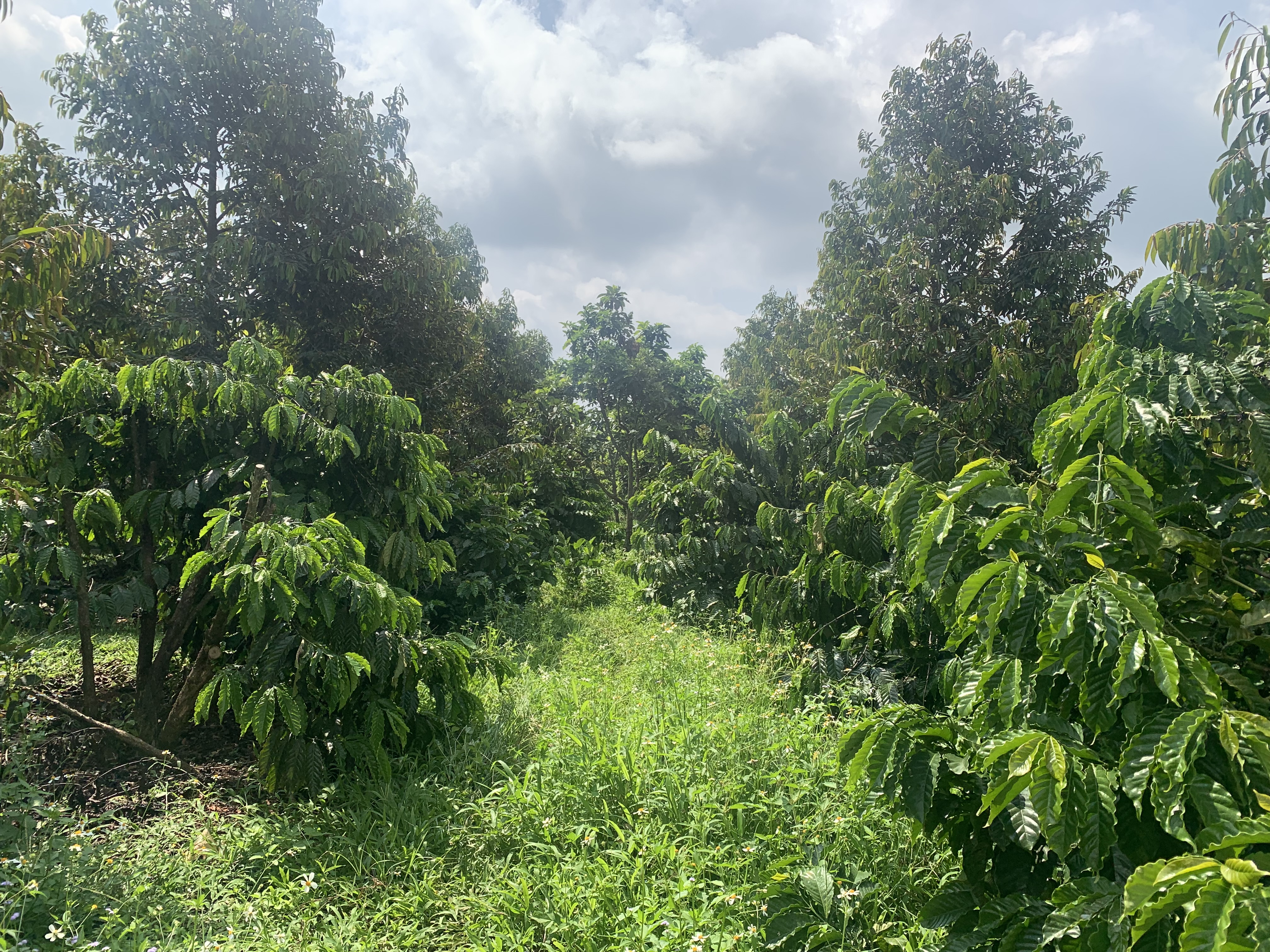
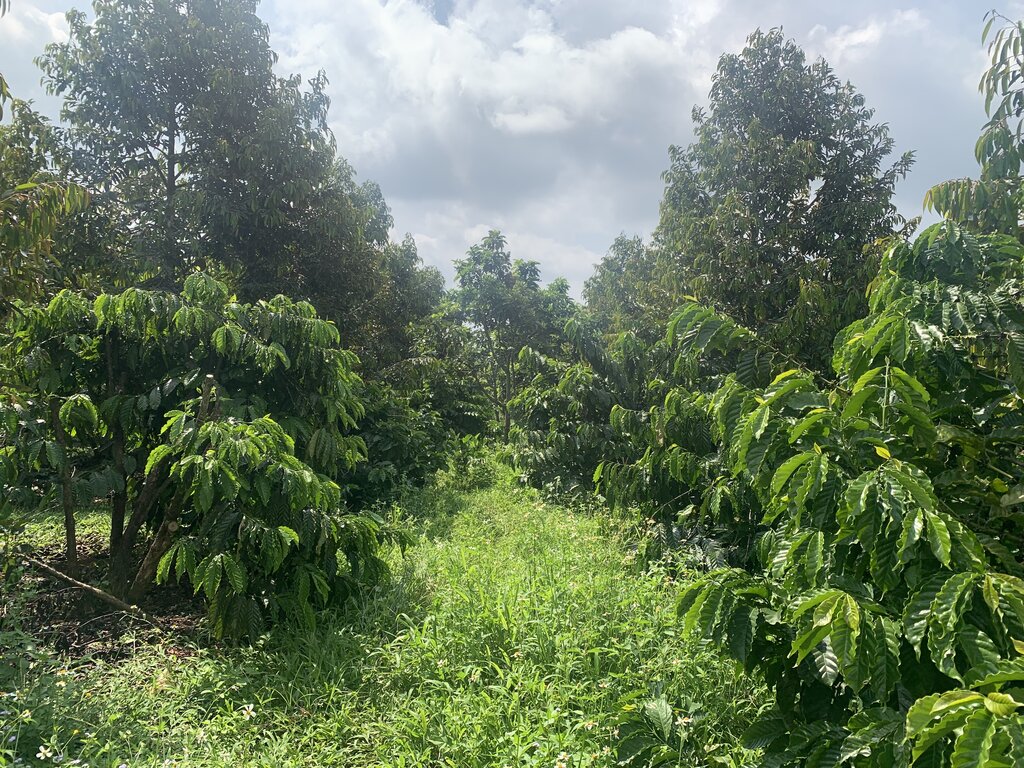
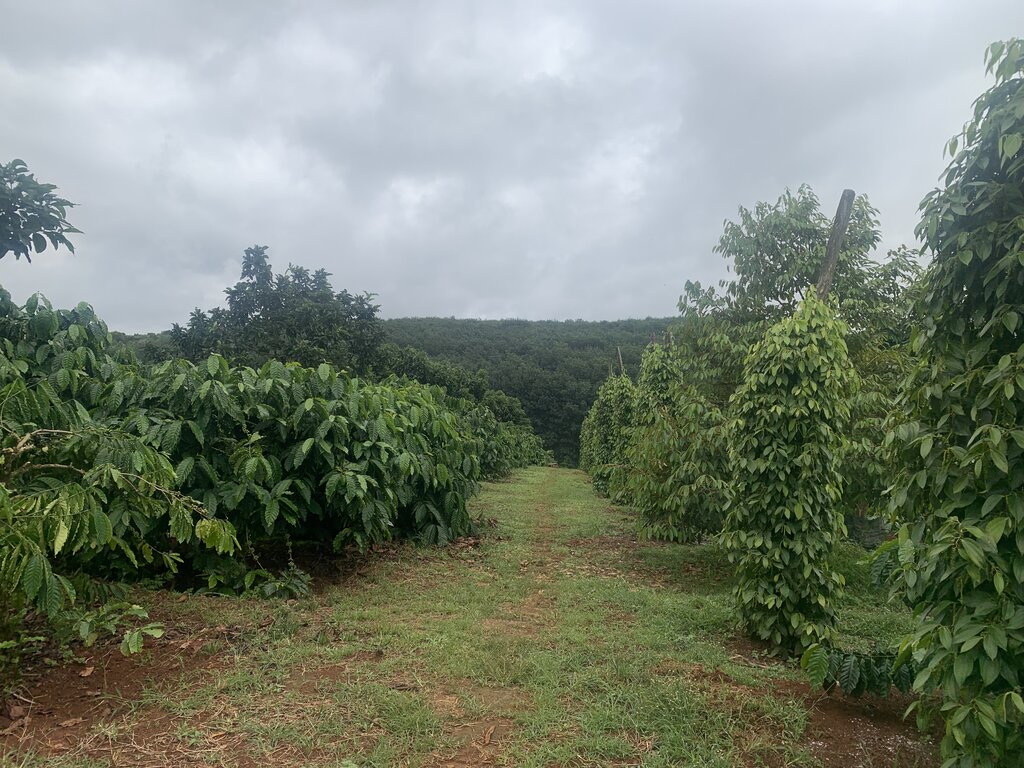
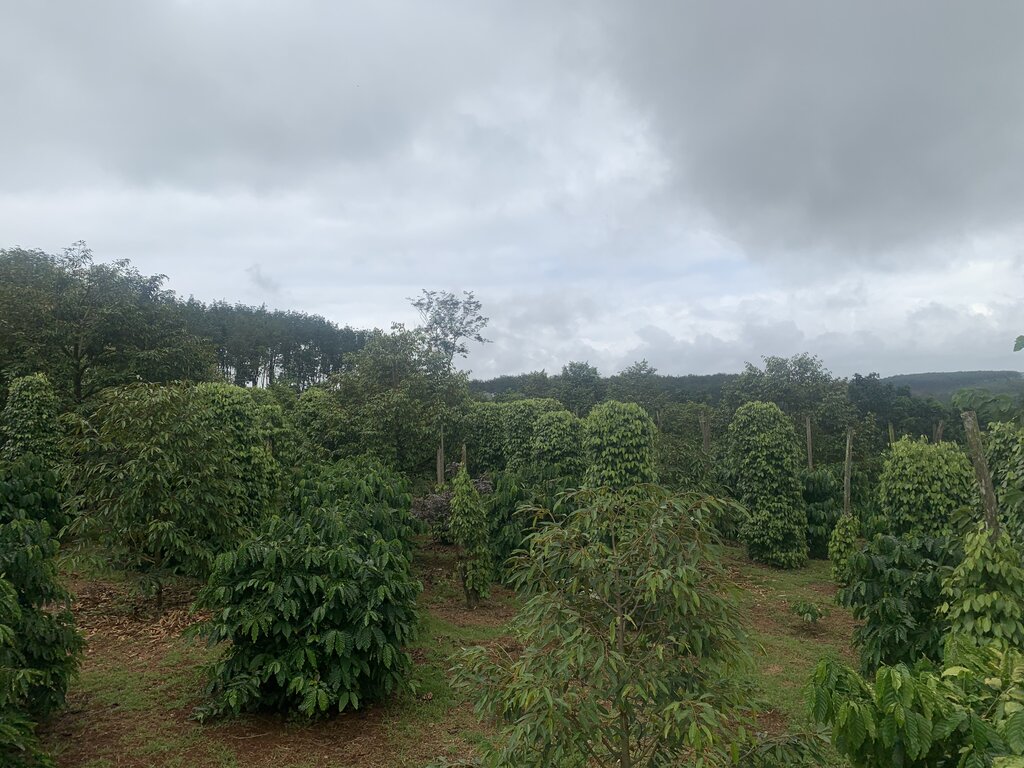
Multi-storey intercropping with coffee and fruit trees [فيتنام]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Carlos Gil Picon
- المحرر: Eric Rahn
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Mô hình trồng xen cây ăn quả trong vườn cà phê
technologies_7387 - فيتنام
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
Ha Tuan
Nguyen University and CIAT
فيتنام
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture -Vietnam (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Robusta coffee in the Central Highlands of Vietnam is intercropped with pepper vines and fruit trees thus increasing the total planting density. This leads to higher land equivalent ratios compared to monocropping, thereby increasing land use efficiency, profitability, soil protection and resilience.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Robusta coffee in the Central Highlands of Vietnam is intercropped with pepper vines and fruit trees, increasing the total planting density. This leads to higher land equivalent ratios (LER) compared to monocropping, thereby increasing land use efficiency, profitability and resilience. The increased plot-level biomass stock also confers better soil protection, and more biomass is returned to the soil through prunings and natural litter formation.
There are a variety of multi-storey intercropping designs based on coffee (Coffea canephora), black pepper (Piper nigrum), avocado (Persea americana), durian (Durio zibethinus) and macadamia (Macadamia integrifolia). An example of a recommended intercropping design is coffee with pepper vines (supported by living poles of Ceiba pentandra, Cassia siamea, Paulownia spp. etc) and fruit trees at densities of 887 coffee bushes, 336 pepper vines, 28 avocado trees and 28 durian trees per hectare (D’Haeze 2022; Rigal et al. 2023). Agronomic practices such as irrigation and nutrient management need to be adapted to this system. For example, water demand by coffee in the shade of fruit trees is less than in monocropping systems. Other practices can be combined, such as the use of cover crops (e.g., Crotalaria) planted between the other crops to avoid bare land.
This technology is increasingly applied in Dak Lak, Gia Lai, Lam Dong and Dak Nong in the Central Highlands of Vietnam, primarily by the Kinh farmers, while ethnic minorities currently rely more frequently on monocropped coffee systems.
The main purpose of this diversified mixed cropping system it to increase land use efficiency as well as productive, climatic and economic resilience. Price volatility is a huge challenge for farmers, particularly with perennial cropping systems where crop changes as response to economic signals is costly and risky due to time-lag effects.
Quality planting material (e.g., use of scion avocado cultivar 034 for grafting), water-saving irrigation systems, and organic and mineral fertilizers are required alongside a careful planting design that minimizes potential competition between associated crops. For example, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) provides guidelines (Decision No. 3702, 2018) for designing intercropping systems based on coffee.
The main benefit is economic resilience to volatile prices of perennial commodity crops. Given that perennial crops cannot be easily substituted with other crops that have better prices, diversification of cropping systems is key to economic resilience. Furthermore, land use efficiency is increased and thereby more crops can be produced using less area. Tree-level yields remain the same as in monocropping systems, however, after certain years of fruit tree growth (e.g., avocado) there is a potential of coffee tree-level yield decline due to shade effects. It also helps to manage production costs when crops need to be rejuvenated or replanted. Furthermore, carbon stocks in aboveground biomass are increased compared to monocropping systems. This increase in aboveground carbon stocks leads to higher biomass input to the soil due to fresh litter (prunings) and senescent litter (natural).
Land users choose this intercropping model to diversify their income on the same unit of land. This reduces the risks associated with unpredictable price fluctuations. They also note that this system improves resource use efficiency, requiring less fertilizers and irrigation compared to the monocropping systems.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
فيتنام
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Dak Nong
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Hung Binh commune
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Next to land user's own innovation, the technology is also being introduced and promoted by the department of crop production of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) and the extension systems after refinement through research institutions under MARD such as WASI in the Central Highlands. Furthermore, it is also being introduced by Universities and companies.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- Reduce economic risks due to price volatility
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
حدد:
this questionnaire refers to a variety of crops with different growing season characteristics
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Coffee (Coffea canephora), black pepper (Peper nigrum) poles (Ceiba pentandra; Cassia Siamea; Paulownia spp.), avocado (Persea americana, durian (Durio zibethinus), macadamia (Macadamia integrifolia).
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Composting using agricultural residues, and a change from mono-cropping to agroforestry
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Intercropping in combination with cover crops, Intercropping and cover cropping helps increase soil moisture.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
While the main goal of land users in adopting this technology is to diversify income sources and reduce risks related to price volatility, it also reduces soil degradation by leaving less soil bare compared with the interrows of monocropped coffee and increases biomass input to the soil.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Planting density of coffee (Coffea canephora) is 3m by 3m. Coffee trees typically grow to a height of 1.5 to 2m, with a canopy width of around 2m. For the associated tree species, the densities depend on the species and the number of species. For example, black pepper (piper nigrum) can be intercropped at a density of 9m x 9m on living tree poles such as Cassia Siamea, Leucena Leucocephala, etc. Pepper vines grow up to 5 m in height and can also be planted at higher density (e.g. 6 x 3m) at the expense of fruit trees. Avocado (Persea americana), Durian (Durio zibethinus), and macadamia (Macadamia integrifolia) can be intercropped at 12m x 12m. These fruit trees share similar sizes and shapes and grow to a height ranging from 5-10m, with a canopy spanning from 6-8m. The study by Rigal et al. (2023) provide a great overview of the diversity of intercropping / agroforestry designs with different species mixtures and planting densities: Rigal C., Duong T., Vo C., Bon L.V., Hoang q.T., Chau T.M.L. (2023) Transitioning from monoculture to mixed cropping systems: The case of coffee, pepper, and fruit trees in Vietnam. Ecological Economics 214:107980.
المؤلف:
Own illustration based on Rigal et al. (2023) and MARD: Good Agricultural Practices for Robusta Coffee Production.
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 hectare
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
12
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery with grafted material | Dry season |
| 2. | Soil preparation | April or May; before the onset of the rainy season |
| 3. | Planting | rainy season |
| 4. | Fertilizer application | rainy season |
| 5. | irrigation | dry season |
التعليقات:
Establishment will take 3 years until first coffee harvests. Harvests of other fruit trees will start later.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
7000,0
التعليقات:
This estimate is based on a system of 887 coffee plants, 336 pepper vines, 28 avocado trees (based on grafting with improved variety) and 28 durian trees.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Creating a basin around the tree base for keeping water during irrigation phase | |
| 2. | Application of fertilizers and pesticides | |
| 3. | Irrigation | |
| 4. | Weeding and pruning | |
| 5. | Guiding the black pepper vines onto the poles and trimming branches of living poles | |
| 6. | Tying durian fruits to branches by plastic ropes for support | |
| 7. | Sanitation after each harvest |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
4000,0
التعليقات:
The maintenance costs refer to the establishment stage (first 3 years) until first harvest and are based on a system of 887 coffee plants, 336 pepper vines, 28 avocado trees (based on grafting with improved variety) and 28 durian trees.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
production inputs (fertilizers, pesticides), and hired labor. Initial establishment cost of irrigation systems is also costly.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Considering that it is relative to other sites of the region, I would classify it as medium. Forests have highest diversity, and the mixed coffee agroforestry systems have medium diversity. While other agricultural land has low diversity.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Profitability and risk mitigation has increased, which is the main reason why there is adoption at scale.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Profitability and risk mitigation has increased, which is the main reason why there is adoption at scale.
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Product diversity could still be increased.
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Costs increase initially, but over time the benefits outweigh the costs. In some cases, external financial support is needed to adopt the practice.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Income sources increase from 1 (i.e., coffee) to several (e.g., pepper, avocado, durian).
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Work efficiency increases when intercropping, compared to having the crops separately on different fields as monocrops. Nonetheless, the workload is larger when simply comparing to 1 coffee monocropping field.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil moisture increases due to the change in microclimate from shade trees and cover crops.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil cover increases through the use of selective weeding or cover crops. Current practices often leave their soils bare exposing them to erosion during heavy rainfall.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation cover increases, which is particularly beneficial for soil conservation.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Above- and belowground C increases, however there is potential to integrate additional trees with higher biomass values.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Plant diversity increases. However there is potential to further increase the diversity on the farm.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Microclimate benefits from shade trees reduce the impact of droughts.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Combination of literature studies (e.g., Rigal et al. 2023; D'haeze 2022) and own (yet) unpublished observations.
- Rigal C., Duong T., Vo C., Bon L.V., Hoang q.T., Chau T.M.L. (2023)
Transitioning from Monoculture to Mixed Cropping Systems: The Case of Coffee, Pepper, and Fruit Trees in Vietnam,
Ecological Economics 214:107980
- D’haeze, D. (2022). Optimizing water use in the central highlands of Viet Nam: Focus on
the Robusta coffee sector. Hanoi, Viet Nam: IUCN and Gland, Switzerland.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased soil cover improves soil properties and filtering capacity.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Literature based and own observations.
For example:
-Cannavo, P., Sansoulet, J., Harmand, J.-M., Siles, P., Dreyer, E., & Vaast, P. (2011). Agroforestry associating coffee and Inga densiflora results in complementarity for water uptake and decreases deep drainage in Costa Rica. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 140(1–2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2010.11.005
- Chatterjee, N., Nair, P. K. R., Nair, V. D., Bhattacharjee, A., Filho, E. D. M. V., Muschler, R. G., & Noponen, M. R. A. (2019). Do Coffee Agroforestry Systems Always Improve Soil Carbon Stocks Deeper in the Soil?—A Case Study from Turrialba, Costa Rica. Forests, 11(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11010049
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | باعتدال |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الانزلاق الأرضي | باعتدال |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدا |
التعليقات:
The practice is considered an important climate change adaptation strategy, however, more research is needed to provide the the required evidence.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
It can take between 5 to 10 years until the relative advantage is achieved, as the associated crops first need to reach their productive stage. Hence, investment costs will be higher until the associated crops can be harvested.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 11-50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 51-90%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- الأسواق المتغيرة
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
Farmers are very sensitive to market signals. For example, the price of durian has increased, so farmers plant more durian. Earlier the same happened with pepper.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The main advantage is the increased profitability and market/climate risk management. |
| There are additional benefits such as improvement in soil ecology to manage soil-borne pests and diseases and reduced irrigation need for coffee. |
| Interest from coffee buyers in sustainable production systems provides another incentive to change practices. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| More resilient livelihoods |
| More diversified landscapes |
| Increased carbon storage capacity |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Initial investment costs can be high for some smallholder farmers | External financial support is needed through market mechanisms. |
| There continues to be a need to adapt agronomic practices to the new system design. This knowledge is not yet fully available. | Research activities to provide the required evidence and enable the development of guidelines. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There continues to be a need to adapt agronomic practices to the new system design. This knowledge is not yet fully available. | Research activities to provide the required evidence and enable the development of guidelines. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Rigal et al. (2023) Transitioning from monoculture to mixed cropping systems: the case of coffee, pepper, and fruit trees in Vietnam
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2023.107980
العنوان/الوصف:
Dave D'Haeze (2022) Optimizing water use in the Central Highlands of Viet Nam. Focus on the Robusta coffee sector
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://iucn.org/sites/default/files/content/documents/2022/bridge_ch_coffee_transformation_final_february_2022-_revised_2_ddh_for_publication.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
MARD (2003) Good Agricultural Practices for Robusta Coffee Production.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية