Improved Forest management [ألمانيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Anke Benndorf
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Waldbewirtschaftung
technologies_7129 - ألمانيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Böttcher Hannes
Öko-Institut e.V.
ألمانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Öko-Institut (Öko-Institut) - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
There are opportunities for robust forest management strategies in Germany to enhance land-based climate change mitigation. Through targeted measures, forest management can contribute to the continuous uptake of CO2 from the atmosphere by trees, and to the increase of carbon stocks in living and dead biomass, as well as in the soil.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Through targeted measures, forest management (FM) to enhance land-based climate change mitigation can be applied to all forested land within Germany. The aim is to increase carbon (C) uptake and storage in forests. FM options generally include forest protection (e.g. by taking forest area out of wood use), increasing forest carbon stocks (e.g. by extending the harvest cycle, and reducing the number of harvested trees), forest adaptation (e.g. increasing resilience of forest stands through the introduction of adapted species and varieties), and increasing the carbon stock in harvested wood products (e.g. by increasing the share of long-lived products).
This case study covers the whole 11.4 million hectares under forest in Germany. Coniferous trees make up 54% and deciduous trees cover 46% of the forest area. Half of the forests are privately owned, with an average property size of 3 ha. About 50% of private forest properties are under 20 ha and only 13% of private forest owners manage forests of more than 1,000 ha.
Incentive systems for rewarding ecosystem and environmental protection services in land use in general, and climate protection services in forest management in particular, should be established, so that forest owners have a source of income besides cutting and selling timber. Such a system should reward the efforts and ambitions to develop forests’ contribution towards a more climate resilient ecosystem that further provides society with clean air, water retention capacities, healthy soils, biodiversity and contributes crucially to the goal of C removal.
The measures to promote carbon sinks in the forest can be implemented on the existing forest area, which means that, in contrast to other land-based climate protection measures, there is no direct competition for land.
Synergies with the protection of biodiversity can result if native deciduous tree species are promoted and, above all, a higher proportion of older deciduous trees is left in the forest. In addition, a higher proportion of deadwood and a greater diversity of deadwood structures (lying, standing; different dimensions) also contribute. Promoting more deciduous trees in the forest can lead to higher groundwater percolation rates compared to coniferous stands.
Oeko-Institut has been developing the Forestry and Agriculture Biomass Model (FABio) since 2015. FABio-Forest describes the growth of individual trees as a distance-independent individual tree growth model. Parameters for tree growth and mortality are derived from National Forest Inventory (NFI) data. Assumptions on forest management as well as for climate change drive the future development of tree stands.
In addition, FABio includes modules for estimating carbon stored of wood products, forest litter and soil. The model is based on the following components:
•a model for the characterisation of tree growth based on diameter, height, site productivity and forest stand density;
•an ingrowth model for the characterisation of new trees based on stand density and tree species;
•a mortality model for the characterisation of dieback processes depending on tree species, site productivity, age and stand density;
•a deadwood model factoring in decomposition of dead trees;
•a soil carbon model simulating the decomposition of biomass in litter and soil over time depending on climate factors; and
•a model for the sorting and classification of wood products, i.e., to sort harvested trees into use categories and quantify carbon retention times of wood products.
FABio supports scenario analyses for various silvicultural practices and management scenarios and their effects on wood supply, carbon sequestration and aspects of nature conservation.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
ألمانيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Germany
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Nationwide
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- > 10,000 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Total area potentially covered by the improved forest management technology is 11.4 Mha: the technology is modeled for - and applicable to - all the forest area in Germany.
2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
- إزالة الخشب الميت/مخلفات التقليم
- استخدام الغابات غير الخشبية
نوع الغابة الطبيعية /شبه الطبيعية:
- النباتات الطبيعية في الغابات القارية المعتدلة
- النباتات لطبيعيةفي لأنظمة الجبلية المعتدلة
نوع الشجرة:
- أنواع الشوح Abies
- أنواع شجرة التنوب Picea species
- أنواع الصنوبر
- Quercus robur, Quercus petraea, Fagus sylvatica
هل الأشجار المذكورة أعلاه ملحاء أم دائمة الخضرة؟:
- مختلطة ملحاء / دائمة الخضرة
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- حفظ/حماية الطبيعة
- الترفيه / السياحة
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M5: التحكم في/تغيير تركيبة الأنواع
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
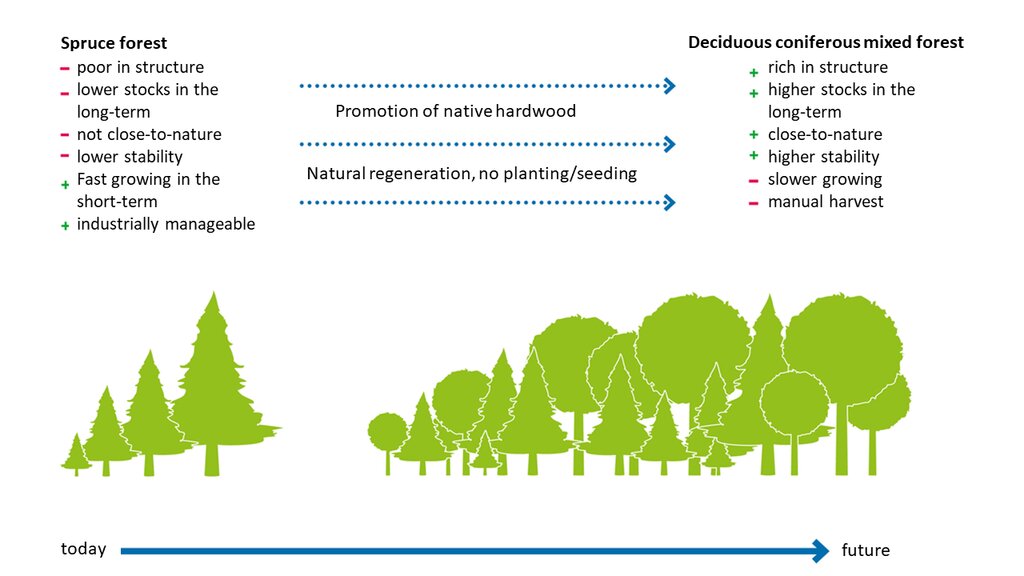
Spruce is the dominant tree species regarding coniferous trees growing outside their optimal habitat. So, a change from coniferous to deciduous coniferous mixed forest, mostly only affects spruce and not any other conifer tree species within Germany.
The drawing shows disadvantages (marked with a minus) and benefits (marked with a plus) of the forest types . The arrows indicate the measures to be taken to facilitate the transformation from a pure spruce forest to a mixed forest stand.
المؤلف:
Hannes Böttcher
التاريخ:
15/03/2018
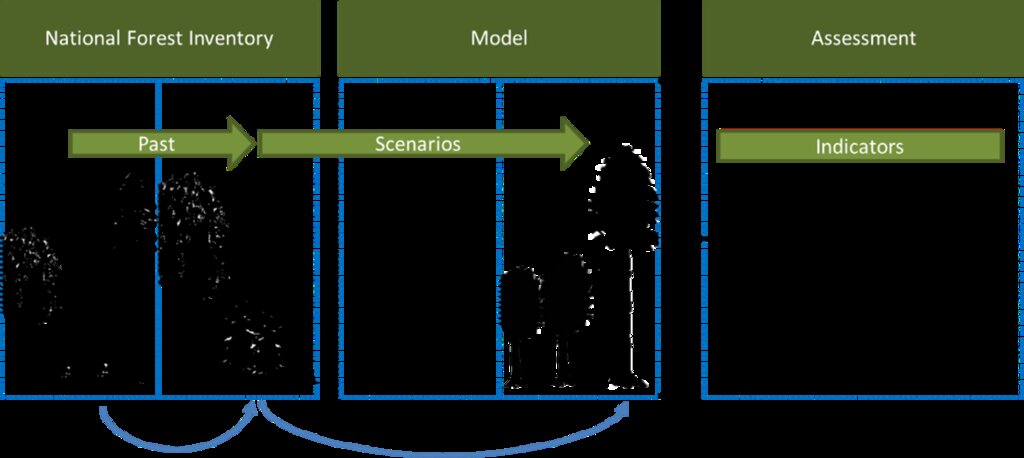
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Work and information flow of the FABio forest model used for the SLM forest management.
FABio-Forest describes the growth of individual trees as a distance-independent individual tree growth model. Parameters for tree growth and mortality are derived from National Forest Inventory (NFI) data. Assumptions on forest management as well as for climate change drive the future development of tree stands
المؤلف:
Klaus Hennenberg
التاريخ:
15/03/2018
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 ha
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
€
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,93
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
39,50
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | fencing to allow undisturbed regeneration without game pressure | all year |
| 2. | planting new trees | spring, no frequency |
| 3. | game control to allow natural regeneration/planted trees to grow | hunting season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
10000,0
التعليقات:
The range is between 5.000 - 15.000 €/ha per hectare, the cost vary, e.g. depending on what tree species are chosen, how many saplings are planted or how much natural regeneration is allowed. Total area is 11,4 mio hectares.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tending, thinning of young trees for managing tree species composition | every few years |
| 2. | monitoring of areas taken out of use | througout the year |
| 3. | wildlife management | hunting season, 1-2 per year |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
2000,0
التعليقات:
The range is between 500 - 4000 € /ha depending, among others, on the age and structure of the forest stands. If areas are taken out of wood production or leaving dead wood on the site after calamities then opportunity costs occur in the range between 200 €/ha and 1000 €/ha. Souce: https://www.bmuv.de/download/foerderrichtlinie-klimaangepasstes-waldmanagement-plus. Total area is 11,4 mio hectares.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Availability of labor, availability of seedlings, density of deer population, costs for fencing.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
740,00
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Evaluation from the Federal Environment Agency of Germany based on data provided by the German Weather Service (DWD)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
The length of the growing period in Germany is around 200 days. Germany is part of the temperate, rainy climate zone of the mid-latitudes. The annual mean temperature from 1961 to 1990 was 8.2°C.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Forests in Germany are found in all different types of landscapes. In the north everything is rather flat, the center of Germany consists of mountains around the elevation of up to 1000 m a.s.l and the very south has high mountain ranges of an altitude of almost 3000 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Same as above as the SLM covers the entire area of the country all different soils with the above mentioned parameters are represented that occur in the respective climatic zone.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Flooding occurs only after very heavy rainfall, when certain weather conditions apply. The latest major floods were in 2003, 2013 and 2024.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
It differs very much from region to region, depending on what type of forest is there, regarding mountainous or flat area, species composition and age structure.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
This applies to all to different forest owners with different forest land sizes. The average size of privately owned forest area is 2,4 ha. Publicly owned forest is typically larger.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
- all of the above
- all of the above
- no information
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The model provides information that if timber extraction is reduced that it will impact positively the C sequestration rate and C storage of the forest. There are no other impacts modeled explicitly but impacts can be expected also on the water cycle, soil quality, and biodiversity.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
not assessed
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | باعتدال |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | غير معروف |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Regarding forests, long-term refers to a time span of a minimum of 60 years.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
unknown
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The payment for ecosystem services creates a new field of income and thus diversifies its' revenues. |
| The establishment of a more resilient forest provides benefits to the forest owner as he can longer profit from the resources the forest produces/provides. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| It is expected that there will be an increase of biodiversity as a higher diversity in tree species attracts other fauna and new habitats are created. Areas taken out of use might contribute to that aspect as well. |
| Natural development of forest sites taken out of use provides the opportunity to have old-growth trees in the forest again and diversify the age structure in forested areas. Old trees also provide great habitats to a variety of different species. |
| The increase of wood stock as less trees are harvested will increase CO2 sequestration. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| reduction of timber supply | import, reduce demand |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| management of multi species forests requires silvicultural knowledge | training |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
in-house specialists: 4
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
4 (s. references below)
التعليقات:
Data collection for a national forest inventory takes about 2 years ahead of the official release. It is similar regarding the C inventory, data collection was done in the year ahead.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Forest Vision Germany - Description of methodology, assumptions and results , Böttcher et al., 2018
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://www.oeko.de/fileadmin/oekodoc/Forest-Vision-Methods-and-Results.pdf
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Referenzszenario der Holzverwendung und der Waldentwicklung im UBA-Projekt BioSINK, Pfeiffer et al., 2023
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
file:///C:/Users/a.benndorf/Downloads/WP-Referenzszenario-BioSINK.pdf
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Zukunftsaufgabe Waldanpassung, ANDREAS BOLTE, MARKUS HÖHL, PETRA HENNIG, TOBIAS SCHAD, FRANZ KROIHER, BJÖRN SEINTSCH, HERMANN ENGLERT, LYDIA ROSENKRANZ, 2018
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Zukunftsaufgabe Waldanpassung
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Portal on Forest Inventories
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://bwi.info/start.aspx
العنوان/الوصف:
Förderrichtlinie Klimaangepasstes Waldmanagement PLUS
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.bmuv.de/download/foerderrichtlinie-klimaangepasstes-waldmanagement-plus
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية