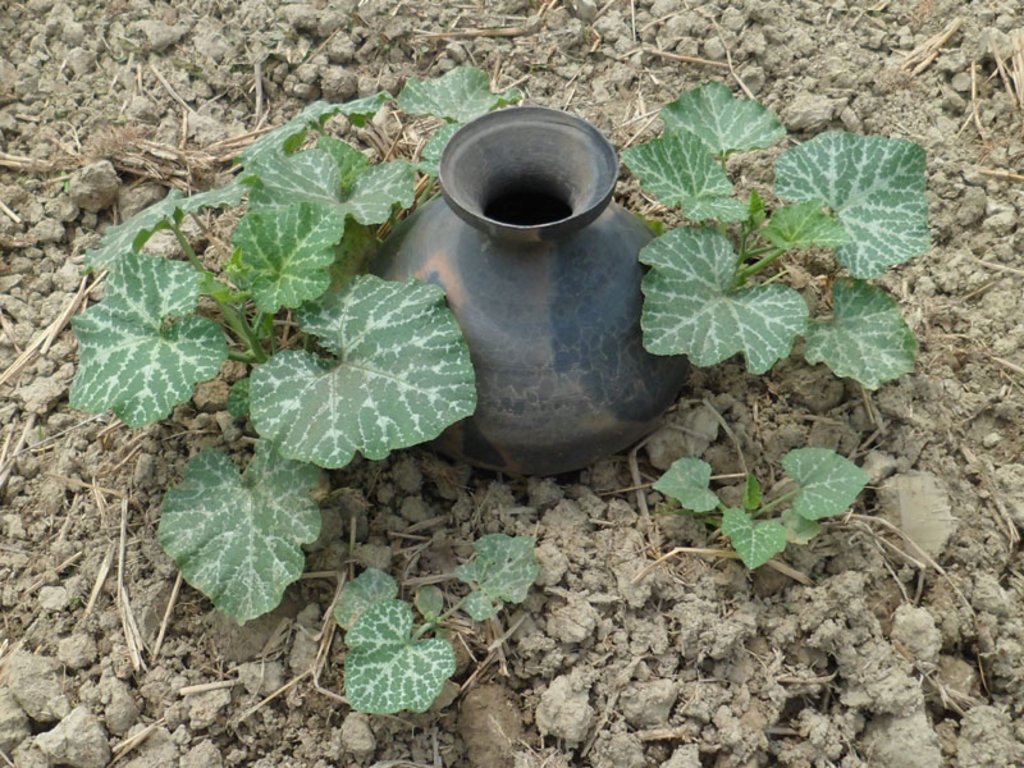
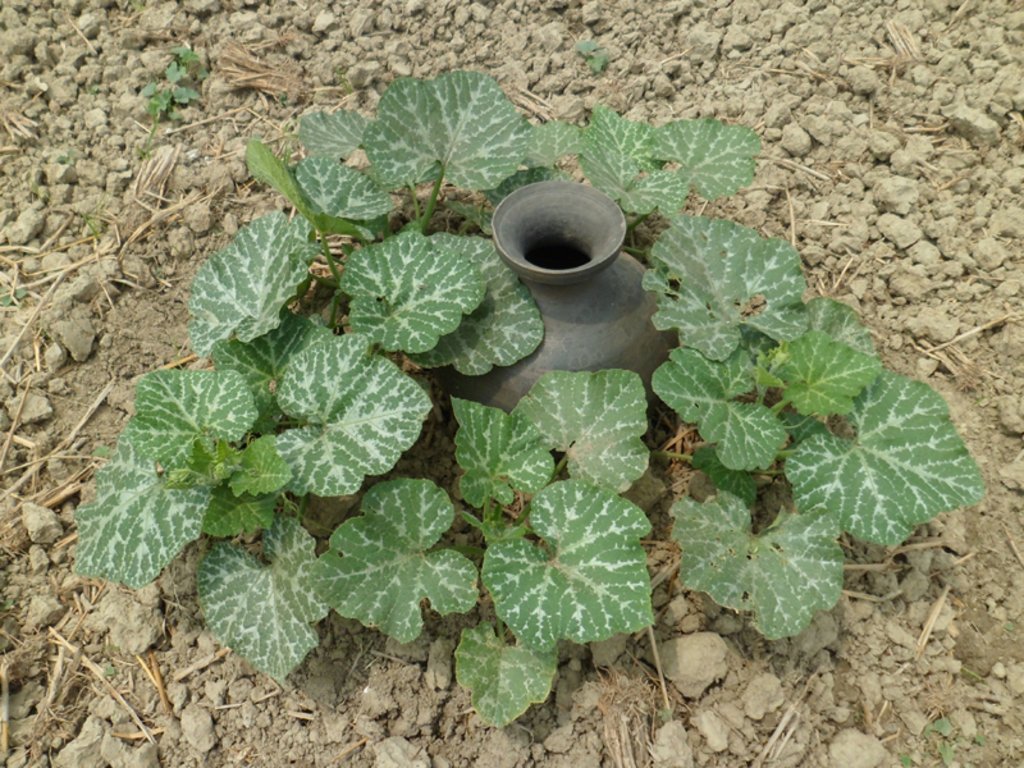
The technology is called pitcher irrigation technology because irrigation water is provided from an earthen pitcher which has several small holes on its bottom. The earthen pitcher is placed on a raised bed which is filled with fresh irrigation water having several pores on its bottom. Then jute fibres are entered into the pores.Then, the pitchers are filled with fresh irrigation water to reduce soil salinity, increase irrigation water use efficiency, increase land cover as well as soil productivity. The technology is popular in case of vegetable cultivation in moderately salt affected area in Bangladesh.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Agriculture is a major sector of Bangladesh's economy and the coastal area of Bangladesh is suitable for growing rice. More than 30% of the cultivable land in Bangladesh is in the coastal area. Out of 2.86 million hectares of coastal and off-shore lands, about 1.056 million ha of arable lands are affected by varying degrees of salinity. Farmers mostly cultivate low yielding, traditional rice varieties during wet season. Most of the land remain fallow in the dry season (January- May) because of soil salinity, lack of good quality irrigation water and late draining condition ( Karim et al., 1990; Mondal,1997 and SRDI, 2001). Crop production of the salt affected areas in the coastal regions differs considerably from non saline areas. Because of salinity, a special environmental and hydrological situation exists, that restricts the normal crop production throughout the year. In the recent past, with the changing degree of salinity of some areas due to further intrusion of saline water from the sea, normal crop production becomes very risky. Crop yields, cropping intensity, production levels and people’s quality of livelihood are much lower than that in other parts of the country, which have enjoyed the fruits of modern agriculture technologies based on high-yielding varieties, improved fertilizer and water management and improved pest and disease control measures ( BBS, 2001). At the same time food demand in the area is increasing with the steady increase in human population.
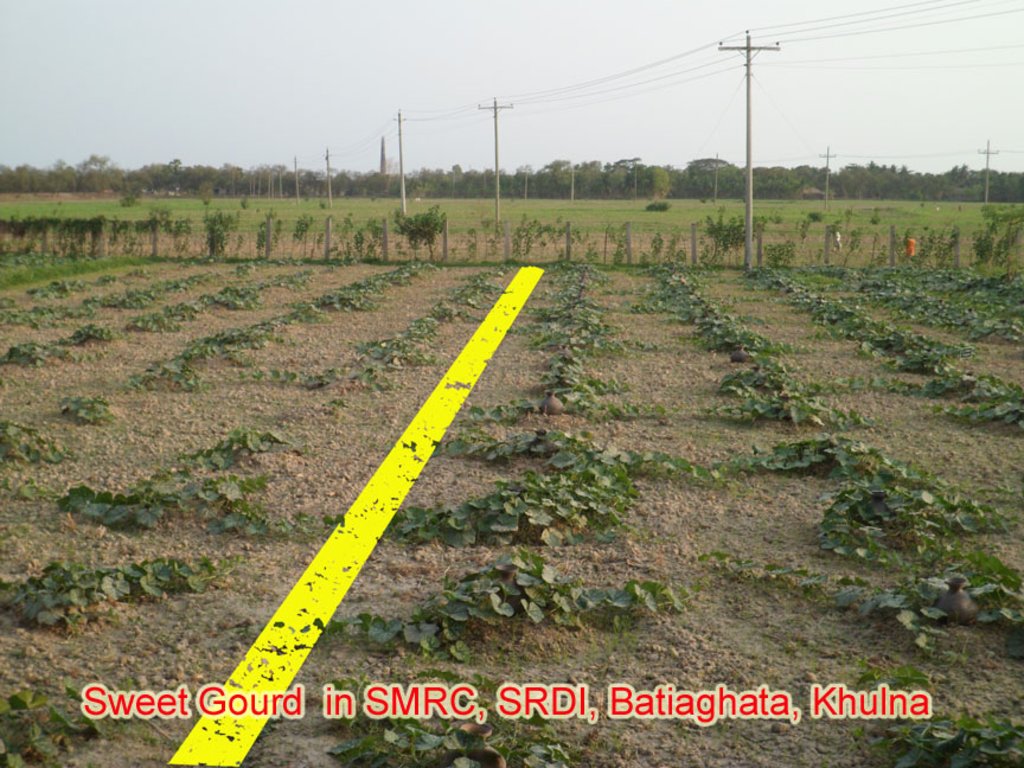
In this circumstances, Salinity Management and Research Centre( SMRC) of the Soil Resource Development Institute, located in Batiaghata, Khulna has developed some technologies which can reduce soil salinity, increase irrigation water use efficiency, increase land vegetative cover as well as soil productivity. Now the pitcher irrigation technology is popular in Khulna, Satkhira and Bagherhat districts of Bangladesh.
In this irrigation method, at first, several pores ( 2.2 mm in diameter) are made on the bottom of an earthen pitcher. Then, some jute fibres ( 30 cm long) are entered into the holes keeping 20 cm outside of the pitcher. After that, the pitcher is placed on a raised bed and fill it up with fresh water. Some seed / seedlings (Lagenaria siceraria, Solanum spp, Abelmoschus esculentus, Cucumis sativus, Benincasa hispida) are sown on different corners of the raised bed. It is done before setting the pitcher on the bed. Then water comes out / seeps very slowly through the fibres. It has several benefits as concerns the scientific point of view. First of all, it reduces irrigation water loss at least 70% as compared to flood irrigation due to reduced run off and evaporation . It supplies irrigation water continuously at the surface of the plant bed and rootzone of the crops. The pitcher needs to be refilled at 15 days interval. As a result, the salt movement is hampered / hindered to rise to the surface through capillary pores because of continuous drip irrigation. So, salinity level in the soil doesn't increase throughout the cropping season. Secondly, this technology enhances the seed germination percentage and creates a favourable environment for uptaking soil nutrient by plants and increasing the crop yield.
The farmers responded quickly to adopt the technology, because thousand hectares of land remain fallow in coastal areas in the dry season. During this period, there are two major problems: soil salinity, water salinity and scarcity of suitable irrigation water. The pitcher irrigation technology is playing an important role to reduce soil salinity as well as increasing the efficiency of irrigation and increasing crop yield.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بنغلاديش
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khulna region
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
The region consists of Bagerhat, Satkhira, Khulna, Jessore and Kustia districts.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- overcome soil salinity
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Bottle gourd, sponge gourd, okra, indian spinach, cucumber, ash gourd, sweet gourd etc.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Rainfed rice - vegetables
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- Mitigate soil salinity
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
التعليقات:
Pitcher irrigation technology is being used in moderately saline soil areas. In case of extreme salinity, it cannot reduce the salinity to an optimal level.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر
التعليقات:
Instead of flood irrigation, controlled irrigation (pitcher irrigation) has been used in coastal areas of Bangladesh to keep moderate soil salinity in check.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- التكيف مع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
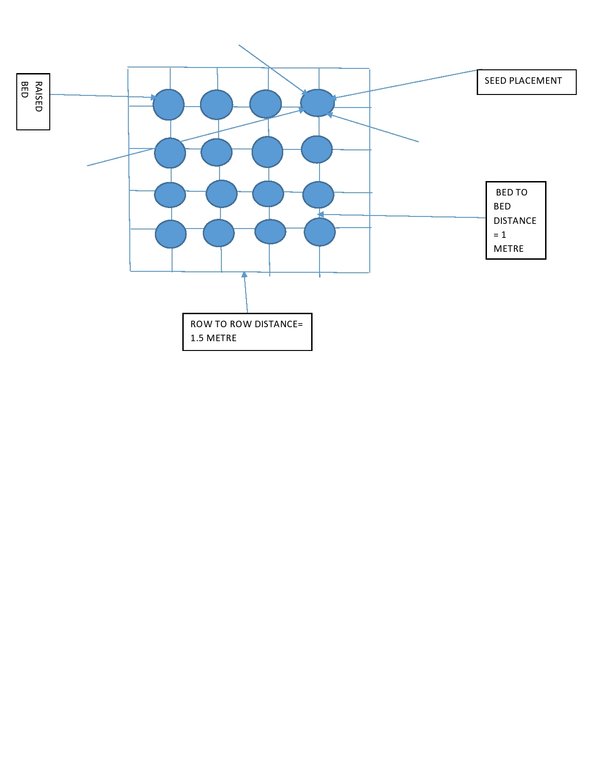
Common sized pitchers (15 litre) have to be collected. At their bottom, 5-6 holes will be made in the form of ballpoint pens (circumference at approximately 2.2 cm). Thereafter, strings of jute fibre (30 centimetre long) will be inserted into the holes. After that, the earthen pitcher will be placed in the raised soil bed (diameter 40 centimetres) in such a way that the holes and jute fibers remain in contact with the soil. Thereafter, 4 seeds should be sown on the 4 corners of the raised bed . The seeds so sown will germinate easily due to moist soil. The jute attached to the holes of the pit will allow water to infiltrate the soil so enable water supply at the root zone of the plants. The mada (raised soil bed) will always be wet. As a result, salt water from the ground level will not come up to the soil surface, thereby preventing the soil salinity in the mada (raised soil bed) area from increasing. Besides, the plants will be able to get adequate water and plant nutrients. Majaor elements of the technology are:
A large size pitcher( 15 litre water holding capacity)
5-6 pores of approx. 2.2 cm diameter are drilled into the bottom of the pitcher
Jute fibres of 30 cm length
Pitcher placed in the middle of the bed (Mada)
4 seeds are sown in the 4 corners of the bed
Salinity reduces: 2.0-2.5 dS/metre
Water requirement: 3-4 filled pitcher amount to complete a crop( Vegetable) life cycle. The irrigation water will be used only in the raised soil bed not in the whole field.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 bigha
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، أشر إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد:
0.134 hectare
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Taka (tk)
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
82,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
500 Taka
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | زراعية | November |
| 2. | Raised bed preparation | زراعية | November |
| 3. | Earthen pitcher collection | إدارية | December |
| 4. | Jute fibre collection | تدابير أخرى | December |
| 5. | Making pore on the bottom of the pitcher | إدارية | December |
| 6. | Filling the pitchers with irrigation water | تدابير أخرى | January |
| 7. | Placing the pitchers on the beds | إدارية | January |
| 8. | Seed sown on the bed | زراعية | January |
التعليقات:
8 hours labour cost equals to 1 day labour
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Land preparation | persons/day | 5,0 | 500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Raised bed preparation | persons/day | 7,0 | 500,0 | 3500,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Earthen pitcher collection | persons/day | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Jute fibre collection | persons/day | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Making pores on the bottom of the pitcher | persons/day | 5,0 | 500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Filling pitcher with irrigation water | persons/day | 5,0 | 500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Placing pitcher on the bed | persons/day | 5,0 | 500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Seed sown on the bed | persons/day | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Earthen pot | number | 40,0 | 25,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Jute fibre | kg | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Drilling machine | number | 2,0 | 100,0 | 200,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seed( Bottle gourd, sweet gourd, cucumber etc) | kg | 2,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Urea( Nitrogen) | kg | 15,0 | 16,0 | 240,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | TSP( Triple super phosphate) | kg | 6,0 | 22,0 | 132,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | MOP( Muriate of potash) | kg | 10,0 | 30,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Gypsum( Sulphur) | kg | 35,0 | 3,0 | 105,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Irrigation water cost | Tk/bigha | 3000,0 | |||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 18477,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Loosening the soil by labourer with spade | زراعية | March |
| 2. | Putting soil on the bed by labourer with spade | زراعية | March |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Loosening the soil by labourer with spade | persons/day | 5,0 | 500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Putting soil on the bed by labourer with spade | persons/day | 6,0 | 500,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 5500,0 | |||||
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour costs affect the total technology cost. Labour scarcity is severe in coastal areas of Bangladesh.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
2500,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Monsoon rainfall (June to October), in winter season very little rain (October to March).
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Khulna
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
غير صالحة للإستعمال
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
نعم
حدد:
In dry winter season, the water as well as soil is moderately to highly saline. In the rainy season, salt washed out by heavy rain and flood water.
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
مرارًا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
.
جودة المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the technology has been proved promising for salt affected soil management, its usage has spreaded for crop production in large area.
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Agricultural inputs decreased
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Production of different vegetables increased. So, the produces are being used in agro based industries for different purposes.
فروقات اقتصادية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Different classes of people are now being involved in vegetable production in saline areas and the poor and unemployed people are earning money by selling agricultural products.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the technology requires so many people for pitcher setting on the bed, so workload will be increased.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Evaporation decreases due to drip irrigation comparison to flood irrigation.
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تراكم التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to loosening of raised soil beds.
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
الملوحة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الحموضة
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the soil will be kept moist during crop production, soil acidity will be reduced.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cropping intensity has increased due to the technology adoption and the crops are absorbing more CO2.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | فصل جاف | انخفاض | جيدة جدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة إستوائية | جيدا |
| عاصفة رعدية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
| هبوب العواصف / الفيضانات الساحلية | باعتدال |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
التعليقات:
As the beds under the technology is a little bit raised from the level ground and the agronomic practices are more intensive than the traditional cultivation system, so insect/pest infestation is below economic injury level.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 90-50%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Increase crop production. Due to soil salinity the crop yield was very poor before adopting the technology. |
| Reduces soil salinity. The water enters into the soil through jute fibre , as a result, salt cannot come into soil surface through capillary movement. |
| Decrease cost of production. The whole field is not irrigated, instead the raised soil bed is irrigated with pitcher water. So, labour cost reduces. |
| Less irrigation water use. Water of 3-4 pitcher can complete a vegetable's life cycle. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Increase land cover in degraded land. Reducing salinity helps to grow crops vigorously throughout the field. |
| Increase soil productivity. Through decrease of soil salinity, most of the soil nutrients become available for plants. |
| Decrease soil pollution. |
| Have opportunity to extend in moderately saline areas. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Not suitable for large scale crop production. | Mechanization can be introduced instead of manual labour to cover large area. |
| Establishment cost is higher. | With proper agronomic practices, farmers are trying to get higher yield and they are producing high value crops like rock melon. |
| In case of high salinity, yield is not sufficient. | Adoption of the technology for long period of time, will help to decrease high salinity. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Labour scarcity. | Farm mechanization is badly in need. |
| Establishment cost higher. | Financial assistance should be given from the Government. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
25
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
20
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
10
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
3
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Saline soils of Bangladesh, 2010
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Soil Resource Development Institute, www.srdi.gov.bd. Free of cost
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Causes of Salinity Intrusion in Coastal Belt of Bangladesh
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://journal.sapub.org/plant
العنوان/الوصف:
SALINITY CHANGES IN SOUTH WEST BANGLADESH AND ITS IMPACT ON RURAL LIVELIHOODS
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/.../264419412_Salinity_Pr... -
العنوان/الوصف:
Environment and Livelihoods in Tropical Coastal Zones: Managing Agriculture .
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://books.google.com.bd/books?isbn=1845931076
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية