Gravity Irrigation for enhancing Community-Based Restoration efforts in the degraded forests of Paktya [أفغانستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Mohammad Wazir Ahmadzai
- المحررون: Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal, Mohammad Mustafa Sahebzada, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi, Megha bajaj
Obu Zakhira
technologies_7481 - أفغانستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistanاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - أفغانستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
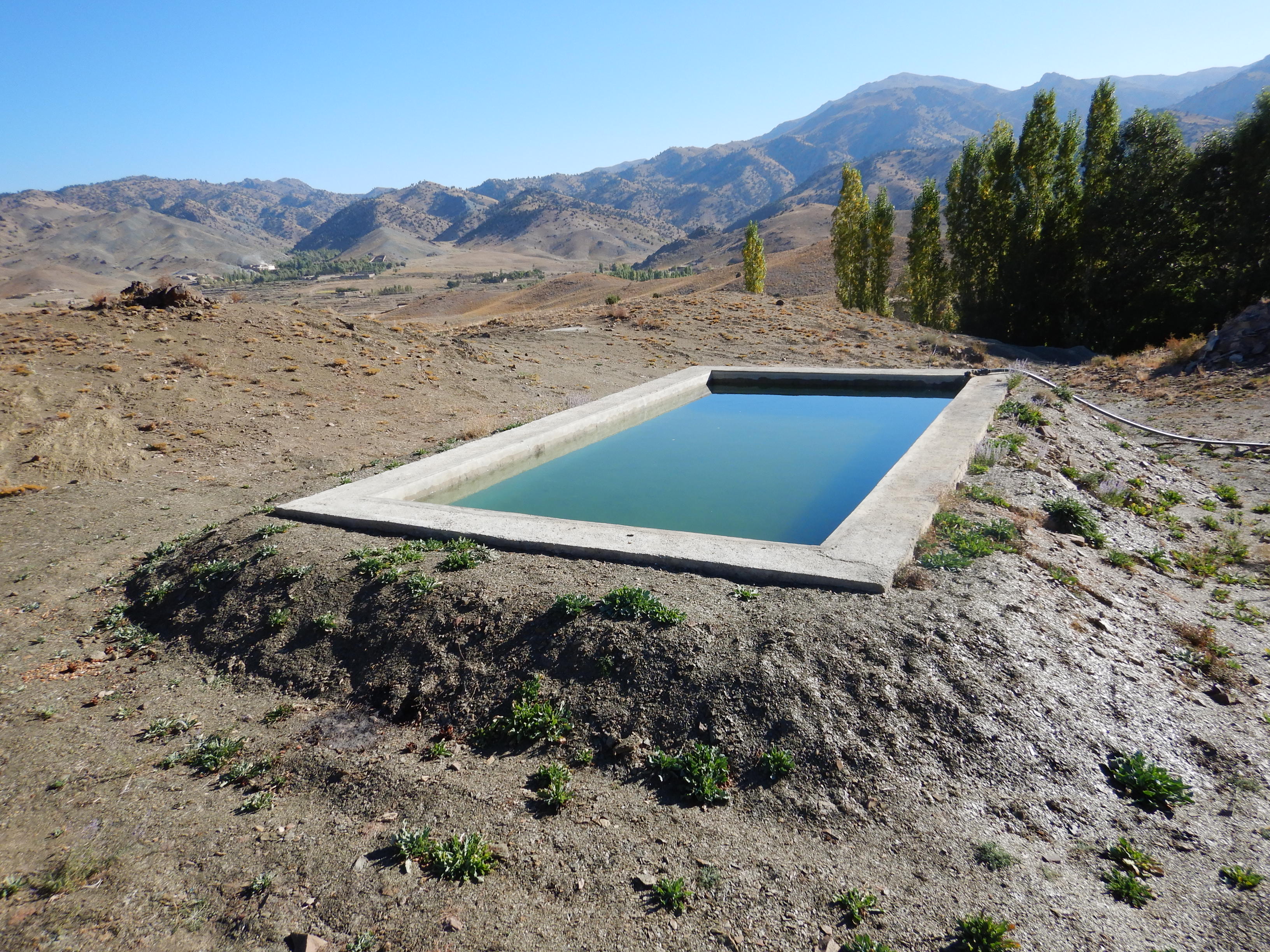
Using a gravity-irrigation system, spring water is diverted to fill reservoirs and then distributed to fields for the restoration of degraded forest areas, with the active involvement of local communities and a focus on the sustainable use of water resources (spring water).
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
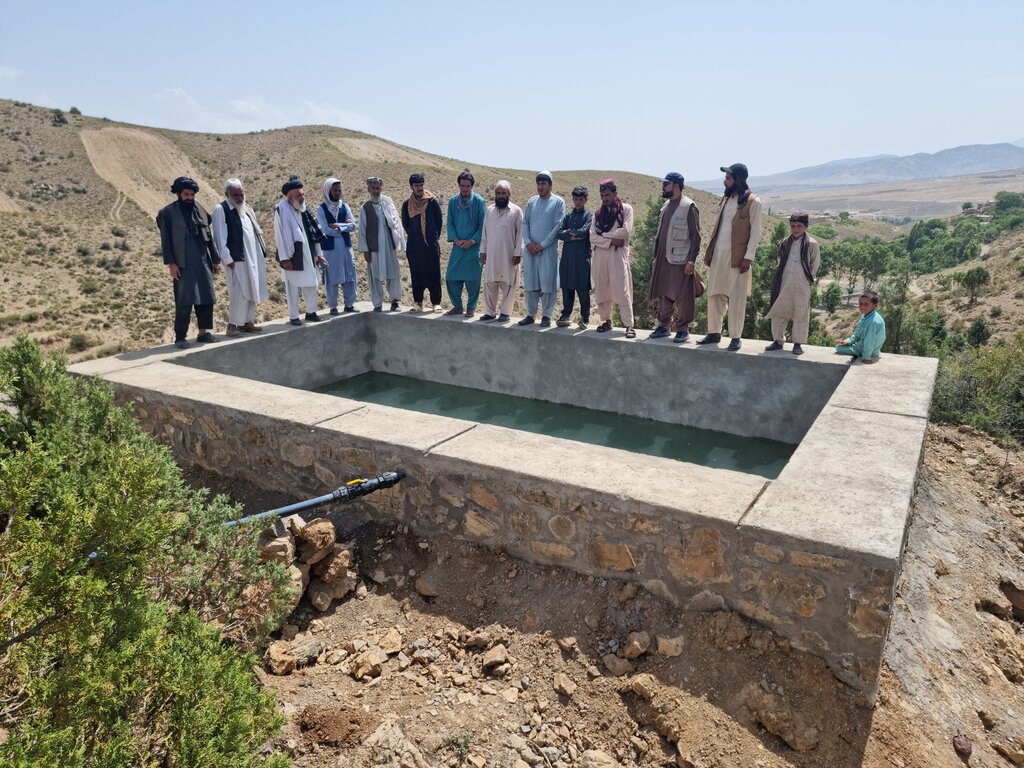
The Paktya province in Afghanistan, known for its mountainous terrain and rich forests of pine nuts deodar, cedar, and conifers, faces severe challenges. Most water in the province comes from rivers, springs, and tube wells, with high mountains acting as natural reservoirs. Unfortunately, many traditional water sources have been destroyed over decades of conflict and natural drought, forcing farmers to rely on costly tube wells for irrigation.
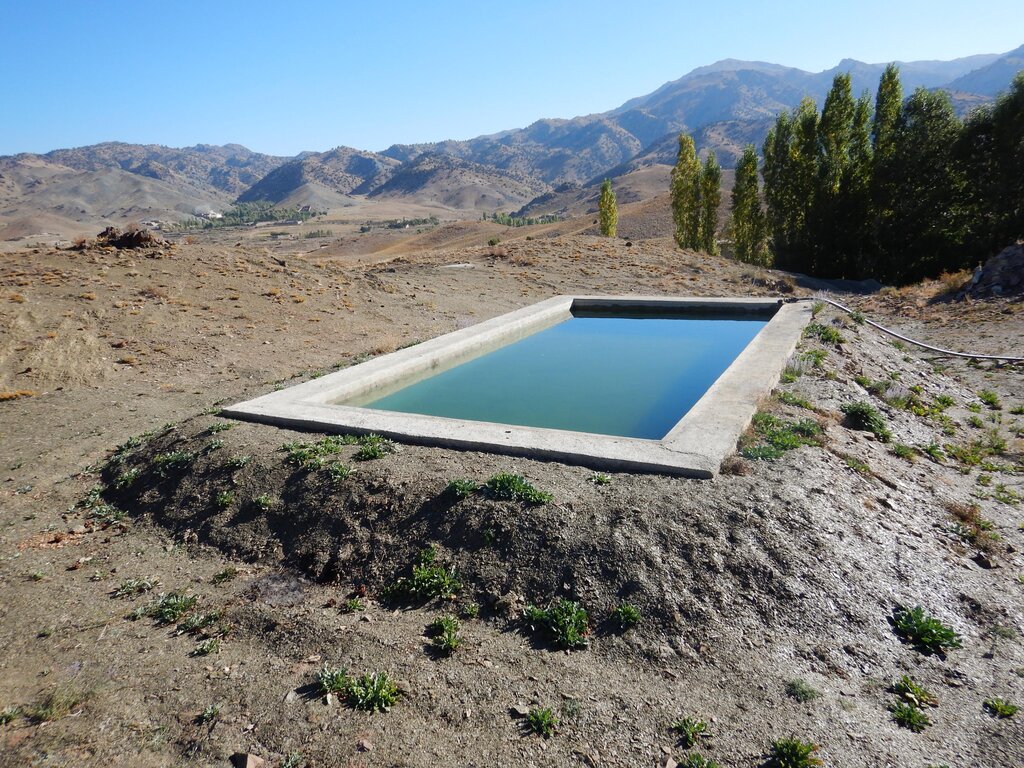
To support sustainable water management in the mountainous areas of Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam districts, 60 water reservoirs with a total storage capacity of 6,000 m³ were constructed. The volume of individual reservoirs varies depending on the availability and flow of upstream spring water ranging from 36 m³ to 192 m³.
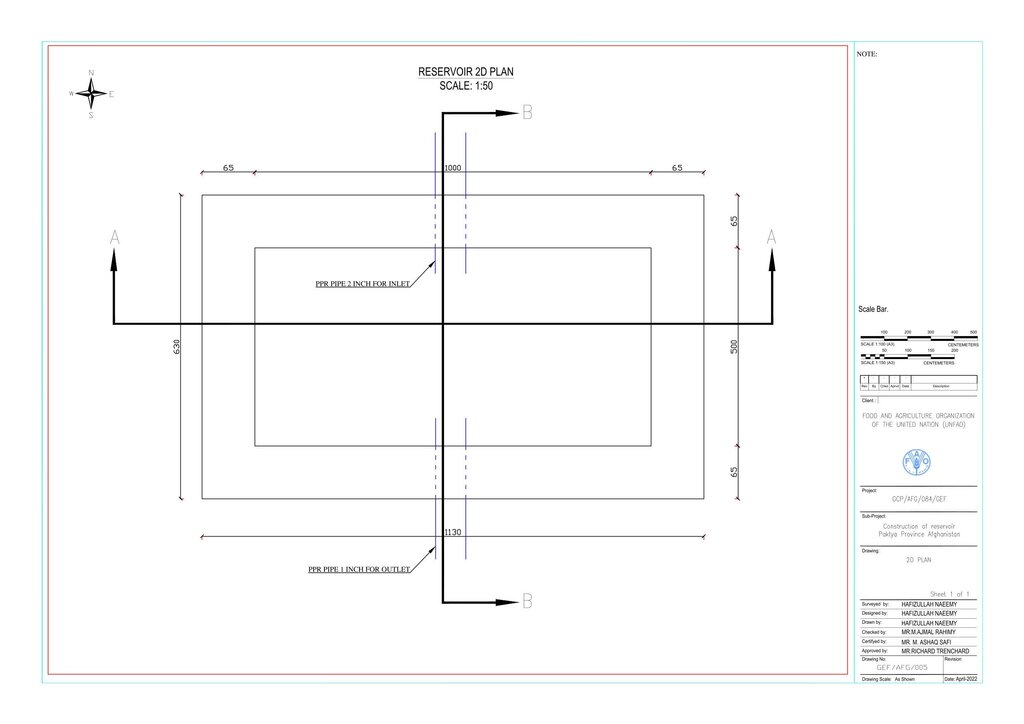
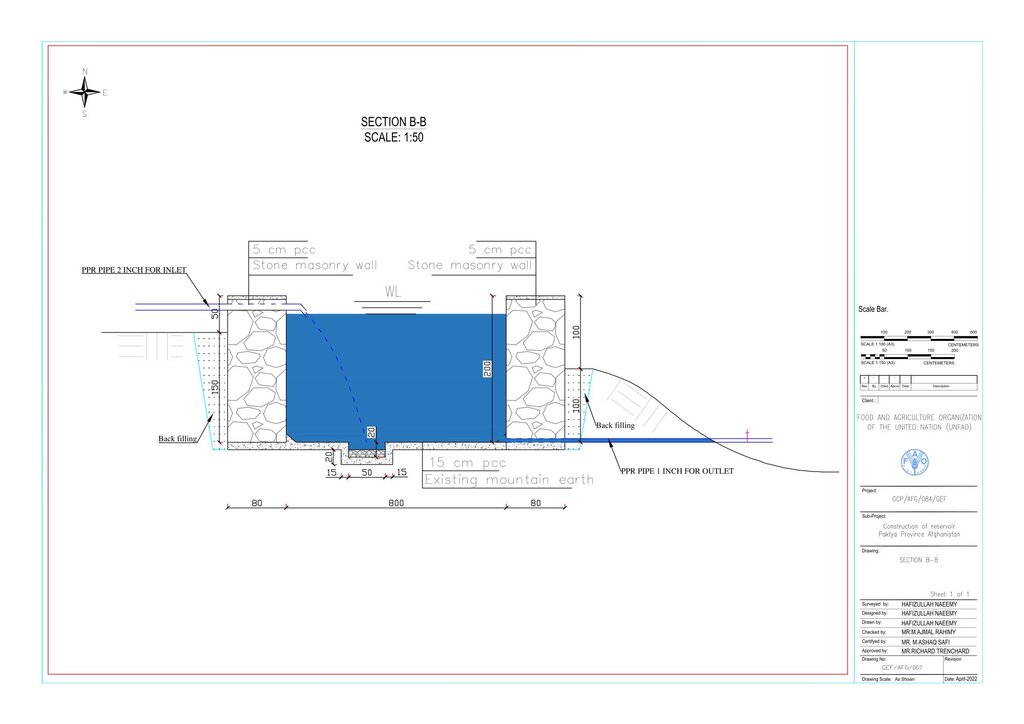
Water is diverted from a small intake near the source and delivered to the reservoir inlet through a 2-inch Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe. For irrigation of the restored areas, the outlets from the reservoirs are connected to 1-inch PVC pipes for distributing water to various plantation sites.
This technology is applied in a natural environment and is designed to support environmental sustainability by recharging the groundwater table, as water is harvested into reservoirs, it can infiltrate through the side walls and bottom. This percolation process contributes to the natural hydrological cycle, harvesting surplus water (water evaporate or percolating into atmosphere or soil) into reservoirs for irrigation of planted saplings, and extending existing forest boundaries.
The system enables the local community to sustainably manage and utilize spring water for gravity-based irrigation of restored areas, while also supporting the expansion of forested land through sapling plantation.
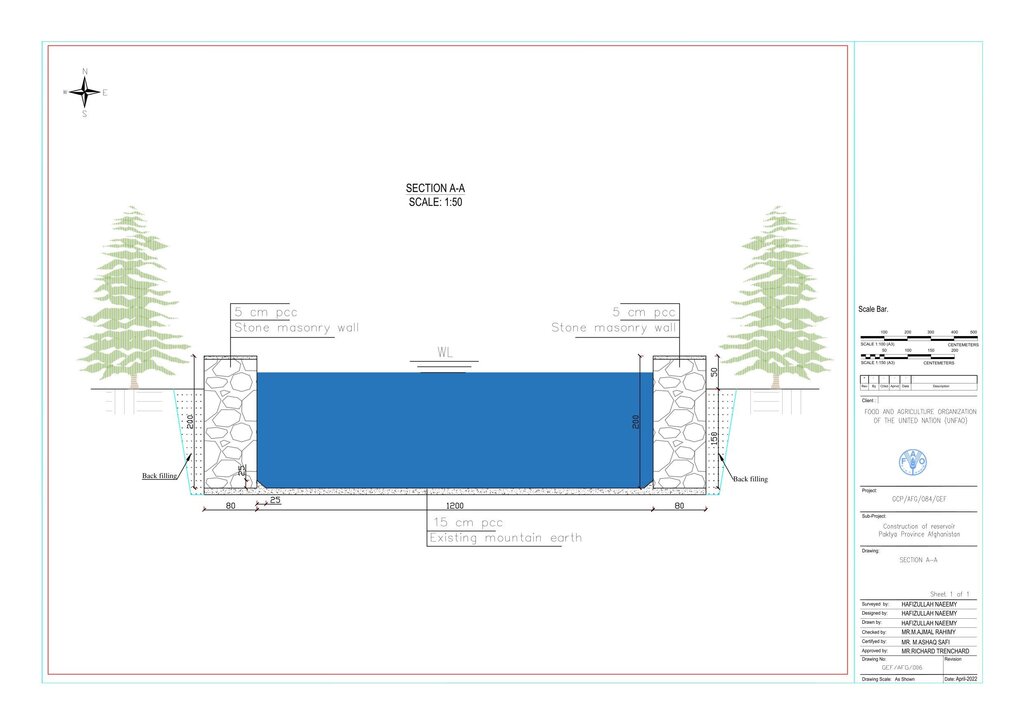
Before constructing the reservoirs, a feasibility survey of the water source (the spring) was conducted to verify the perennial availability of water and to determine the optimal distance between the spring and the designated reforestation sites. The preliminary selection of reservoir locations was based on key criteria including the year-round reliability of the water source, the size of the target reforestation area, and the discharge capacity of the spring. Excavation of the rocky mountain earth was carried out using a hand excavator as per the specified requirements as per technical drawing and approved design. The stone masonry work was completed using random rubble coursed stone with a cement-sand mortar mix (1:2, Type A). As per the design, Plain Cement Concrete (PCC M20) was applied to the top of the stone masonry and on all floors of the reservoirs. A 20 mm thick plastering was carried out on the internal walls using cement-sand mix (1:2). The external walls were backfilled to a height of 1.5 meters.
The benefits of this gravity-fed irrigation technique include increased reforestation rates, reduced water loss due to evaporation and runoff, achieved by using closed piping systems instead of open channels, and improved water use efficiency. These improvements have led to higher sapling survival rates and better growth. Overall, the socio-economic and environmental conditions of rural populations have been improved. Additionally, the implementation of the gravity irrigation system has reduced the cost of restoring degraded forests.
As a low-cost, environmentally friendly technology, it allows for the efficient harvesting of spring water for irrigation, supports sapling planting for carbon sequestration, and helps mitigate the severe impacts of climate change.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أفغانستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Paktya
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ahamd Aba and Sayed Karam district
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
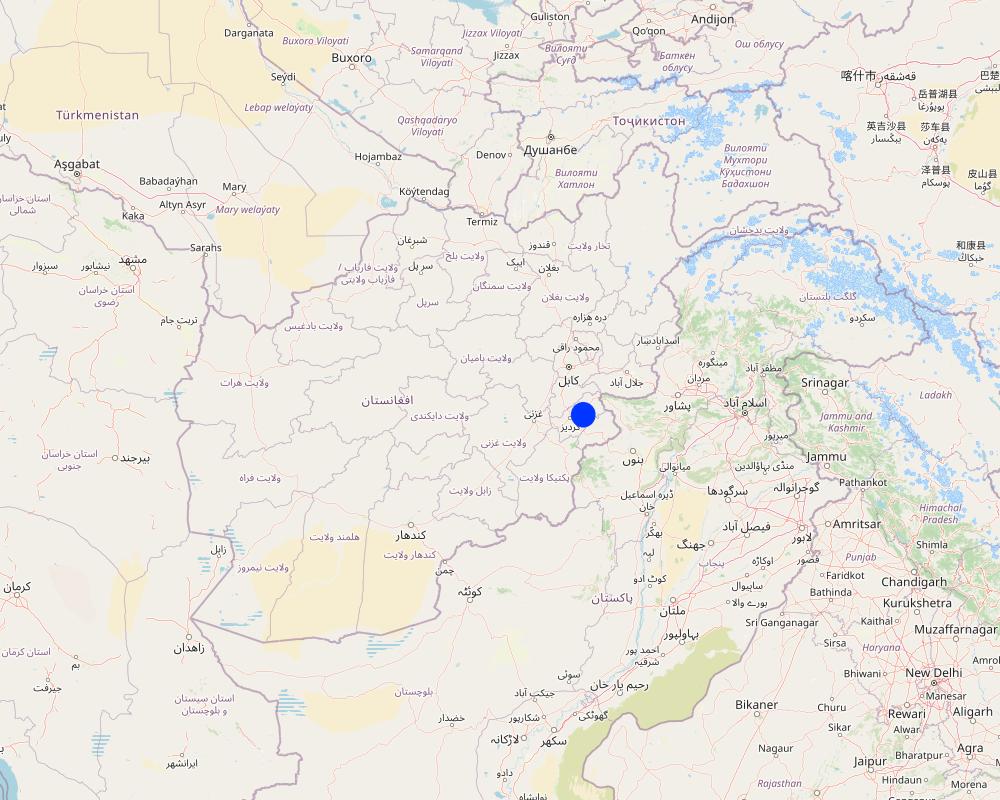
The technology being applied in various location of forest areas, while in the map only two points highlighted in Ahmad Aba and Sayed Karam district of Paktya
However, 46 water reservoirs constructed in Sayed Karam, while 14 water reservoirs constructed in Ahmad Ab
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- حماية مستجمعات المياه / المناطق الواقعة في اتجاه مجرى النهر - مع تقنيات أخرى
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
- خلق أثر اجتماعي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- زراعة الأشجار، التشجير
زراعة الأشجار والتشجير: تحديد أصل وتكوين الأنواع:
- زراعة محصول واحد من صنف محلي
نوع مزارع الأشجار، التشجير:
- مزارع الغابات شبه الاستوائية الجافة-أنواع الصنوبريات
نوع الشجرة:
- أنواع الصنوبر
هل الأشجار المذكورة أعلاه ملحاء أم دائمة الخضرة؟:
- مختلطة ملحاء / دائمة الخضرة
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
التعليقات:
With the implementation of the technology, degraded land has been restored to forested areas through reforestation.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة مزارع الغابات
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
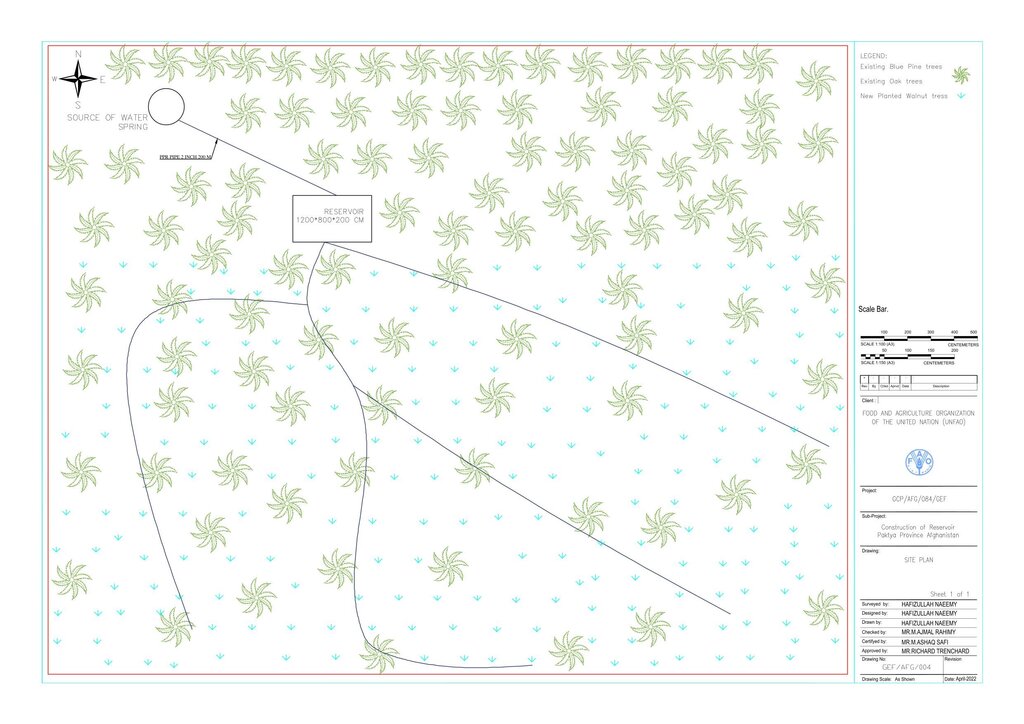
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical drawing: indicated the details of the dimension of water reservoirs
المؤلف:
Hafizullah Neemy
التاريخ:
30/03/2022
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical drawing
المؤلف:
Hafizullah Neemy
التاريخ:
23/03/2022
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical drawing
المؤلف:
Hafizullah Neemy
التاريخ:
30/03/2022
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation to build reservoirs | When construction work is possible |
| 2. | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | After construction the reservoir |
| 3. | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | When construction work is possible |
| 4. | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | When construction work is possible |
| 5. | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | When construction work is possible |
| 6. | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | After construction work |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Excavation to build the reservoris | M3 | 62,0 | 10,0 | 620,0 | |
| العمالة | Stone masonry using random rubble coursed stone, laid with a cement-sand mortar mix of 1:2 (Type A) | M3 | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| العمالة | Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) M20 with formwork and waterproof compound applied under and on top of the stone masonry, as well as on the reservoir floor | M3 | 6,0 | 14,0 | 84,0 | |
| العمالة | Plastering of internal reservoir wall with cement sand (mix 1:2), 20 mm thick | M3 | 42,0 | 14,0 | 588,0 | |
| العمالة | Back filling of all outside of reservoir through soil | Man-days | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| العمالة | Installation of pipes; 1 and 2 inch with elbow, joints , and connectors and valves for fitting in outlet and inlet area of reservoir | Man-days | 8,0 | 5,0 | 40,0 | |
| معدات | Shovel | PC | 5,0 | 5,0 | 25,0 | |
| معدات | Hammer | PC | 2,0 | 10,0 | 20,0 | |
| معدات | Excavator (taking by rent for excavation) | Cubic meter cost | 192,0 | 10,0 | 1920,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Cement | Package | 75,0 | 6,0 | 450,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Stone | Cubic meters | 23,0 | 14,0 | 322,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Polyethelen pipe 1 inch | Meter | 500,0 | 0,8 | 400,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Polyethelen pipe 2 inch | Meter | 200,0 | 1,0 | 200,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Elbow joint | Piece | 3,0 | 1,0 | 3,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Valves | Piece | 4,0 | 4,0 | 16,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Sand | Cumbic meter | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Transportation | LS | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 5835,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 5835,0 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of pipes to outlet and inlet area of water reservoir | Spring season |
| 2. | Maintenance of reservoir for clearing and unclogging the inlet area | As per requirement |
| 3. | Replacement and installation of valves and elbow joints to prevent water clogging in the pipes | During non-function |
| 4. | The embankment constructed to accumulate the water and put the pipes inside to water for diverting to the reservoir | Spring season |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour for repairing of pipes at outlet and valves | Person | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Labour for clearing and unclogging | Person | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Valves | PC | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Elbow joint | Pc | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 170,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 170,0 | |||||
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The distance between the spring and reservoir can affect the total cost of technology
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
553,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
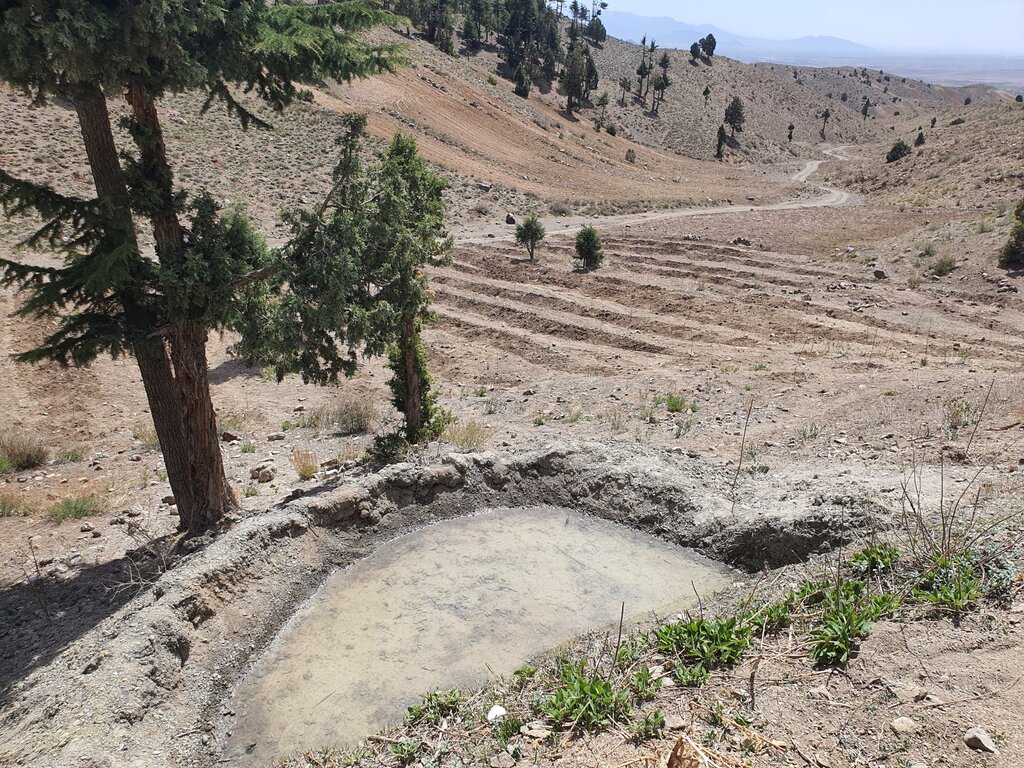
The construction site is situated at an elevation of 2500-3000 meters above sea level, with a terrain slope ranging from 15% to 20%. Photo related to field skitch, indicated that the area of reforestation is around the reservoir.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
زائدة
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
As the water from spring harvesting through pipes and accumulated in reservoirs can reduced the evaporation and stored for 2 or 3 days in reservoirs that can excess the water quantity for irrigation purposes.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
All age group excluding children
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
The small-scale covered the reforestation areas about 10 ha for irrigation, while the medium scale covered about 20 ha for irrigation purposes.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
The water reservoirs were constructed on communal land for use by the local community, allowing shared access for irrigating reforested areas. Access and use are managed through a community-agreed contribution system.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
The establishment of woodlots and other forest can increase the fuel wood for heating the house and cooking, fodder for livestock and fruit for home consumption. The established woodlots consist of a mix of fruit and non-fruit tree species.
إنتاج الغابات غير الخشبية
التعليقات/ حدد:
The non-wood forest productions increased with increasing the area of production through gravity irrigation systems enhanced the community-based efforts in degraded forest.
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
The production areas of NTFPs have expanded due to the annual planting of saplings in degraded forest areas, supported by water reservoirs that provide irrigation and enable the extension of existing forest boundaries.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
The irrigation water availability has improved due to efficient management of the spring water. As the spring water gradually decreases from June to December months which considered as dry period, while January to March months is the wettest period that water is excessive and can be harvested for the following dry period.
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the construction of water reservoirs can significantly improve the water availability during the year both in the wettest period and followed by dry period, by storing the water can balance the demand for the irrigation water.
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Households living in rural areas rely on income from non-timber forest products (NTFPs) and agricultural production, resulting in a diversification of their income sources.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
the workload for the irrigation of reforestation areas reduced with application of technology because the number of days for irrigation done manually reduced and also the cost of irrigation.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
Vegetation Cover
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation cover has improved each year due to ongoing tree planting and the protection of designated areas through quarantine measures.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
تراكم التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
آثار الجفاف
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | جيدة جدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الربيع | زيادة | جيدة جدا |
التعليقات:
The forest function for the regulating of climate, rainfall and snowfall. By increasing the forest cover that can help in regulating the annual rainfall.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- تغير المناخ / التطرف
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
The technology adapted well to reduce the severe impacts of the water on the plant growth and development during water scarity situation in summer.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The technology is cost-effective for irrigating afforested areas and is easy to use and conducive to implementation. |
| The workload for irrigating the afforested area has been reduced, resulting in fewer man-days required for irrigation. |
| The harvesting of water from ground spring allows to expand the forest area through plantation of saplings, otherwise it not possible. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The sustainable management of ground water spring contributed to the expansion of restoration efforts in the community level. |
| By implementation of technology at specific point, the soil vegetation cover improved from 10 to 15 percent. |
| The biodiversity enhanced with restoration of degraded forest area, through plantation of native species, regeneration of native bushes, grasses. |
| The unproductive soil converted into productive soil through plantation of bio energy plants to produce fuel wood, fodder and fruit. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Initial capital for construction of water reservoir. | Government should provide subsidy for construction of reservoir. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Communities' willingness and technical knowledge for the resource management depends on the component of the project . | Providing supporting from the government side for establishment and technical knowledge. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Sixty field visits were conducted to assess the constructed water systems.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Four land users interviewed using SLM technology questionnaire.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Two SLM specialists were interviewed to gather their insights on aspects of the project.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية