5-Year Crop Rotation [سلوفينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Gregor Kramberger
- المحرر: Tamara Korošec
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
5-letni kolobar
technologies_6239 - سلوفينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
Horvat Timotej
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
سلوفينيا
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
Viltužnik Martina
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
سلوفينيا
مستخدم الأرض:
Ropič Andrej
Farmer
سلوفينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kep Tina
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
سلوفينيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - سلوفينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
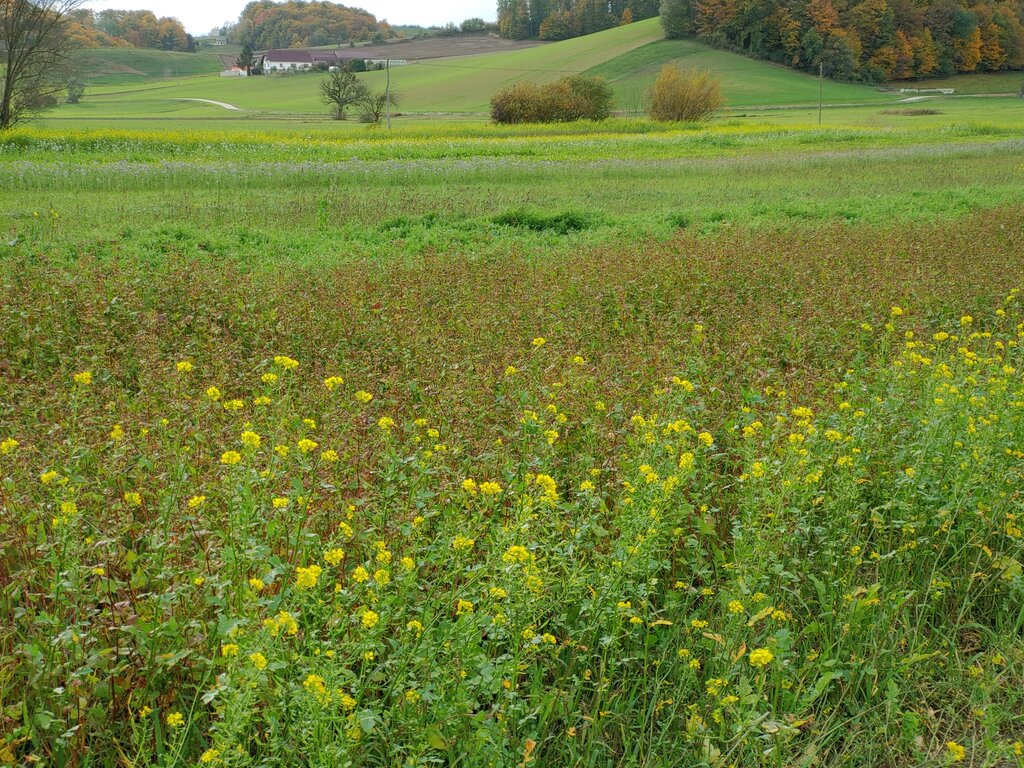
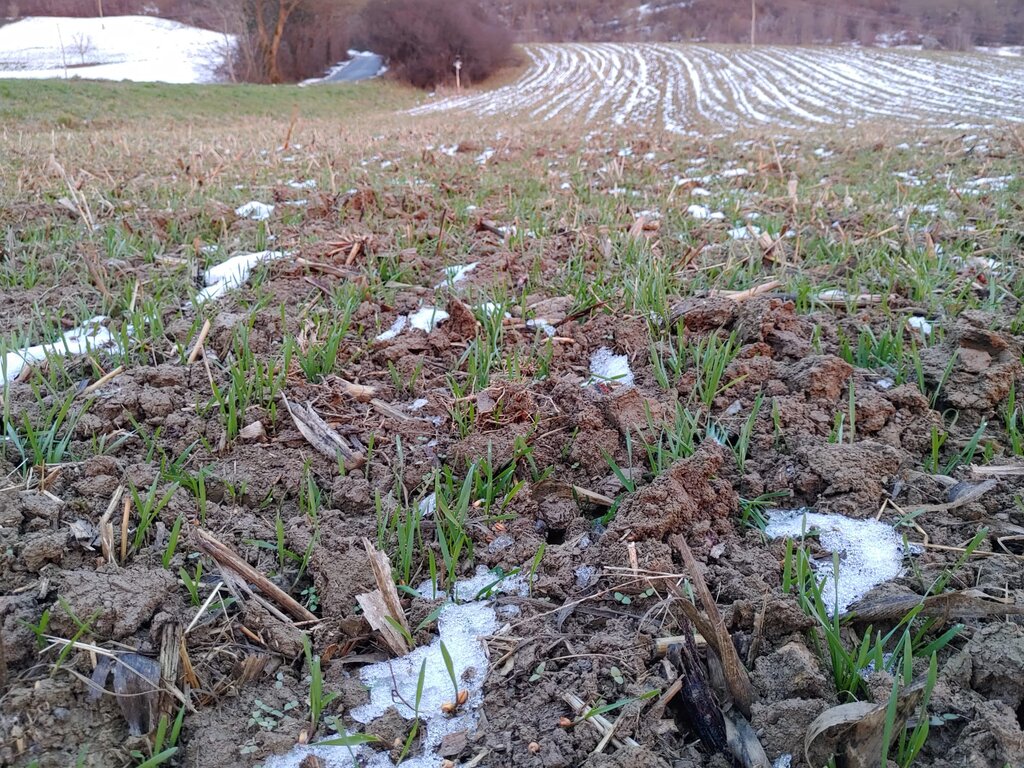
Crop rotation is good practice in agricultural production. It comprises alternating different types of crops, usually in a specific order. Crop rotation maintains soil fertility, reduces the risk of diseases and pests, and optimizes nutrient utilization. In Slovenia, a 5-year rotation is proving especially effective.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Crop rotation is a system of alternating arable crops, forage plants, aromatic herbs, and vegetables, generally in a specific sequence. It can be applied in fields, gardens, or enclosed growing spaces. Crop rotation is adaptable and can be used under different farming systems, such as organic, integrated, and conventional farming. It maximises the efficiency of biological, organizational, and spatial influences on soil and plants. The fundamental element of crop rotation is the selection of plant species that are most effectively alternated on the same piece of land over different years. To ensure the best selection, it is essential to understand the farming technology, the type and structure of the soil, and its nutrient composition.
By implementing good crop rotation, nutrient utilization is optimized, and the risk of diseases and pests is reduced. Crop rotation also ensures the sustainable use of soil by improving its structure and fertility. The inclusion of cover crops in a rotation helps to maintain continuous soil cover. Crop rotation also facilitates better adaptation to climate change (drought, hail, floods etc), depending on the plants included in the rotation. The inclusion of green manure crops and the use of organic fertilizers can reinforce crop rotation and further support soil fertility enhancement and conservation.
To establish and maintain crop rotation, a detailed plan must be prepared, including the selection of crops based on soil characteristics, nutrient requirements, and crop sequencing needs. A fertilization plan should also be developed in parallel. It is crucial to ensure appropriate agricultural machinery, especially for specialty crops, and to have sufficient labour available, as more complex rotations may increase workload. Additionally, market research for new crops and demand assessment should be conducted.
In summary, crop rotation offers numerous benefits:
- Enhances soil fertility and improves soil structure.
- Reduces diseases, pests, and weeds.
- Minimises nutrient leaching and soil erosion.
- Increases organic matter content in the soil.
- Boosts biodiversity and strengthens soil resilience to weather changes.
- Enables efficient resource utilization and reduces production costs.
Thus, crop rotation offers numerous benefits that farmers appreciate – all of which help ensure higher and more sustainable yields. However, this technology requires specific knowledge, precise planning, and careful scheduling, which increases the complexity of production. It also demands more labour and sometimes additional machinery, leading to higher production costs. Furthermore, marketing various crops requires careful consideration, which can pose a challenge for farmers.
Crop rotation in Slovenia is supported by Agri-Environmental-Climate Payments (CAP), which enables farmers to receive funding for implementing a diverse and effective crop rotation system.
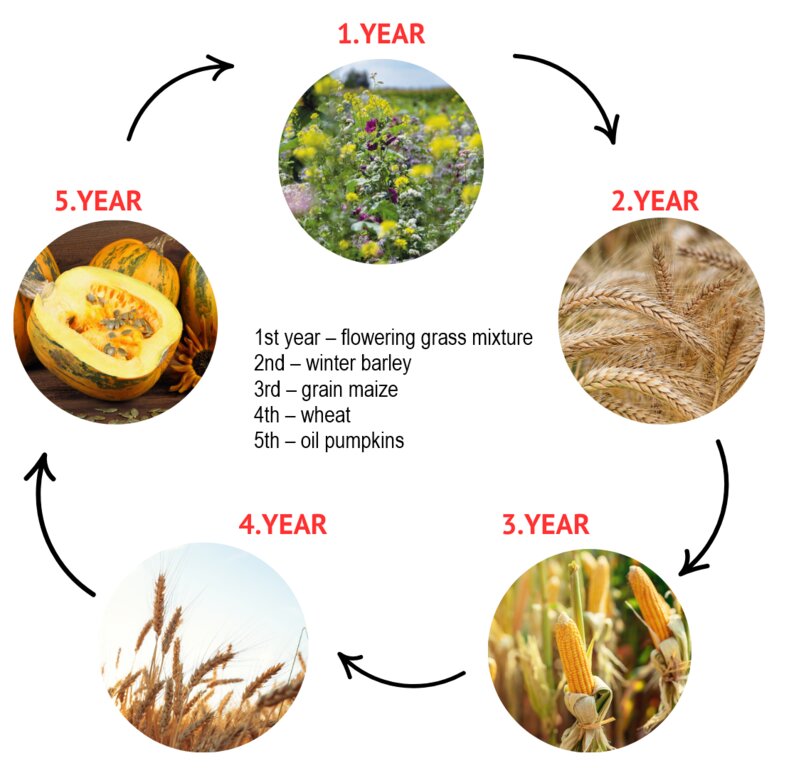
An effective 5-year rotation system in Slovenia typically follows the following sequence:
1st year – flowering grass mixture
2nd – winter barley
3rd – grain maize
4th – wheat
5th – oil pumpkins
This ensures that at least three different annual crops are grown within the five years, while integrating legumes like alfalfa or red clover every 3–4 years to enrich soil nitrogen levels. Cereals may appear up to three times in the rotation, but never in consecutive years. After cereal crops the farmer may alternatively sow non-winter-hardy honey-producing cover crops. Despite this structured guidance, many rotations in Slovenia remain too narrow. National laws and guidelines for agri-environmental measures support farmers in designing good crop sequences.
2.3 صور التقنية
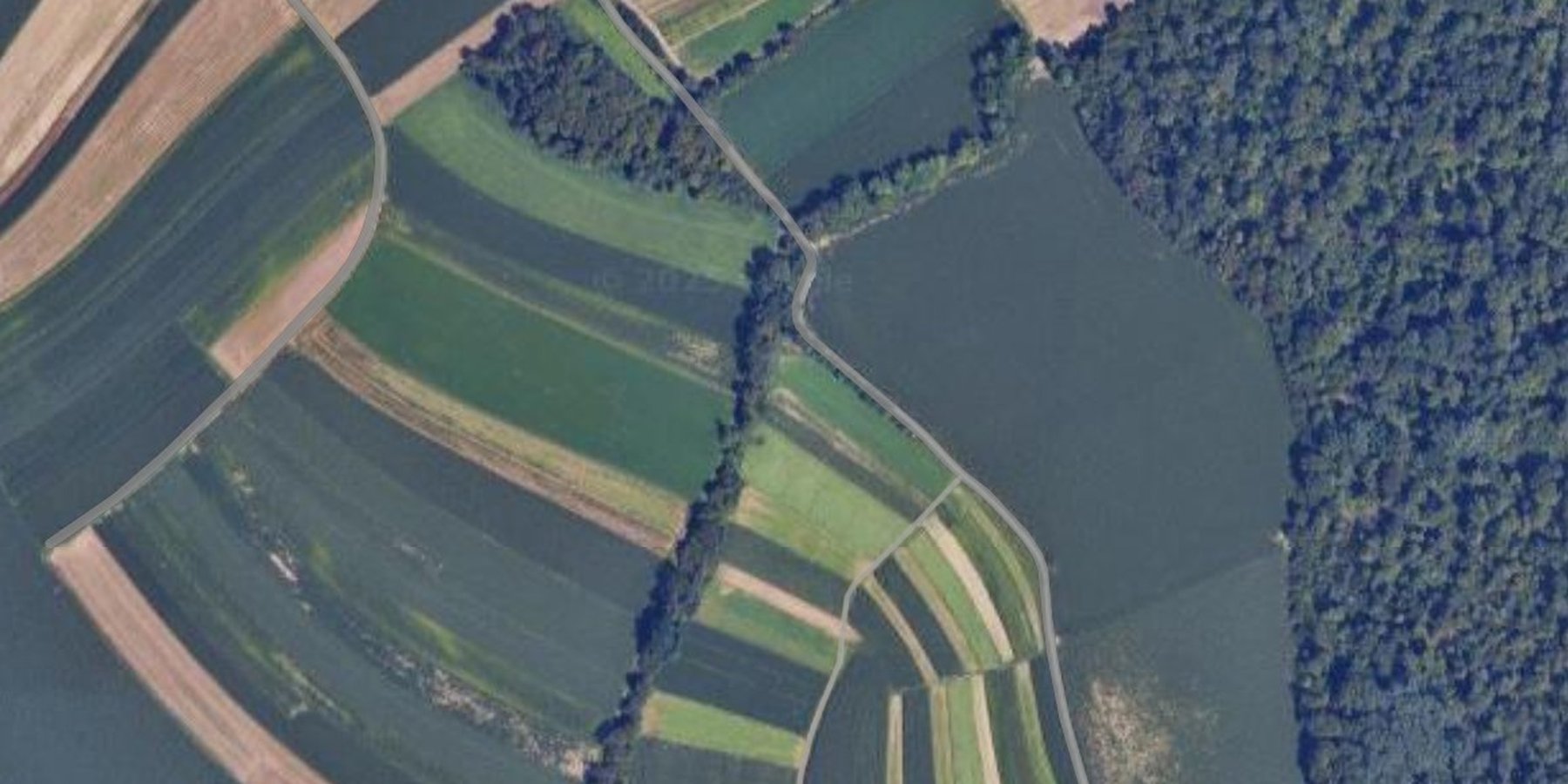
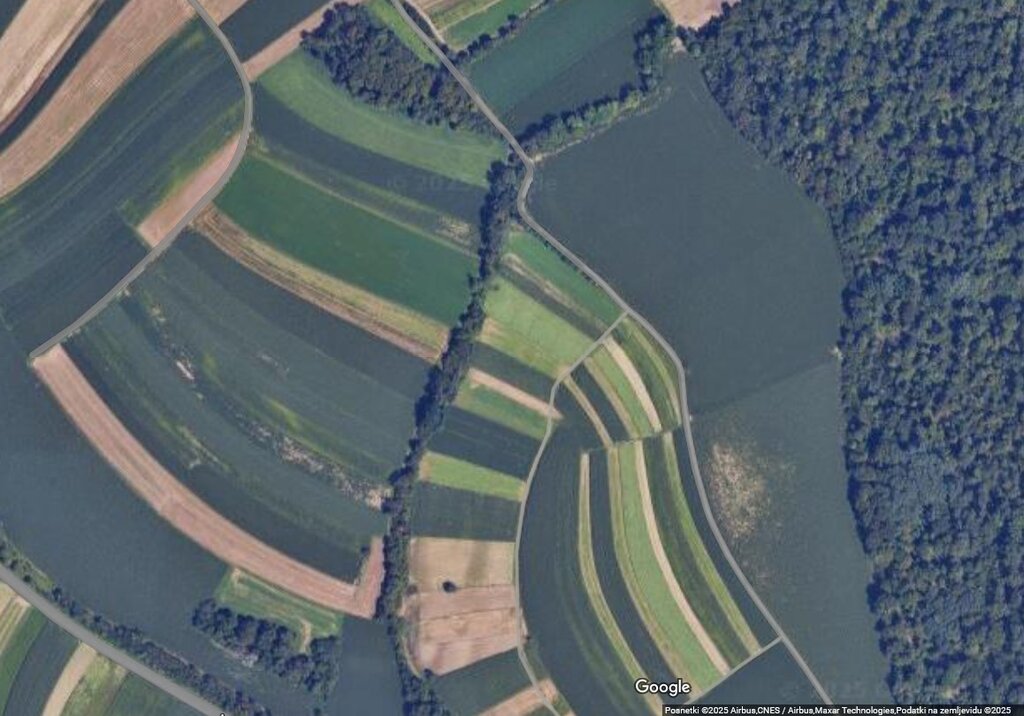
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سلوفينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Jareninski dol, Pernica
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Vosek
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
137,0
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
In the case study area of Pesnica, OPTAIN project.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Over the years, the farmer has experimented with different farming methods and discovered the benefits of crop rotation. His rotation plan is tailored to the farm’s needs, specific production requirements related to on-farm animal husbandry, and market opportunities. He is one of several farmers in the area practicing crop rotation, which is also supported and encouraged through CAP subsidies.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الشعير
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - قمح (شتوي)
- محاصيل الزهور
- المحاصيل الزيتية - عباد الشمس، بذور اللفت، وغيرها
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
The technology is based on a 5-year crop rotation, which includes the following crops:
1st year: flowering grass mixture,
2nd year: winter barley,
3rd year: grain maize,
4th year: wheat,
5th year: oil pumpkins.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- أنظمة التناوب (تعاقب المحاصيل، البور، الزراعة المتنقلة)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة

تدهور المياه
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Crop sequencing: At least three different types of annual crops must be included within a five-year period.
Time intervals: Leguminous plants such as alfalfa or red clover must be incorporated every 3–4 years. In the case of maize, it can be included in the rotation a maximum of three times within five years, but never consecutively. Similarly, cereals can be included a maximum of three times in the five-year rotation.
Cover Crops: Mandatory in areas prone to erosion and where maize constitutes more than 50% of the rotation. Do not count as one of the three different agricultural crops that must be included in the five-year rotation.
المؤلف:
Martina Viltužnik
التاريخ:
21/02/2025
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
28.6 hectares
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
1 ha = 10.000 m2
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,85
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
114
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of a roller | 1st year |
التعليقات:
At the beginning, the farm is assumed to be equipped with standard agricultural machinery. However, to expand the crop rotation to a 5-year system, additional specialized equipment is usually required for cultivating new crops. Such machinery is later typically used for around 20 years or more, although the standard depreciation period for such equipment is approximately 12 years. This is only an estimated time frame, as actual usage may vary. Farmers generally continue using the roller as long as it remains functional and economically viable. Depreciation was not included in the cost calculation, as it is generally accounted for at the whole-farm level rather than per individual measure/crop production.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Roller | piece | 1,0 | 6100,0 | 6100,0 | 70,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 6100,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 7176,47 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Part of the agricultural machinery intended for the implementation of environmental measures can be funded through non-repayable grants from European and national funds under the CAP.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Total variable costs of grain maize production | Once a year |
| 2. | Total variable costs of barley production | Once a year |
| 3. | Total variable costs of wheat production | Once a year |
| 4. | Total variable costs of oil pumpkin production | Once a year |
| 5. | Total variable costs of flowering grass mixture production | Once a year |
التعليقات:
Variable costs represent the total production costs for each specific crop, including seeds, plant nutrients, plant protection products, other material costs, variable machinery and labor costs, insurance, and financing costs.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| غير ذلك | Variable costs of grain maize production | ha | 5,72 | 1518,0 | 8682,96 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Variable costs of barley production | ha | 5,72 | 1112,0 | 6360,64 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Variable costs of wheat production | ha | 5,72 | 1354,0 | 7744,88 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Variable costs of oil pumpkin production | ha | 5,72 | 2061,0 | 11788,92 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Variable costs of flowering grass mixture production | ha | 5,72 | 477,3 | 2730,16 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 37307,56 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 43891,25 | |||||
التعليقات:
The farmer cultivates a total of 28.6 hectares of arable land, theoretically divided into five equal parts under the 5-year crop rotation system. For comparison purposes only, if a simpler system with just maize, wheat, and barley were used and the 28.6 ha were equally divided into three parts (9.53 ha per crop), the total variable costs would amount to 37,967.52 €. Such an even distribution is not practiced in reality—it is used here solely to illustrate the cost comparison.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The total area is theoretically divided into five equal parts, following the 5-year crop rotation system. However, in practice, this division is not perfectly even. Other important cost factors include variations in input prices (such as seeds, fertilizers, and plant protection products), machinery costs, labor availability, and weather conditions that impact yields and operational efficiency.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1032,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are August and September, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Jareninski Vrh (1991-2020)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
The average annual air temperature at Jareninski Vrh during the reference period 1991–2020 was 10.1 °C.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Hydromelioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
Based on national legal system.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
A diverse crop rotation helps maintain stable yields over a longer period by improving soil fertility, reducing disease pressure, and optimizing nutrient availability.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced disease and pest pressure lead to healthier, more resilient plants, while increased natural soil fertility enhances overall crop quality.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
The crop rotation provides an additional opportunity to grow forage crops for feed.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
A diverse crop rotation enhances system resilience, reducing the risk of production failure in cases of natural disasters such as droughts or heavy rainfall and decreases the possibility of pest invasion and disease.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Additional crops in the rotation contribute to production diversification, reducing dependence on a single crop.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Crop rotation requires more complex land management, planning, and agronomic expertise.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الشرب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced use of plant protection products and synthetic fertilizers helps protect drinking water quality.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Lower use of plant protection products and synthetic fertilizers reduces input costs. Some crops in the rotation have somewhat higher seed and labour costs.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The diversity of crops leads to a more diversified income from multiple sources.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
A diverse crop rotation increases workload due to more complex crop management, additional agronomic tasks, and greater administrative demands, requiring efficient planning and organization.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some crops that currently dominate monocultures can be replaced with alternative plants, contributing to increased overall self-sufficiency.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced use of plant protection products and synthetic fertilizers helps improve overall water quality. Various root systems help to better use the nitrogen and other nutrients.
التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Including nitrogen-fixing legumes in the crop rotation enhances nutrient cycling and soil recharge. Different crops have different nutrient requirements and different root systems extract nutrients from different depths.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Including crops with higher organic residues contributes to increased soil organic matter and carbon storage.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Flowering plants included in the rotation provide a beneficial habitat for pollinators and other insects.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased organic residues contribute to higher above-ground biomass and carbon storage.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased diversity of plant species in the crop rotation.
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Crop rotation helps prevent the establishment of invasive species by creating less favorable conditions for their spread.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The inclusion of more flowering plants supports a higher population of beneficial insects.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
A diverse crop rotation helps prevent the spread of diseases and pests.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The data have not been obtained through specific measurements but rather through a questionnaire with the farmer and insights from other farms and agricultural advisors.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced use of plant protection products and fertilizers helps minimize groundwater and river pollution.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The data have not been obtained through specific measurements but rather through a questionnaire with the farmer and insights from other farms and agricultural advisors.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | جيدا |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الخريف | زيادة | جيدا |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الشتاء | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الخريف | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | باعتدال |
| عاصفةبَرَد محلية | ليس جيدا على الاطلاق |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | باعتدال |
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | باعتدال |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فترة نمو ممتدة | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
The establishment costs are relatively high due to investments in new machinery, which can be quite expensive. As a result, the short-term return is considered slightly negative. However, when comparing benefits with these costs, the long-term advantages—such as higher product quality, reduced yield losses, environmental protection, and increased diversification—have a neutral/ balanced impact, leading to more stable and resilient production. In the short term, the comparison of benefits with maintenance and recurrent costs is slightly negative, primarily due to increased labor requirements, the need for more knowledge, and a higher risk of errors. However, as these challenges are addressed and efficiency improves, the long-term outlook is slightly positive, especially due to the potential reduction in costs over time.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
Most of the farmers decide for sustainable practices because of the subsidies, but there are three main reasons why many farmers don't adopt the subsidized form of 5 years crop rotation under the agri-environmental scheme (KOPOP), despite available support:
1. One of the specific conditions of the KOPOP measure is that farmers are not allowed to reduce their arable land area over the 5-year period. Due to uncertainty—especially regarding leased land—many farmers hesitate to commit.
2. Farmers prefer to maintain flexibility in their production choices so they can respond to market demand, grow more profitable crops, or focus on crops that are easier to cultivate.
3. Many farmers prioritize lower-cost production systems that offer higher profit margins, which discourages them from choosing more diverse and potentially riskier rotations.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- الأسواق المتغيرة
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
The specific changes in crop rotation often involve adjustments based on market conditions, input costs, or weather-related risks. For example, a farmer may decide to stop producing soy due to lower prices or higher production risks and instead increase the area under barley, which is less input-intensive and more market-stable. Such changes are made annually, allowing farmers to remain flexible within the broader rotation framework, even if they maintain a diverse system overall.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Reduced costs of pesticides and mineral fertilizer use. |
| Improved soil fertility and higher yields. |
| Reduced weed pressure. |
| Improved soil structure. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Reduction of nitrate leaching into drinking water. |
| Contribution to environmental protection and emission reduction. |
| Preservation of biodiversity. |
| Support for sustainable agricultural practices. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Need for additional knowledge. | Providing targeted training and advisory services to improve knowledge and technical skills. |
| More time required for planning and monitoring. | Using digital tools and software for more efficient planning and monitoring. |
| Monoculture is not allowed. | Emphasizing long-term benefits, such as improved soil fertility and yield stability, to outweigh the limitations of monoculture. |
| Higher labor costs. | Optimizing mechanization and labor organization to reduce workload and improve efficiency. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Improperly implemented crop rotation can lead to the spread of pests and diseases and soil depletion. | Providing training and guidelines on proper crop rotation planning to prevent pest and disease buildup and maintain soil fertility. |
| Incorrectly collected soil samples for soil analysis, which serves as the basis for fertilizer planning, can result in inaccurate calculations for optimal fertilization and nutrient management. | Educating farmers on correct soil sampling techniques to ensure accurate soil analysis and nutrient management planning. |
| Lack of farm records and planning can make it difficult to optimize crop rotation. | Encouraging systematic record-keeping and the use of digital tools to document and optimize crop rotation strategies. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
1 (Andrej Ropič, farmer)
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2 (Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor; Tamara Korošec and Timotej Horvat)
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
CAP and Slovenian Strategic Plan 2023-2027.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
17/01/2023
التعليقات:
I conducted an on-site visit and interviewed the farmer.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Ballot, R., Guilpart, N., and Jeuffroy, M.-H. (2023). The first map of crop sequence types in Europe over 2012–2018, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 15, 5651–5666.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-15-5651-2023
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Nowak, B., Michaud, A., & Marliac, G. (2022). Assessment of the diversity of crop rotations based on network analysis indicators. Agricultural Systems, 199, 103402.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2022.103402
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Improved Crop Rotation – Ecologic Institute (2022)
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.ecologic.eu/19055
العنوان/الوصف:
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Food. (2024). Unified Application 2024: Guidelines for the implementation of interventions under the Strategic Plan of the Common Agricultural Policy 2023–2027. Ljubljana, Slovenia.
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.kgzs.si/uploads/eiv24/NAVODILA%201/00_VELIKA_NAVODILA_2024_-_CELOTA_-_28_5_24.pdf
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية