Vegetable Intercropping in Apple Orchards [بوتان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Tshering Yangzom
- المحرر: Kuenzang Nima
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Apple Dhum Ra Nang Tshoe Sey La Sey Tsug Ni (ཨེ་པཱལ་ལྡུམ་ར་ནང་ཚོད་བསྲེ་སླ་བསྲེ་བཙུགས་ནི་།)
technologies_6844 - بوتان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Sharman Rai
n/a
بوتان
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - بوتان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
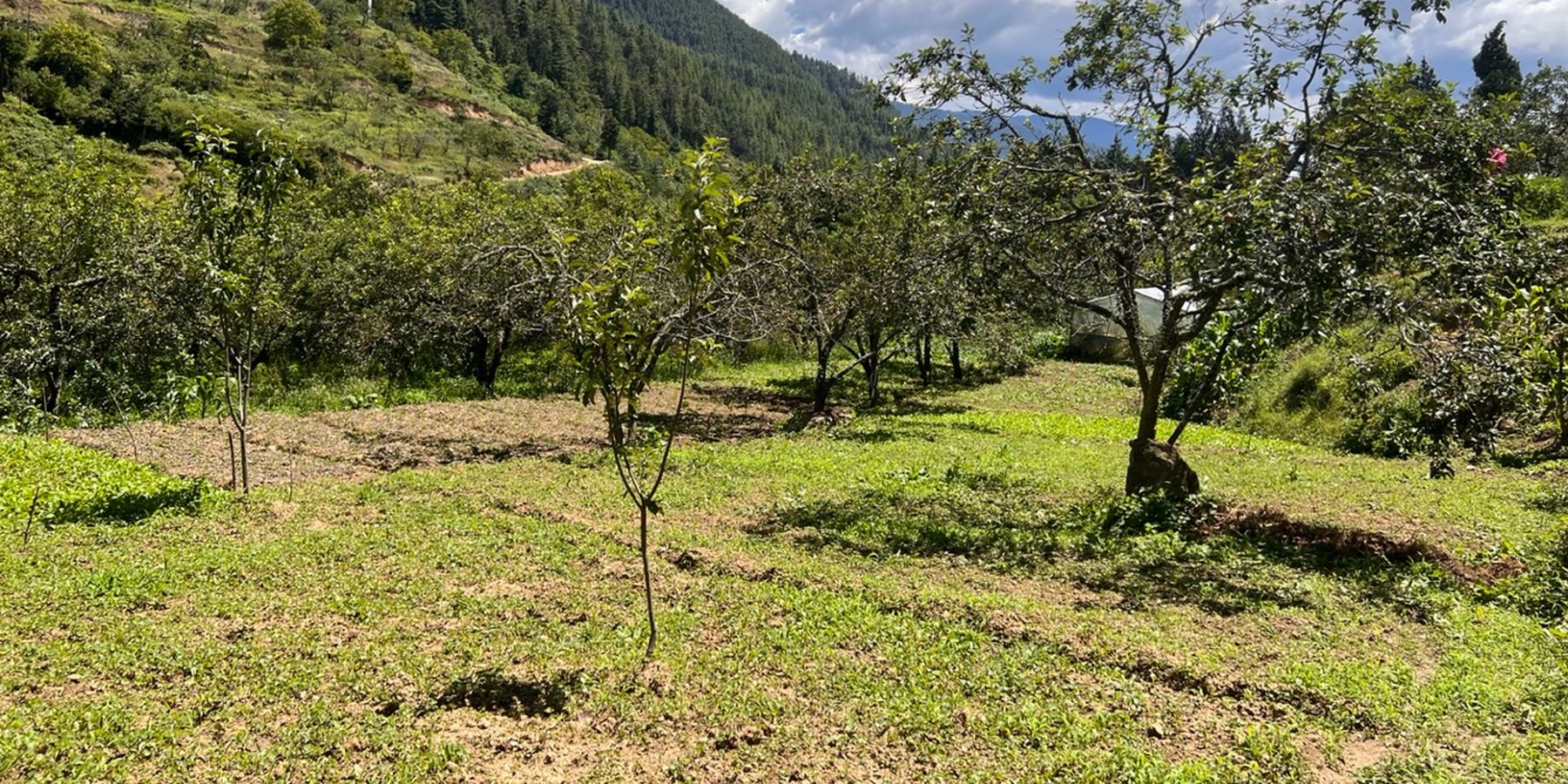
Vegetables are intercropped between fruit-bearing trees in orchards. This maximizes land utilization, increases agrobiodiversity, and optimizes agricultural productivity.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
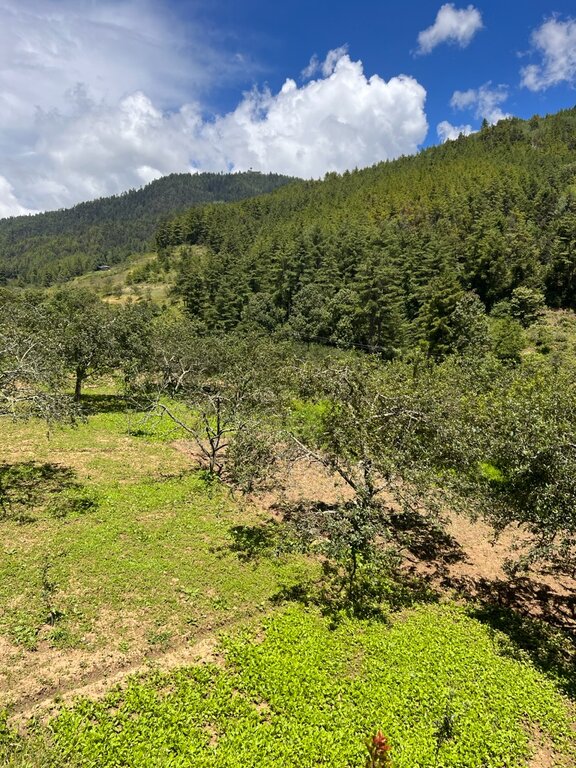
Intercropping of vegetables with fruit-bearing trees in orchards can be an effective system in terms of production and agroecology. It is a sustainable farming technique that optimizes land use, increases agrobiodiversity, diversifies production, and enhances overall yields. Land users in Yusipang grow peas, beans, and cole crops (cabbages, kale, etc.) in their apple orchards.
Intercropping vegetables in orchard land optimizes the use of space, sunlight, water and nutrients. Intercropping also increases biodiversity within the orchard ecosystem. This coexistence of species reduces the vulnerability of the orchard to crop failure and pest infestation: it improves the residence of the overall system.
Trees in the system absorb nutrients from the soil and return them through fallen leaves, thereby improving soil fertility and reducing reliance on external fertilizers. This nutrient recycling improves the overall health of the orchard ecosystem. Intercropping can also help in natural pest management through various mechanisms – including the attraction of beneficial insects - thus reducing the need for chemical pesticides. It also fosters a beneficial microclimate.
To establish intercropping of vegetables in orchards, careful planning and design is required with respect to crop selection, spacing of trees and intercrops, irrigation, and nutrient management. Regular weeding and mulching are required alongside adequate irrigation, integrated pest management, and pruning of fruit trees to prevent competition for light and space.
Intercropping of vegetables in orchards thus offers multiple benefits to farmers and the overall agricultural system, including increased farm productivity. It increases climate resilience and improves the health of the agroecosystem. However, it is important to be aware of potential drawbacks. These include competition between crops for resources - and labour. Sound management practices can overcome these challenges and maximize the effectiveness of intercropping.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
الموقع:
n/a
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بوتان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Thimphu
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Yusipang, Chang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
0,4
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The area does not fall under any protected area or parks.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- خضروات - اخرى
- الخضروات - الخضروات الجذرية (الجزر والبصل والشمندر وغيرها)
- Cole crops, chili, beans, peas
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Vegetables and fruit trees are intercropped.
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Vegetables are rotated in the orchard.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- أنظمة التناوب (تعاقب المحاصيل، البور، الزراعة المتنقلة)
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 acre
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
1 acre
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
BTN
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
81,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
Nu. 800
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Assess the orchard: Evaluate the orchard's existing conditions, including soil fertility, drainage, sunlight availability, and pest and disease history. This assessment will help determine the feasibility and suitability of intercropping vegetables in the orchard. | Anytime |
| 2. | Select compatible vegetable crops: Choose vegetable crops that are compatible with the existing fruit trees in terms of their growth requirements, sunlight tolerance, water needs, and harvesting periods. Consider crops that are less competitive and can thrive in the orchard's microclimate. | Year-round |
| 3. | Plan the intercropping layout: Develop a planting design that optimises space utilisation and resource distribution. Consider factors such as crop spacing, row orientation, and the arrangement of vegetable crops within the orchard. Ensure that the intercropped vegetables are positioned to minimise shading and competition with the fruit trees. | Anytime |
| 4. | Prepare the soil: Prior to planting, prepare the soil by clearing any existing vegetation and weeds. Conduct soil testing to assess nutrient levels and pH, and amend the soil if necessary to create optimal growing conditions for both the vegetables and fruit trees. | Spring |
| 5. | Implement irrigation systems: Install or adapt irrigation systems to accommodate the intercropped vegetables' water requirements. Consider the water needs of both the vegetables and fruit trees when determining irrigation frequency and duration. | Anytime |
| 6. | Manage nutrients: Determine the nutrient requirements of the intercropped vegetables and fruit trees. Based on soil test results, develop a fertilization plan that addresses the nutritional needs of both crops. Apply organic or synthetic fertilizers as appropriate, considering the specific nutrient requirements of each crop. | Anytime |
| 7. | Implement pest and disease management strategies: Develop an integrated pest management (IPM) plan to control pests and diseases effectively. Monitor the orchard regularly for signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate preventive or corrective actions, such as using natural predators, applying organic pesticides, or practising cultural methods like crop rotation. | After plantation |
| 8. | Weed management: Employ weed control measures to minimise competition between the vegetables and fruit trees. This can include mulching the soil around plants, practising regular manual weeding, or using targeted herbicides that are safe for both crops. | After plantation |
| 9. | Monitor and adjust: Continuously monitor the growth and performance of both the vegetables and fruit trees throughout the growing season. Make necessary adjustments to irrigation, fertilisation, pest control, and other management practices based on observations and the specific needs of each crop. | Year-round |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
23000,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The land users bore 100% of costs.
التعليقات:
Taking into consideration the labour charge for layout making, pit digging, pit filling, use of equipment such as spades and crowbars, and plantation of fruit trees and then some seasonal vegetables in between the fruit trees in 1 ac of land, the approximate cost of establishment is Nu 23000 (USD 284).
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
6000,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The land users bore 100% of costs.
التعليقات:
Taking into consideration maintenance activities such as weeding, watering, manuring, pruning, and pest and disease management in 1 ac of land, the approximate cost of maintenance per year is Nu 6000 (USD 74).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The average rainfall ranges from 650-850 mm.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under. Bhutan is divided into AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
The area falls under Cool Temperate Zone. Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
2698 m.a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Moisture content-1.97%
Organic matter-6.19%
Organic carbon-3.60%
pH-6.61
Electrical conductivity-420.00 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.18
Phosphorus-0.16
Potassium-155.07 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Sand Clay Loam
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
There are no risks of flooding as the area is located on hills.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Intercropping of vegetables with fruit-bearing trees in orchards increases biodiversity within the orchard ecosystem.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
1 acre of land
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
The land user right follows national policy and rights.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Crop production has increased due to intercropping.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
The risk of production failure is decreased due to crop diversity. Even if one commodity fails, other surviving commodities make up for the loss.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Crop diversity has increased.
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Intercropping has led to maximum utilization of the orchard area.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land management has improved with better land utilization through intercropping.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in water requirement due to full, efficient utilization of the land and more number of diverse plants growing on the land.
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farm income has increased due to diverse sources of income.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The land user has two different sources of income, fruits and vegetables.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased workload due to many different crops covering the land.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farm income has increased due to diverse sources of income from intercropping.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Intercropping reduces nutrient depletion associated with monoculture.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil cover has increased due to intercropping of different vegetables between apple trees.
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil erosion has decreased due to increased soil cover.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Nutrient cycling has improved. Fruit trees absorb nutrients from the soil and release them back into the soil through decomposed fallen leaves, branches, or other parts.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation cover has increased due to the growing of a mix of vegetables between the trees in the orchard.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Different vegetables are intercropped and rotated in the orchard.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Different crops provide habitats to a variety of living organisms.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
Micro-climate has increased as fruit trees provide shade and regulate temperature, act as windbreaks, and the soil cover through various vegetables helps retain moisture in the soil by preventing erosion.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Intercropping enhances carbon sequestration in the soil.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ثلجية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة باردة | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
No subsidies
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| 1. Increased land productivity: Intercropping vegetables in orchards allows for more efficient use of land by utilizing the space between fruit trees. This increases overall productivity and maximizes the yield from the same area of land. |
| 2. Diversified income streams: By intercropping vegetables, orchard owners can generate additional income from the sale of different crops. This helps to diversify their revenue streams and reduce dependence on a single crop, thereby minimizing financial risks. |
| 3. Improved pest and disease management: Certain vegetable crops can act as natural pest repellents or trap crops, effectively reducing the population of pests that target fruit trees. By intercropping, orchard owners can create a more balanced ecosystem, leading to better pest and disease management without relying heavily on chemical interventions. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| 1. Enhanced soil fertility and nutrient cycling: Intercropping systems often involve the planting of leguminous vegetables, such as peas or beans, which are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen and improving soil fertility. These vegetables can replenish nitrogen levels in the soil, benefiting the overall health and growth of both the fruit trees and the intercropped vegetables. |
| 2. Weed suppression: Intercropping vegetables can help suppress weed growth in orchards. The dense foliage of intercropped vegetables can shade out and outcompete weeds, reducing the need for manual weeding or herbicide application. This results in reduced labour and cost associated with weed control. |
| 3. Microclimate regulation: Intercropping can modify the microclimate within the orchard. The intercrop plants provide shade and windbreak, which can help regulate temperature, humidity, and air movement. These microclimate modifications can protect fruit trees from extreme weather conditions and create more favorable growing conditions, promoting overall orchard health. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Competition for resources: Intercropped vegetables and fruit trees compete for essential resources such as water, nutrients, sunlight, and space. This competition can result in reduced growth and yield for both crops. | Supply adequate nutrients. |
| Increased management complexity: Intercropping adds complexity to the management of the orchard. Different crops may have different requirements in terms of irrigation, fertilization, pest control, and harvesting, requiring additional attention and labour. | Proper planning and management taking into consideration differing requirements. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Difficulty in weed control: Intercropping can make weed control more challenging. Different crops may have different susceptibilities to weeds, and managing weeds without harming the intercropped vegetables or fruit trees can be demanding. | Weed management and different control measures should be taken. |
| Reduced crop specialisation: Intercropping can limit the space available for each crop, leading to reduced specialisation. This may result in lower yields compared to cultivating a single crop in a dedicated area with optimised growing conditions. | Must keep proper/required spaces between each of the plants. |
| Harvesting difficulties: Harvesting intercropped vegetables in an orchard can be more time-consuming and labour-intensive compared to harvesting a single crop. The presence of fruit trees and the arrangement of different crops may hinder access and make harvesting more challenging. | Mechanized harvesting may reduce time taken for harvest. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Three fields
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Two land users were interviewed.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Interviewd soil specialist and vegetable specialist of National Centre for Organic Agriculture (NCOA).
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/07/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Mishra, U. & Wani, N. A. (2022). An integrated circular economic model with controllable carbon emission and deterioration from an apple orchard.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Google Scholar
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Hashemi, A. & Karamidehkordi, E. (2010). FARMERS'KNOWLEDGE OF INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY IN THE ZANJAN PROVINCE IN IRAN.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free website
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kumar, L. & Chhogyel, N. (2018). Climate change and potential impacts on agriculture in Bhutan: a discussion of pertinent issues.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free source
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
An integrated circular economic model with controllable carbon emission and deterioration from an apple orchard
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133962
العنوان/الوصف:
FARMERS'KNOWLEDGE OF INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY IN THE ZANJAN PROVINCE IN IRAN.
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://hal.science/hal-00510402
العنوان/الوصف:
Climate change and potential impacts on agriculture in Bhutan: a discussion of pertinent issues
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://agricultureandfoodsecurity.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40066-018-0229-6
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The land users in Yusipang commented that the production of vegetables in the orchard was done on a small scale and for self-consumption.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية