Drought-resistant crops [سويسرا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Seraina Lerf
- المحررون: Tatenda Lemann, Maria Eliza Turek, Joana Eichenberger
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6272 - سويسرا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Brunner Stefan
Brunner Eichhof
سويسرا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The technology described covers one such response in Switzerland.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The key is the improved adaptation of the crops to heat and drought. These adaptations are based on plant physiological and morphological characteristics that confer increased drought tolerance, as well as phenology, which can also affect the plants' water requirements. The goal is to reduce production losses and promote a regional, plant-based food system in Switzerland. To introduce and maintain drought-resistant crops requires specific activities and inputs, such as selecting suitable seeds and ensuring long-term profitable cultivation. This technology is applied to cropland in Switzerland, especially in the Swiss Plateau, where climate change is causing increasingly warmer and drier summers, as well as more intense precipitation in the winter months. These climatic changes favour the cultivation of crops that can better cope with drought periods, allowing for the replacement of crops that require irrigation in the same growing areas.
The main purpose is to adapt agricultural production to the effects of climate change while simultaneously reducing the emissions caused by farming. By cultivating drought-resistant crops, the risk of production losses during drought periods can be minimized, and a transformation towards more diverse, plant-based, and regional food production systems can be promoted. A major advantage of this technology lies in the adaptability of the selected crops to climate change. Since they are better adapted to tolerating drought periods, no additional irrigation is needed: this saves labour and other resources. Moreover, growing drought tolerant crops enables the production of regional, plant-based, and protein-rich foods (especially legumes) that are appreciated by certain consumer groups and can be better marketed.
However, there are also challenges and disadvantages that are not yet appreciated by land users. The lack of knowledge about non-traditional crops in Switzerland is a significant problem. Both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in cultivation are lacking, leading to high risk for farmers who must experiment with cultivation. Additionally, despite climate scenarios predicting drier summers, there is still the risk of cool and wet summers with increased precipitation. Besides the biophysical challenges, there are also socio-economic obstacles, as the demand from wholesalers is often focused on traditional crops, and niche crops like millet are commonly not popular.
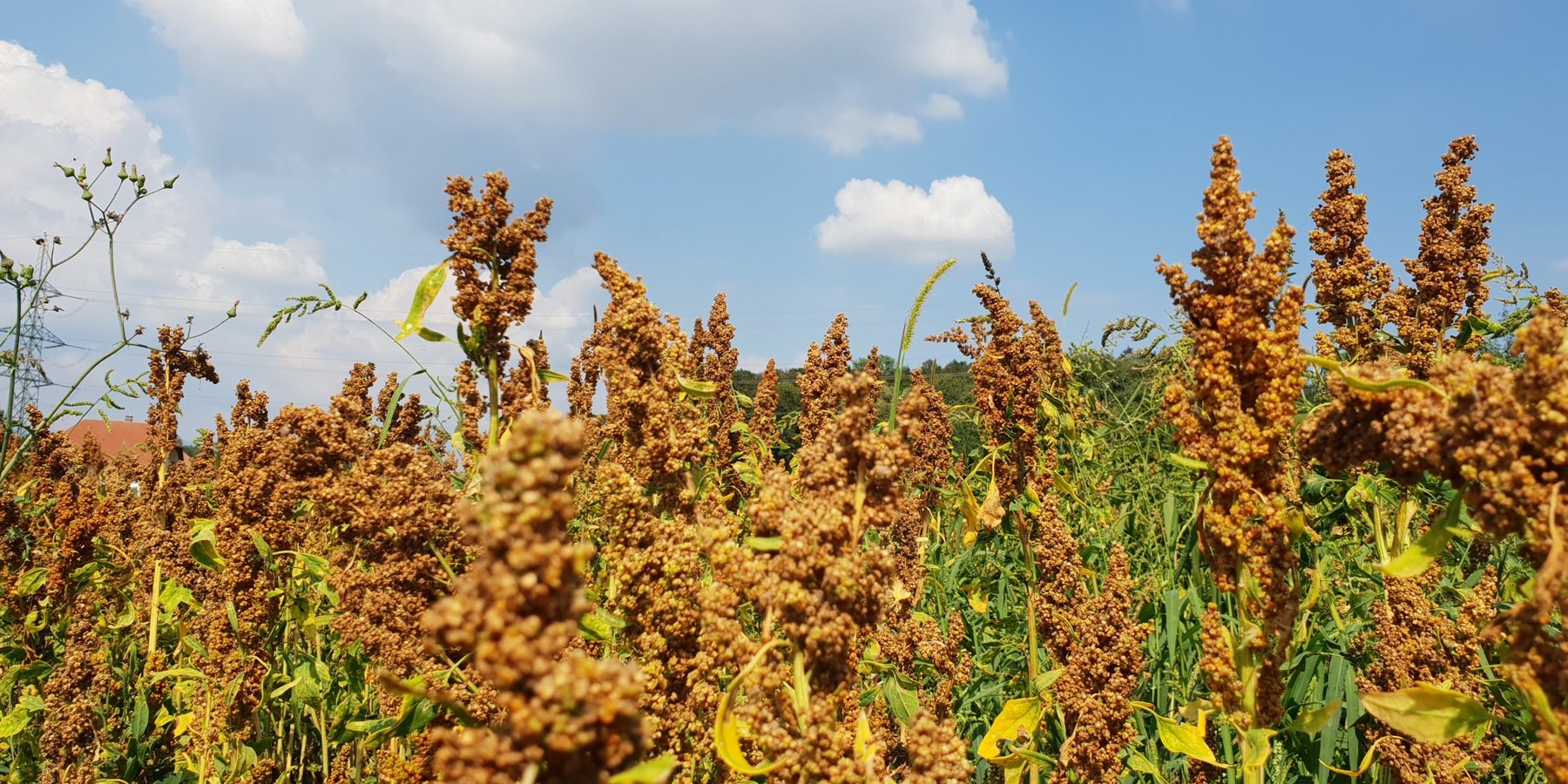
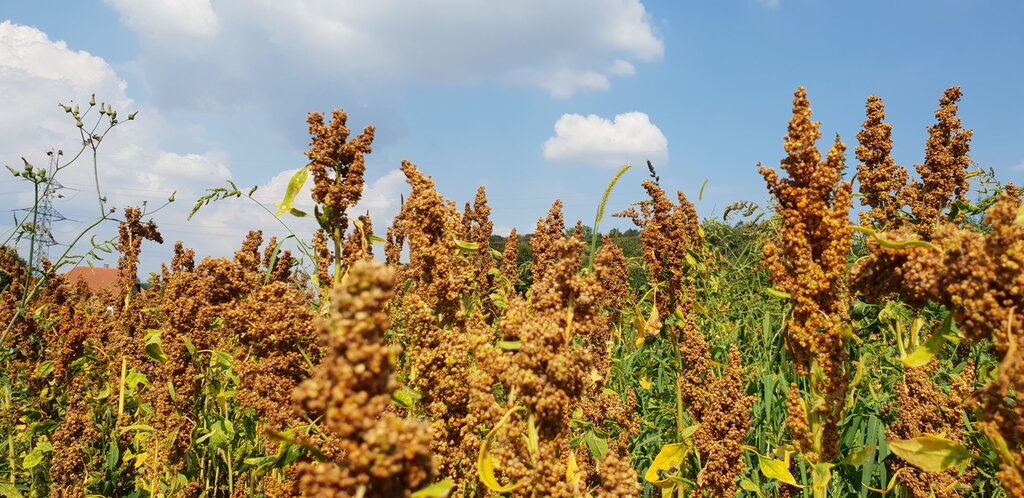
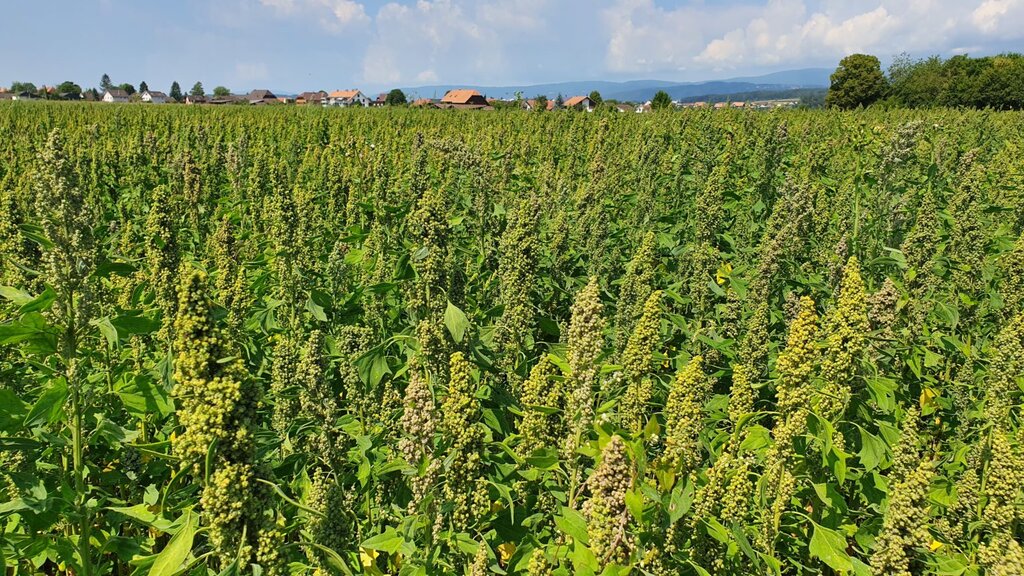
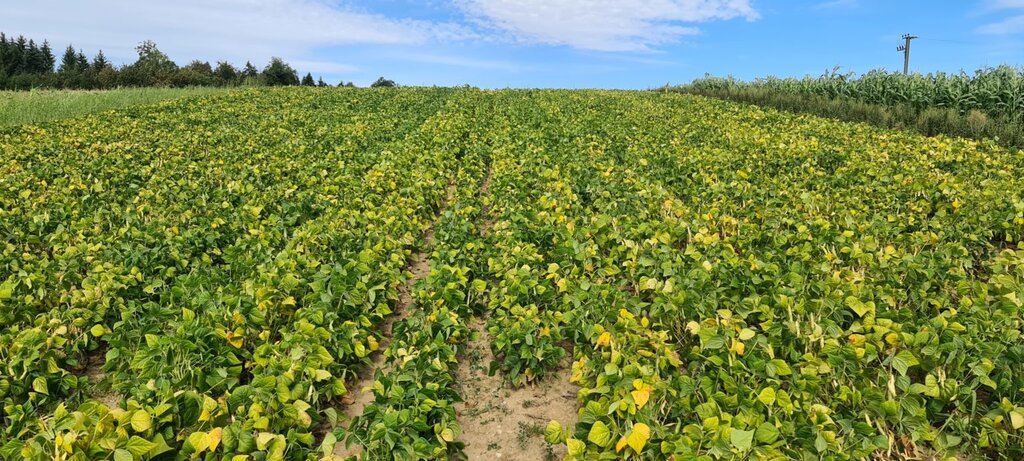
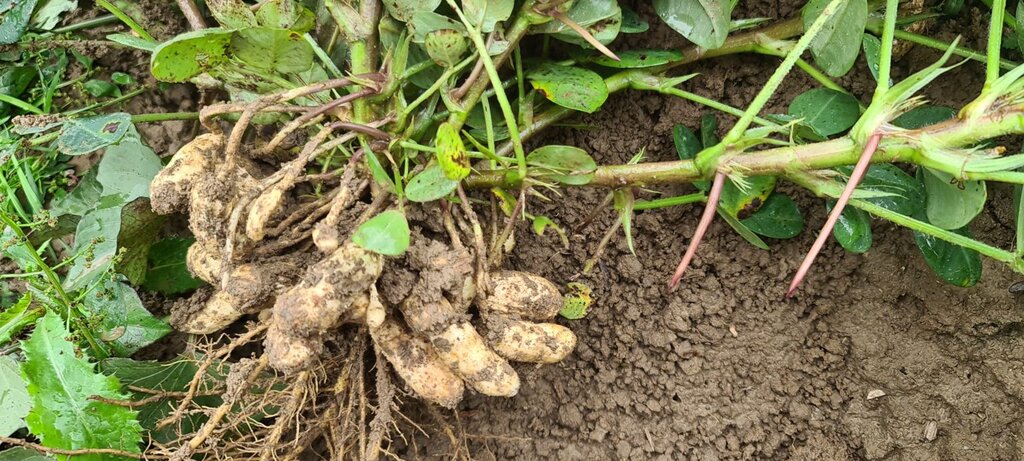
This documentation focuses on an example of an innovative farmer in Spins, Switzerland. Stefan Brunner has been testing a wide variety of drought-resistant legumes such as lentils, lupins and black runner beans on his Eichhof farm since 2017. In addition to the large-scale cultivation of these drought-resistant crops, he also cultivates quinoa, peanuts, chia, sorghum, millet and rice in a demonstration plot. Stefan Brunner simultaneously attaches great importance to sustainable cultivation methods which include surface tillage and mulching.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
All pictures were taken on the agricultural land of Stefan Brunner in Spins near Aarberg. The pictures of the quinoa field, the bean cultivation and the peanut harvest were taken from the website of the Brunner family's Eichhof farm:
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سويسرا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
western midlands of switzerland
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
western midlands of switzerland (Broye catchment area), example farm in the canton of berne in Spins (near Aarberg)
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The regions in which the technology is used are located in the agricultural zone of Switzerland
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2017
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - الكينوا أو الأمارنث
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
- الحبوب - قمح (شتوي)
- محاصيل الأعلاف - الأعشاب
- البقوليات والحبوب - العدس
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
The number of growing seasons depends on the crops grown. With a crop rotation of 6 years, winter cereals, winter lentils/winter legumes and lupins are grown overlapping after three years of permanent grassland (grass production). Brunner also uses green manure between the different crops and therefore has around 2 growing seasons per year
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
6 years crop rotation:
3 years grass
Winter cereals
Winter lentil (winter legumes)
Lupin

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
التعليقات:
Stefan Brunner is able to irrigate all his fields in Spins near Aarberg. He owes this to the nearby location of the "Alte Aare" river, which gives him the privilege of having sufficient water available even during the summer.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحسين أصناف النباتات/سلالات الحيوانات
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A5: إدارة البذور، الأصناف المحسنة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Brunner sees soil degradation as an unavoidable consequence of all agricultural tillage. However, this can vary greatly depending on the type of tillage. Brunner does not see a direct improvement in soil degradation through the cultivation of drought-resistant plants. However, in combination with soil-conserving forms of cultivation. Brunner attaches particular importance to shallow tillage (maximum depth of 5 cm). Accordingly, crops that can be sown at this depth are suitable. Brunner strives for permanent rooting of the soil and prefers crops that can be sown in the fall so that the soil is rooted over the winter or can handle green manure. These measures (shallow cultivation and root penetration) keep the soil looser. The roots form flow paths, which increases the water storage capacity of the soil. The shallow tillage with small machines, which Brunner uses for his drought resistent crops, also reduces the physical pressure on the soil compaction.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
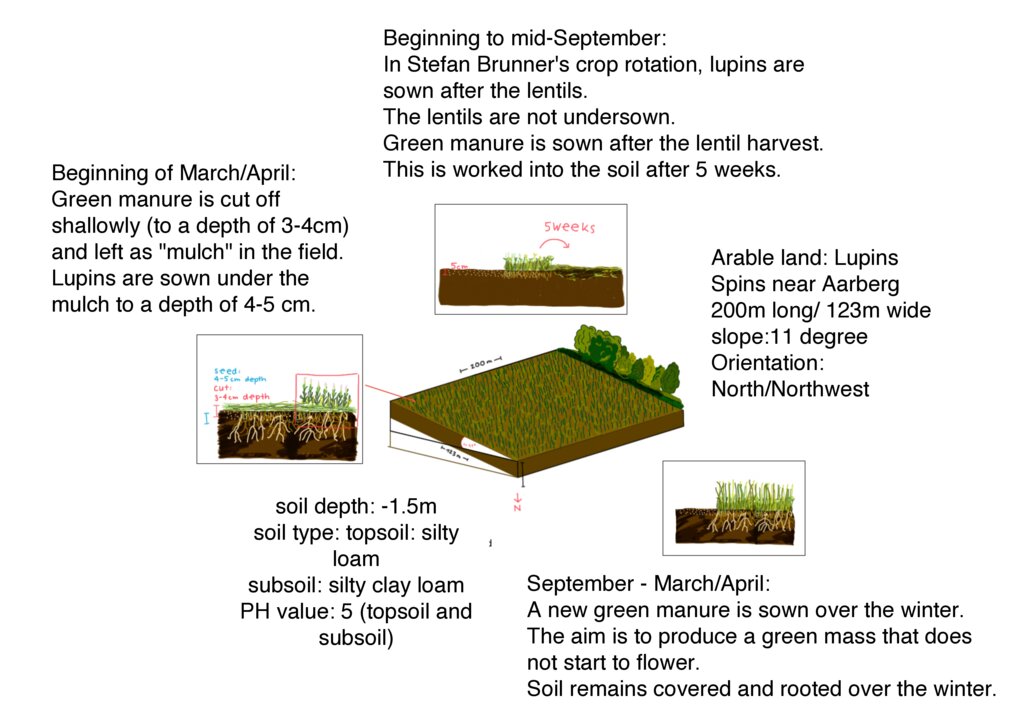
The depicted technical drawing shows the farmland of Stefan Brunner, where lupins were sown in the spring of 2024. This field is representative of all the arable land, totaling 14 hectares of crop rotation areas managed by Brunner. The cultivation areas are situated at an altitude of 487 meters above sea level on flat or slightly sloping terrain on a hill range in the Bernese Mittelland. The depicted field is 200 meters long and 100 meters wide, with a slope of approximately 11° and an orientation towards the north/northwest. The soil is classified as silty loam based on the finger roll test, with the subsoil containing more clay compared to the topsoil. The pH value is 5, which is in the slightly acidic range.
The fields in Spins are located near the river "Alte Aare." Due to the proximity to the water, the farmer has the privilege of having irrigation available for all his fields. Since the implementation of large-scale cultivation of drought-resistant crops in 2017, Brunner has been growing a variety of crops on his land. According to Brunner, the following crops that he cultivates can cope well with drought: lentils, lupins, sorghum, corn, peanuts, millet, and cabbage. In combination with the method of surface rotting and mulching, the soil is protected against drying out and erosion and can retain moisture for longer. The cultivation of various crops can be combined with this farming method, leading to better drought resistance.The graphic illustrates the cultivation of lupins using a green manure cultivation method.
المؤلف:
Seraina Lerf
التاريخ:
21/06/2024
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
18 ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage: and sowing | (once per cultivation period) |
| 2. | maintenance: weeding (recurring work step, but less labor-intensive than tillage) | (Recurring work throughout the year) |
| 3. | harvesting: threshing | (once a year for grain legumes) |
| 4. | Threshing the previous crop. Before the lupins, lentils were grown in Stefan Brunner's crop rotation. | summer (july-september) |
| 5. | If there is no undersowing (as with the lentils), the soil must be tilled. This is very shallow, i.e. no more than 5 cm deep. | summer (july-september) |
| 6. | A varied green manure is sown in the cultivated soil. The aim of this is to keep the soil rooted and to incorporate nutrients into the soil | summer (july-september) |
| 7. | After 6-7 weeks, the green manure is worked back into the soil. When the plants are still young, they have the highest nutrient input before they extract the nutrients from the soil again if they continue to grow. As a result, the nutrients are mineral-bound in the soil, i.e. stored so that they are available to the plants. | autumn (early/mid-September) |
| 8. | Another green manure is sown, which produces a lot of mass but freezes off in winter before it starts to flower. The aim is to keep the soil covered and rooted throughout the winter. | autumn |
| 9. | In spring, the soil is again worked shallowly. This means a maximum depth of 3-4 cm. The winter green manure is "planed". This means cutting it to a depth of 3-4 cm and leaving the plant material on the ground. | spring |
| 10. | The lupins are sown under the plant material to a depth of 4-5 cm, so that the soil remains moist and the plant material protects the soil from drying out. | spring (beginning of March/April) |
التعليقات:
The first three information does not refer to a specific crop, but describes general maintenance activities that Brunner takes into account when cultivating his crops.
Stefan Brunner's crop rotation also includes 3 years of grassland. This cultivation reduces the workload, as no maintenance work has to be taken into account in addition to the harvest.
The activities 4-10 described relate to the cultivation of lupins. This crop was cultivated at the time of documentation in spring 2024.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
22575,0
التعليقات:
The costs of cultivating drought-resistant plants cannot be precisely quantified. Based on the interview results, it is therefore not possible to make any general statements about the costs of cultivation.
Nevertheless, in order to be able to make a rough estimate of the input costs required to implement the technology (Example based on the cultivation of lupins), information from REFLEX 2024 (AGRIDEA's business database) and FiBL (Research Institute of Organic Agriculture) was used. According to REFLEX 2024, the target price for lupins in 2023 and 2024 is 144Fr./dt. A FiBL leaflet also states a requirement of 130-170kg seed/ha (blue lupins).
According to the results collected, the documented farm uses a disk coulter seed drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm, sows approx. 3-4 cm deep and requires 200 kg/ha of seed.
With a field size of the documented farm of approx. 2 ha, the costs for the required lupin seed amount to CHF 576 according to the data from REFLEX 2024.
Then there are the labor costs and the machines. Depending on which machines are required and whether the required machines are already available or whether a new investment or rental would be necessary.
The estimate only refers to the seed required. Additional recurring costs include maintenance/ rental costs for machinery and labour. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more precise information on this. It depends on the machines and labor costs used.
However, according to the interview results with a farmer who grows drought-resistant crops, there are no significant additional costs if the drought-resistant crops can be grown with the same machinery as for conventional crops.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The greatest difficulty in terms of costs lies in the lack of knowledge in the cultivation of these crops. The fact that very little scientific and practical knowledge and experience is available means that farmers take a greater risk in cultivating these crops. If cultivation is not carried out correctly and the farmer suffers production losses as a result, he bears the consequences. This is why they have to look for inventive solutions.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
865,00
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Payerne
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Production losses during periods of drought can be minimised
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Product diversity can be increased by growing alternative drought-resistant crops
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
By improving the soil's ability to cope with weather extremes (drought/heavy rainfall), land management in cultivation is simplified through greater flexibility.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Gentle tillage without the use of pesticides in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops (good groundwater quality)
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Drought-resistant crops require less irrigation. In addition, the tillage method (surface rotting) also prevents the soil from drying out.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Gentle soil cultivation with minimal use of machinery (and application of surface rotting) requires more labour, even if the cultivation of drought-resistant crops does not mean additional work compared to conventional crops
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less water required for irrigation
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Avoiding the use of pesticides leads to improved water and soil quality
Harvesting/collection of water
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods) can lead to improved groundwater recharge
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Surface runoff can be minimised by improving the water absorption capacity of the soil (permanent root penetration).
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods), less excess water is formed
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil can lead to improved groundwater recharge
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Permanent ground cover can reduce soil drying out
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The permanent ground cover reduces drying out and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This can improve the soil water balance.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The ground should be permanently covered. The permanent ground cover reduces drying out.
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The permanent covering and rooting of the soil prevents surface run-off. This can prevent soil loss.
تراكم التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Green manuring can ensure an improved hummus structure.
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The permanent ground cover reduces dehydration and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This prevents soil sealing.
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The soil should remain permanently rooted and covered and be worked with as few and light machines as possible. This minimises soil compaction.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
By applying green manure, the soil can be enriched with nutrients (nutrient cycle of the soil).
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
greater plant diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the improved ability of plants to cope with drought. to deal with drought. In combination with good water storage capacity of the soil, the effects of drought on the harvest can be minimised.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Information in this chapter on practical experience in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops is based on interview results from Stefan Brunner. He cultivates drought-resistant crops in combination with surface cultivation and mulching. As a result the effects of the two technologies cannot be considered entirely separately.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
The use of herbicides and fungicides was avoided in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, thus preventing contamination
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
improved water absorption capacity (through soil cultivation methods) of the soil
Stability of production
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the improved adaptability to climatic conditions, production remains more stable
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. Annelie Holzkämper
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | باعتدال |
| موجة باردة | غير معروف |
| ظروف شتاء قاسية | غير معروف |
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. rer. nat. Annelie Holzkämper
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The more equipment has to be used in cultivation, the more expensive the maintenance costs become. As Brunner is able to cultivate drought-resistant crops such as lupins and lentils with the existing equipment, he did not incur any additional costs. Even if a new machine for gentle soil cultivation in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, such as a “planer”, had to be purchased, a plow could be sold in return. As long as the same mechanization can be used as Brunner was already using for conventional crops, the costs remain the same. As a result, Brunner's cost-benefit ratio was assessed as positive, even in the short term.
In the long term (over a period of 10 years), Brunner also sees an increased positive cost/benefit ratio. Consistently good soil cultivation regenerates the soil so well that it is able to absorb much more water. The amount of work required to implement this form of cultivation increases in the short term. However, the improved soil conditions in connection with the cultivation of drought-resistant crops have a positive effect on the workload and yield in the long term, as the crops on healthy soil are more flexible in the face of extreme weather conditions such as increasingly frequent droughts. Brunner also emphasizes that, from his perspective, it is worth incurring higher start-up costs for careful cultivation in order to generate long-term benefits.
The start-up costs are often relatively high, but the long-term benefits are all the more valuable. Start-up capital is therefore essential to be able to generate long-term benefits.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
Information based on the experience of Stefan Brunner (Spins)
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
breeding
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
Continuous adaptation in the context of breeding
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| No Irrigation Needed: These crops do not require irrigation, thus saving water and reducing labor. |
| Promotion of Soil Health: The cultivation of these crops is beneficial for the soil, as as the tillage is shallow and legumes do not require additional nutrient inputs through fertilization. |
| Benefits in Direct Marketing: These crops are niche products produced in limited quantities in Switzerland. Conscious consumers who value regional food products appreciate these items and understand the higher costs due to the high labor requirements. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Reduced Irrigation Needs: If the crops can tolerate more drought, less irrigation is needed. |
| Minimized Economic Risk: Drought tolerance reduces the risk of crop failure during dry periods. |
| Crop Rotation Benefits: Better adaptation through diverse crop cultivation. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High Labour Requirements: initial labour requirements are significantly higher due to limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation, but with time this reduces - as less and less work is required on healthy and nutrient rich soils. | More practical knowledge should be gathered by encouraging more farmers to cultivate these crops and facilitating knowledge exchange. |
| Lack of Mechanization: Available market machines are not suited for the desired cultivation methods. | Alternative machines are needed, which are smaller and lighter and only minimally till the soil. New approaches and inventions in machinery are required. |
| The wholesale market is not particularly interested in domestically produced alternative foods. Wholesalers are profit-oriented and primarily offer what is consumed in Switzerland. | A reorientation of dietary habits is necessary. Millet, for example, is ideally suited to the climatic conditions in the Seeland region. Increased consumption could lead to more extensive cultivation. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge: limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation | More research should be carried out in this area and practical experience in cultivation should be gained through practical implementation. Inovative farmers are in demand. |
| Weather Variability: There is no guarantee that heavy rains won't occur, potentially ruining the harvest. | The extent to which crops are affected by severe weather events depends on when they occur. Severe weather events have an impact on every crop, but of course you don't know when they will occur. A useful strategy is therefore to build a highly diverse production system at farm and landscape level. |
| Practical and Socioeconomic Challenges: Market preferences and practical issues, such as livestock not favoring sorghum feed, can be obstacles. | No answer given. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
On June 10, 2024, an interview was conducted with farmer Stefan Brunner on his farm in Spins near Aarberg. Additionally, the cultivated area was inspected
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
On June 20, 2024, an interview was conducted with PD Dr. Annelie Holzkämper.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/06/2024
التعليقات:
Inspection of the cultivation aera
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Heinz, Malve et al. (2023): How to find alternative crops for climate-resilient regional food production, in: Agricultural Systems, Bd. 213, S. 103793, doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103793.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Wuyts, Nathalie et al. (2023): Klimaresilienter Ackerbau 2035, Agrarforschung Schweiz, doi:10.34776/afs13-135.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Heinz, Malve. (2021): Prospects of cultivating alternative crops in a changing climate in Switzerland, Master’s Thesis, University of Bern.
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Internet platform of the Eichhof of the Brunner family from Spins near Aarberg
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.brunnereichhof.ch
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The information used to complete this documentation is mainly based on the experience reports of Stefan Brunner from an interview on June 10, 2024
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية