Peatland Rewetting [هولندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: William Powell
- المحرر: Carlos Gil Picon
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Peatland Rewetting
technologies_7140 - هولندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Powell William
JIN Climate & Sustainability
هولندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
JIN Climate and Sustainability (JIN) - هولندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Peatland rewetting is a climate change mitigation technology that involves raising and maintaining high water tables in agricultural peatland through controlled drainage. It reduces soil subsidence and CO2 emissions while preserving biodiversity. This technology offers environmental benefits but faces challenges in policy support and economic viability.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
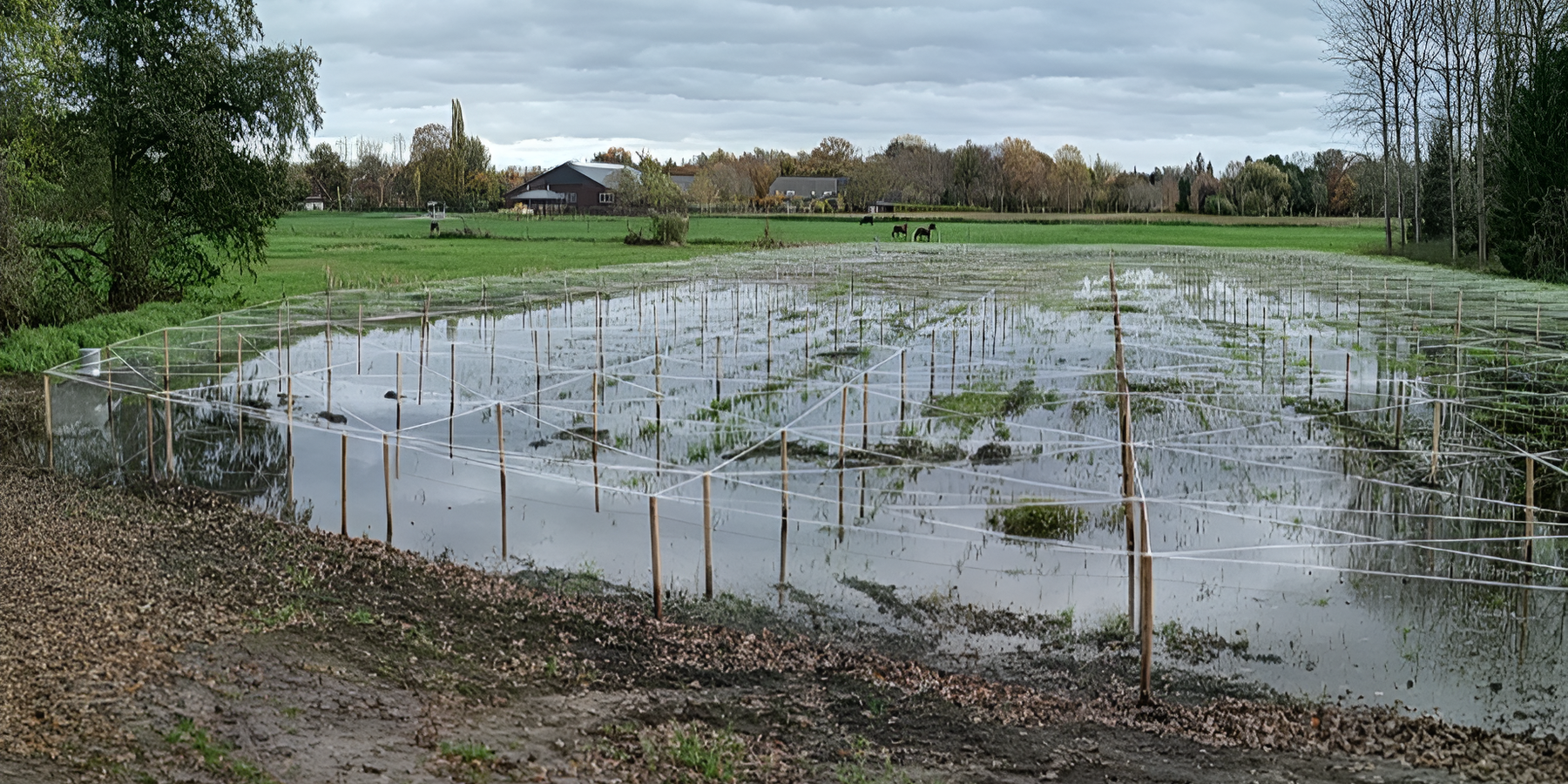
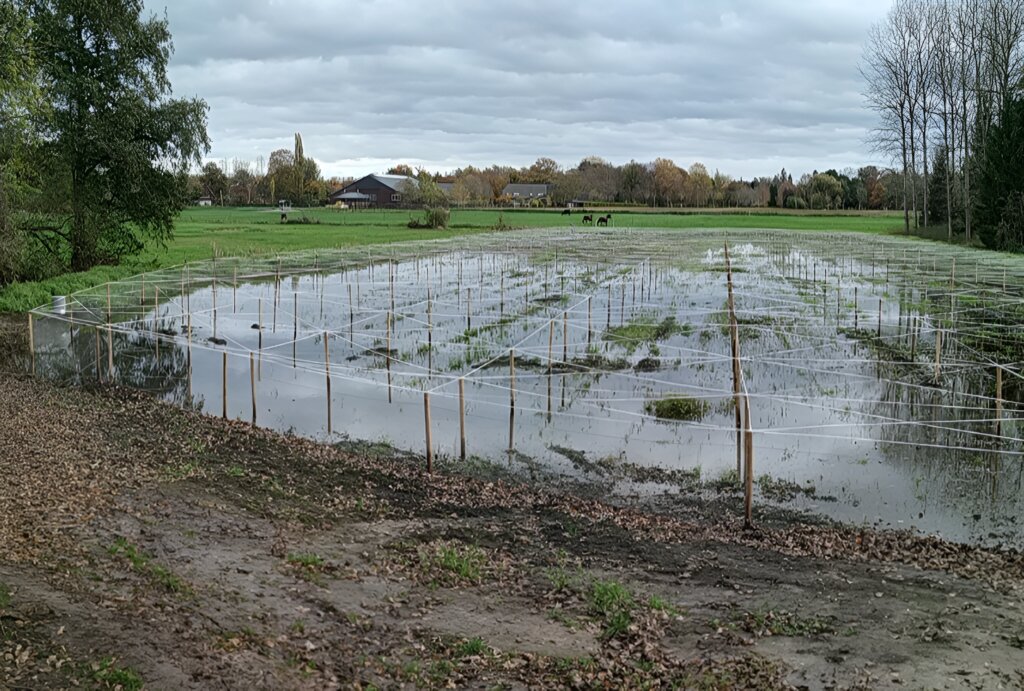
Peatland rewetting is increasingly being applied in the Netherlands, particularly in the province of Zuid Holland, as a critical environmental management strategy. This technology is implemented in agricultural fields on peatland soil, representing an important shift in land management practices. The method can be characterised by raising and maintaining a high water table in peatland areas through the implementation and careful control of a sophisticated drainage system.
The system's technical infrastructure includes an integrated network of pipes, pumps (including innovative solar-powered options), and strategically placed ditches to control the water level. Advanced monitoring equipment is installed to track water table levels with precision, ensuring optimal management of the wetland conditions. The primary purpose of peatland rewetting is to mitigate climate change by reducing soil subsidence and consequent CO2 emissions from drained peatlands, which globally contribute around 2 Gt of CO2 annually.
Implementation requires several key components and activities. The initial phase involves comprehensive site assessment and installation of the drainage system, including careful placement of monitoring equipment and, where applicable, solar panels for sustainable pump operation. Ongoing maintenance activities are crucial and involve regular system monitoring, component repairs, and water level adjustments to maintain optimal conditions between -10 and +20 cm, as demonstrated in projects like the Swinkels case study.
The benefits and impacts of peatland rewetting are multifaceted. Primary environmental benefits include significant reduction in CO2 emissions by preventing peat oxidation, preservation of valuable peatland habitats and biodiversity, and improved regional water management. The practice also helps avoid substantial costs associated with soil subsidence, such as infrastructure repairs and dam reinforcement that would otherwise be necessary in degraded peatland areas.
From the land user's (farmer's) perspective, the transition to peatland rewetting presents both opportunities and challenges. The main benefits include access to potential subsidies, avoided costs due to soil subsidence, and the opportunity to participate in innovative agricultural practices like paludiculture - the cultivation of wet-tolerant crops such as cattail, which can be used for various applications including fodder. However, farmers may face challenges including significant initial investment costs, the necessity to adapt to new farming techniques and business models, and potential yield impacts during the transition period as they navigate the learning curve of wet agriculture.
Some environmental considerations require careful management. While peatland rewetting generally provides positive environmental outcomes, there can be challenges with nutrient leaching affecting water quality, which necessitates careful monitoring and management strategies. Additionally, stakeholders express concerns about the lack of consistent long-term subsidies and policy support for maintaining these practices, highlighting the need for more robust institutional frameworks to support sustainable peatland management.
Scientific monitoring of these sites, as demonstrated in the LANDMARC project, includes sophisticated tools such as soil sampling for physical and chemical analysis, molecular microbial identification, greenhouse gas measurements, and the use of satellite data and field mapping to track progress and impact. This comprehensive monitoring approach helps ensure the effectiveness of rewetting initiatives and provides valuable data for scaling up these solutions to national and continental levels.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
هولندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
South Holland
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Alblasserwaard-Vijfheerenlanden
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
There is no indication that the sites have a special protected status. The sites are active agricultural lands used for dairy farming. The peatland rewetting sites are on working farms, two organic dairy farms and one conventional dairy farm. The land is described as a permanent grassland. They are actively managed agricultural areas rather than protected natural reserves.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2022
2.7 إدخال التقنية
- regional collaboration
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Key partners of peatland rewetting in this region include farmers, research institutes, local water authorities, and nature organizations
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
نوع الحيوان:
- ماشية - الألبان
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
The technology aims to combine peatland conservation and dairy farming. It involves both land and livestock.
المنتجات والخدمات:
- الحليب
- grass/fodder production, carbon sequestration, water management.
الصنف:
ماشية - الألبان

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
There will be pressurized draining systems installed, suggesting water management beyond reliance on rainfall.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحويل المياه والصرف
- حماية/ إدارة الأراضي الرطبة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
التعليقات:
Drainage systems are a significant structural intervention to the landscape. The hydrology of the area is modified through engineered solutions. This technology allows for control of groundwater levels independently from ditch water levels.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
- (Hw): تناقص القدرة التخفيفية للمناطق الرطبة
التعليقات:
The most significant issues being addressed by peatland rewetting is Ps: subsidence of organic soils, setting of soil.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
The primary goal of peatland rewetting is to reduce land degradation. By implementing pressurized drainage systems, the technology seeks to slow down the rate of peat decomposition and subsequent soil subsidence.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
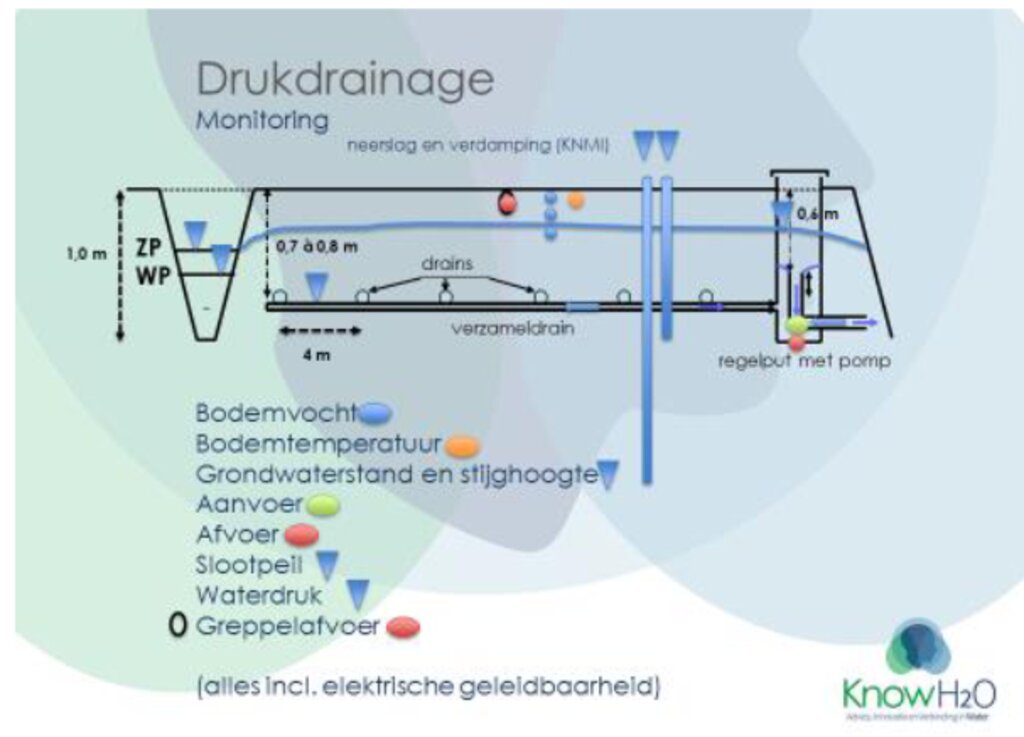
Schematic representation of the pressurized drainage system and monitoring setup for a peatland rewetting plot. The system includes drainage pipes at 4m intervals, a central collection pipe, control wells, and various monitoring equipment for measuring soil moisture, groundwater levels, ditch water levels, and water flows. Solar-powered pumps control water levels independently of ditch water levels. Monitoring also includes soil temperatures, biodiversity assessments, and continuous measurement of soil surface height changes.
المؤلف:
Gé van den Eertwegh
التاريخ:
2020
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
8.4 ha
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
EUR
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
60 EUR per hour is the estimated average cost of labour in the Netherlands
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | selection of test plots | Winter/Spring |
| 2. | creating drainage plans | Winter/Spring |
| 3. | obtaining permits | Winter/Spring |
| 4. | installing drainage systems | Summer |
| 5. | installing monitoring equipment | Summer |
| 6. | damming ditches | Late Summer/Early Fall |
| 7. | installing pumps | Summer |
| 8. | setting up reference plots for comparison | Full Year |
| 9. | conducting baseline measurements | Full Year |
التعليقات:
No clear data available on specific timing, however estimations are made based on the technical requirements and the climate of the Netherlands.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | installation | |||||
| العمالة | maintenance | |||||
| معدات | drainage and collection pipes | |||||
| معدات | pumps and solar panels | |||||
| معدات | control wells | |||||
| معدات | monitoring equipment (soil moisture sensors, etc.) |
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
579000,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
There is local and national government involvement in sharing the costs. Farmers also contribute 25% of the installation costs and provide in-kind contributions through their time.
التعليقات:
The total cost of establishment and ongoing costs for the whole area of 8.4 hectares are estimated to be EUR 570000 including VAT. The breakdown is:
a. Monitoring/ analysis 44%
b. Education 2%
c. Communication 7%
d. Reporting 8%
e. Management 11%
f. Materials/ apparatus 16%
g. Drainage system including ditches 9%
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ongoing monitoring of soil moisture, groundwater levels, and soil movement | |
| 2. | Management of water levels using the pumping system | |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage pipes and pumps | |
| 4. | Data collection and analysis | |
| 5. | Ecological monitoring (biodiversity, wading birds) | |
| 6. | Grass yield measurements | |
| 7. | Soil temperature monitoring | |
| 8. | Water quality testing | |
| 9. | Reporting and communication activities |
التعليقات:
See comment under 4.4
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Systems operation and monitoring | |||||
| العمالة | Maintenance and potential replacement of equipment | |||||
| العمالة | Data analysis and reporting costs | |||||
| العمالة | ecological survey costs | |||||
| غير ذلك | Energy costs for pumps (some are solar) |
التعليقات:
See comment under 4.4 and note that Euros 579000 (including VAT) is an estimate of both establishment AND ongoing costs
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most important factors affecting the costs are the installation of the drainage systems, monitoring equipment and activities, scale of implementation, types of drainage pipes, solar-powered pumping systems, project management and research activities, adaptation of surrounding water management, duration of the project, labor costs, and location-specific factors (such as the soil profile of the area of implementation).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
790,00
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
statista
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The Netherlands is flat, although the technology is applied to an area with a 1 to 3 ditches.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
نعم
الإنتظام:
بشكل عرضي
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Although these areas support some important biodiversity values, their primary current use is agricultural.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
I do not have specific information available on off-farm income or the gender of the land-users, although it is well-known that 60% of Dutch farm land is family-owned.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
likely to be considered small-scale
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Peatland rewetting aims to maintain or slightly improve grass yields
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الشرب
توافر مياه الري
الآثار الايكولوجية
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Aims to improve biodiversity, especially for wading birds and aquatic life
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
helps manage drought and heavy rainfall situations
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Potential improvement in water quality of ditches and surrounding water bodies
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The implementation of peatland rewetting through raised water levels and submerged drains has shown significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, with measurements indicating a decrease from 19-50 t CO2 per hectare annually to approximately half those levels. While this water management approach impacts dairy farming viability, the use of innovative drainage systems has demonstrated that agricultural production can be maintained. Monitoring data shows reduced soil subsidence rates, from an average of 8 mm/year to lower rates, while also indicating potential improvements in habitat conditions for meadow birds and wetland biodiversity.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rewetting improves regional hydrology by keeping water longer in the landscape, enhancing water retention capacity.
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water retention in rewetted peatlands helps maintain more stable water flows during dry periods.
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Restored peatlands act as natural water buffers, reducing peak flows and downstream flooding risks.
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rewetting reduces nutrient runoff (particularly nitrate) into groundwater and surface waters, improving water quality.
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Restored wetland conditions enhance the natural filtering capacity of peatlands, improving water quality in the wider landscape.
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Rewetting helps reduce soil subsidence which otherwise damages roads, buildings and other infrastructure.
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Measurements show significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, from 19-50 t CO2 per hectare annually to approximately half those levels through water management.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The project includes monitoring of water quality and ecology in surrounding ditches. Greenhouse gas emissions are expected to greatly decrease.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | غير معروف |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | انخفاض | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
The prediction is more for extreme weather patterns than a decrease of rainfall overall. The technology's effectiveness may be challenged by these changes, as maintaining optimal water levels becomes more difficult as rainfall decreases. Therefore there may be an impact on this technology during extended dry periods.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The short-term returns on peatland rewetting are negative due to their (sometimes significantly) high establishment costs. The establishment costs, however, are the highest cost associated with this technology and the long-term returns and benefits are what make the high upfront costs attractive for land-users.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
In this case, it was a collaborative effort
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Provides better control over water levels, helping to manage both drought and excess water situations |
| Potential to maintain or improve grass yields while addressing environmental concerns |
| Opportunity to contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and soil subsidence |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Offers a solution to reduce peat soil subsidence and associated greenhouse gas emissions |
| Improves water management and quality in the area, potentially benefiting biodiversity. |
| Provides a model for sustainable dairy farming on peatlands, balancing economic and environmental needs. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High initial investment costs | Provide more substantial subsidies or financial support for implementation |
| Uncertainty about long-term economic benefits | Conduct longer-term studies to demonstrate economic viability; develop compensation schemes for ecosystem services |
| Requires changes in farming practices | Provide training and support for adapting to new management techniques |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent policy support across different water boards | Develop a united, long-term policy framework for peatland management |
| Potential for increased nutrient leaching | Implement additional measures to mitigate nutrient runoff; continue monitoring water quality |
| Limited data on long-term effectiveness | Continue monitoring and research to build a comprehensive understanding of long-term impacts |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
التعليقات:
The interviews and data collection done for these cases of peatland rewetting in the Netherlands were completed as a part of the EU-funded LANDMARC project, which went from 2020 to 2024. Most of the data collection used to fill in this questionnaire was completed in 2022 and accessed again in 2024. For specific information on this case study, the publications from LANDMARC can be referenced here: https://www.landmarc2020.eu/
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Scientific assessment and policy analysis: peatlands and carbon flows: outlook and importance for the netherlands,A. Verhagen J.J.H. van den Akker C. Blok W.H. Diemont J.H.J. Joosten M.A. Schouten R.A.M. Schrijver R.M. den Uyl P.A. Verweij J.H.M Wösten, 2009, WAB 500102 027
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Available for free from the WAB (Dutch Scientific Assessment and Policy Analysis on Climate Change)
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية